样例GeoQuiz应用开发 第2章
先介绍一下MVC,Model View Controller,是软件架构中最常见的一种框架。
简单来说就是通过 controller 的控制去操作 model 层的数据,并且返回给 view 层展示,具体见下图
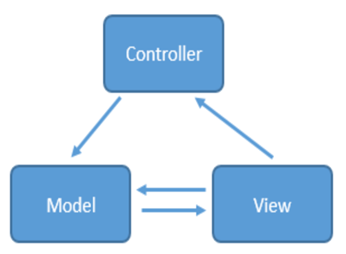
当用户出发事件的时候,view 层会发送指令到 controller 层,接着 controller 去通知model层更新数据,model层更新完数据以后直接显示在view层上,这就是MVC的工作原理。
1)模型(Model)
Model是一个应用系统的核心部分,代表了该系统实际要实现的所有功能处理。比如:在视频播放器中,模型代表一个视频数据库及播放视频的程序函数代码;在拍照应用中,模型代表一个照片数据库,及看图片时的程序函数代码。在一个电话应用中,Model代表一个电话号码簿,以及拨打电话和发送短信的程序函数代码。Model在values目录下通过xml文件格式生成,也可以通过硬编码的方式直接Java代码生成。
2)视图(View)
View是软件应用传送给用户的一个反馈结果。它代表软件应用中的图形展示、声音播放、触觉反馈等职责。视图的根节点是应用程序的自身窗口。比如,视频播放器中可能包含当前播放的画面,这个画面就是一个视图。另一个视图组件可能是该视频的文字标题。再一个就是一些播放按键,View在layout目录下通过xml文件格式生成,用findViewById()获取;也可以通过硬编码的方式直接Java代码生成。
3)控制器(Controller)
Controller在软件应用负责对外部事件的响应,包括:键盘敲击、屏幕触摸、电话呼入等。Controller实现了一个事件队列,每一个外部事件均在事件队列中被唯一标识。框架依次将事件从队列中移出并派发出去。
任务要求实现GeoQuiz 能从多个题目之间切换。(所有的代码都会更新)

代码更新:
activity_main.xml代码:
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- android:gravity="center"
- android:orientation="vertical">
- <TextView
- android:id="@+id/question_text_view"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:padding="24dp"
- />
- <LinearLayout
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:orientation="horizontal">
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/true_button"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="@string/true_button"/>
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/false_button"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="@string/false_button"/>
- </LinearLayout>
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/next_button"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="@string/next_button"/>
- </LinearLayout>
MainActivity.java代码 :
- package com.example.a83856.myapplication1;
- import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.widget.Button;
- import android.widget.ImageButton;
- import android.widget.TextView;
- import android.widget.Toast;
- public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
- private Button mTrueButton;
- private Button mFalseButton;
- private Button mNextButton;
- private TextView mQuestionTextView;
- private Question[] mQuestionBank=new Question[]{
- new Question(R.string.question_ocean,true),
- new Question(R.string.question_mideast,false),
- new Question(R.string.question_africa,false),
- new Question(R.string.question_americas,true),
- new Question(R.string.question_asia,true),
- };
- private int mCurrentIndex=0;
- private void updateQuestion(){
- int question=mQuestionBank[mCurrentIndex].getTextResId();
- mQuestionTextView.setText(question);
- }
- private void checkAnswer(boolean uesrPressesTrue){
- boolean answerIsTrue=mQuestionBank[mCurrentIndex].isAnswerTrue();
- int messageResId=0;
- if(uesrPressesTrue==answerIsTrue)
- messageResId=R.string.correct_toast;
- else
- messageResId=R.string.incorrect_toast;
- Toast.makeText(this,messageResId,Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
- }
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
- mQuestionTextView=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.question_text_view);
- updateQuestion();
- mTrueButton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.true_button);
- mTrueButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- checkAnswer(true);
- }
- });
- mFalseButton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.false_button);
- mFalseButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- checkAnswer(false);
- }
- });
- mNextButton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.next_button);
- mNextButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- mCurrentIndex=(mCurrentIndex+1)%mQuestionBank.length;
- updateQuestion();
- }
- });
- updateQuestion();
- }
- }
strings.xml代码:
- <resources>
- <string name="app_name">My Application1</string>
- <string name="question_text">Constantinople is the largest city in Turkey</string>
- <string name="true_button">TRUE</string>
- <string name="false_button">FALSE</string>
- <string name="correct_toast">Correct!</string>
- <string name="incorrect_toast">Incorrect!</string>
- <string name="next_button">NEXT</string>
- <string name="question_ocean">The Pacific Ocean is larger than the Atlantic Qcean.</string>
- <string name="question_mideast">The Suez Canal connects the Red Sea and the Indian Ocean.</string>
- <string name="question_africa">The source of the Nile River is in Egypt.</string>
- <string name="question_americas">The Amazon River is the longest river in the Americas.</string>
- <string name="question_asia">Lake Baikal is the world\'s oldest and deepest freshwater lake.</string>
