企业搜索引擎开发之连接器connector(二十三)
我们在前面的文章已经看到,ConnectorCoordinatorImpl类也实现了ChangeHandler接口,本文接下来分析实现该接口的作用
class ConnectorCoordinatorImpl implements
ConnectorCoordinator, ChangeHandler, BatchResultRecorder
我们先查看一下ChangeHandler接口声明了哪些方法
/**
* Handles change notifications from a {@link ChangeListener}
* for a specific connector instance.
*/
interface ChangeHandler {
void connectorAdded(TypeInfo typeInfo, Configuration configuration)
throws InstantiatorException; void connectorRemoved() throws InstantiatorException; void connectorCheckpointChanged(String checkpoint)
throws InstantiatorException; void connectorScheduleChanged(Schedule schedule)
throws InstantiatorException; void connectorConfigurationChanged(TypeInfo typeInfo,
Configuration configuration) throws InstantiatorException;
}
通过注释我们可以了解到,该接口主要是一个事件句柄,当ChangeListener对象监听到连接器实例的相关事件时,便由该事件处理器处理连接器实例的相关状态
上面的方法分别为添加连接器实例、一处连接器实例、设置连接器实例断点状态、改变连接器实例的定时调度、改变连接器实例配置信息等
ConnectorCoordinatorImpl类实现ChangeHandler接口方法如下
/**
* 新增连接器实例
*/
/* @Override */
public void connectorAdded(TypeInfo newTypeInfo, Configuration configuration)
throws InstantiatorException {
if (instanceInfo != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Create new connector when one already exists.");
}
File connectorDir = getConnectorDir(newTypeInfo);
//生成连接器目录
boolean didMakeConnectorDir = makeConnectorDirectory(connectorDir);
try {
connectorConfigurationChanged(newTypeInfo, configuration);
} catch (InstantiatorException ie) {
if (didMakeConnectorDir) {
removeConnectorDirectory(connectorDir);
}
throw (ie);
}
} /**
* 移除连接器实例
* Removes this {@link Connector} instance. Halts traversals,
* removes the Connector instance from the known connectors,
* and removes the Connector's on-disk representation.
*/
/* @Override */
public synchronized void connectorRemoved() {
LOGGER.info("Dropping connector: " + name);
try {
resetBatch();
if (instanceInfo != null) {
File connectorDir = instanceInfo.getConnectorDir();
shutdownConnector(true);
removeConnectorDirectory(connectorDir);
}
} finally {
instanceInfo = null;
typeInfo = null;
traversalSchedule = null;
traversalDelayEnd = 0;
}
} /**
* 改变断点状态
* Handle a change to the Connector's traversal state. The only change
* that matters is a change from non-null to null. This indicates that
* the Repository should be retraversed from the beginning.
*
* @param checkpoint a String representation of the traversal state.
*/
/* @Override */
public void connectorCheckpointChanged(String checkpoint) {
// If checkpoint has been nulled, then traverse the repository from scratch.
if (checkpoint == null) {
synchronized(this) {
// Halt any traversal in progress.
resetBatch(); // Shut down any Lister.
stopLister(); try {
// Restart Lister.
startLister();
} catch (InstantiatorException e) {
LOGGER.log(Level.WARNING, "Failed to restart Lister for connector "
+ name, e);
} // Kick off a restart immediately.
delayTraversal(TraversalDelayPolicy.IMMEDIATE);
}
LOGGER.info("Restarting traversal from beginning for connector " + name);
}
} /**
* 改变连接器实例定时调度
* Handles a change to the traversal {@link Schedule} for the
* {@link Connector}.
*
* @param schedule new Connector Schedule
*/
/* @Override */
public synchronized void connectorScheduleChanged(Schedule schedule) {
LOGGER.config("Schedule changed for connector " + name + ": " + schedule); // Refresh the cached Schedule.
traversalSchedule = schedule; // Update the LoadManager with the new load.
loadManager.setLoad((schedule == null)
? HostLoadManager.DEFAULT_HOST_LOAD : schedule.getLoad()); // Let the traversal manager know the schedule changed.
setTraversalSchedule(traversalManager, schedule); // Let the lister know the schedule changed.
setTraversalSchedule(lister, schedule); // New Schedule may alter DelayPolicy.
delayTraversal(TraversalDelayPolicy.IMMEDIATE);
} /**
* 改变连接器配置
* Handles a change to a Connector's Configuration. Shuts down any
* current instance of the Connector and starts up a new instance with
* the new Configuration.
