JavaScript 高级之面向对象
1. 对象属性及方法
- 创建对象的方式
<script>
//创建对象的方式一
var obj = {};
//创建对象的方式一
var obj = new Object();
</script>
- 挂载在对象上的变量叫对象的属性;挂载在对象上的函数叫对象的方法
obj.name = "David";
obj.say = function () {
alert(this.name)
}
obj.say();
2. 创建对象的发展
- 普通创建模式
var obj1 = new Object();
obj1.name = "David";
obj1.say = function () {
alert(this.name)
}
obj1.say();
var obj2 = new Object();
obj2.name = "Mike";
obj2.say = function () {
alert(this.name)
}
obj2.say();
- 工厂模式
function create(name,age){
var obj = new Object();
obj.name = name;
obj.age = age;
obj.say = function () {
alert("姓名:"+ this.name + "年龄:" + this.age);
}
return obj;
}
var obj1 = create("David",22);
obj1.say();
var obj2 = create("Mike",18);
obj2.say();
- 构造函数模式
- obj1.say != obj2.say,同样的方法占用了两块内存
function create(name,age){
obj.name = name;
obj.age = age;
obj.say = function () {
alert("姓名:"+ this.name + "年龄:" + this.age);
}
}
var obj1 = new create("David",22);
obj1.say();
var obj2 = new create("Mike",18);
obj2.say();
- 原型模式
- obj1.say = obj2.say,同样的方法占用了一块内存,即两个对象共用了一个方法
- 不同的属性放在构造函数里,相同的方法放在原型对象上
- 原型对象也是对象
function create(name,age) {
obj.name = name;
obj.age = age;
}
create.prototype.say = function () {
alert("姓名:"+ this.name + "年龄:" + this.age);
}
var obj1 = new create("David",22);
obj1.say();
var obj2 = new create("Mike",18);
obj2.say();
3. 实现tab选项卡
- 面向过程实现tab选项卡
css代码
#big div{
border: 1px solid #000;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
display: none;
}
#big .block{
display: block;
}
input.active{
background-color: red;
}
html代码
<div id = "big">
<input type = "button" value ="选项一" class = "active"/>
<input type = "button" value = "选项二"/>
<input type = "button" value = "选项三"/>
<div class = "block">我是内容一</div>
<div>我是内容二</div>
<div>我是内容三</div>
</div>
js代码
window.onload = function(){
var big = document.getElementById("big");
var inputs = big.getElementsByTagName("input");
var divs = big.getElementsByTagName("div");
for(var i = 0;i < inputs.length;i++){
inputs[i].index = i;
inputs[i].onclick = function(){
for(var j = 0;j < inputs.length;j++){
inputs[j].className = "";
divs[j].className = "";
}
this.className = "active";
divs[this.index].className = "block";
}
}
}
- 面向对象实现tab选项卡
css代码
#big1 div,#big2 div{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
display: none;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
#big1 .block,#big2 .block{
display: block;
}
input.active{
background-color: red;
}
html代码
<div id = "big1">
<input type = "button" value = "选项一" class = "active"/>
<input type = "button" value = "选项二"/>
<input type = "button" value = "选项三"/>
<div class = "block">我是内容一</div>
<div>我是内容二</div>
<div>我是内容三</div>
</div>
<div id="big2">
<input type = "button" value = "选项一" class = "active"/>
<input type = "button" value = "选项二"/>
<input type = "button" value = "选项三"/>
<div class = "block">我是内容一</div>
<div>我是内容二</div>
<div>我是内容三</div>
</div>
js代码
window.onload = function(){
var tab1 = new Tab("big1");
var tab2 = new Tab("big2");
}
function Tab(id){
var big = document.getElementById(id);
this.inputs = big.getElementsByTagName("input");
this.divs = big.getElementsByTagName("div");
var that = this;
for(var i = 0;i < this.inputs.length;i++){
this.inputs[i].index = i;
this.inputs[i].onclick = function(){
that.show(this);
}
}
}
Tab.prototype.show = function(obtn){
for(var j = 0;j < this.inputs.length;j++){
this.inputs[j].className = "";
this.divs[j].className = "";
}
obtn.className = "active";
this.divs[obtn.index].className = "block";
}
4. 引用
- 引用赋值
// 引用赋值,共用一块内存空间
var arr1 = [1,2,3,4];
var arr2 = [];
for(var i = 0;i < arr1.length;i++){
arr2[i] = arr1[i];
}
arr2.push(5);
- 继承基本语法
- 继承属性
