HashMap中的TreeNode,红黑树源码分析
在看HashMap的源码时候看到了TreeNode。因此需要对其进行一个了解。是一个红黑树。可以百度一下红黑树的数据结构。分析了下源码,还是比较枯燥的
红黑树的性质:本身是一个二叉查找树(所有左节点的值都比右节点的小)。另:
- 节点是红色或者黑色
- 根节点是黑色
- 每个叶节点(Nil节点,空节点)是黑色的
- 每个红节点对应的两个子节点都是黑色的(不可能有两个相连的红节点)。
- 从任意节点出发,到每个叶子节点都有相同的黑色节点。
这保证了红黑数是平衡的,从根到叶子的最长的可能路径不多于最短的可能路径的两倍长,因此插入、删除查找的最坏情况是有所保证的,与树的高度成正比。原因有两点:
- 最短的可能路径都是黑色节点。
- 最长的路径是红黑节点交替的路径。
因为从同一节点出发,到每一个叶子有相同的黑色节点,所以保证了最长路径是最短路径的两倍长。
一、成员变量与构造函数
- static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
- //父节点
- HashMap.TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links
- //左节点
- HashMap.TreeNode<K,V> left;
- //右节点
- HashMap.TreeNode<K,V> right;
- //用来删除下一个节点用的,因此prev也就是上一个节点
- HashMap.TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
- //节点是否为红色
- boolean red;
- TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, HashMap.Node<K,V> next) {
- super(hash, key, val, next);
- }
- }
二、Function root
- /**
- * 返回包含此节点的树的根节点
- */
- final HashMap.TreeNode<K,V> root() {
- //定义两个TreeNode,一个是父节点指针,指向当前节点的parent,所以功能很明显了。就是遍历直到头节点
- for (HashMap.TreeNode<K,V> r = this, p;;) {
- if ((p = r.parent) == null)
- return r;
- r = p;
- }
- }
三、Function checkInvariants
- /**
- * 不变性检查,保证红黑树的结构不改变。
- */
- static <K, V> boolean checkInvariants(HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> t) {
- HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> tp = t.parent, tl = t.left, tr = t.right,
- tb = t.prev, tn = (HashMap.TreeNode<K, V>) t.next;
- if (tb != null && tb.next != t)
- return false;
- if (tn != null && tn.prev != t)
- return false;
- if (tp != null && t != tp.left && t != tp.right)
- return false;
- if (tl != null && (tl.parent != t || tl.hash > t.hash))
- return false;
- if (tr != null && (tr.parent != t || tr.hash < t.hash))
- return false;
- if (t.red && tl != null && tl.red && tr != null && tr.red)
- return false;
- if (tl != null && !checkInvariants(tl))
- return false;
- if (tr != null && !checkInvariants(tr))
- return false;
- return true;
- }
- }
四、Function moveRootToFront
- /**
- * 确保所给的root是第一个节点。也就是把所给的root移到第一个节点。确保桶的红黑树的跟节点是root
- */
- static <K, V> void moveRootToFront(HashMap.Node<K, V>[] tab, HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> root) {
- int n;
- if (root != null && tab != null && (n = tab.length) > 0) {
- //根节点的位置
- int index = (n - 1) & root.hash;
- //链表的操作,把root移到第一个节点。root的next指向原先的头节点,原先的头节点的prev指向root;
- //root的next的prev指向root的prev,root的prev指向root的next,即把root在prev和next中去掉
- HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> first = (HashMap.TreeNode<K, V>) tab[index];
- if (root != first) {
- HashMap.Node<K, V> rn;
- tab[index] = root;
- HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> rp = root.prev;
- if ((rn = root.next) != null)
- ((HashMap.TreeNode<K, V>) rn).prev = rp;
- if (rp != null)
- rp.next = rn;
- if (first != null)
- first.prev = root;
- root.next = first;
- root.prev = null;
- }
- //红黑树的一致性检查
- assert checkInvariants(root);
- }
- }
五、Function find
- /**
- * Finds the node starting at root p with the given hash and key.
- * The kc argument caches comparableClassFor(key) upon first use
- * comparing keys.
