Python之开发自动化管理工具paramiko
一、paramiko模块使用
1)远程执行主机命令获取结果
方法一
import paramiko # 创建SSH对象
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
# 允许连接不在know_hosts文件中的主机
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
# 连接服务器
ssh.connect(hostname='192.168.12.217', port=, username='root', password='') # 执行命令
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('ls /root')
# 获取命令结果
result = stdout.read()
print(result.decode('utf-8'))
# 关闭连接
ssh.close()
方法二
import paramiko
transport = paramiko.Transport(('192.168.12.217', ))
transport.connect(username='root', password='')
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh._transport = transport
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('df')
res=stdout.read()
print(res.decode('utf-8'))
transport.close()
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy()) 意义在于,ssh 第一次连接没有连接过的主机,可以跳过会弹出的yes,并且在 /root/.ssh/known_hosts里面添加主机信息
2)基于公钥连接,制作密钥连接服务器群,
服务端必须有文件名:authorized_keys(在用ssh-keygen时,必须制作一个authorized_keys,可以用ssh-copy-id来制作)
import paramiko
private_key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file('/tmp/id_rsa')
# 创建SSH对象
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
# 允许连接不在know_hosts文件中的主机
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
# 连接服务器
ssh.connect(hostname='120.92.84.249', port=, username='root', pkey=private_key)
# 执行命令
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command('df')
# 获取命令结果
result = stdout.read()
print(result.decode('utf-8'))
# 关闭连接
ssh.close()
3)上传下载文件,强调是文件
import paramiko
transport = paramiko.Transport(('192.168.12.55',))
transport.connect(username='root',password='xxx')
sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(transport)
# 将location.py 上传至服务器 /tmp/test.py
sftp.put('/tmp/id_rsa', '/etc/test.rsa')
# 将remove_path 下载到本地 local_path
sftp.get('remove_path', 'local_path')
transport.close()
基于公钥上传下载
import paramiko
private_key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file('/tmp/id_rsa')
transport = paramiko.Transport(('192.168.12.55', ))
transport.connect(username='root', pkey=private_key )
sftp = paramiko.SFTPClient.from_transport(transport)
# 将location.py 上传至服务器 /tmp/test.py
sftp.put('/tmp/id_rsa', '/tmp/a.txt')
# 将remove_path 下载到本地 local_path
sftp.get('remove_path', 'local_path')
transport.close()
原文连接:http://www.cnblogs.com/linhaifeng/articles/6817679.html#_label5
二、paramiko模块源码分析
1)下载源码
git clone https://github.com/paramiko/paramiko.git
或下载zip文件
2)执行脚本
[root@jenkens demos]# pwd
/root/paramiko-master/paramiko-master/demos
[root@jenkens demos]# python3 demo.py
3)修改 interactive.py 文件
# Copyright (C) - Robey Pointer <robeypointer@gmail.com>
#
# This file is part of paramiko.
#
# Paramiko is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the
# terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
# Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option)
# any later version.
#
# Paramiko is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY
# WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR
# A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License for more
# details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
# along with Paramiko; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
# Temple Place, Suite , Boston, MA - USA. import socket
import sys
import time # 新增内容
from paramiko.py3compat import u # windows does not have termios...
try:
import termios
import tty has_termios = True
except ImportError:
has_termios = False def interactive_shell(chan):
if has_termios:
posix_shell(chan)
else:
windows_shell(chan) def posix_shell(chan):
import select oldtty = termios.tcgetattr(sys.stdin)
try:
tty.setraw(sys.stdin.fileno())
tty.setcbreak(sys.stdin.fileno())
chan.settimeout(0.0) cmd = [] # 增加的内容
f = open('ssh_test.log','w') # 新增内容
while True:
r, w, e = select.select([chan, sys.stdin], [], [])
if chan in r:
try:
x = u(chan.recv())
if len(x) == :
sys.stdout.write("\r\n*** EOF\r\n")
break
sys.stdout.write(x)
sys.stdout.flush()
except socket.timeout:
pass
if sys.stdin in r:
x = sys.stdin.read()
if len(x) == :
break
if x =='\r': # 新增内容
print('input>',''.join(cmd)) # 新增内容
log = "%s %s\n" %(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X",time.gmtime()),''.join(cmd)) # 新增内容
f.write(log) # 新增内容
cmd = [] # 新增内容
