多线程系列之 Java多线程的个人理解(一)
前言:多线程常常是程序员面试时会被问到的问题之一,也会被面试官用来衡量应聘者的编程思维和能力的重要参考指标;无论是在工作中还是在应对面试时,多线程都是一个绕不过去的话题。本文重点围绕多线程,借助Java语言来展开讨论
文章结构
- 什么是多线程
- 为什么要使用多线程
- 如何实现多线程
- 在实际项目中遇到的多线程问题
1.什么是多线程
1.1 先来聊一聊什么是进程
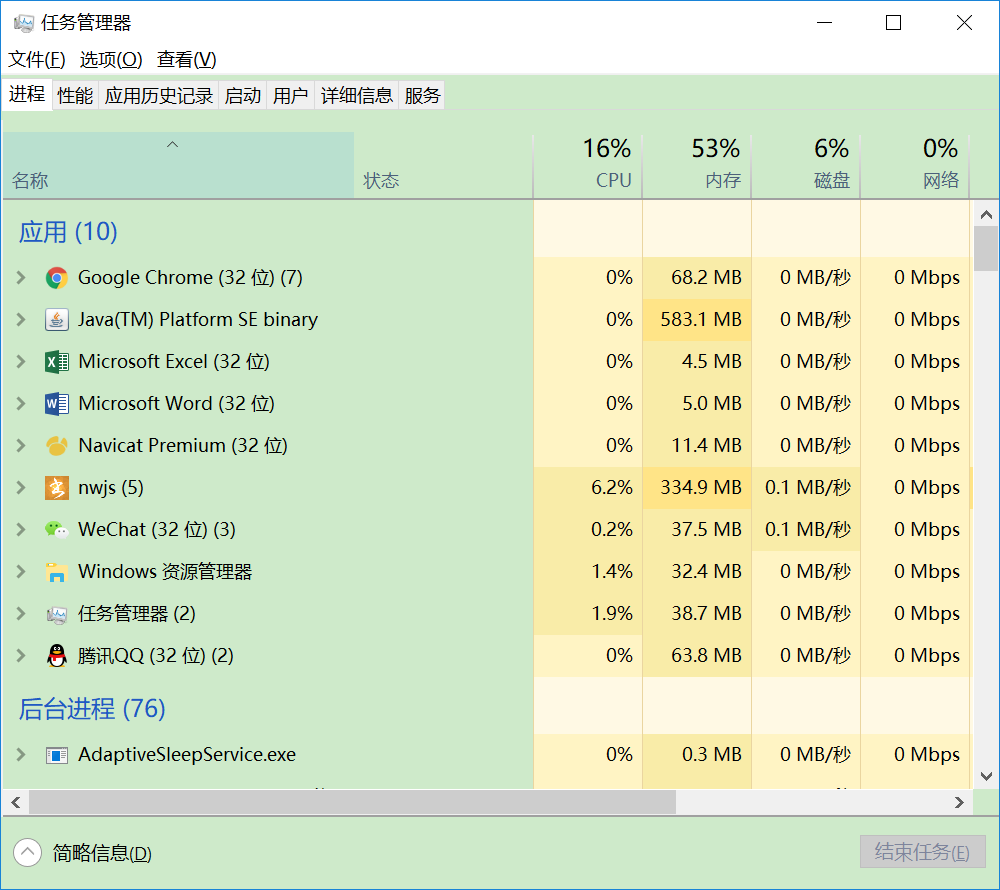
如上图所示,以window操作系统为例,在win10操作系统进程管理,可以清楚的的看到在我们使用计算机的时候,后台是有很多像这样一个一个的进程在运行,这样一个一个的进程其实就是一个正在运行的程序;系统进行资源分配和调度的基本单位,竟争计算机系统资源的基本单位,是并发执行的程序在执行过程中分配和管理资源的基本单位。
1.2 什么是线程
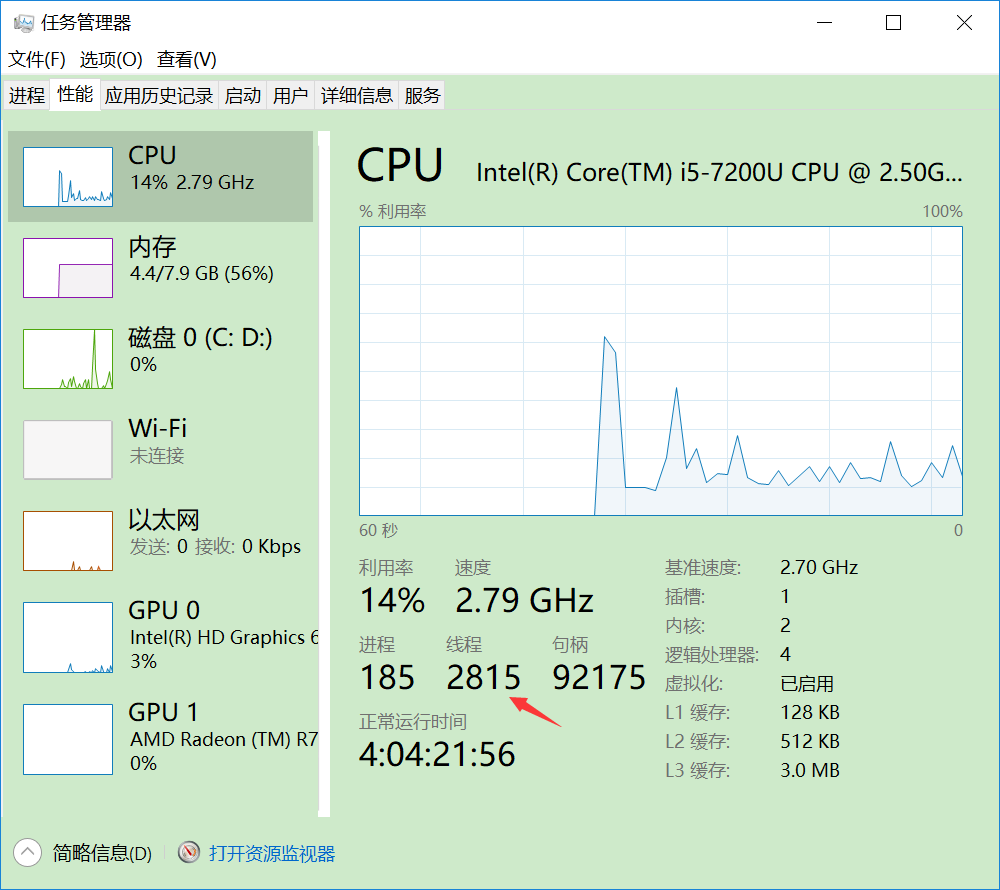
如上图所示,可以看到操作系统上现在有185个进程,有2815个线程;线程是进程的一个实体,是CPU调度和分派的基本单位,它是比进程更小的能独立运行的基本单位。线程自己基本上不拥有系统资源,只拥有一点在运行中必不可少的资源;(程序计数器,一组寄存器和栈),但是它可与同属一个进程的其他的线程共享进程所拥有的全部资源。
1.3 什么是多线程
百度上是这么说的,多线程(英语:multithreading),是指从软件或者硬件上实现多个线程并发执行的技术。 个人理解,线程是要依赖于进程而存在的,毕竟他不能单独运行,所有在一个进程里面只有一个线程实例在执行就可以理解为单线程,有多个实例在执行则可以理解为多线程。
1.4 多线程与多进程的区别
- 多进程:操作系统能同时运行多个任务(程序)。
- 多线程:同一程序中有多个顺序流(线程)在执行。
2.为什么要使用多线程
换句话说,使用多线程到底有什么好处?
- 线程在程序中是独立的,并发的执行流,但是,与分隔的进程相比,进程中的线程之间的隔离程度要小。它们共享内存,文件句柄和其他每个进程应有的状态。
- 线程比进程具有更高的性能,这是由于同一个进程中的线程都有共性:多个线程将共享同一个进程虚拟空间。线程共享的环境包括:进程代码段,进程的公有数据等。利用这些共享的数据等,线程很容易实现相互之间的通信。
- 当操作系统创建一个进程时,必须为进程分配独立的内存空间,并分配大量相关资源:但创建一个线程则简单很多,因此使用多线程来实现并发比使用多进程实现并发的性能要高得多。
- 总结起来,使用多线程编程包含如下几个优点: (1)进程间不能共享内存,但线程之间可以共享内存非常容易。 (2)系统创建进程需要为该进程重新分配系统资源,但创建线程则代价小的多,因此使用多线程来实现多任务并发比多进程的效率高。 (3)Java语言内置多线程功能支持,而不是单纯地作为底层操作系统的调度方式,从而简化了Java的多线程编程。
3.如何实现多线程
首先要说一下,本文是基于Java语言来实现的多线程编程。在面向对象的编程思想指导下,实现多线程的方式有:
- 继承Thread类创建多线程
- 实现Runnable接口创建多线程
- 实现Callable接口通过FutureTask包装器来创建Thread线程
3.1继承Thread类实现多线程
JDK 为我们提供了一个线程类Thread 我们可以继承这个类并重写run()方法 ,如下:
package com.ultrapower.Mutilthread;
/**
* @Description: 继承Thread类实现多线程
* @author fangtao
*/
public class myThread extends Thread {
private int index=0; @Override
public void run(){
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("进程号:"+this.currentThread().getId()+"执行-->"+(index++));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
执行结果:

小节: 通过继承Thread 类并重写run()方法 就可以启动新线程并执行自己定义在run()里的逻辑 。
3.2 实现Runnable接口创建多线程
如果自己的类已经继承另一个类,由于Java语言的单继承特性,就无法直接继承Thread;此时,可以实现一个Runnable接口,如下:
package com.ultrapower.Mutilthread;
/**
* @Description: 实现Runable接口
* @author fangtao
* @date 2019-1-2 下午4:03:38
*/
public class myThread2 implements Runnable { @Override
public void run(){
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getId()+" I'm running!");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
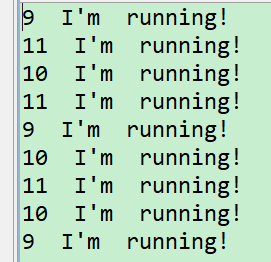
执行结果:
public class TestmyThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1=new Thread(new myThread2());
Thread t2=new Thread(new myThread2());
Thread t3=new Thread(new myThread2());
t1.start();t2.start();t3.start();
}
}
执行结果:
事实上,当传入一个Runnable target参数给Thread后,Thread的run()方法就会调用target.run(),参考JDK源代码:
执行结果:
3.3 实现Callable接口通过FutureTask包装器来创建Thread线程
3.3.1 Callable
Callable位于java.util.concurrent包下,它也是一个接口,在它里面也只声明了一个方法,只不过跟Runnable接口不一样,这个方法比较叫做call();
public interface Callable<V> {
/**
* Computes a result, or throws an exception if unable to do so.
*
* @return computed result
* @throws Exception if unable to compute a result