- */
- final HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> find(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) {
- HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> p = this;
- do {
- int ph, dir;
- K pk;
- HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> pl = p.left, pr = p.right, q;
- //p的hash > 目标hash, 则查找左子树,否则右子树
- if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
- p = pl;
- else if (ph < h)
- p = pr;
- //找到则返回
- else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk)))
- return p;
- //如果左节点是Null则找右子树,右节点是Null则找左子树
- else if (pl == null)
- p = pr;
- else if (pr == null)
- p = pl;
- //如果不按照hash比较,则按照比较器比较,查找左子树还是右子树
- else if ((kc != null ||
- (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) &&
- (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0)
- p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr;
- //如果在右子树找到则直接返回
- else if ((q = pr.find(h, k, kc)) != null)
- return q;
- //否则在左子树查找
- else
- p = pl;
- } while (p != null);
- //否则返回Null
- return null;
- }
六、Function tieBreakOrder
- /**
- * 在像红黑树插入即节点的时候,为了确定相同hashCode的节点插入的顺序,
- * 设定了插入顺序的规则,结果一定是不想等的。非左即右。
- */
- static int tieBreakOrder(Object a, Object b) {
- int d;
- //会对两个类名相等的类进行比较
- if (a == null || b == null ||
- (d = a.getClass().getName().
- compareTo(b.getClass().getName())) == 0)
- //返回两个类内存地址的hashCode比较结果,小的或者相都是-1,否则1,并非是类的hashCode的比较
- d = (System.identityHashCode(a) <= System.identityHashCode(b) ?
- -1 : 1);
- return d;
- }
七、Function rotateLeft, 左旋
图片来源(https://blog.csdn.net/sun_tttt/article/details/65445754)

- static <K, V> HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> rotateLeft(HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> root,
- HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> p) {
- //三个节点,右节点,parent的parent节点,右的左节点
- HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> r, pp, rl;
- //该节点不为null并且右节点不为null
- if (p != null && (r = p.right) != null) {
- //因为是左旋,所以如果右节点的左节点如果不为null,则rl的根节点设为p
- if ((rl = p.right = r.left) != null)
- rl.parent = p;
- //如果左旋后的头节点为根节点,则根据红黑树的性质,颜色为黑色
- if ((pp = r.parent = p.parent) == null)
- (root = r).red = false;