else: # 新增内容
cmd.append(x) # 新增内容
chan.send(x) finally:
termios.tcsetattr(sys.stdin, termios.TCSADRAIN, oldtty)
f.close() # 新增内容 # thanks to Mike Looijmans for this code
def windows_shell(chan):
import threading sys.stdout.write(
"Line-buffered terminal emulation. Press F6 or ^Z to send EOF.\r\n\r\n"
) def writeall(sock):
while True:
data = sock.recv()
if not data:
sys.stdout.write("\r\n*** EOF ***\r\n\r\n")
sys.stdout.flush()
break
sys.stdout.write(data)
sys.stdout.flush() writer = threading.Thread(target=writeall, args=(chan,))
writer.start() try:
while True:
d = sys.stdin.read()
if not d:
break
chan.send(d)
except EOFError:
# user hit ^Z or F6
pass
修改后的文件
4)查看执行效果,获取到实时的日志记录
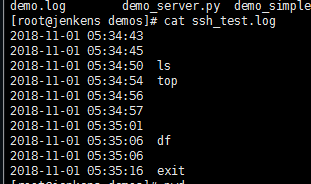
5)分析,用到的文件为
demo.py 执行入口文件
interactive.py 实时输入命令的交互文件
二)实现Django后台传值实时交互
1)调用程序 ssh_connect函数
调用ssh_connect连接,self指传送的对象,封装了ip,端口,用户名,密码
from backend import paramiko_ssh
paramiko_ssh.ssh_connect(self, selected_host_to_user_obj )
2)paramiko_ssh文件代码编写,即ssh_connect入口文件
#!/usr/bin/env python # Copyright (C) - Robey Pointer <robeypointer@gmail.com>
#
# This file is part of paramiko.
#
# Paramiko is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the
# terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
# Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option)
# any later version.
#
# Paramiko is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY
# WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR
# A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License for more
# details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
# along with Paramiko; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
# Temple Place, Suite , Boston, MA - USA. import base64
from binascii import hexlify
import getpass
import os
import select
import socket
import sys
import time
import traceback
from paramiko.py3compat import input import paramiko
try:
import interactive
except ImportError:
from . import interactive def manual_auth(t,hostname,username, password):
default_auth = 'p'
#auth = input('Auth by (p)assword, (r)sa key, or (d)ss key? [%s] ' % default_auth)
# if len(auth) == :
# auth = default_auth
auth = default_auth
if auth == 'r':
default_path = os.path.join(os.environ['HOME'], '.ssh', 'id_rsa')
path = input('RSA key [%s]: ' % default_path)
if len(path) == :
path = default_path
try:
key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file(path)
except paramiko.PasswordRequiredException:
password = getpass.getpass('RSA key password: ')
key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file(path, password)
t.auth_publickey(username, key)
elif auth == 'd':
default_path = os.path.join(os.environ['HOME'], '.ssh', 'id_dsa')
path = input('DSS key [%s]: ' % default_path)
if len(path) == :
path = default_path
try:
key = paramiko.DSSKey.from_private_key_file(path)
except paramiko.PasswordRequiredException:
password = getpass.getpass('DSS key password: ')
key = paramiko.DSSKey.from_private_key_file(path, password)
t.auth_publickey(username, key)
else:
#pw = getpass.getpass('Password for %s@%s: ' % (username, hostname))
t.auth_password(username, password) def ssh_connect(ssh_handler_instance,host_to_user_obj):
hostname = host_to_user_obj.host.ip_addr
port = host_to_user_obj.host.port
username = host_to_user_obj.remote_user.username
password = host_to_user_obj.remote_user.password # now connect
try:
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock.connect((hostname, port))
except Exception as e:
print('*** Connect failed: ' + str(e))
traceback.print_exc()
sys.exit() try:
t = paramiko.Transport(sock)
try:
t.start_client()
except paramiko.SSHException:
print('*** SSH negotiation failed.')
sys.exit() try:
keys = paramiko.util.load_host_keys(os.path.expanduser('~/.ssh/known_hosts'))
except IOError:
try:
keys = paramiko.util.load_host_keys(os.path.expanduser('~/ssh/known_hosts'))
except IOError:
print('*** Unable to open host keys file')
keys = {} # check server's host key -- this is important.
key = t.get_remote_server_key()
if hostname not in keys:
print('*** WARNING: Unknown host key!')
elif key.get_name() not in keys[hostname]:
print('*** WARNING: Unknown host key!')
elif keys[hostname][key.get_name()] != key:
print('*** WARNING: Host key has changed!!!')