*/
V call() throws Exception;
}
可以看到,这是一个泛型接口,call()函数返回的类型就是传递进来的V类型。
那么怎么使用Callable呢?一般情况下是配合ExecutorService来使用的,在ExecutorService接口中声明了若干 个submit方法的重载版本:
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
第一个submit方法里面的参数类型就是Callable。
暂时只需要知道Callable一般是和ExecutorService配合来使用的,具体的使用方法讲在后面讲述。
一般情况下我们使用第一个submit方法和第三个submit方法,第二个submit方法很少使用。
3.3.2 Future
Future就是对于具体的Runnable或者Callable任务的执行结果进行取消、查询是否完成、获取结果。必要时 可以通过get方法获取执行结果,该方法会阻塞直到任务返回结果。
Future类位于java.util.concurrent包下,它是一个接口:
public interface Future<V> {
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
boolean isCancelled();
boolean isDone();
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
在Future接口中声明了5个方法,下面依次解释每个方法的作用:
- cancel方法用来取消任务,如果取消任务成功则返回true,如果取消任务失败则返回false。参数mayInterruptIfRunning表示是否允许取消正在执行却没有执行完毕的任务,如果设置true,则表示可以取消正在执行过程中的任务。如果任务已经完成,则无论mayInterruptIfRunning为true还是false,此方法肯定返回false,即如果取消已经完成的任务会返回false;如果任务正在执行,若mayInterruptIfRunning设置为true,则返回true,若mayInterruptIfRunning设置为false,则返回false;如果任务还没有执行,则无论mayInterruptIfRunning为true还是false,肯定返回true。
- isCancelled方法表示任务是否被取消成功,如果在任务正常完成前被取消成功,则返回 true。
- isDone方法表示任务是否已经完成,若任务完成,则返回true;
- get()方法用来获取执行结果,这个方法会产生阻塞,会一直等到任务执行完毕才返回;
- get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)用来获取执行结果,如果在指定时间内,还没获取到结果,就直接返回null。
也就是说Future提供了三种功能:
1)判断任务是否完成;
2)能够中断任务;
3)能够获取任务执行结果;
因为Future只是一个接口,所以是无法直接用来创建对象使用的,因此就有了下面的FutureTask。
3.3.3 FutureTask
我们先来看一下FutureTask的实现:
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V>
FutureTask类实现了RunnableFuture接口,我们看一下RunnableFuture接口的实现:
public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> { void run(); }
可以看出RunnableFuture继承了Runnable接口和Future接口,而FutureTask实现了RunnableFuture接口。所以它既可以作为Runnable被线程执行,又可以作为Future得到Callable的返回值。
FutureTask提供了2个构造器:
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) { }
public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) { }
事实上,FutureTask是Future接口的一个唯一实现类
代码示例:
1) 使用Callable+Future获取执行结果
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Task task = new Task();
Future<Integer> result = executor.submit(task);
executor.shutdown();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("主线程在执行任务");
try {
System.out.println("task运行结果"+result.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("所有任务执行完毕");
}
}
class Task implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("子线程在进行计算");
Thread.sleep(3000);
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<100;i++)
sum += i;
return sum;
}
}
执行结果:

2)使用Callable+FutureTask获取执行结果
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//第一种方式
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Task task = new Task();
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<Integer>(task);
executor.submit(futureTask);
executor.shutdown();
//第二种方式,使用的是ExecutorService,一个使用的是Thread
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("主线程在执行任务");
try {
System.out.println("task运行结果"+futureTask.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("所有任务执行完毕");