- //因为是左旋,所以p的位置由pr取代,所以p的parent节点的p位置设为现在pr的位置。
- else if (pp.left == p)
- pp.left = r;
- else
- pp.right = r;
- //然后r的left是p,p的父节点是r
- r.left = p;
- p.parent = r;
- }
- return root;
- }
八、Function rightRotate, 右旋
图片来源(https://blog.csdn.net/sun_tttt/article/details/65445754)
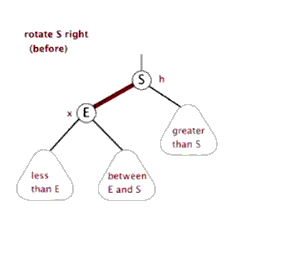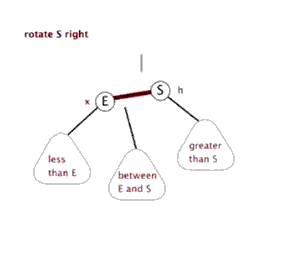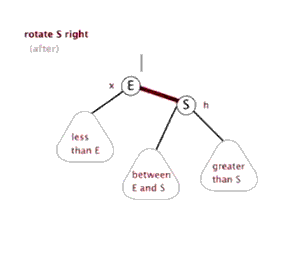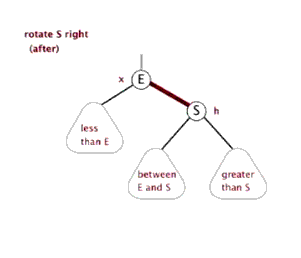
- static <K, V> HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> rotateRight(HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> root,
- HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> p) {
- //定义3个节点,左节点,头节点的头节点,左节点的右节点
- HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> l, pp, lr;
- //要旋转的节点和左节点不为空时
- if (p != null && (l = p.left) != null) {
- //根据右旋,(原)头节点的左节点为原先左节点的右节点,并且把其父节点设为原头节点,即p
- if ((lr = p.left = l.right) != null)
- lr.parent = p;
- //同样,如果现在的头节点为根节点的话,标记节点的颜色为黑色
- if ((pp = l.parent = p.parent) == null)
- (root = l).red = false;
- //头节点的头节点设定其自节点
- else if (pp.right == p)
- pp.right = l;
- else
- pp.left = l;
- //同样,根据右旋,指定现在的头节点的右节点为原先的头节点,原先的头节点的父节点为现在的头节点
- l.right = p;
- p.parent = l;
- }
- return root;
- }
九、Function balanceInsertion 代码和图结合看很好理解过程,至于为什么会平衡还要分析。
图片来源https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42340670/article/details/80550932
1.无旋转
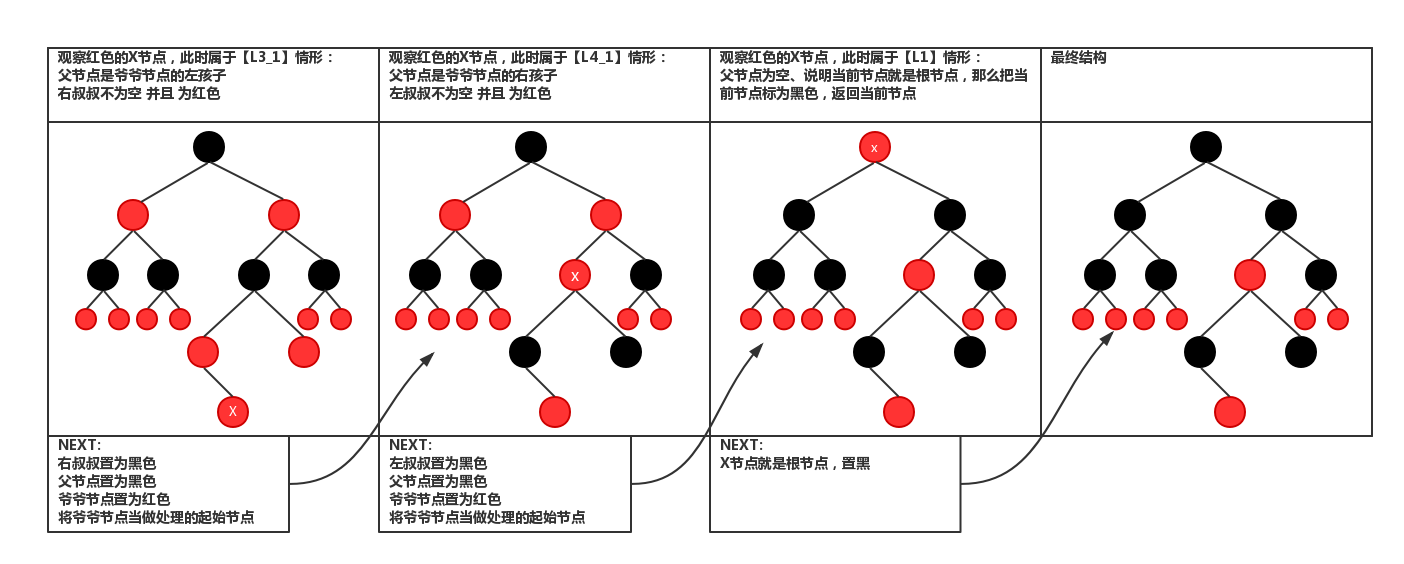
2.旋转情况1
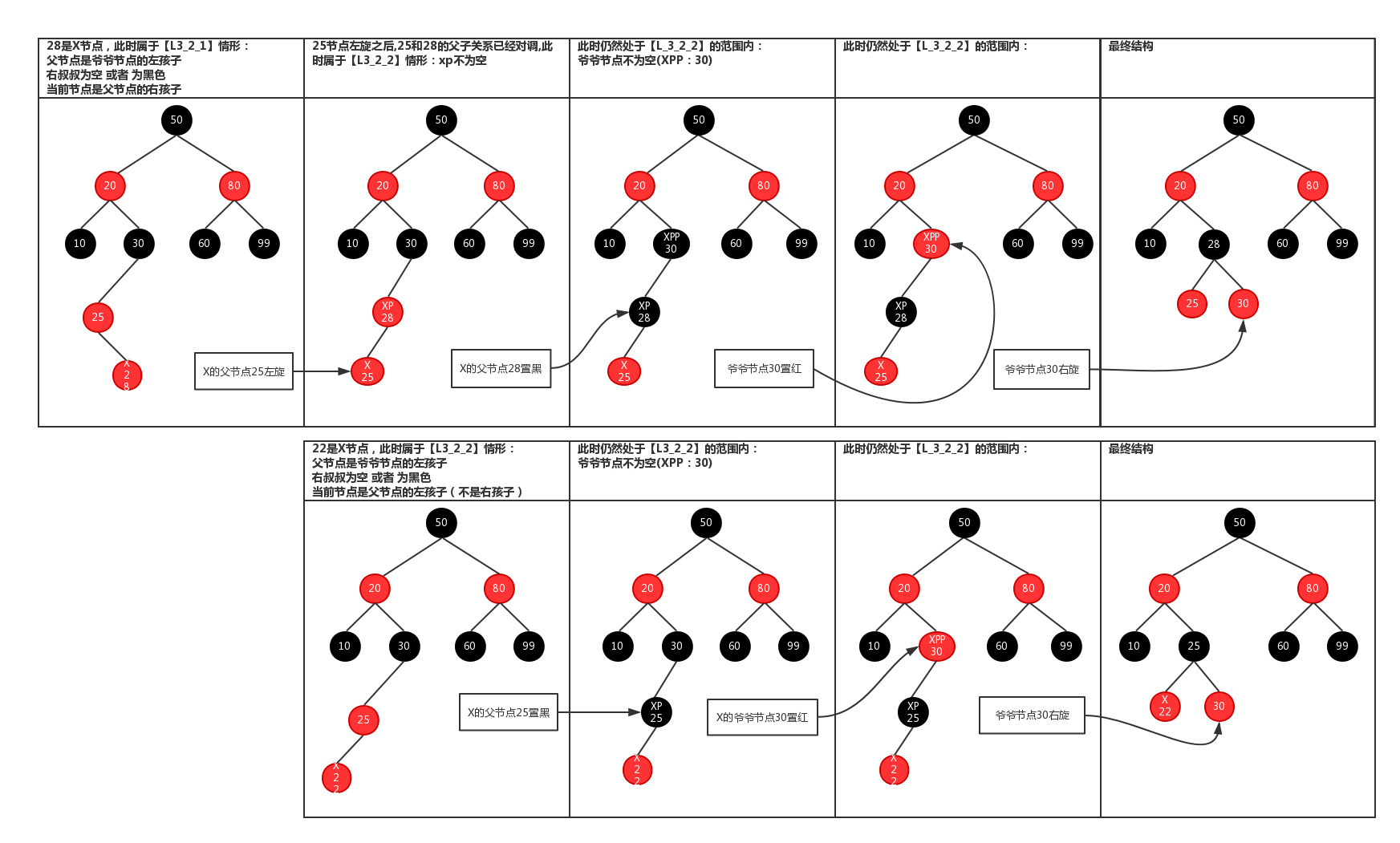
3.旋转情况2

- /*
- 保证插入节点后,红黑树仍然是平衡的,代码很长,结合图看更好理解点,这样看太抽象了。但是虽然逻辑复杂,但是足以
- 见证红黑树的高效性,因为更新树的话只是旋转操作,即改变下指针的位置,并且设置一下节点的位置就可以了
- */
- static <K, V> HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> balanceInsertion(HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> root,
- HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> x) {
- //先把节点设为红色
- x.red = true;
- //定义四个节点
- for (HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> xp, xpp, xppl, xppr; ; ) {
- //如果x是根节点,则把它设为黑色,并返回根节点
- if ((xp = x.parent) == null) {
- x.red = false;
- return x;
- }
- //如果x的父节点即xp是黑色,并且xp为根节点,则返回,什么也不做。
- else if (!xp.red || (xpp = xp.parent) == null)
- return root;
- //如果xp为xp父节点的左节点
- if (xp == (xppl = xpp.left)) {