sys.exit()
else:
print('*** Host key OK.') if not t.is_authenticated():
manual_auth(t,hostname,username, password)
if not t.is_authenticated():
print('*** Authentication failed. :(')
t.close()
sys.exit() chan = t.open_session()
chan.get_pty()
chan.invoke_shell() chan.crazyeye_account = ssh_handler_instance.user
chan.host_to_user_obj = host_to_user_obj
chan.models = ssh_handler_instance.models
print('*** Here we go!\n')
ssh_handler_instance.models.AuditLog.objects.create(
user = ssh_handler_instance.user ,
log_type = ,
host_to_remote_user = host_to_user_obj,
content = "***user login***"
) interactive.interactive_shell(chan)
chan.close()
t.close() ssh_handler_instance.models.AuditLog.objects.create(
user=ssh_handler_instance.user,
log_type=,
host_to_remote_user=host_to_user_obj,
content="***user logout***"
) except Exception as e:
print('*** Caught exception: ' + str(e.__class__) + ': ' + str(e))
traceback.print_exc()
try:
t.close()
except:
pass
sys.exit()
ssh_connnect
3)与命令交互接口
# Copyright (C) - Robey Pointer <robeypointer@gmail.com>
#
# This file is part of paramiko.
#
# Paramiko is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the
# terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
# Software Foundation; either version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option)
# any later version.
#
# Paramiko is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY
# WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR
# A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License for more
# details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
# along with Paramiko; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
# Temple Place, Suite , Boston, MA - USA. import socket
import sys
import time
from paramiko.py3compat import u # windows does not have termios...
try:
import termios
import tty
has_termios = True
except ImportError:
has_termios = False def interactive_shell(chan):
if has_termios:
posix_shell(chan)
else:
windows_shell(chan) def posix_shell(chan):
import select oldtty = termios.tcgetattr(sys.stdin)
try:
tty.setraw(sys.stdin.fileno())
tty.setcbreak(sys.stdin.fileno())
chan.settimeout(0.0)
cmd = []
#f = open('ssh_test.log','w')
while True:
r, w, e = select.select([chan, sys.stdin], [], [])
if chan in r:
try:
x = u(chan.recv())
if len(x) == :
sys.stdout.write('\r\n*** EOF\r\n')
break
sys.stdout.write(x)
sys.stdout.flush()
except socket.timeout:
pass
if sys.stdin in r:
x = sys.stdin.read()
if len(x) == :
break
if x == '\r':
print('input>',''.join(cmd))
#log = "%s %s\n" %(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", time.gmtime()), ''.join(cmd))
#print(log)
chan.models.AuditLog.objects.create(
user=chan.crazyeye_account,
log_type=,
host_to_remote_user=chan.host_to_user_obj,
content=''.join(cmd)
)
#f.write(log)
cmd = []
else:
cmd.append(x)
chan.send(x) finally:
termios.tcsetattr(sys.stdin, termios.TCSADRAIN, oldtty)
#f.close() # thanks to Mike Looijmans for this code
def windows_shell(chan): print("window chan",chan.host_to_user_obj)
print("window chan",chan.crazyeye_account)
import threading sys.stdout.write("Line-buffered terminal emulation. Press F6 or ^Z to send EOF.\r\n\r\n") def writeall(sock):
while True:
data = sock.recv()
if not data:
sys.stdout.write('\r\n*** EOF ***\r\n\r\n')
sys.stdout.flush()
break
sys.stdout.write(data)
sys.stdout.flush() writer = threading.Thread(target=writeall, args=(chan,))
writer.start() try:
while True:
d = sys.stdin.read()
if not d:
break
chan.send(d)
except EOFError:
# user hit ^Z or F6
pass
interactive
三、修改上面的代码,方便个人扩展,不使用表结构
1)修改ssh_connect文件
#!/usr/bin/env python
import getpass
import os
import socket
import sys
import traceback
from paramiko.py3compat import input
import paramiko try:
import interactive
except ImportError:
from . import interactive def manual_auth(t, hostname, username, password):
default_auth = 'p'
auth = default_auth
if auth == 'r':
default_path = os.path.join(os.environ['HOME'], '.ssh', 'id_rsa')
path = input('RSA key [%s]: ' % default_path)
if len(path) == :
path = default_path
try:
key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file(path)
except paramiko.PasswordRequiredException:
password = getpass.getpass('RSA key password: ')
key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file(path, password)
t.auth_publickey(username, key)
elif auth == 'd':
default_path = os.path.join(os.environ['HOME'], '.ssh', 'id_dsa')
path = input('DSS key [%s]: ' % default_path)
if len(path) == :
path = default_path
try:
key = paramiko.DSSKey.from_private_key_file(path)
except paramiko.PasswordRequiredException:
password = getpass.getpass('DSS key password: ')
key = paramiko.DSSKey.from_private_key_file(path, password)
t.auth_publickey(username, key)
else:
t.auth_password(username, password) def ssh_connect(hostname, port, username, password):
hostname = hostname
port = port
username = username
password = password try:
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock.connect((hostname, port))
except Exception as e:
print('*** Connect failed: ' + str(e))
traceback.print_exc()
sys.exit() try:
t = paramiko.Transport(sock)
try:
t.start_client()
except paramiko.SSHException:
print('*** SSH negotiation failed.')
