hadoop高速扫盲帖,从零了解hadoop
1、MapReduce理论简单介绍
1.1 MapReduce编程模型
MapReduce採用"分而治之"的思想,把对大规模数据集的操作,分发给一个主节点管理下的各个分节点共同完毕,然后通过整合各个节点的中间结果,得到终于结果。简单地说,MapReduce就是"任务的分解与结果的汇总"。
在Hadoop中,用于运行MapReduce任务的机器角色有两个:一个是JobTracker;还有一个是TaskTracker,JobTracker是用于调度工作的,TaskTracker是用于运行工作的。一个Hadoop集群中仅仅有一台JobTracker。
在分布式计算中,MapReduce框架负责处理了并行编程中分布式存储、工作调度、负载均衡、容错均衡、容错处理以及网络通信等复杂问题,把处理过程高度抽象为两个函数:map和reduce,map负责把任务分解成多个任务,reduce负责把分解后多任务处理的结果汇总起来。
须要注意的是,用MapReduce来处理的数据集(或任务)必须具备这种特点:待处理的数据集能够分解成很多小的数据集,并且每个小数据集都能够全然并行地进行处理。
1.2 MapReduce处理过程
在Hadoop中,每一个MapReduce任务都被初始化为一个Job,每一个Job又能够分为两种阶段:map阶段和reduce阶段。这两个阶段分别用两个函数表示,即map函数和reduce函数。map函数接收一个<key,value>形式的输入,然后相同产生一个<key,value>形式的中间输出,Hadoop函数接收一个如<key,(list of values)>形式的输入,然后对这个value集合进行处理,每一个reduce产生0或1个输出,reduce的输出也是<key,value>形式的。
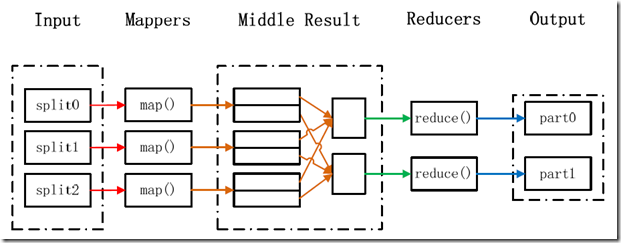
MapReduce处理大数据集的过程
2、执行WordCount程序
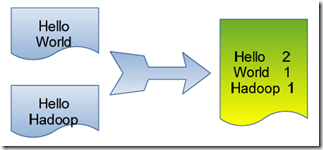
单词计数是最简单也是最能体现MapReduce思想的程序之中的一个,能够称为MapReduce版"Hello World",该程序的完整代码能够在Hadoop安装包的"src/examples"文件夹下找到。单词计数主要完毕功能是:统计一系列文本文件里每一个单词出现的次数,例如以下图所看到的。
2.1 准备工作
如今以"hadoop"普通用户登录"Master.Hadoop"server。
1)创建本地演示样例文件
首先在"/home/hadoop"文件夹下创建文件夹"file"。
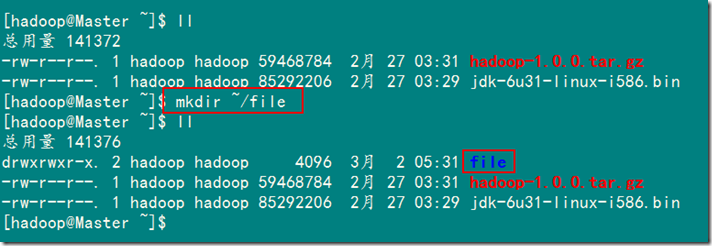
接着创建两个文本文件file1.txt和file2.txt,使file1.txt内容为"Hello World",而file2.txt的内容为"Hello Hadoop"。
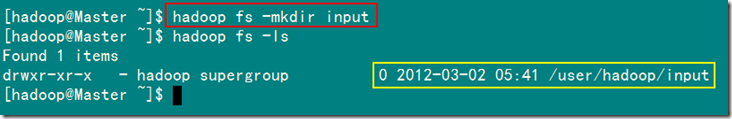
2)在HDFS上创建输入目录
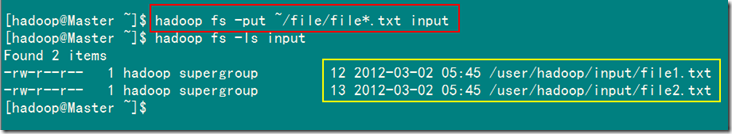
3)上传本地file中文件到集群的input文件夹下
2.2 执行样例
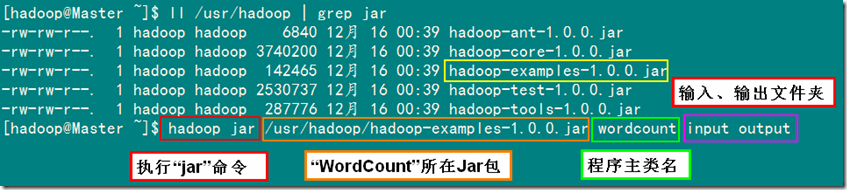
1)在集群上执行WordCount程序
备注:以input作为输入文件夹,output文件夹作为输出文件夹。
已经编译好的WordCount的Jar在"/usr/hadoop"以下,就是"hadoop-examples-1.0.0.jar",所以在以下运行命令时记得把路径写全了,不然会提示找不到该Jar包。
2)MapReduce运行过程显示信息
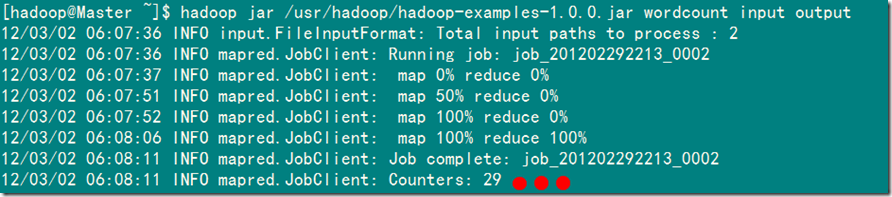
Hadoop命令会启动一个JVM来执行这个MapReduce程序,并自己主动获得Hadoop的配置,同一时候把类的路径(及其依赖关系)增加到Hadoop的库中。以上就是Hadoop Job的执行记录,从这里能够看到,这个Job被赋予了一个ID号:job_201202292213_0002,并且得知输入文件有两个(Total input paths to process : 2),同一时候还能够了解map的输入输出记录(record数及字节数),以及reduce输入输出记录。比方说,在本例中,map的task数量是2个,reduce的task数量是一个。map的输入record数是2个,输出record数是4个等信息。
2.3 查看结果
1)查看HDFS上output文件夹内容
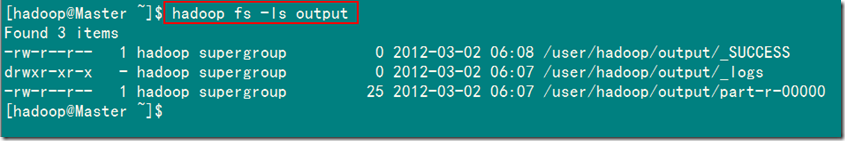
从上图中知道生成了三个文件,我们的结果在"part-r-00000"中。
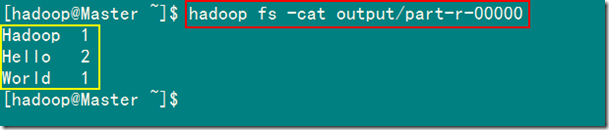
2)查看结果输出文件内容
3、WordCount源代码分析
3.1 特别数据类型介绍
Hadoop提供了例如以下内容的数据类型,这些数据类型都实现了WritableComparable接口,以便用这些类型定义的数据能够被序列化进行网络传输和文件存储,以及进行大小比較。
BooleanWritable:标准布尔型数值
ByteWritable:单字节数值
DoubleWritable:双字节数
FloatWritable:浮点数
IntWritable:整型数
LongWritable:长整型数
Text:使用UTF8格式存储的文本
NullWritable:当<key,value>中的key或value为空时使用
3.2 旧的WordCount分析
1)源码程序