- //如果xpp的右节点非空并且是红色的,那么把其设为黑色,xpp的左节点也设为黑色,xpp设为红色,并且x等于xpp
- if ((xppr = xpp.right) != null && xppr.red) {
- xppr.red = false;
- xp.red = false;
- xpp.red = true;
- x = xpp;
- }
- //如果xpp的右节点是空或者为黑色的话
- else {
- //如果x是xp的右节点,那么左旋xp节点,并且重新更新xp和xpp
- if (x == xp.right) {
- root = rotateLeft(root, x = xp);
- xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent;
- }
- //如果x的父节点不为空,先把它设为黑色
- if (xp != null) {
- xp.red = false;
- //如果xp的父节点不为空,则先把xpp设为红色,然后再右旋
- if (xpp != null) {
- xpp.red = true;
- root = rotateRight(root, xpp);
- }
- }
- }
- }
- //如果xp为xp父节点的右右节点
- else {
- //如果xpp的左节点非空并且是红色的话,把xppl设为黑色,xp设为黑色,xp的父节点设为红色
- if (xppl != null && xppl.red) {
- xppl.red = false;
- xp.red = false;
- xpp.red = true;
- x = xpp;
- }
- //如果xpp的左节点是空或者是黑色的话
- else {
- //如果x为父节点的左节点,则右旋xp节点,并重新设置xp,xpp
- if (x == xp.left) {
- root = rotateRight(root, x = xp);
- xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent;
- }
- //如果x的父节点为空,
- if (xp != null) {
- //先把其设为黑色
- xp.red = false;
- //如果xp的父节点不为空,则xpp设为红色,并左旋xpp节点
- if (xpp != null) {
- xpp.red = true;
- root = rotateLeft(root, xpp);
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
十、Function treeify
- /**
- * 把链表生成红黑树,返回头节点
- */
- final void treeify(HashMap.Node<K, V>[] tab) {
- HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> root = null;
- //两个指针,一个是链表的表头,一个是下一个指针
- for (HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> x = this, next; x != null; x = next) {
- next = (HashMap.TreeNode<K, V>) x.next;
- x.left = x.right = null;
- //先设定 root为头节点,parent为null,根节点为黑色,
- if (root == null) {
- x.parent = null;
- x.red = false;
- root = x;
- } else {
- K k = x.key;
- int h = x.hash;
- Class<?> kc = null;
- //遍历红黑树
- for (HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> p = root; ; ) {
- int dir, ph;
- K pk = p.key;
- //如果当前树节点的hash > 链表节点的hash则dir值为-1
- if ((ph = p.hash) > h)
- dir = -1;
- //否则为1
- else if (ph < h)
- dir = 1;
- //如果不按照hash值比较的话,并且比较器不存在或者比较器比较的值是0的话,则把死结打开
- else if ((kc == null &&
- (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) ||
- (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0)
- dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk);