}
}
class Task implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("子线程在进行计算");
Thread.sleep(3000);
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i<100;i++)
sum += i;
return sum;
}
}
如果为了可取消性而使用 Future 但又不提供可用的结果,则可以声明 Future<?> 形式类型、并返回 null 作为底层任务的结果。
(项目中多线程的分享下次再写吧。。。。)
blockquote:first-child, #write > div:first-child, #write > ol:first-child, #write > p:first-child, #write > pre:first-child, #write > table:first-child, #write > ul:first-child { margin-top: 30px; }
#write li > table:first-child { margin-top: -20px; }
img { max-width: 100%; vertical-align: middle; }
button, input, select, textarea { color: inherit; font-style: inherit; font-variant: inherit; font-weight: inherit; font-stretch: inherit; font-size: inherit; line-height: inherit; font-family: inherit; }
input[type="checkbox"], input[type="radio"] { line-height: normal; padding: 0px; }
*, ::after, ::before { box-sizing: border-box; }
h1 { font-size: 2rem; }
h2 { font-size: 1.8rem; }
h3 { font-size: 1.6rem; }
h4 { font-size: 1.4rem; }
h5 { font-size: 1.2rem; }
h6 { font-size: 1rem; }
p { -webkit-margin-before: 1rem; -webkit-margin-after: 1rem; -webkit-margin-start: 0px; -webkit-margin-end: 0px; }
.mathjax-block { margin-top: 0px; margin-bottom: 0px; -webkit-margin-before: 0px; -webkit-margin-after: 0px; }
.hidden { display: none; }
.md-blockmeta { color: rgb(204, 204, 204); font-weight: 700; font-style: italic; }
a { cursor: pointer; }
sup.md-footnote { padding: 2px 4px; background-color: rgba(238, 238, 238, 0.7); color: rgb(85, 85, 85); border-radius: 4px; }
#write input[type="checkbox"] { cursor: pointer; width: inherit; height: inherit; }
#write > figure:first-child { margin-top: 16px; }
figure { overflow-x: auto; margin: -8px 0px 0px -8px; max-width: calc(100% + 16px); padding: 8px; }
tr { break-inside: avoid; break-after: auto; }
thead { display: table-header-group; }
table { border-collapse: collapse; border-spacing: 0px; width: 100%; overflow: auto; break-inside: auto; }
.CodeMirror-line, .md-fences { break-inside: avoid; }
table.md-table td { min-width: 80px; }
.CodeMirror-gutters { border-right: 0px; background-color: inherit; margin-right: 4px; }
.CodeMirror-placeholder { opacity: 0.3; }
.CodeMirror pre { padding: 0px 4px; }
.CodeMirror-lines { padding: 0px; }
div.hr:focus { cursor: none; }
.md-fences { font-size: 0.9rem; display: block; overflow: visible; white-space: pre; background: inherit; position: relative !important; }
.md-diagram-panel { width: 100%; margin-top: 10px; text-align: center; padding-top: 0px; padding-bottom: 8px; overflow-x: auto; }
.md-fences .CodeMirror.CodeMirror-wrap { top: -1.6em; margin-bottom: -1.6em; }
.md-fences.mock-cm { white-space: pre-wrap; }
.show-fences-line-number .md-fences { padding-left: 0px; }
.show-fences-line-number .md-fences.mock-cm { padding-left: 40px; }
.footnotes { opacity: 0.8; font-size: 0.9rem; margin-top: 1em; margin-bottom: 1em; }
.footnotes + .footnotes { margin-top: 0px; }