package org.apache.hadoop.examples;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JobClient;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.JobConf;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.MapReduceBase;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.OutputCollector;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.Reporter;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TextOutputFormat;public class WordCount {
public static class Map extends MapReduceBase implements
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();public void map(LongWritable key, Text value,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output, Reporter reporter)
throws IOException {
String line = value.toString();
StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(line);
while (tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(tokenizer.nextToken());
output.collect(word, one);
}
}
}public static class Reduce extends MapReduceBase implements
Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
public void reduce(Text key, Iterator<IntWritable> values,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output, Reporter reporter)
throws IOException {
int sum = 0;
while (values.hasNext()) {
sum += values.next().get();
}
output.collect(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
JobConf conf = new JobConf(WordCount.class);
conf.setJobName("wordcount");conf.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
conf.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);conf.setMapperClass(Map.class);
conf.setCombinerClass(Reduce.class);
conf.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);conf.setInputFormat(TextInputFormat.class);
conf.setOutputFormat(TextOutputFormat.class);FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(conf, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(conf, new Path(args[1]));JobClient.runJob(conf);
}
}
3)主方法Main分析
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
JobConf conf = new JobConf(WordCount.class);
conf.setJobName("wordcount");conf.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
conf.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);conf.setMapperClass(Map.class);
conf.setCombinerClass(Reduce.class);
conf.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);conf.setInputFormat(TextInputFormat.class);
conf.setOutputFormat(TextOutputFormat.class);FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(conf, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(conf, new Path(args[1]));JobClient.runJob(conf);