- function A(){ this.color = "black"; } A.prototype.show = function(){ alert("Hello!"); } function B(){ A.call(this); } var b = new B(); console.log(b.color);//通过callnew出来的b有color属性
- 继承方法
function A(){
this.color = "black";
}
A.prototype.show = function(){
alert("Hello!");
}
function B(){
A.call(this);
}
for(var i in A.prototype){
B.prototype[i] = A.prototype[i];
}
var b = new B();
b.show();
- 拖拽案例
html代码
<div id = "box" style="width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: red;position: absolute;">
</div>
- 原生js实现拖拽
window.onload = function(){
var box = document.getElementById("box");
box.onmousedown = function(event){//鼠标按下事件
var ev = event||window.event;
var divX = ev.clientX - box.offsetLeft;
var divY = ev.clientY - box.offsetTop;
document.onmousemove = function(event){//鼠标移动事件
var ev = event || window.event;
box.style.left = ev.clientX - divX + "px";
box.style.top = ev.clientY - divY + "px";
}
document.onmouseup = function(){//鼠标抬起事件
document.onmouseup = null;
document.onmousemove = null;
}
}
}
- 面向对象实现拖拽
window.onload = function(){
new Drag("box");
}
function Drag(id){
this.divX = null;
this.divY = null;
this.box = document.getElementById(id);
var that = this;
this.box.onmousedown = function(event){
that.down(event);
}
}
Drag.prototype.down = function(){
var ev = event||window.event;
this.divX = ev.clientX - this.box.offsetLeft;
this.divY = ev.clientY - this.box.offsetTop;
var that = this;
document.onmousemove = function(event){
that.move(event);
}
document.onmouseup = function(){
that.up();
}
}
Drag.prototype.move = function(){
var ev = event||window.event;
this.box.style.left = ev.clientX - this.divX + "px";
this.box.style.top = ev.clientY - this.divY + "px";
}
Drag.prototype.up = function(){
document.onmouseup = null;
document.onmousemove = null;
}
- 继承实现拖拽
html代码
<div id = "box1" style = " width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: red; position: absolute;">
</div>
<div id = "box2" style = "width: 200px;height: 200px;background-color: red;position: absolute;">
</div>
js代码
window.onload = function(){
new Drag("box1");
new LimitDrag("box2");
}
function Drag(id){
this.divX = null;
this.divY = null;
this.box = document.getElementById(id);
var that = this;
this.box.onmousedown = function(event){
that.down(event);
}
}
Drag.prototype.down = function(){
var ev = event||window.event;
this.divX = ev.clientX - this.box.offsetLeft;
this.divY = ev.clientY - this.box.offsetTop;
var that = this;
document.onmousemove = function(event){
that.move(event);
}
document.onmouseup = function(){
that.up();
}
}
Drag.prototype.move = function(){
var ev = event||window.event;
this.box.style.left = ev.clientX - this.divX + "px";
this.box.style.top = ev.clientY - this.divY + "px";
}
Drag.prototype.up = function(){
document.onmouseup = null;
document.onmousemove = null;
}
function LimitDrag(id){
Drag.call(this,id);
}
for(var i in Drag.prototype){
LimitDrag.prototype[i] = Drag.prototype[i];
}
LimitDrag.prototype.move = function(event){
var ev = event||window.event;
var posX = event.clientX - this.divX;
var posY = event.clientY - this.divY;
if(posX < 0){
posX = 0;
}
if(posX > document.documentElement.clientWidth - this.box.offsetWidth){
posX = document.documentElement.clientWidth - this.box.offsetWidth;
}
if(posY < 0){
posY = 0;
}
if(posY > document.documentElement.clientHeight - this.box.offsetHeight){
posY = document.documentElement.clientHeight - this.box.offsetHeight;
}
this.box.style.left = posX + "px";
this.box.style.top = posY + "px";
}
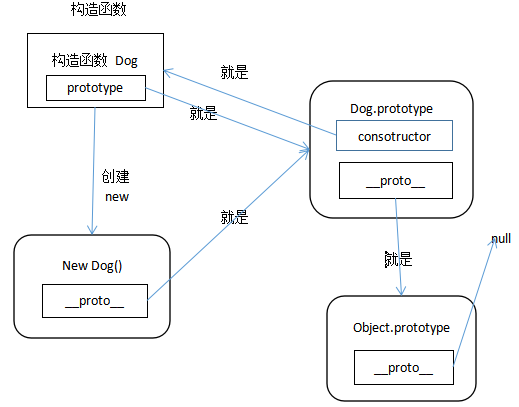
5. 原型链
JavaScript 高级之面向对象的更多相关文章
- javascript高级特性(面向对象)
javascript高级特性(面向对象): * 面向对象: * 面向对象和面向过程的区别: * 面向对象:人就是对象,年龄\性别就是属性,出生\上学\结婚就是方法. * 面向过程:人出生.上学.工作. ...