*
* @param newTypeInfo the {@link TypeInfo} for this this Connector.
* @param config a new {@link Configuration} for this Connector.
*/
/* @Override */
public void connectorConfigurationChanged(TypeInfo newTypeInfo,
Configuration config) throws InstantiatorException {
if (LOGGER.isLoggable(Level.CONFIG)) {
LOGGER.config("New configuration for connector " + name + ": " + config);
} File connectorDir = getConnectorDir(newTypeInfo); // We have an apparently valid configuration. Create a connector instance
// with that configuration.
InstanceInfo newInstanceInfo = new InstanceInfo(name, connectorDir,
newTypeInfo, addGoogleProperties(config, connectorDir)); // Tell old connector instance to shut down, as it is being replaced.
resetBatch();
shutdownConnector(false); setDatabaseAccess(newInstanceInfo);
instanceInfo = newInstanceInfo;
typeInfo = newTypeInfo; // Prefetch an AuthorizationManager to avoid AuthZ time-outs
// when logging in to repository at search time.
try {
getAuthorizationManager();
} catch (ConnectorNotFoundException cnfe) {
// Not going to happen here, but even if it did, we don't care.
} catch (InstantiatorException ie) {
// Likely failed connector.login(). This attempt to cache AuthZMgr failed.
// However it is not important yet, so log it and continue on.
LOGGER.log(Level.WARNING,
"Failed to get AuthorizationManager for connector " + name, ie);
} // The load value in a Schedule is docs/minute.
loadManager.setLoad(getSchedule().getLoad()); // Start up a Lister, if the Connector supports one.
startLister(); // Allow newly modified connector to resume traversals immediately.
delayTraversal(TraversalDelayPolicy.IMMEDIATE);
}
接了下来我们进一步分析作为事件监听器ChangeListener的相关方法
/**
* Accepts change notifications from a {@link ChangeDetector}.
*/
interface ChangeListener {
void connectorAdded(String instanceName, Configuration configuration)
throws InstantiatorException;
void connectorRemoved(String instanceName); void connectorCheckpointChanged(String instanceName, String checkpoint);
void connectorConfigurationChanged(String instanceName,
Configuration configuration) throws InstantiatorException;
void connectorScheduleChanged(String instanceName, Schedule schedule);
}
当监听器监听到相关事件时,便调用ChangeHandler接口对象进行处理,这里的事件处理器也就是上面的ConnectorCoordinatorImpl类的实例对象
ChangeListenerImpl类实现了ChangeHandler接口,作为具体的事件监听器类,在其相关方法里面都是调用ChangeHandler接口类型对象的相应方法
/**
* Accepts change notifications from a {@link ChangeDetector}, and
* calls the change handlers in ConnectorCoordinator.
*/
class ChangeListenerImpl implements ChangeListener {
private static final Logger LOGGER =
Logger.getLogger(ChangeListenerImpl.class.getName()); private final TypeMap typeMap;
private final ConnectorCoordinatorMap coordinatorMap; ChangeListenerImpl(TypeMap typeMap, ConnectorCoordinatorMap coordinatorMap) {
this.typeMap = typeMap;
this.coordinatorMap = coordinatorMap;
} /* @Override */
public void connectorAdded(String instanceName, Configuration configuration)
throws InstantiatorException {
LOGGER.config("Add connector " + instanceName + " of type "
+ configuration.getTypeName());
try {
ChangeHandler handler = coordinatorMap.getChangeHandler(instanceName);
TypeInfo type = typeMap.getTypeInfo(configuration.getTypeName());
handler.connectorAdded(type, configuration);
} catch (InstantiatorException e) {
LOGGER.log(Level.WARNING, "Failed to handle addition of new connector "
+ instanceName, e);
// Propagate InstantiatorException, so ChangeDetector can retry later.