}
首先解说一下Job的初始化过程。main函数调用Jobconf类来对MapReduce
Job进行初始化,然后调用setJobName()方法命名这个Job。对Job进行合理的命名有助于更快地找到Job,以便在JobTracker和Tasktracker的页面中对其进行监视。
JobConf conf = new JobConf(WordCount. class ); conf.setJobName("wordcount" );
接着设置Job输出结果<key,value>的中key和value数据类型,由于结果是<单词,个数>,所以key设置为"Text"类型,相当于Java中String类型。Value设置为"IntWritable",相当于Java中的int类型。
conf.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class );
conf.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class );
然后设置Job处理的Map(拆分)、Combiner(中间结果合并)以及Reduce(合并)的相关处理类。这里用Reduce类来进行Map产生的中间结果合并,避免给网络传输数据产生压力。
conf.setMapperClass(Map.class );
conf.setCombinerClass(Reduce.class );
conf.setReducerClass(Reduce.class );
接着就是调用setInputPath()和setOutputPath()设置输入输出路径。
conf.setInputFormat(TextInputFormat.class );
conf.setOutputFormat(TextOutputFormat.class );
(1)InputFormat和InputSplit
InputSplit是Hadoop定义的用来传送给每一个单独的map的数据,InputSplit存储的并非数据本身,而是一个分片长度和一个记录数据位置的数组。生成InputSplit的方法能够通过InputFormat()来设置。
当数据传送给map时,map会将输入分片传送到InputFormat,InputFormat则调用方法getRecordReader()生成RecordReader,RecordReader再通过creatKey()、creatValue()方法创建可供map处理的<key,value>对。简而言之,InputFormat()方法是用来生成可供map处理的<key,value>对的。
Hadoop提前定义了多种方法将不同类型的输入数据转化为map可以处理的<key,value>对,它们都继承自InputFormat,各自是:
InputFormat
|
|---BaileyBorweinPlouffe.BbpInputFormat
|---ComposableInputFormat
|---CompositeInputFormat
|---DBInputFormat
|---DistSum.Machine.AbstractInputFormat
|---FileInputFormat
|---CombineFileInputFormat
|---KeyValueTextInputFormat
|---NLineInputFormat
|---SequenceFileInputFormat
|---TeraInputFormat
|---TextInputFormat
当中TextInputFormat是Hadoop默认的输入方法,在TextInputFormat中,每一个文件(或其一部分)都会单独地作为map的输入,而这个是继承自FileInputFormat的。之后,每行数据都会生成一条记录,每条记录则表示成<key,value>形式:
- key值是每一个数据的记录在数据分片中字节偏移量,数据类型是LongWritable;
value值是每行的内容,数据类型是Text。
(2)OutputFormat
每一种输入格式都有一种输出格式与其相应。默认的输出格式是TextOutputFormat,这样的输出方式与输入类似,会将每条记录以一行的形式存入文本文件。只是,它的键和值能够是随意形式的,由于程序内容会调用toString()方法将键和值转换为String类型再输出。
3)Map类中map方法分析
public static class Map extends MapReduceBase implements
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();public void map(LongWritable key, Text value,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output, Reporter reporter)
throws IOException {
String line = value.toString();
StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(line);
while (tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(tokenizer.nextToken());
output.collect(word, one);
}
}
}