.md-reset { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border: 0px; vertical-align: top; background: 0px 0px; text-shadow: none; position: static; width: auto; height: auto; white-space: nowrap; cursor: inherit; -webkit-tap-highlight-color: transparent; line-height: normal; font-weight: 400; text-align: left; box-sizing: content-box; }
.md-toc-inner, a img, img a { cursor: pointer; }
li div { padding-top: 0px; }
blockquote { margin: 1rem 0px; }
li .mathjax-block, li p { margin: 0.5rem 0px; }
li { margin: 0px; position: relative; }
blockquote > :last-child { margin-bottom: 0px; }
blockquote > :first-child { margin-top: 0px; }
.footnotes-area { color: rgb(136, 136, 136); margin-top: 0.714rem; padding-bottom: 0.143rem; white-space: normal; }
@media print {
body, html { border: 1px solid transparent; height: 99%; break-after: avoid; break-before: avoid; }
#write { margin-top: 0px; border-color: transparent !important; }
.typora-export * { -webkit-print-color-adjust: exact; }
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6 { break-after: avoid-page; orphans: 2; }
p { orphans: 4; }
html.blink-to-pdf { font-size: 13px; }
.typora-export #write { padding-left: 1cm; padding-right: 1cm; padding-bottom: 0px; break-after: avoid; }
.typora-export #write::after { height: 0px; }
@page { margin: 20mm 0px; }
}
.footnote-line { white-space: pre-wrap; margin-top: 0.714em; font-size: 0.7em; }
pre.md-meta-block { font-size: 0.8rem; min-height: 0.8rem; white-space: pre-wrap; background: rgb(204, 204, 204); display: block; overflow-x: hidden; }
p > img:only-child { display: block; margin: auto; }
.md-line > .md-image:only-child, p > .md-image:only-child { display: inline-block; width: 100%; text-align: center; }
.mathjax-block:not(:empty)::after, .md-toc-content::after, .md-toc::after { display: none; }
#write .MathJax_Display { margin: 0.8em 0px 0px; }
.mathjax-block { white-space: pre; overflow: hidden; width: 100%; }
p + .mathjax-block { margin-top: -1.143rem; }
[contenteditable="true"]:active, [contenteditable="true"]:focus { outline: 0px; box-shadow: none; }
.md-task-list-item { position: relative; list-style-type: none; }
.task-list-item.md-task-list-item { padding-left: 0px; }
.md-task-list-item > input { position: absolute; top: 0px; left: 0px; margin-left: -1.2em; margin-top: calc(1em - 10px); }
.math { font-size: 1rem; }
.md-toc { min-height: 3.58rem; position: relative; font-size: 0.9rem; border-radius: 10px; }
.MathJax_SVG, .mathjax-block .MathJax_SVG_Display { text-indent: 0px; max-width: none; max-height: none; min-height: 0px; }
.md-toc-content { position: relative; margin-left: 0px; }
.md-toc-item { display: block; color: rgb(65, 131, 196); }
.md-toc-inner:hover { }
.md-toc-inner { display: inline-block; }
.md-toc-h1 .md-toc-inner { margin-left: 0px; font-weight: 700; }
.md-toc-h2 .md-toc-inner { margin-left: 2em; }
.md-toc-h3 .md-toc-inner { margin-left: 4em; }
.md-toc-h4 .md-toc-inner { margin-left: 6em; }