throw e;
} catch (ConnectorTypeNotFoundException e) {
LOGGER.log(Level.WARNING, "Failed to handle addition of new connector "
+ instanceName, e);
}
} /* @Override */
public void connectorRemoved(String instanceName) {
LOGGER.config("Remove connector " + instanceName);
try {
coordinatorMap.getChangeHandler(instanceName).connectorRemoved();
} catch (InstantiatorException e) {
LOGGER.log(Level.WARNING,
"Failed to handle removal of connector " + instanceName, e);
}
} /* @Override */
public void connectorCheckpointChanged(String instanceName,
String checkpoint) {
LOGGER.finest("Checkpoint changed for connector " + instanceName);
try {
coordinatorMap.getChangeHandler(instanceName)
.connectorCheckpointChanged(checkpoint);
} catch (InstantiatorException e) {
LOGGER.log(Level.WARNING, "Failed to handle checkpoint change for "
+ "connector " + instanceName, e);
}
} /* @Override */
public void connectorScheduleChanged(String instanceName, Schedule schedule) {
LOGGER.config("Schedule changed for connector " + instanceName + ": "
+ schedule);
try {
coordinatorMap.getChangeHandler(instanceName)
.connectorScheduleChanged(schedule);
} catch (InstantiatorException e) {
LOGGER.log(Level.WARNING, "Failed to handle schedule change for "
+ "connector " + instanceName, e);
}
} /* @Override */
public void connectorConfigurationChanged(String instanceName,
Configuration configuration) throws InstantiatorException {
LOGGER.config("Configuration changed for connector " + instanceName);
try {
ChangeHandler handler = coordinatorMap.getChangeHandler(instanceName);
TypeInfo type = typeMap.getTypeInfo(configuration.getTypeName());
handler.connectorConfigurationChanged(type, configuration);
} catch (InstantiatorException e) {
LOGGER.log(Level.WARNING, "Failed to handle configuration change for "
+ "connector " + instanceName, e);
// Propagate InstantiatorException, so ChangeDetector can retry later.
throw e;
} catch (ConnectorTypeNotFoundException e) {
LOGGER.log(Level.WARNING, "Failed to handle configuration change for "
+ "connector " + instanceName, e);
}
}
}
现在事件监听器和事件处理器都具备了,那么事件由哪里发出,接下来要进一步追溯事件源了,即下面要分析的ChangeDetector接口,该接口声明的方法很简单
/**
* Checks for changes in a persistent store. Intended to be run both
* manually to handle local servlet changes, and periodically to check
* for remote connector manager changes.
*
* @see com.google.enterprise.connector.persist.PersistentStore
* @see ChangeListener
*/
interface ChangeDetector {
/**
* Compares the version stamps for the in-memory objects and
* persisted objects, and notifies the {@link ChangeListener} of the
* needed updates.
*
* <p>
* The in-memory objects should reflect the persistent store, even
* if the store contains older objects. If the version stamp for a
* persisted object is older, then the in-memory object should be
* reverted.
*/
void detect();
}
从该接口的注释我们可以知道,连接器实现了两种事件依赖的机制 ,其一是我们手动操作连接器实例时;其二是由连接器的自动更新机制
ChangeDetectorImpl类实现了ChangeDetector接口,该类对象实例依赖于连接器实例的存储类对象和监听器对象实例
/**
* Checks for changes in a persistent store. Intended to be run both
* manually to handle local servlet changes, and periodically to check
* for remote connector manager changes.
*
* @see com.google.enterprise.connector.persist.PersistentStore
* @see ChangeListener
*/
// TODO: Change StoreContext to String and x.getConnectorName() to x.
class ChangeDetectorImpl implements ChangeDetector {
private final PersistentStore store;
private final ChangeListener listener; /** The stamps from the previous run. */
private ImmutableMap<StoreContext, ConnectorStamps> inMemoryInventory =
ImmutableMap.of(); /** A sorted set of the keys of {@code inMemoryInventory}. */
private SortedSet<StoreContext> inMemoryInstances =
new TreeSet<StoreContext>(); /**
* Constructs the detector.
*
* @param store the persistent store to look for changes in
* @param listener the change listener to notify of changes
*/
ChangeDetectorImpl(PersistentStore store, ChangeListener listener) {
this.store = store;
this.listener = listener;
} /* @Override */
public synchronized void detect() {
NDC.push("Change");
try {
ImmutableMap<StoreContext, ConnectorStamps> persistentInventory =
store.getInventory();
SortedSet<StoreContext> persistentInstances =
new TreeSet<StoreContext>(persistentInventory.keySet()); // Compare the last known (inMemory) inventory with the new inventory
// from the persistent store. Notify ChangeListeners of any differences.