Map类继承自MapReduceBase,而且它实现了Mapper接口,此接口是一个规范类型,它有4种形式的參数,分别用来指定map的输入key值类型、输入value值类型、输出key值类型和输出value值类型。在本例中,由于使用的是TextInputFormat,它的输出key值是LongWritable类型,输出value值是Text类型,所以map的输入类型为<LongWritable,Text>。在本例中须要输出<word,1>这种形式,因此输出的key值类型是Text,输出的value值类型是IntWritable。
实现此接口类还须要实现map方法,map方法会详细负责对输入进行操作,在本例中,map方法对输入的行以空格为单位进行切分,然后使用OutputCollect收集输出的<word,1>。
4)Reduce类中reduce方法分析
public static class Reduce extends MapReduceBase implements
Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
public void reduce(Text key, Iterator<IntWritable> values,
OutputCollector<Text, IntWritable> output, Reporter reporter)
throws IOException {
int sum = 0;
while (values.hasNext()) {
sum += values.next().get();
}
output.collect(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
}
Reduce类也是继承自MapReduceBase的,须要实现Reducer接口。Reduce类以map的输出作为输入,因此Reduce的输入类型是<Text,Intwritable>。而Reduce的输出是单词和它的数目,因此,它的输出类型是<Text,IntWritable>。Reduce类也要实现reduce方法,在此方法中,reduce函数将输入的key值作为输出的key值,然后将获得多个value值加起来,作为输出的值。
3.3 新的WordCount分析
1)源码程序
package org.apache.hadoop.examples;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser;
public class WordCount {
public static class TokenizerMapper
extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable>{
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken());
context.write(word, one);
}
}
}
public static class IntSumReducer
extends Reducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable> {
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable val : values) {
sum += val.get();
}
result.set(sum);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = new Job(conf, "word count");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
1)Map过程
public static class TokenizerMapper
extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable>{
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken());
context.write(word, one);
}
}
Map过程须要继承org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce包中Mapper类,并重写其map方法。通过在map方法中加入两句把key值和value值输出到控制台的代码,能够发现map方法中value值存储的是文本文件里的一行(以回车符为行结束标记),而key值为该行的首字母相对于文本文件的首地址的偏移量。然后StringTokenizer类将每一行拆分成为一个个的单词,并将<word,1>作为map方法的结果输出,其余的工作都交有MapReduce框架处理。
2)Reduce过程
public static class IntSumReducer
extends Reducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable> {
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable val : values) {
sum += val.get();
}
result.set(sum);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