- </resources>
1. Question类中封装了什么东西?为什么能这么用?
Question类中封装了两部分数据:问题文本和问题答案。
但是注意mTextResId是int类型而不是String 类型,是因为该变量保存的是地理知识问题的字符串资源的ID而资源ID总是int类型同时为这两个变量设置获取方法和设置方法。
同时根据我们上面说到的MVC模式,可以知道,模型对象不关心用户界面,它存在的目的就是存储和管理应用数据。这里面的Question类其实就很类似,它只存储对应的地理知识的题面和答案,其他的和它并没有什么关系,所以只需要再控制视图层,逐条显示对应的题面就可以了。
挑战题:
1. 用户点击应用的Textview文字区域,也可以跳转到下一题。
- mQuestionTextView=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.question_text_view);
- updateQuestion();
- 被替换为,设置监听器即可。(TextView也是View的一个子类,和Button一样都可以设置监听器)
- mQuestionTextView=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.question_text_view);//给TextView设计监听器,达到点击也会进行题面变化
- mQuestionTextView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- mCurrentIndex=(mCurrentIndex+1)%mQuestionBank.length;
- updateQuestion();
- }
- });
2. 添加后退按钮。
string.xml增加:
- <string name="pre_button">PRE</string>
actiity_main.xml中:
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/next_button"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="@string/next_button"/>
- 这块要增加对应的模块,变化为:
- <LinearLayout
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:orientation="horizontal">
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/pre_button"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="@string/pre_button"
- android:drawableLeft="@drawable/arrow_left"
- android:drawablePadding="4dp"/>
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/next_button"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="@string/next_button"
- android:drawableRight="@drawable/arrow_right"
- android:drawablePadding="4dp"/>
- </LinearLayout>
对应的MainActivity.java中增加:
- mPreButton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.pre_button);
- mPreButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- if(mCurrentIndex== 0){
- int question = mQuestionBank[mQuestionBank.length -1].getTextResId();
- mQuestionTextView.setText(question);
- mCurrentIndex=4;
- } else{
- mCurrentIndex=(mCurrentIndex -1);
- updateQuestion();
- }
- }
- });
- 注意0的时候要特判一下,不然会运行错误。
3. 从按钮到图标按钮:
完成这个需要使用ImageButton组件,对应的代码改变。
activity_main.xml中:
- <LinearLayout
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:orientation="horizontal">
- <ImageButton
- android:id="@+id/pre_button"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:src="@drawable/arrow_left"/>
- <ImageButton
- android:id="@+id/next_button"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:src="@drawable/arrow_right"/>
- </LinearLayout>
Activity_main.java中:
- mPreButton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.pre_button);
- mNextButton=(Button)findViewById(R.id.next_button);
- 替换为,其他的没有什么变化。
- mPreButton=(ImageButton)findViewById(R.id.pre_button);
- mNextButton=(ImageButton)findViewById(R.id.next_button);
样例GeoQuiz应用开发 第2章的更多相关文章
- 样例GeoQuiz应用开发 第1章
1. Activity是Android SDK的Activity类的一个具体实例,负责管理用户和信息屏的交互.应用的功能是通过编写一个Activity子类来实现的.简单的可能只有一个子类,复杂的应用则 ...
- nginx https 配置样例
站点nginx https 配置模板 第一章 nginx 支持https 配置样例 其他 相关链接地址 第一章 nginx 支持https 配置样例 说明:https 段配置参数说明 Server 段 ...
- C#开发Unity游戏教程循环遍历做出推断及Unity游戏演示样例
C#开发Unity游戏教程循环遍历做出推断及Unity游戏演示样例 Unity中循环遍历每一个数据,并做出推断 非常多时候.游戏在玩家做出推断以后.游戏程序会遍历玩家身上大量的所需数据,然后做出推断. ...