// Save in memory, the new inventory of unchanged items and successfully
// applied changes.
inMemoryInventory = compareInventoriesAndNotifyListeners(
inMemoryInstances.iterator(), persistentInstances.iterator(),
persistentInventory);
inMemoryInstances = persistentInstances; } finally {
NDC.pop();
}
} /**
* Gets the next element of an {@code Iterator} iterator, or
* {@code null} if there are no more elements.
*
* @return the next element or {@code null}
*/
private StoreContext getNext(Iterator<StoreContext> it) {
return it.hasNext() ? it.next() : null;
} /**
* Iterates over the sorted sets of instance names to find additions
* and deletions. When matching names are found, compare the version
* stamps for changes in the individual persisted objects.
*
* @param mi the sorted keys to the in-memory instances
* @param pi the sorted keys to the persistent instances
* @param persistentInventory the persistent object stamps
* @return a new inventory of stamps, derived from the
* persistentInventory, but reflecting instantiation failures.
*/
private ImmutableMap<StoreContext, ConnectorStamps>
compareInventoriesAndNotifyListeners(
Iterator<StoreContext> mi, Iterator<StoreContext> pi,
ImmutableMap<StoreContext, ConnectorStamps> persistentInventory) {
// This map will accumulate items for the new in-memory inventory.
// Generally, this map will end up being identical to the
// persistentInventory. However, failed connector instantiations
// may cause changes to be dropped from this map, so that they may
// be retried next time around.
ImmutableMap.Builder<StoreContext, ConnectorStamps> mapBuilder =
new ImmutableMap.Builder<StoreContext, ConnectorStamps>(); StoreContext m = getNext(mi);
StoreContext p = getNext(pi);
while (m != null && p != null) {
// Compare instance names.
int diff = m.getConnectorName().compareTo(p.getConnectorName());
NDC.pushAppend((diff < 0 ? m : p).getConnectorName());
try {
if (diff == 0) {
// Compare the inMemory vs inPStore ConnectorStamps for a
// connector instance. Notify ChangeListeners for items whose
// Stamps have changed.
ConnectorStamps stamps = compareInstancesAndNotifyListeners(
m, p, inMemoryInventory.get(m), persistentInventory.get(p)); // Remember the new ConnetorStamps for our new inMemory inventory.
mapBuilder.put(p, stamps); // Advance to the next connector instance.
m = getNext(mi);
p = getNext(pi);
} else if (diff < 0) {
listener.connectorRemoved(m.getConnectorName());
m = getNext(mi);
} else { // diff > 0
try {
listener.connectorAdded(p.getConnectorName(),
store.getConnectorConfiguration(p));
mapBuilder.put(p, persistentInventory.get(p));
} catch (InstantiatorException e) {
// Forget about this one and retry on the next time around.
pi.remove();
}
p = getNext(pi);
}
} finally {
NDC.pop();
}
}
while (m != null) {
NDC.pushAppend(m.getConnectorName());
try {
listener.connectorRemoved(m.getConnectorName());
} finally {
NDC.pop();
}
m = getNext(mi);
}
while (p != null) {
NDC.pushAppend(p.getConnectorName());
try {
listener.connectorAdded(p.getConnectorName(),
store.getConnectorConfiguration(p));
mapBuilder.put(p, persistentInventory.get(p));
} catch (InstantiatorException e) {
// Forget about this one and retry on the next time around.
pi.remove();
} finally {
NDC.pop();
}
p = getNext(pi);
}
return mapBuilder.build();
} /**
* Compares the version stamps for the given instance. Notify ChangeListeners
* of any differences.
*
* @param m the key for the in-memory instance
* @param p the key for the persistent instance
* @param ms the stamps for the in-memory instance
* @param ps the stamps for the persistent instance
* @return possibly modified stamps for the persistent instance
*/
// TODO: When StoreContext becomes String, we only need one key
// parameter because we will have m.equals(p). NOTE: This may be
// false now, if the connector type has changed.
private ConnectorStamps compareInstancesAndNotifyListeners(
StoreContext m, StoreContext p, ConnectorStamps ms, ConnectorStamps ps) { if (compareStamps(ms.getCheckpointStamp(),
ps.getCheckpointStamp()) != 0) {
listener.connectorCheckpointChanged(p.getConnectorName(),
store.getConnectorState(p));
} if (compareStamps(ms.getScheduleStamp(), ps.getScheduleStamp()) != 0) {
listener.connectorScheduleChanged(p.getConnectorName(),
store.getConnectorSchedule(p));
} // Save configuration for last, because it may fail.
if (compareStamps(ms.getConfigurationStamp(),
ps.getConfigurationStamp()) != 0) {
try {
listener.connectorConfigurationChanged(p.getConnectorName(),
store.getConnectorConfiguration(p));
} catch (InstantiatorException e) {
// Instantiation of the connector failed. Remember a null configuration
// stamp so we will try the new configuration again next time through.