Reduce过程须要继承org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce包中Reducer类,并重写其reduce方法。Map过程输出<key,values>中key为单个单词,而values是相应单词的计数值所组成的列表,Map的输出就是Reduce的输入,所以reduce方法仅仅要遍历values并求和,就可以得到某个单词的总次数。
3)运行MapReduce任务
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs();
if (otherArgs.length != 2) {
System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>");
System.exit(2);
}
Job job = new Job(conf, "word count");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
在MapReduce中,由Job对象负责管理和执行一个计算任务,并通过Job的一些方法对任务的參数进行相关的设置。此处设置了使用TokenizerMapper完毕Map过程中的处理和使用IntSumReducer完毕Combine和Reduce过程中的处理。还设置了Map过程和Reduce过程的输出类型:key的类型为Text,value的类型为IntWritable。任务的输出和输入路径则由命令行參数指定,并由FileInputFormat和FileOutputFormat分别设定。完毕对应任务的參数设定后,就可以调用job.waitForCompletion()方法执行任务。
4、WordCount处理过程
本节将对WordCount进行更具体的解说。具体运行过程例如以下:
1)将文件拆分成splits,因为測试用的文件较小,所以每一个文件为一个split,并将文件按行切割形成<key,value>对,如图4-1所看到的。这一步由MapReduce框架自己主动完毕,当中偏移量(即key值)包含了回车所占的字符数(Windows和Linux环境会不同)。

图4-1 切割过程
2)将切割好的<key,value>对交给用户定义的map方法进行处理,生成新的<key,value>对,如图4-2所看到的。
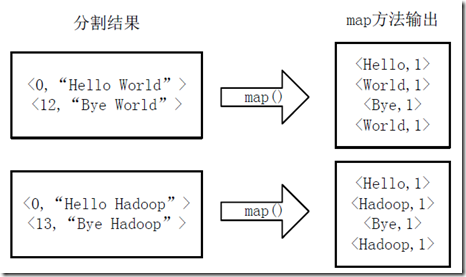
图4-2 运行map方法
3)得到map方法输出的<key,value>对后,Mapper会将它们依照key值进行排序,并运行Combine过程,将key至同样value值累加,得到Mapper的终于输出结果。如图4-3所看到的。

图4-3 Map端排序及Combine过程
4)Reducer先对从Mapper接收的数据进行排序,再交由用户自己定义的reduce方法进行处理,得到新的<key,value>对,并作为WordCount的输出结果,如图4-4所看到的。
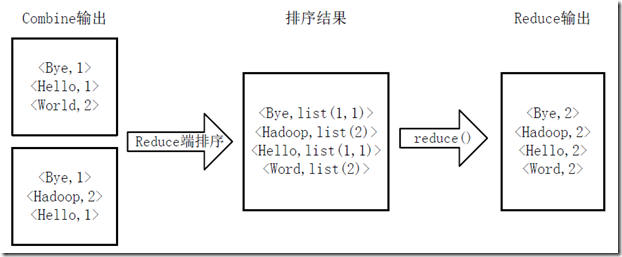
图4-4 Reduce端排序及输出结果
5、MapReduce新旧改变
Hadoop最新版本号的MapReduce Release 0.20.0的API包含了一个全新的Mapreduce JAVA API,有时候也称为上下文对象。
新的API类型上不兼容曾经的API,所以,曾经的应用程序须要重写才干使新的API发挥其作用 。
新的API和旧的API之间有以下几个明显的差别。
- 新的API倾向于使用抽象类,而不是接口,由于这更easy扩展。比如,你能够加入一个方法(用默认的实现)到一个抽象类而不需改动类之前的实现方法。在新的API中,Mapper和Reducer是抽象类。
- 新的API是在org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce包(和子包)中的。之前版本号的API则是放在org.apache.hadoop.mapred中的。
- 新的API广泛使用context object(上下文对象),并同意用户代码与MapReduce系统进行通信。比如,MapContext基本上充当着JobConf的OutputCollector和Reporter的角色。
- 新的API同一时候支持"推"和"拉"式的迭代。在这两个新老API中,键/值记录对被推mapper中,但除此之外,新的API同意把记录从map()方法中拉出,这也适用于reducer。"拉"式的一个实用的样例是分批处理记录,而不是一个接一个。
- 新的API统一了配置。旧的API有一个特殊的JobConf对象用于作业配置,这是一个对于Hadoop通常的Configuration对象的扩展。在新的API中,这样的差别没有了,所以作业配置通过Configuration来完毕。作业控制的运行由Job类来负责,而不是JobClient,它在新的API中已经荡然无存。
hadoop高速扫盲帖,从零了解hadoop的更多相关文章
- 从零自学Hadoop系列索引
本文版权归mephisto和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但须保留此段声明,并给出原文链接,谢谢合作. 文章是哥(mephisto)写的,SourceLink 从零自学Hadoop(01):认识Hadoop ...
- 从零自学Hadoop(01):认识Hadoop
本文版权归mephisto和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但须保留此段声明,并给出原文链接,谢谢合作. 文章是哥(mephisto)写的,SourceLink 阅读目录 序 Hadoop 项目起源 优点 核心 ...