sys.exit() try:
keys = paramiko.util.load_host_keys(os.path.expanduser('~/.ssh/known_hosts'))
except IOError:
try:
keys = paramiko.util.load_host_keys(os.path.expanduser('~/ssh/known_hosts'))
except IOError:
print('*** Unable to open host keys file')
keys = {} key = t.get_remote_server_key()
if hostname not in keys:
print('*** WARNING: Unknown host key!')
elif key.get_name() not in keys[hostname]:
print('*** WARNING: Unknown host key!')
elif keys[hostname][key.get_name()] != key:
print('*** WARNING: Host key has changed!!!')
sys.exit()
else:
print('*** Host key OK.') if not t.is_authenticated():
manual_auth(t, hostname, username, password)
if not t.is_authenticated():
print('*** Authentication failed. :(')
t.close()
sys.exit() chan = t.open_session()
chan.get_pty()
chan.invoke_shell() # 获取到登录时的用户信息
print('*** Here we go!\n')
# 创建登录时的用户信息,时间等,写入表 print('登录成功') interactive.interactive_shell(chan)
chan.close()
t.close() # 创建退出时的用户信息,时间等,写入表
print('退出成功') except Exception as e:
print('*** Caught exception: ' + str(e.__class__) + ': ' + str(e))
traceback.print_exc()
try:
t.close()
except:
pass
sys.exit() if __name__ == '__main__':
hostname = '192.168.10.13'
port =
username = 'root'
password = ''
ssh_connect(hostname, port, username, password)
2)修改命令交互接口
import socket
import sys
import time
from paramiko.py3compat import u try:
import termios
import tty
has_termios = True
except ImportError:
has_termios = False def interactive_shell(chan):
if has_termios:
posix_shell(chan)
else:
windows_shell(chan) def posix_shell(chan):
import select oldtty = termios.tcgetattr(sys.stdin)
try:
tty.setraw(sys.stdin.fileno())
tty.setcbreak(sys.stdin.fileno())
chan.settimeout(0.0)
cmd = []
#f = open('ssh_test.log','w') # 创建操作日志文件写入,后面也可用表
while True:
r, w, e = select.select([chan, sys.stdin], [], [])
if chan in r:
try:
x = u(chan.recv())
if len(x) == :
sys.stdout.write('\r\n*** EOF\r\n')
break
sys.stdout.write(x)
sys.stdout.flush()
except socket.timeout:
pass
if sys.stdin in r:
x = sys.stdin.read()
if len(x) == :
break
if x == '\r':
print('input>',''.join(cmd))
#log = "%s %s\n" %(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X", time.gmtime()), ''.join(cmd))
#f.write(log)
# 或
# 记录操作日志表信息
cmd = []
else:
cmd.append(x)
chan.send(x) finally:
termios.tcsetattr(sys.stdin, termios.TCSADRAIN, oldtty)
#f.close() # windows_shell 该函数没有用
def windows_shell(chan): print("window chan",chan.host_to_user_obj)
print("window chan",chan.crazyeye_account)
import threading sys.stdout.write("Line-buffered terminal emulation. Press F6 or ^Z to send EOF.\r\n\r\n") def writeall(sock):
while True:
data = sock.recv()
if not data:
sys.stdout.write('\r\n*** EOF ***\r\n\r\n')
sys.stdout.flush()
break
sys.stdout.write(data)
sys.stdout.flush() writer = threading.Thread(target=writeall, args=(chan,))
writer.start() try:
while True:
d = sys.stdin.read()
if not d:
break
chan.send(d)
except EOFError:
# user hit ^Z or F6
pass
执行效果。python ssh_connnect.py
[root@jenkens tools]# python3 ssh_connnect.py
*** Unable to open host keys file
*** WARNING: Unknown host key!
*** Here we go! 登录成功
Last login: Thu Nov :: from 192.168.10.13
hello centos7
Python之开发自动化管理工具paramiko的更多相关文章
- Python黑帽编程1.3 Python运行时与包管理工具
Python黑帽编程1.3 Python运行时与包管理工具 0.1 本系列教程说明 本系列教程,采用的大纲母本为<Understanding Network Hacks Attack and ...