.md-toc-h5 .md-toc-inner { margin-left: 8em; }
.md-toc-h6 .md-toc-inner { margin-left: 10em; }
@media screen and (max-width: 48em) {
.md-toc-h3 .md-toc-inner { margin-left: 3.5em; }
.md-toc-h4 .md-toc-inner { margin-left: 5em; }
.md-toc-h5 .md-toc-inner { margin-left: 6.5em; }
.md-toc-h6 .md-toc-inner { margin-left: 8em; }
}
a.md-toc-inner { font-size: inherit; font-style: inherit; font-weight: inherit; line-height: inherit; }
.footnote-line a:not(.reversefootnote) { color: inherit; }
.md-attr { display: none; }
.md-fn-count::after { content: "."; }
code, pre, tt { font-family: var(--monospace); }
.md-comment { color: rgb(162, 127, 3); opacity: 0.8; font-family: var(--monospace); }
code { text-align: left; }
a.md-print-anchor { border-width: initial !important; border-style: none !important; border-color: initial !important; display: inline-block !important; position: absolute !important; width: 1px !important; right: 0px !important; outline: 0px !important; background: 0px 0px !important; text-decoration: initial !important; text-shadow: initial !important; }
.md-inline-math .MathJax_SVG .noError { display: none !important; }
.mathjax-block .MathJax_SVG_Display { text-align: center; margin: 1em 0px; position: relative; min-width: 100%; width: auto; display: block !important; }
.MathJax_SVG_Display, .md-inline-math .MathJax_SVG_Display { width: auto; margin: inherit; display: inline-block !important; }
.MathJax_SVG .MJX-monospace { font-family: monospace; }
.MathJax_SVG .MJX-sans-serif { font-family: sans-serif; }
.MathJax_SVG { display: inline; font-style: normal; font-weight: 400; line-height: normal; zoom: 90%; text-align: left; text-transform: none; letter-spacing: normal; word-spacing: normal; word-wrap: normal; white-space: nowrap; min-width: 0px; border: 0px; padding: 0px; margin: 0px; }
.MathJax_SVG * { transition: none; }
.os-windows.monocolor-emoji .md-emoji { font-family: "Segoe UI Symbol", sans-serif; }
.md-diagram-panel > svg, [lang="flow"] svg, [lang="mermaid"] svg { max-width: 100%; }
[lang="mermaid"] .node text { font-size: 1rem; }
table tr th { border-bottom: 0px; }
:root { --side-bar-bg-color: #fafafa; --control-text-color: #777; }
@font-face { font-family: "Open Sans"; font-style: normal; font-weight: normal; src: local("Open Sans Regular"), url("./github/400.woff") format("woff"); }
@font-face { font-family: "Open Sans"; font-style: italic; font-weight: normal; src: local("Open Sans Italic"), url("./github/400i.woff") format("woff"); }
@font-face { font-family: "Open Sans"; font-style: normal; font-weight: bold; src: local("Open Sans Bold"), url("./github/700.woff") format("woff"); }
@font-face { font-family: "Open Sans"; font-style: italic; font-weight: bold; src: local("Open Sans Bold Italic"), url("./github/700i.woff") format("woff"); }
html { font-size: 16px; }
body { font-family: "Open Sans", "Clear Sans", "Helvetica Neue", Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; color: rgb(51, 51, 51); line-height: 1.6; }