- 从零自学Hadoop(22):HBase协处理器
阅读目录 序 介绍 Observer操作 示例下载 系列索引 本文版权归mephisto和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但须保留此段声明,并给出原文链接,谢谢合作. 文章是哥(mephisto)写的,Sour ...
- 从零自学Hadoop(20):HBase数据模型相关操作上
阅读目录 序 介绍 命名空间 表 系列索引 本文版权归mephisto和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但须保留此段声明,并给出原文链接,谢谢合作. 文章是哥(mephisto)写的,SourceLink 序 ...
- 从零自学Hadoop(21):HBase数据模型相关操作下
阅读目录 序 变量 数据模型操作 系列索引 本文版权归mephisto和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但须保留此段声明,并给出原文链接,谢谢合作. 文章是哥(mephisto)写的,SourceLink 序 ...
- 从零自学Hadoop(19):HBase介绍及安装
阅读目录 序 介绍 安装 系列索引 本文版权归mephisto和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但须保留此段声明,并给出原文链接,谢谢合作. 文章是哥(mephisto)写的,SourceLink 序 上一篇, ...
- 从零自学Hadoop(18):Hive的CLI和JDBC
阅读目录 序 Hive CLI(old CLI) Beeline CLI(new CLI) JDBC Demo下载 系列索引 本文版权归mephisto和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但须保留此段声明,并给出 ...
- 从零自学Hadoop(02):环境准备
阅读目录 起因 虚拟机 Linux 系统安装 系列索引 本文版权归mephisto和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但须保留此段声明,并给出原文链接,谢谢合作. 文章是哥(mephisto)写的,SourceL ...
- 从零自学Hadoop(03):Linux准备上
阅读目录 序 检查列表 常用Linux命令 搭建环境 系列索引 本文版权归mephisto和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但须保留此段声明,并给出原文链接,谢谢合作. 文章是哥(mephisto)写的,Sou ...
随机推荐
- 5.7.1.4 window对象
ECMAScript虽然没有指出如何直接访问Global对象,但web浏览器都是将这个全局对象作为window对象的一部分加以实现的.因此,在全局作用域中声明的所有变量和函数,就都成为了window对 ...
- Sublime Text3中最常用的快捷键
ctrl+D 选词快捷键 反复按这快捷键,可以方便的向下选择相同的词~ alt + shift +2 分2屏 数字为几就是几屏 Alt + F3 可以一次性选择一个文件里面的所有相同的文本进行编辑 ...
- <正向/反向>最大匹配算法(Java)
算法描述(正向): 给定最大词长n,待分词文本str,指针f=0,词典dic文档 1 取子串sub=str(f,f+n) 2 如果(遍历dic,有匹配sub) f++; 3 否则 n--; 4 注意: ...
- 转:angular的decorator方法
AngularJS实例 – 装饰$log 在AngularJS中,我们可以使用Angular内置或者自定义的services,在应用的各个部分之间分享数据和方法.假设你已经定义了一个service,但 ...
- php基础知识总结
PHP 代表 PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor PHP 文件可包含文本.HTML.JavaScript代码和 PHP 代码 PHP 代码在服务器上执行,结果以纯 HTML 形式返 ...
- WA(Write Amplification)写入放大
WA是闪存及SSD相关的一个极为重要的属性.由于闪存必须先擦除才能再写入的特性,在执行这些操作时,数据都会被移动超过1次.这些重复的操作不单会增加写入的数据量,还会减少闪存的寿命,更吃光闪存的可用带宽 ...
- Android网络框架技术
网络相关1. Asynchronous Http Client for Android Android异步Http请求项目地址:https://github.com/loopj/android-asy ...
- tree(简单并差集)
tree Accepts: 156 Submissions: 807 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65 ...
- WebRTC学习笔记_Demo收集
1. WebRTC学习 1.1 WebRTC现状 本人最早接触WebRTC是在2011年底,那时Google已经在Android源代码中增加了webrtc源代码,放在/external/w ...
- 判断两个XML文件结构与内容是否相同
1. 引入 目前公司的这款软件导入导出数据库信息的方法是:组织数据的内容和结构 利用MS com的sax解析 储存数据为XML格式 优点是可以选择部分导出 缺点是速度慢文件导出的文件庞大,若客户出现 ...
