Spring(DI,AOP) 理解(一)
感觉自己的spring理解的不好.所以重新开始学习.
这篇文章主要是来理解DI(依赖注入),Aop(切面)
一.DI(依赖注入,这里没有涉及到注释.只是用xml文件和Bean的方法来注册pojo,)
依赖注入就是将创建bean对象的权利交给spring框架(控制反转) 然后用Applicationcontext.getBean() 来获取对象.
容器:spring容器创建对象,管理对象,并负责管理对象的生命周期. 容器有两种 BeanFactiory ..ApplicationContext ..多的就不解释了,BeanFactiory 比较low,这里使用ApplicaitonContext
ApplicaitonContext:
1 FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:以基于文件系统的XML配置文件创建ApplicationContext实例。
2 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:以类加载路径下的XML配置文件创建的ApplicationContext实例
3 XmlWebApplicationContext:从web应用下的一个或者多个xml配置文件加载创建ApplicationContext实例
4 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 从一个或者多个基于java的配置类中加载Spring ApplicaitonContext实例
5 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext 基于一个或者多个java的配置类来创建spring web 的应用上下文
二. Aop :面向切面编程.(将复用性很强的模块抽离出来,然后通过配置,将抽离出来的模块(比如日志模块),覆盖到其他需要日志模块的服务上)
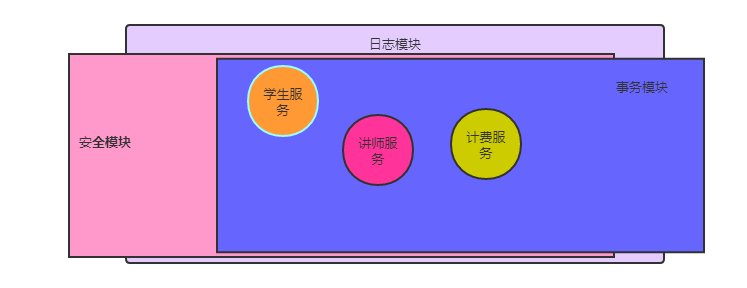
一个项目假设有讲师服务,学生服务,计费服务.......还有日志模块,安全模块,事务模块
讲师服务,学生服务,计费服务 每一个服务都需要与日志模块,安全模块,事务模块 进行耦合.....如果这个样子,,每一个服务里面的代码不能够专注于解决本服务的问题.需要调用日志模块,安全模块,事务模块的代码.
这样,代码的复用性会很低,耦合性很高.
创建一个Person类...里面有一个doSomething方法
- package com.start.demo;
- /**
- * 男孩,女孩,工程师,程序员....
- */
- public class Person {
- private String name;
- private int age;
- private Play play;
- public Person(Play p) {
- this.play = p;
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- public void setAge(int age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- void doSomething() {
- System.out.println(" we can play " + play.getType() +"together");
- }
- }
创建一个Play类 type 表示可以做的事情
- package com.start.demo;
- /**
- * 各种活动,,玩游戏,读书,看电视.....
- */
- public class Play {
- private String type="computer game";
- public String getType() {
- return type;
- }
- public void setType(String type) {
- this.type = type;
- }
- }
测试Aop的一个类
- package com.start.demo;
- /**
- * 这个类是用来测试Aop.在切点之前,之后,分别调用对应的方法
- */
- public class Asker {
- private String name;
- void doSomethingBefore(){
- System.out.println("what can we do ");
- }
- void doSomethingAfter(){
- System.out.println("that's fine");
- }
- }
装配bean的xml
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
- <!--装配bean-->
- <bean id="person" class="com.start.demo.Person">
- <constructor-arg ref="play"/>
- </bean>
- <bean id="play" class="com.start.demo.Play"/>
- <bean id="asker" class="com.start.demo.Asker"/>
- <aop:config>
- <aop:aspect ref="asker">
- <!-- pointcut 的id 不能与 配置切点bean的id一样了,会报错.-->
- <aop:pointcut id="personPointcut"
- expression="execution(* *.doSomething())"/><!--execution(* * .doSomething(..)) 要是有参数,需要在方法体里面加 ..-->
- <aop:before pointcut-ref="personPointcut" method="doSomethingBefore"/>
- <aop:after pointcut-ref="personPointcut" method="doSomethingAfter"/>
- </aop:aspect>
- </aop:config>
- </beans>
用javaBean来装配对象
- package com.start.confBean;
- import com.start.demo.Person;
- import com.start.demo.Play;
- import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
- import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
- @Configuration
- public class PersonConf {
- @Bean
- public Person person() {
- return new Person(play());
- }
- @Bean
- public Play play() {
- return new Play();
- }
- }
测试Main类
- package com.start.demo;
- import com.start.confBean.PersonConf;
- import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
- import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
- public class TestMain {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext appcontext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); //从beans.xml 文件获取ApplicaitonContext
- // AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PersonConf.class);//PersonConf.java 文件获取ApplicaitonContext
- // Person person1 = annotationApplicationContext.getBean(Person.class); //获取bean ,直接指定Bean 为Person
- // Person person = (Person) appcontext.getBean("person");//获取bean person 为配置文件里面的 id
- Person pers = (Person) appcontext.getBean("person");
- pers.doSomething();
- }
- }
这些代码虽然很简单,却让我认识清楚了DI和Aop的作用
Spring(DI,AOP) 理解(一)的更多相关文章
- spring ioc aop 理解
OC,依赖倒置的意思,所谓依赖,从程序的角度看,就是比如A要调用B的方法,那么A就依赖于B,反正A要用到B,则A依赖于B.所谓倒置,你必须理解如果不倒置,会怎么着,因为A必须要有B,才可以调用B,如果 ...