// This is an attempt to handle connectors that fail instantiation
// due to transient causes (such as a server off-line).
return new ConnectorStamps(ps.getCheckpointStamp(),
null, ps.getScheduleStamp());
}
} // Return the original stamps.
return ps;
} /**
* Compares two version stamps. Stamps may be {@code null}, in which
* case they are sorted lower than any non-{@code null} object.
*
* @param memoryStamp the stamp for the in-memory object
* @param persistentStamp the stamp for the persistent object
* @return a negative integer, zero, or a positive integer as the
* in-memory stamp is less than, equal to, or greater than the
* persistent stamp
* @see java.util.Comparator#compare(Object, Object)
*/
private int compareStamps(Stamp memoryStamp, Stamp persistentStamp) {
if (memoryStamp == null && persistentStamp == null) {
return 0;
} else if (memoryStamp == null) {
return -1;
} else if (persistentStamp == null) {
return +1;
} else {
return memoryStamp.compareTo(persistentStamp);
}
}
}
当detect()方法检测到连接器存储状态改变时,便通知事件监听器对象(事件监听器对象调用事件处理器处理该事件)
现在问题是由谁来调用detect()方法检测连接器实例的存储状态的变化呢,连接器在内部通过定时线程不断扫描连接器实例的存储状态
抽象类ScheduledTimerTask扩展了(extends)TimerTask类(定时任务类*TimerTask implements Runnable)
/**
* Extends {@link TimerTask} to include the desired schedule. Note
* that unlike {@link java.util.Timer} schedules, the schedule here is
* specified in seconds for consistency with other time specifications
* in the connector manager.
*/
public abstract class ScheduledTimerTask extends TimerTask {
/** Gets the delay in seconds before the task is to be executed. */
public abstract long getDelay(); /** Gets the time in seconds between successive task executions. */
public abstract long getPeriod();
}
ChangeDetectorTask类继承自抽象类ScheduledTimerTask,在其run方法里面调用changeDetector.detect()方法
public class ChangeDetectorTask extends ScheduledTimerTask {
private final ChangeDetector changeDetector;
private final long delay;
private final long period;
/**
* Constructs a task with a schedule. Note that unlike
* {@link java.util.Timer} schedules, the schedule here is specified
* in seconds for consistency with other time specifications in the
* connector manager.
*
* @param delay delay in seconds before task is to be executed
* @param period time in seconds between successive task executions
*/
public ChangeDetectorTask(ChangeDetector changeDetector, long delay,
long period) {
this.changeDetector = changeDetector;
this.delay = delay;
this.period = period;
}
@Override
public long getDelay() {
return delay;
}
@Override
public long getPeriod() {
return period;
}
@Override
public void run() {
changeDetector.detect();
}
}
最后我们看到,在SpringInstantiator类对象的初始化方法里面,由定时执行器执行了上面的定时任务ScheduledTimerTask
//定时执行器
private final ScheduledTimer timer = new ScheduledTimer(); /**
* Initializes the Context, post bean construction.
*/
public synchronized void init() {
LOGGER.info("Initializing instantiator");
// typeMap must be initialized before the ChangeDetector task is run.
typeMap.init(); //启动定时任务
// Run the ChangeDetector periodically to update the internal
// state. The initial execution will create connector instances
// from the persistent store.
timer.schedule(changeDetectorTask);
}
定时执行器ScheduledTimer timer是对java的Timer timer对象的封装
/**
* A timer for {@link ScheduledTimerTask}s. This class does not start
* a timer thread until a task is scheduled to be executed in the
* future.
*/
/*
* In order to not create a thread during construction, this class
* must not extend Timer.
*/
public class ScheduledTimer {
@VisibleForTesting
static final String THREAD_NAME = "ScheduledTimer"; private Timer timer; /**
* Schedules the task to run. If a delay of zero is given, it will
* be run immediately in the calling thread, rather than running in
* the timer thread.