- //设置一个红黑树的节点
- HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> xp = p;
- //设置节点的走向,如果dir <= 0则p为做节点,否则为右,也就是找到链表节点应该插入的位置
- if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) {
- //设置链表节点的父节点
- x.parent = xp;
- if (dir <= 0)
- xp.left = x;
- else
- xp.right = x;
- //插入节点,并且不破坏红黑树的性质
- root = balanceInsertion(root, x);
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- //设置头节点
- moveRootToFront(tab, root);
- }
十一、Function split
- /**
- * 树减枝,
- * 只有在resize的时候才调用该方法
- * @param map the map
- * @param tab 新的table
- * @param index 老的table的index
- * @param bit oldCap
- */
- final void split(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, int index, int bit) {
- TreeNode<K,V> b = this;
- // Relink into lo and hi lists, preserving order
- TreeNode<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
- TreeNode<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
- // 如果size很小的话则把树变成链表,用lc和hc来计数
- int lc = 0, hc = 0;
- // 遍历红黑树
- for (TreeNode<K,V> e = b, next; e != null; e = next) {
- next = (TreeNode<K,V>)e.next;
- e.next = null;
- // 判断将树的节点归为哪一部分
- if ((e.hash & bit) == 0) {
- if ((e.prev = loTail) == null)
- loHead = e;
- else
- loTail.next = e;
- loTail = e;
- ++lc;
- }
- else {
- if ((e.prev = hiTail) == null)
- hiHead = e;
- else
- hiTail.next = e;
- hiTail = e;
- ++hc;
- }
- }
- //lo这部分树放入的位置,index即原先的位置
- if (loHead != null) {
- if (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
- tab[index] = loHead.untreeify(map);
- else {
- tab[index] = loHead;
- if (hiHead != null) // (else is already treeified)
- loHead.treeify(tab);
- }
- }
- //index+bit这部分改变了
- if (hiHead != null) {
- if (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
- tab[index + bit] = hiHead.untreeify(map);
- else {
- tab[index + bit] = hiHead;
- if (loHead != null)
- hiHead.treeify(tab);
- }
- }
- }
HashMap中的TreeNode,红黑树源码分析的更多相关文章
- 物联网安全himqtt防火墙数据结构之红黑树源码分析
物联网安全himqtt防火墙数据结构之红黑树源码分析 随着5G的发展,物联网安全显得特别重要,himqtt是首款完整源码的高性能MQTT物联网防火墙 - MQTT Application FireWa ...
- HashMap实现原理(jdk1.7),源码分析
HashMap实现原理(jdk1.7),源码分析 HashMap是一个用来存储Key-Value键值对的集合,每一个键值对都是一个Entry对象,这些Entry被以某种方式分散在一个数组中,这个数 ...