#write { max-width: 860px; margin: 0px auto; padding: 20px 30px 100px; }
#write > ul:first-child, #write > ol:first-child { margin-top: 30px; }
body > :first-child { margin-top: 0px !important; }
body > :last-child { margin-bottom: 0px !important; }
a { color: rgb(65, 131, 196); }
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6 { position: relative; margin-top: 1rem; margin-bottom: 1rem; font-weight: bold; line-height: 1.4; cursor: text; }
h1:hover a.anchor, h2:hover a.anchor, h3:hover a.anchor, h4:hover a.anchor, h5:hover a.anchor, h6:hover a.anchor { text-decoration: none; }
h1 tt, h1 code { font-size: inherit; }
h2 tt, h2 code { font-size: inherit; }
h3 tt, h3 code { font-size: inherit; }
h4 tt, h4 code { font-size: inherit; }
h5 tt, h5 code { font-size: inherit; }
h6 tt, h6 code { font-size: inherit; }
h1 { padding-bottom: 0.3em; font-size: 2.25em; line-height: 1.2; border-bottom: 1px solid rgb(238, 238, 238); }
h2 { padding-bottom: 0.3em; font-size: 1.75em; line-height: 1.225; border-bottom: 1px solid rgb(238, 238, 238); }
h3 { font-size: 1.5em; line-height: 1.43; }
h4 { font-size: 1.25em; }
h5 { font-size: 1em; }
h6 { font-size: 1em; color: rgb(119, 119, 119); }
p, blockquote, ul, ol, dl, table { margin: 0.8em 0px; }
li > ol, li > ul { margin: 0px; }
hr { height: 4px; padding: 0px; margin: 16px 0px; background-color: rgb(231, 231, 231); border-width: 0px 0px 1px; border-style: none none solid; border-top-color: initial; border-right-color: initial; border-left-color: initial; border-image: initial; overflow: hidden; box-sizing: content-box; border-bottom-color: rgb(221, 221, 221); }
body > h2:first-child { margin-top: 0px; padding-top: 0px; }
body > h1:first-child { margin-top: 0px; padding-top: 0px; }
body > h1:first-child + h2 { margin-top: 0px; padding-top: 0px; }
body > h3:first-child, body > h4:first-child, body > h5:first-child, body > h6:first-child { margin-top: 0px; padding-top: 0px; }
a:first-child h1, a:first-child h2, a:first-child h3, a:first-child h4, a:first-child h5, a:first-child h6 { margin-top: 0px; padding-top: 0px; }
h1 p, h2 p, h3 p, h4 p, h5 p, h6 p { margin-top: 0px; }
li p.first { display: inline-block; }
ul, ol { padding-left: 30px; }
ul:first-child, ol:first-child { margin-top: 0px; }
ul:last-child, ol:last-child { margin-bottom: 0px; }
blockquote { border-left: 4px solid rgb(221, 221, 221); padding: 0px 15px; color: rgb(119, 119, 119); }
blockquote blockquote { padding-right: 0px; }
table { padding: 0px; word-break: initial; }
table tr { border-top: 1px solid rgb(204, 204, 204); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; }
table tr:nth-child(2n) { background-color: rgb(248, 248, 248); }
table tr th { font-weight: bold; border-width: 1px 1px 0px; border-top-style: solid; border-right-style: solid; border-left-style: solid; border-top-color: rgb(204, 204, 204); border-right-color: rgb(204, 204, 204); border-left-color: rgb(204, 204, 204); border-image: initial; border-bottom-style: initial; border-bottom-color: initial; text-align: left; margin: 0px; padding: 6px 13px; }