- Javascript高级程序设计——面向对象小结
ECMAScript支持面向对象编程,对象可以在代码执行时创建,具有动态扩展性而非严格意义上的实体. 创建对象方法: 工厂模式:简单的函数创建引用类型 构造函数模式:可以创建自定义引用类型,可以想创建 ...
- Javascript高级程序设计——面向对象之理解对象
在面向对象语言中都有类的概念,通过类来创建具有属性和方法的对象.而ECMAScript中没有类的概念,ECMAScript中定义了对象:无需属性的集合,其属性值可以包含基本值.对象.或者函数. 在Ja ...
- JavaScript高级与面向对象
对象:任何事物都可以看作是对象. 1.面向对象与面向过程的概念 面向过程:凡是自己亲力亲为,自己按部就班的解决现有问题. 面向对象:自己充当一个指挥者的角色,指挥更加专业的对象帮我解决问题. 联系:面 ...
- 2020/06/06 JavaScript高级程序设计 面向对象的程序设计
ECMAScript虽然是一种面向对象的语言,但是他没有类的概念.所以他的对象也与其他语言中的对象有所不同. ECMA-262定义对象:一组没有特定顺序的值. 6.1 理解对象 创建对象的方法: 1. ...
- Javascript高级程序设计——面向对象之实现继承
原型链: 构造函数中都有一个prototype属性指针,这个指针指向原型对象,而创建的实例也有指向这个原型对象的指针__proto__.当实例查找方法时先在实例上找,找不到再通过__proto__到原 ...
- Javascript高级程序设计——面向对象之创建对象
对象创建方法: 工厂方法 构造函数模式 原型模式 组合构造函数和原型模式 寄生构造函数模式 问题构造函数模式 工厂模式: function Person(name, age){ var obj = n ...
- Javascript高级篇-面向对象的特性
一.创建对象 1.1初始化器 var any={ name:"some", age:10, action:function(){ alert(this.name+":&q ...
- javascript高级特性
01_javascript相关内容02_函数_Arguments对象03_函数_变量的作用域04_函数_特殊函数05_闭包_作用域链&闭包06_闭包_循环中的闭包07_对象_定义普通对象08_ ...
随机推荐
- GoogleMock初探(0)
在进行测试过程中,待测的类或者方法经常会依赖其他类或方法的实现.如果此时这些依赖还没有实现,则需要打桩.另外测试讲求独立,测试之间的互相依赖会导致测试最终混乱不堪. GoogleMock提供一套方法来 ...
- Ubuntu install 错误 E:Unable to locate package
今天在 Ubuntu 上执行 sudo apt install sl 命令,结果报错:E:Unable to locate package sl 上网查询了一下,先更新一下 apt-get,执行:su ...
- microPython环境安装及使用
1.ESP8266_12E(NodeMCU1.0)(AI Thinker)板Arduino IDE环境安装 (1)方法1(自动安装,windows,mac,linux平台都可) http://ardu ...
- python学习笔记:第9天 函数初步
1. 函数的定义及调用 函数:所谓的函数可以看作是对一段代码的封装,也是对一个功能模块的封装,这样方便在下次想用这个功能的时候直接调用这个功能模块,而不用重新去写. 函数的定义:我们使用def关键字来 ...
- 批处理之 for /f 中的delims和tokens
0x00 前言 今天在对windows进行提权之前的系统信息收集的时候,需要使用到一条批处理语句把特定部分的内容从一个txt的文本当中提取出来:该条语句是如下: for /f "tokens ...
- 检测com端口代码实现
1:scan HRESULT CDevHound::Scan(const vector<CString> &guiInfo, vector<DEV_INFO> & ...
- 关于typedef在struct使用上的一些问题
typedef struct lnode{ int data; struct lnode next; }lnode,linklist; 第一行的lnode是结构体名,最后一行的lnode是由typed ...
- Git最常用的命令 总结
stage/unstage git add xxx.xx 和 git reset HEAD xxx.xx 前者将本地的修改提交到index(此操作成为stage,参考备注1),后者将已提交到inde ...
- Java基本修饰符
java中的修饰符分为类修饰符,字段修饰符,方法修饰符.根据功能的不同,主要分为以下几种: *权限访问修饰符(可以用来修饰类.方法和字段) 适用范围<访问权限范围越小,安全性越高> 访问权 ...
- C++基本概念复习
照着https://www.w3cschool.cn/cpp/,把C++的基础概念顺了一遍,虽然很久没用C++,还是整理一下. #include "stdafx.h"; #incl ...