- 2单表CRUD综合样例开发教程
东软集团股份有限公司 基础软件事业部 单表CRUD综合样例开发教程 东软机密 tui 更改履历 版本号 更改时间 更改的 图表和章节号 状态 更改简要描述 更改申 请编号 更改人 批准人 V1.0 2 ...
- 构造Scala开发环境并创建ApiDemos演示样例项目
从2011年開始写Android ApiDemos 以来.Android的版本号也更新了非常多,眼下的版本号已经是4.04. ApiDemos中的样例也添加了不少,有必要更新Android ApiDe ...
- 让你提前认识软件开发(19):C语言中的协议及单元測试演示样例
第1部分 又一次认识C语言 C语言中的协议及单元測试演示样例 [文章摘要] 在实际的软件开发项目中.常常要实现多个模块之间的通信.这就须要大家约定好相互之间的通信协议,各自依照协议来收发和解析消息. ...
- 【COCOS2D-HTML5 开发之三】演示样例项目附源代码及执行的GIF效果图
本站文章均为李华明Himi原创,转载务必在明显处注明:(作者新浪微博:@李华明Himi) 转载自[黑米GameDev街区] 原文链接: http://www.himigame.com/cocos2d- ...
- SNF快速开发平台MVC-各种级联绑定方式,演示样例程序(包含表单和表格控件)
做了这么多项目,经常会使用到级联.联动的情况. 如:省.市.县.区.一级分类.二级分类.三级分类.仓库.货位. 方式:有表单需要做级联的,还是表格行上需要做级联操作的. 实现:实现方法也有很多种方式. ...
- SNF开发平台WinForm-审核流使用方法样例
一.效果如下: 二.如何实现 1.程序的数据表设计规范,参考<09.SNF-C#编程规范V1.5.docx>文件. 2.程序操作程序 2.1.在程序页面拖拽控件 2.2.程序的Load事件 ...
随机推荐
- 【190】修改 PowerShell & CMD 显示字体
方法一:Windows7更改替换cmd(powershell)字体完全方法教程 说明:该方法将字体修改成只能显示英文,对于某些中文会乱码!(chcp 850) 方法二:添加中文字体(chcp 936) ...
- POJ2486 Apple Tree 【树上背包】
一句话题意:一棵树,一共n个点,每个点上有一个权值,求从1出发,走k步,最多能遍历到的权值.可以往回走. 第一(二)道树上背包题,先是看了dalao的题解,改了一点就过样例了.然而....TLE??? ...
- linux 查看进程和端口
1.进程查看 #ps aux | grep java 2.查看系统与内核相关信息 #uname [-asrmpi] 查看系统位数 # uname -m 3.查看端口 #netstat [-aatunl ...
- Poj 2947 widget factory (高斯消元解同模方程)
题目连接: http://poj.org/problem?id=2947 题目大意: 有n种类型的零件,m个工人,每个零件的加工时间是[3,9],每个工人在一个特定的时间段内可以生产k个零件(可以相同 ...
- 文件输入输出C++操作
基于C++的文件操作 在C++中,有一个stream这个类,所有的I/O都以这个"流"类为基础的,包括我们要认识的文件I/O,stream这个类有两个重要的运算符: 1.插入器(& ...
- tac命令的实现 分类: linux 2014-06-02 00:08 344人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
此程序实现简化的linux中的tac命令.即对文件按行倒序输出. 首先将文件指针置于文件尾,从后向前移动指针, 将两个换行符'\n'间的内容作为一行输出. #include<stdio.h> ...
- iOS开发系列--通知与消息机制--转
来自:http://www.cocoachina.com/ios/20150318/11364.html 概述 在多数移动应用中任何时候都只能有一个应用程序处于活跃状态,如果其他应用此刻发生了一些用户 ...
- [转]Monkey测试简介
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/manuosex/p/3215270.html 在android手机上做自动化测试,monkey比cts,Android UnitTest 好用多了 ...
- Webform 三级联动例子
首先分别做三个下拉列表 <body> <form id="form1" runat="server"> <asp:DropDown ...
- hihocoder编程练习赛52-2 亮灯方案
思路: 状态压缩dp.实现: #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; ; ] = {, , ...