table tr td { border: 1px solid rgb(204, 204, 204); text-align: left; margin: 0px; padding: 6px 13px; }
table tr th:first-child, table tr td:first-child { margin-top: 0px; }
table tr th:last-child, table tr td:last-child { margin-bottom: 0px; }
.CodeMirror-gutters { border-right: 1px solid rgb(221, 221, 221); }
.md-fences, code, tt { border: 1px solid rgb(221, 221, 221); background-color: rgb(248, 248, 248); border-radius: 3px; font-family: Consolas, "Liberation Mono", Courier, monospace; padding: 2px 4px 0px; font-size: 0.9em; }
.md-fences { margin-bottom: 15px; margin-top: 15px; padding: 8px 1em 6px; }
.md-task-list-item > input { margin-left: -1.3em; }
@media screen and (min-width: 914px) {
}
@media print {
html { font-size: 13px; }
table, pre { break-inside: avoid; }
pre { word-wrap: break-word; }
}
.md-fences { background-color: rgb(248, 248, 248); }
#write pre.md-meta-block { padding: 1rem; font-size: 85%; line-height: 1.45; background-color: rgb(247, 247, 247); border: 0px; border-radius: 3px; color: rgb(119, 119, 119); margin-top: 0px !important; }
.mathjax-block > .code-tooltip { bottom: 0.375rem; }
#write > h3.md-focus::before { left: -1.5625rem; top: 0.375rem; }
#write > h4.md-focus::before { left: -1.5625rem; top: 0.285714rem; }
#write > h5.md-focus::before { left: -1.5625rem; top: 0.285714rem; }
#write > h6.md-focus::before { left: -1.5625rem; top: 0.285714rem; }
.md-image > .md-meta { border-radius: 3px; font-family: Consolas, "Liberation Mono", Courier, monospace; padding: 2px 0px 0px 4px; font-size: 0.9em; color: inherit; }
.md-tag { color: inherit; }
.md-toc { margin-top: 20px; padding-bottom: 20px; }
.sidebar-tabs { border-bottom: none; }
#typora-quick-open { border: 1px solid rgb(221, 221, 221); background-color: rgb(248, 248, 248); }
#typora-quick-open-item { background-color: rgb(250, 250, 250); border-color: rgb(254, 254, 254) rgb(229, 229, 229) rgb(229, 229, 229) rgb(238, 238, 238); border-style: solid; border-width: 1px; }
#md-notification::before { top: 10px; }
.on-focus-mode blockquote { border-left-color: rgba(85, 85, 85, 0.12); }
header, .context-menu, .megamenu-content, footer { font-family: "Segoe UI", Arial, sans-serif; }
.file-node-content:hover .file-node-icon, .file-node-content:hover .file-node-open-state { visibility: visible; }
.mac-seamless-mode #typora-sidebar { background-color: var(--side-bar-bg-color); }
.md-lang { color: rgb(180, 101, 77); }
.html-for-mac .context-menu { --item-hover-bg-color: #E6F0FE; }
.typora-export p, .typora-export .footnote-line {white-space: normal;}
-->
多线程系列之 Java多线程的个人理解(一)的更多相关文章
- 多线程系列之 java多线程的个人理解(二)
前言:上一篇多线程系列之 java多线程的个人理解(一) 讲到了线程.进程.多线程的基本概念,以及多线程在java中的基本实现方式,本篇主要接着上一篇继续讲述多线程在实际项目中的应用以及遇到的诸多问题 ...
- Java总结篇系列:Java多线程(二)
本文承接上一篇文章<Java总结篇系列:Java多线程(一)>. 四.Java多线程的阻塞状态与线程控制 上文已经提到Java阻塞的几种具体类型.下面分别看下引起Java线程阻塞的主要方法 ...