- RocketMQ中Broker的HA策略源码分析
Broker的HA策略分为两部分①同步元数据②同步消息数据 同步元数据 在Slave启动时,会启动一个定时任务用来从master同步元数据 if (role == BrokerRole.SLAVE) ...
- Java中HashMap底层实现原理(JDK1.8)源码分析
这几天学习了HashMap的底层实现,但是发现好几个版本的,代码不一,而且看了Android包的HashMap和JDK中的HashMap的也不是一样,原来他们没有指定JDK版本,很多文章都是旧版本JD ...
- HashMap底层实现原理(JDK1.8)源码分析
ref:https://blog.csdn.net/tuke_tuke/article/details/51588156 http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaolovewei/p/79 ...
- HashMap和ConcurrentHashMap实现原理及源码分析
HashMap实现原理及源码分析 哈希表(hash table)也叫散列表,是一种非常重要的数据结构,应用场景及其丰富,许多缓存技术(比如memcached)的核心其实就是在内存中维护一张大的哈希表, ...
- 【Java】NIO中Selector的select方法源码分析
该篇博客的有些内容和在之前介绍过了,在这里再次涉及到的就不详细说了,如果有不理解请看[Java]NIO中Channel的注册源码分析, [Java]NIO中Selector的创建源码分析 Select ...
- RocketMQ中Broker的刷盘源码分析
上一篇博客的最后简单提了下CommitLog的刷盘 [RocketMQ中Broker的消息存储源码分析] (这篇博客和上一篇有很大的联系) Broker的CommitLog刷盘会启动一个线程,不停地 ...
- Flink中Idle停滞流机制(源码分析)
前几天在社区群上,有人问了一个问题 既然上游最小水印会决定窗口触发,那如果我上游其中一条流突然没有了数据,我的窗口还会继续触发吗? 看到这个问题,我蒙了???? 对哈,因为我是选择上游所有流中水印最小 ...
随机推荐
- Git Base For Linux
GitHub实战系列汇总:http://www.cnblogs.com/dunitian/p/5038719.html Linux安装git,做个记录吧(使用github提供的隐私邮箱) # git官 ...
- 洛谷P3168 任务查询系统
题意:有n个任务,第i个的存在时间是li~ri,有个权值.求t时刻第k大的权值. 这毒瘤...本来是前缀和 -> 主席树,我是树套树...然后光荣TLE. 其实很裸.一开始我写的是每个位置维护一 ...
- react-native中的state
我们使用两种数据来控制一个组件:props和state.props是在父组件中指定, 而且一经指定,在被指定的组件的生命周期中则不再改变. 对于需要改变的数据,我们需要使用state. 假如我们需要制 ...
- 为什么在Python里推荐使用多进程而不是多线程?(为什么python多线程无法增加CPU使用率?)
最近在看Python的多线程,经常我们会听到老手说:“Python下多线程是鸡肋,推荐使用多进程!”,但是为什么这么说呢? 要知其然,更要知其所以然.所以有了下面的深入研究: 首先强调背景: ...
- Good Bye 2018 D. New Year and the Permutation Concatenation
传送门 https://www.cnblogs.com/violet-acmer/p/10201535.html 题意: 求 n 的所有全排列组成的序列中连续的 n 个数加和为 n*(n+1)/2 的 ...
- text-overflow文本溢出隐藏“...”显示
一.文本溢出省略号显示 1.文本溢出是否“...”显示属性:text-overflow:clip(不显示省略标记)/ellipsis(文本溢出时“...”显示) 定义此属性有四个必要条件:1)须有容器 ...
- 114. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List(M)
. Flatten Binary Tree to Linked List Given a binary tree, flatten it to a linked list in-place. For ...
- (sort 排序)P1583 魔法照片 洛谷
题目描述 一共有n(n≤20000)个人(以1--n编号)向佳佳要照片,而佳佳只能把照片给其中的k个人.佳佳按照与他们的关系好坏的程度给每个人赋予了一个初始权值W[i].然后将初始权值从大到小进行排序 ...
- (贪心)P1223 排队接水 洛谷
题目描述 有n个人在一个水龙头前排队接水,假如每个人接水的时间为Ti,请编程找出这n个人排队的一种顺序,使得n个人的平均等待时间最小. 输入输出格式 输入格式: 输入文件共两行,第一行为n:第二行分别 ...
- Java父类与子类方法调用顺序
父类 FatherClass package 父类与子类方法调用顺序; /** * 父类 * @author shundong * */ public class FatherClass { priv ...