*/
public void schedule(ScheduledTimerTask task) {
long delay;
if (task.getDelay() == 0L) {
task.run();
delay = task.getPeriod();
} else {
delay = task.getDelay();
} // Only schedule the task in the timer if it needs to be executed
// in the future. N.B.: Do not test delay here instead of
// task.getDelay.
if (task.getDelay() > 0L || task.getPeriod() > 0L) {
synchronized (this) {
if (timer == null) {
// Create a timer with a named thread.
timer = new Timer(THREAD_NAME);
}
} // Timer requires milliseconds, rather than seconds.
if (task.getPeriod() > 0L) {
timer.schedule(task, delay * 1000L, task.getPeriod() * 1000L);
} else {
timer.schedule(task, delay * 1000L);
}
}
} public void cancel() {
if (timer != null) {
timer.cancel();
}
}
}
至此,定时任务初始化、定时任务执行器、事件源、事件监听器、事件处理器都已经分析完毕,我们可以通过查看spring容器的配置文件清晰的查看到这一连串对象实例的依赖序列
<bean id="ConnectorCoordinatorMap"
class="com.google.enterprise.connector.instantiator.ConnectorCoordinatorMap">
<property name="connectorCoordinatorFactory" ref="ConnectorCoordinatorFactory" />
</bean> <bean id="TypeMap"
class="com.google.enterprise.connector.instantiator.TypeMap"/> <bean id="ChangeListener"
class="com.google.enterprise.connector.instantiator.ChangeListenerImpl">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="TypeMap"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" ref="ConnectorCoordinatorMap"/>
</bean> <bean id="ChangeDetector"
class="com.google.enterprise.connector.instantiator.ChangeDetectorImpl">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="PersistentStore"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" ref="ChangeListener"/>
</bean> <bean id="ChangeDetectorTask"
class="com.google.enterprise.connector.instantiator.ChangeDetectorTask">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="ChangeDetector"/>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="1"/>
<constructor-arg index="2" value="${config.change.detect.interval}"/>
</bean> <bean id="Instantiator"
class="com.google.enterprise.connector.instantiator.SpringInstantiator">
<property name="connectorCoordinatorMap" ref="ConnectorCoordinatorMap" />
<property name="threadPool" ref="ThreadPool" />
<property name="typeMap" ref="TypeMap" />
<property name="changeDetectorTask" ref="ChangeDetectorTask" />
</bean>
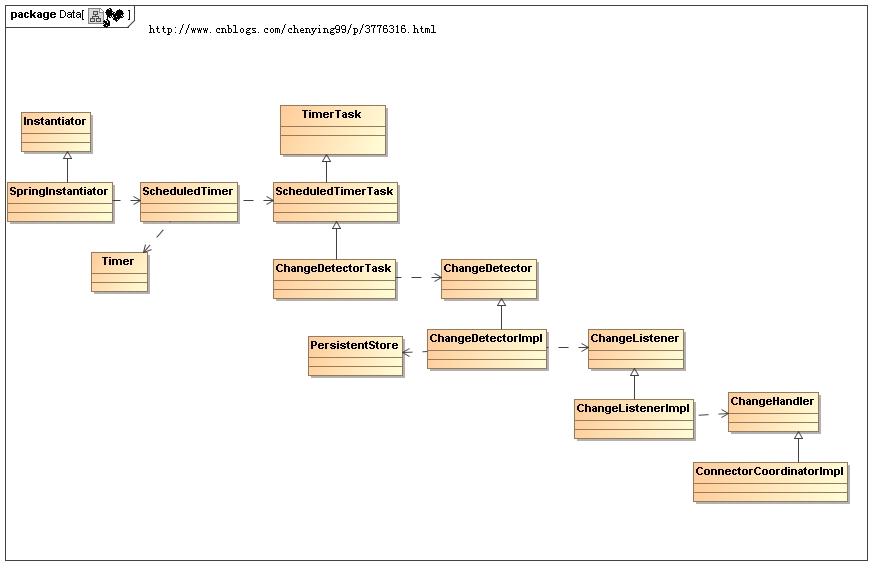
最后,本人画了一张uml类图,可以很清晰的了解相关类的依赖关系
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
本系列企业搜索引擎开发之连接器connector系本人原创
转载请注明出处 博客园 刺猬的温驯
本人邮箱: chenying998179@163#com (#改为.)