- 前端开发自动化工作流工具,JavaScript自动化构建工具grunt、gulp、webpack介绍
前端开发自动化工作流工具,JavaScript自动化构建工具grunt.gulp.webpack介绍 前端自动化,这样的一个名词听起来非常的有吸引力,向往力.当今时代,前端工程师需要维护的代码变得及为 ...
- Ansible批量自动化管理工具(二)
Ansible批量自动化管理工具(二) 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1A3Iq3gGkGS27L_Gt37_I0g 提取码:ncy2 复制这段内容后打开百度网盘手机App,操 ...
- IOS开发依赖管理工具CocoaPods
CocoaPods IOS开发依赖管理工具 CocoaPods is a dependency manager for Swift and Objective-C Cocoa projects. It ...
- 1.Ansible自动化管理工具
1.Ansible基本概述 Ansible是一个IT自动化的配置管理工具,自动化主要体现在Ansible集成了丰富模块,丰富的功能组件, 可以通过一个命令行完成一系列的操作.进而能减少我们重复性的工作 ...
- Python简单主机批量管理工具
一.程序介绍 需求: 简单主机批量管理工具 需求: 1.主机分组 2.主机信息使用配置文件 3.可批量执行命令.发送文件,结果实时返回 4.主机用户名密码.端口可以不同 5.执行远程命令使用param ...
- Jenkins敏捷开发 自动化构建工具
一.序言 Jenkins 是一款自动化构建工具,能够基于 Maven 构建后端 Java 项目,也能够基于 nodejs 构建前端 vue 项目,并且有可视化 web 界面. 所谓自动化构建是按照一定 ...
- python之supervisor进程管理工具
supervisor是python写的一个管理进程运行的工具,可以很方便的监听.启动.停止.重启一个或多个进程:有了supervisor后,就不用字节写启动和监听的shell脚本了,非常方便. sup ...
- GIT: 分布式开发 代码管理工具使用命令大全
代码管理工具: GIT 什么是GIT? Git是一款免费.开源的分布式版本控制系统,用于敏捷高效地处理任何或小或大的项目 Git是一个开源的分布式版本控制系统,用以有效.高速的处理从很小到非常 ...
随机推荐
- Nginx 功能
本文只针对Nginx在不加载第三方模块的情况能处理哪些事情,由于第三方模块太多所以也介绍不完,当然本文本身也可能介绍的不完整,毕竟只是我个人使用过和了解到过得,欢迎留言交流. Nginx能做什么 ...
- centos 6 下KVM 安装学习之旅
一.虚拟化介绍 虚拟化是云计算的基础.简单的说,虚拟化使得在一台物理的服务器上可以跑多台虚拟机,虚拟机共享物理机的 CPU.内存.IO 硬件资源,但逻辑上虚拟机之间是相互隔离的. 物理机我们一般 ...
- appium ,selenium ,webdriver 运行原理与机制
做测试开发的童鞋都知道,UI自动化你绕不开selenium, webdrvier, appium框架,那么这三者之间有什么关联,它们的原理是什么呢? 简单来说就是: Selenium2 将浏览器原生 ...
- JavaScript oop proto与prototype原型图
[_proto_与prototype] 1.prototype(函数的原型):函数才有prototype.prototype是一个对象,指向了当前构造函数的引用地址. 2._proto_(对象的原型对 ...
- oracle中job定时任务96
.INTERVAL参数常用值示例 每天午夜12点 ''TRUNC(SYSDATE + 1)'' 每天早上8点30分 ''TRUNC(SYSDATE + 1) + ...
- WLC5520无法通过无线客户端进行网管故障解决
客户反馈其办公环境中的WLC5520网管需要通过内部有线网络进行管理,通过无线客户端无法进行管理,远程协助其开启WLC5520的无线管理功能后故障解决.
- tomcat启动闪退之内存不足及显著优化
增大内存: 打开catalina.bat,@echo off回车输入 set JAVA_OPTS=-server -Xms256m -Xmx512m -XX:PermSize=128M -XX:Ma ...
- Character 类
Character 类用于对单个字符进行操作. Character 类在对象中包装一个基本类型 char 的值 char ch = 'a'; // Unicode 字符表示形式char uniChar ...
- centos7下haproxy1.7的使用与配置
centos7下haproxy1.7的使用与配置 haproxy是一个使用C语言编写的自由及开放源代码软件,其提供高可用性.负载均衡,以及基于TCP和HTTP的应用程序代理. 一.haproxy下载 ...
- props传递数据
一.传递数据 1.props 传入单数据 就像 data 一样,prop 可以用在模板内,同样也可以在 vm 实例中像“this.message”这样使用 <template> <d ...