- Java总结篇系列:Java多线程(三)
本文主要接着前面多线程的两篇文章总结Java多线程中的线程安全问题. 一.一个典型的Java线程安全例子 public class ThreadTest { public static void ma ...
- 【java多线程系列】java内存模型与指令重排序
在多线程编程中,需要处理两个最核心的问题,线程之间如何通信及线程之间如何同步,线程之间通信指的是线程之间通过何种机制交换信息,同步指的是如何控制不同线程之间操作发生的相对顺序.很多读者可能会说这还不简 ...
- 【系列】Java多线程初学者指南(1):线程简介
原文地址:http://www.blogjava.net/nokiaguy/archive/2009/nokiaguy/archive/2009/03/archive/2009/03/19/26075 ...
- Java总结篇系列:Java多线程(一)
多线程作为Java中很重要的一个知识点,在此还是有必要总结一下的. 一.线程的生命周期及五种基本状态 关于Java中线程的生命周期,首先看一下下面这张较为经典的图: 上图中基本上囊括了Java中多线程 ...
- Java多线程编程核心技术---Java多线程技能
基本概念 进程是操作系统结构的基础,是一次程序的执行,是一个程序及其数据结构在处理机上顺序执行时所发生的活动,是程序在一个数据集合上运行的过程,是系统进行资源分配和调度的独立单位.线程可以理解成是在进 ...
- java多线程基础(二)--java多线程的基本使用
java多线程的基本使用 在java中使用多线程,是通过继承Thread这个类或者实现Runnable这个接口或者实现Callable接口来完成多线程的. 下面是很简单的例子代码: package c ...
- (1)Java多线程编程核心——Java多线程技能
1.为什么要使用多线程?多线程的优点? 提高CPU的利用率 2.什么是多线程? 3.Java实现多线程编程的两种方式? a.继承Thread类 public class MyThread01 exte ...
随机推荐
- jQuery自适应-3D旋转轮播图
3D旋转轮播图 本例源于(站长之家实例http://sc.chinaz.com/jiaoben/170215391070.htm) 其他相似示例(https://www.cnblogs.com/inc ...
- 如何面试Web前端开发
分享一篇HR前端面试心得: 面试前端工程师对我来说是一件非常有意思的事,因为面试过程很大程度上也是自我提升的过程.无论大公司还是小公司,之所以在如何招聘到真正有能力的,前端工程师方面会遇到同样的问题. ...
- 浏览器根对象window之值为数值的属性
1. number属性 1.1 length length 属性返回在当前窗口中frames的数量(包括IFRAMES). 该属性值与window.frames.length属性值相等. 1.2 in ...
- FineReport和泛微OA(Ecology)的单点登录集成方案
最近出现了很多关于帆软报表和泛微OA的集成问题,均出现在“单点登录”上.直接也有相关的文章介绍一些FineReport和泛微集成的背景.价值等,以及FineReport和OA的深度集成的方案,但是并没 ...
- Java期中项目杂七杂八
这是一篇草稿,嗯,等结项以后大概可能会整理其中的一部分吧…… 杂项 1. 用Idea创建Maven项目:直接选就行:至于商定好的Eclipse要怎么做再说…… 2. 联网依赖:选择我们最熟的okhtt ...
- ionic项目编译打包(android平台)
ionic项目相关开发工作完成之后(建立ionic工程项目可以参考上一篇文章ionic项目工程建立),就可以进行项目的编译打包apk应用包. 打包编译需要在平台环境下,这里只记录下android平台打 ...
- python基础——Linux系统下的文件目录结构
单用户操作系统和多用户操作系统 单用户操作系统:指一台计算机在同一时间只能由一个用户使用,一个用户独自享用系统的全部硬件和软件资源. 多用户操作系统:指一台计算机在同一时间可以由多个用户使用,多个用户 ...
- SQL语句的执行顺序 1>优先执行,然后依数字排序
1>…From 表 2>…Where 条件 3>…Group by 列 4>…Having 筛选条件 ...
- apache中配置php支持模块模式、cgi模式和fastcgi模式
首先安装apache.mysql和php,依次顺序安装. 1.apache.mysql的安装比较简单,略过 2. php的安装,我安装的是php5.3.6内置了php-fpm,所以不需要再单独下补丁了 ...
- Linux入门-6 Linux网络基本配置
1. 网络基础知识 网络编址 IP编址 子网掩码 同一网络主机之间通信--MAC地址 不同网络之间的通信 路由 域名 DNS 基本网络参数 2. Linux网络基础配置 以太网连接 配置网络信息 网络 ...