本文链接 http://www.cnblogs.com/chenying99/p/3776316.html
企业搜索引擎开发之连接器connector(二十三)的更多相关文章
- 企业搜索引擎开发之连接器connector(二十九)
在哪里调用监控器管理对象snapshotRepositoryMonitorManager的start方法及stop方法,然后又在哪里调用CheckpointAndChangeQueue对象的resum ...
- 企业搜索引擎开发之连接器connector(二十八)
通常一个SnapshotRepository仓库对象对应一个DocumentSnapshotRepositoryMonitor监视器对象,同时也对应一个快照存储器对象,它们的关联是通过监视器管理对象D ...
- 企业搜索引擎开发之连接器connector(二十七)
ChangeQueue类实现ChangeSource接口,声明了拉取下一条Change对象的方法 * A source of {@link Change} objects. * * @since 2. ...
- 企业搜索引擎开发之连接器connector(二十六)
连接器通过监视器对象DocumentSnapshotRepositoryMonitor从上文提到的仓库对象SnapshotRepository(数据库仓库为DBSnapshotRepository)中 ...
- 企业搜索引擎开发之连接器connector(二十五)
下面开始具体分析连接器是怎么与连接器实例交互的,这里主要是分析连接器怎么从连接器实例获取数据的(前面文章有涉及基于http协议与连接器的xml格式的交互,连接器对连接器实例的设置都是通过配置文件操作的 ...
- 企业搜索引擎开发之连接器connector(二十四)
本人在上文中提到,连接器实现了两种事件依赖的机制 ,其一是我们手动操作连接器实例时:其二是由连接器的自动更新机制 上文中分析了连接器的自动更新机制,即定时器执行定时任务 那么,如果我们手动操作连接器实 ...
- 企业搜索引擎开发之连接器connector(二十二)
下面来分析线程执行类,线程池ThreadPool类 对该类的理解需要对java的线程池比较熟悉 该类引用了一个内部类 /** * The lazily constructed LazyThreadPo ...
- 企业搜索引擎开发之连接器connector(二十一)
从上文中的QueryTraverser对象的BatchResult runBatch(BatchSize batchSize)方法上溯到CancelableBatch类,该类实现了TimedCance ...
- 企业搜索引擎开发之连接器connector(二十)
连接器里面衔接数据源与数据推送对象的是QueryTraverser类对象,该类实现了Traverser接口 /** * Interface presented by a Traverser. Used ...
随机推荐
- SpringBoot2.0 url中出现特殊符号「带括号{}'"等等」时会抛出400错误
访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/api?method=taxiong.goods.list¶ms={"page":1,"pageSize ...
- 自定义linux命令
方法一.修改/etc/bashrc文件 在文件底部加入 alias zone="cd /usr/local/webserver" 在命令行输入zone,则会直接进入到制定目录 ...
- TS流解析 三
应该说真正了解TS,还是看了朋友推荐的<数字电视业务信息及其编码>一书之后,MPEG2 TS和数字电视是紧密不可分割的,值得总结一下其中的一些关系. ISO/IEC-13818-1:系统部 ...
- mysql5.6.23安装 步骤
1. 准备好配置文件 my.cnf 2.建立my.cnf中用到的必要的目录 3.在mysql目录下有个scripts/mysql_install_db, 执行: scripts/mysql_insta ...
- 1.2 auth2.0
多个应用 入sina qq msn 豆瓣 等 在手机登录时或终端登录时如果统一可以根据硬件做 gettid()-为了保证唯一性:方案一: 事先生成唯一验证码:使用一个isue 设置为1 ...
- HDFS NameNode HA 部署文档
简介: HDFS High Availability Using the Quorum Journal Manager Hadoop 2.x 中,HDFS 组件有三个角色:NameNode.DataN ...
- OGNL特殊符号的使用
---------------------siwuxie095 # 的使用 1.使用 # 获取 context 中的数据 「值栈分为 root 和 context 两部分」 2.如:向 Request ...
- 一个合约访问另一个合约中的mapping
参考链接:https://ethereum.stackexchange.com/questions/13616/accessing-a-public-mapping-within-a-contract ...
- Golang之Struct(二叉树定义)
接招吧,看代码: package main import "fmt" //二叉树结构体 //如果每个节点有两个指针,分别用来指向左子树和右子树,我们把这样的结构叫做二叉树 type ...
- golang之指针
先上代码 package main import "fmt" type myInt int //匿名函数 //值的接收 //指针的接收 //*myint表示myInt的指针类型 / ...