- Spring的Aop理解
主要作用:解决代码复用,避免重复性编写代码. 比较典型的场景:日志打印,权限验证,事务处理 参考网址为:http://moon-walker.iteye.com/blog/2381532 spring ...
- 9.秋招复习简单整理之Spring面试AOP和IOC的理解
1.Spring的AOP理解: OOP面向对象,允许开发者定义纵向的关系,但不适用于定义横向的关系,导致了大量代码的重复,而不利于各个模块的重用. AOP,一般称为面向切面,作为面向对象的一种补充,用 ...
- 对于Spring中AOP,DI,IoC概念的理解
IOC IoC(inversion of Control),控制反转.就好像敏捷开发和SCRUM一样,不是什么技术,而是一种方法论,一种工程化的思想.使用IoC的思想意味着你将设计好的对象交给容器控制 ...
- Spring理解IOC,DI,AOP作用,概念,理解。
IOC控制反转:创建实例对象的控制权从代码转换到Spring容器.实际就是在xml中配置.配置对象 实例化对象时,进行强转为自定义类型.默认返回类型是Object强类型. ApplicationCon ...
- 黑马-Spring(IOC&DI) AOP
IOC(控制翻转) 概念 把对象的创建.初始化.销毁等工作交给spring容器来做 案例 环境 步骤 1. 写一个HelloWorld类 2. 写一个配置文件 把hello类放到spring容 ...
- spring+IOC+DI+AOP优点分析(一)
Spring是什么: Spring是一个轻量级的DI和AOP容器框架. 说它轻量级有一大部分原因是相对与EJB的(虽然本人从没有接触过EJB的应用),重要的是,Spring是非侵入式的,基于sprin ...
- Spring系列(二):Spring IoC/DI的理解
这几天重新学习了一下Spring,在网上找了相关的ppt来看,当看到Spring IoC这一章节的时候,先大致浏览了一下内容,有将近50页的内容,内心窃喜~QAQ~,看完这些内容能够对IoC有更深层次 ...
- Spring的AOP简单理解
最近在研究spring的AOP,翻译出来的意思是面向切面. 总结如下: 所谓AOP就是将分散在各个方法处的公共代码提取到一处, 并通过类似拦截器的机制实现代码的动态整合.可以简单地想象成, 在某个方法 ...
随机推荐
- VS配置C++依赖包
处理好三个东西 1.头文件,Configuration Properties → VC++ Directories → Include Directories 2.静态库,Configuration ...
- Scikit-Learn 源码研读 (第二期)基类的实现细节
目录 BaseEstimator `get_params` `set_params` ClassifierMixin RegressorMixin 检查传入的对象 检查样本数和权重系数 实现$R^2$ ...
- 学习笔记----C语言的面向对象
2020-03-26 21:27:17 面向对象的编程语言都有一个类的概念,像Java.python等.类是对特定数据的特定操作的集合体.它包含两个范畴:数据和操作.C语言是没有类的概念的,但是 ...
- ysoserial分析【二】7u21和URLDNS
目录 7u21 gadget链分析 hashCode绕过 参考 URLDNS 7u21 7u21中利用了TemplatesImpl来执行命令,结合动态代理.AnnotationInvocationHa ...
- 2019牛客多校第四场 A meeting
链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/884/A来源:牛客网 时间限制:C/C++ 1秒,其他语言2秒 空间限制:C/C++ 524288K,其他语言10485 ...
- Java集合框架要点概括(Core Knowledge of Java Collection)
目录 有哪些集合类 Set类 Queue类 List类 Map类 HashMap的实现原理,是否线程安全,如何使其做到线程安全 HashMap的实现原理 HashMap的数据结构 HashMap的存取 ...
- OpenCV-Python Canny边缘检测 | 十九
目标 在本章中,我们将学习 Canny边缘检测的概念 OpenCV函数: cv.Canny() 理论 Canny Edge Detection是一种流行的边缘检测算法.它由John F. Canny发 ...
- CodeForces - 1244E
题意:给n个数,可以有k次的 + 1或 - 1,在k次操作之内,让n个数的最大值和最小值差最小. 思路:要让max和min的差值最小,也就等同于min--,max++,如果k==0结束操作,或者min ...
- Flutter Weekly Issue 49
插件/Librarys flutter_date_pickers Allows to use date pickers without dialog. Provides some customizab ...
- Math对象常用方法介绍
<script> /* 001-Math.abs() 绝对值 */ console.log(Math.abs(123), Math.abs(-998), ...
