socket status 的状态变化详解
原文链接:
http://www.diranieh.com/SOCKETS/SocketStates.htm
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Socket States
Summary
WHAT ARE SOCKET STATES
Regardless of the socket type (TCP or UDP), operation mode (blocking, non-blocking, or asynchronous) or application type (single- or multi-threaded), changes in socket states are what propel a network application. Therefore, for a network application to be efficient, it needs to detect and handle changes in socket states as efficient as possible.
The state of a socket determines which network operations will succeed, which operations will block, and which operations with will fail (the socket state even determines the error code). Sockets have a finite number of states, and the WinSock API clearly defines the conditions that trigger a transition from one state to another. Note that different types of sockets ( stream vs. datagram have different states and different transitions.
DATAGRAM SOCKET STATES
The following diagram represents all states that can be detected programmatically for a datagram (UDP) socket. About the only thing that UDP socket applications care about is the readable state:
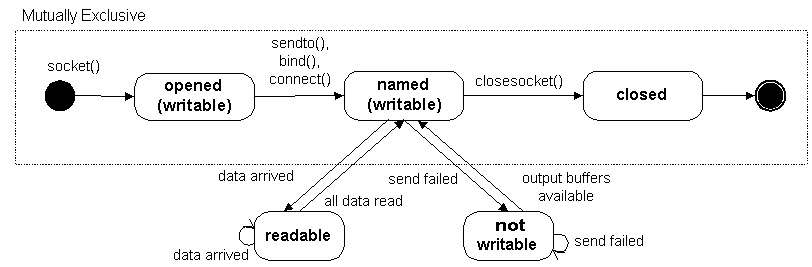
The states in the figure above are detailed as follows:
| Socket State | Meaning |
| opened | socket() returned an unnamed socket (an unnamed socket is one that is not bound to a local address and port). The socket can be named explicitly with bind or implicitly with sendto() or connect(). |
| named | A named socket is one that is bound to a local address and a port. The socket can now send and/or receive. |
| readable | The network system received data and is ready to be read by the application using recv() or recvfrom(). |
| not writable | The network system does not have enough buffers to accommodate outgoing data. |
| closed | The socket handle is invalid. |
STREAM SOCKET STATES
The following diagram represents all states that can be detected programmatically for a stream (TCP) socket:
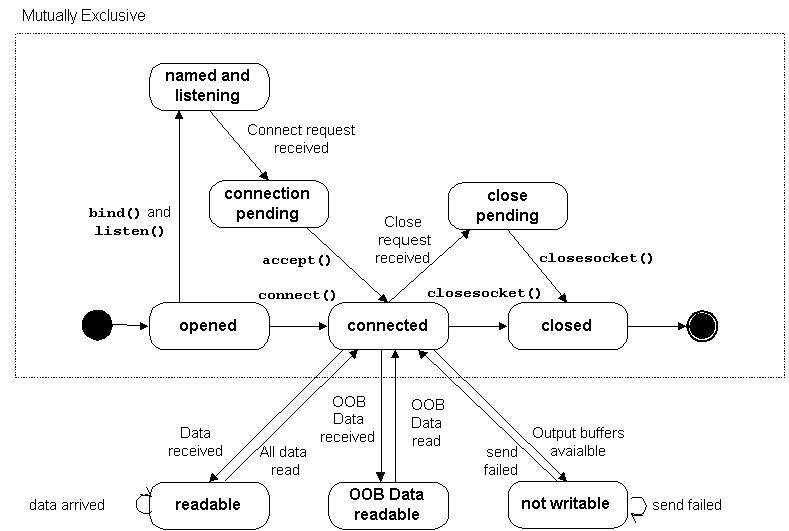
The states in the figure above are detailed as follows:
| Socket State | Meaning |
| opened | socket() returned an unnamed socket (an unnamed socket is one that is not bound to a local address and port). The socket can be named explicitly with bind() or implicitly with conenct(). |
| named and listening | The socket is named (bound to a local address and port) and is ready to accept incoming connection requests. |
| connection pending | The network system received an incoming connection requests and is waiting for the application to respond. |
| connected | An association (virtual circuit) has been established between a local and remote host. Sending and receiving data is now possible |
| readable | The network system received data and is ready to be read by the application using recv() or recvfrom(). |
| OOB readable | Out Of Band data received by the network system received data and is ready to be read by the application (usingrecv() or recvfrom().) |
| Not writable | The network system does not have enough buffers to accommodate outgoing data. |
| close pending | The virtual circuit is close. |
| closed | The socket handle is invalid. |
DETECTING SOCKET CHANGES
How does one detect changes in socket state? There are three different ways
- Using the return value of function calls.
- Using synchronous functions such as select(), ioctlsocket(), or setsockopt().
- Using the asynchronous function, WSAAsyncSelect().
WSAAsyncSelect() is by far the preferred method for detecting socket state changes.
FUNCTION CALL SUCCESS OR FAILURE
The return value of most functions can be used to determine a socket’s state. This strategy works fine with blocking sockets, but is very inefficient with non-blocking sockets, as the application will need to perform polling in order to detect state changes. Use this method only with blocking sockets.
SYNCHRONOUS DETECTION
Synchronous detection is performed by calling blocking or non-blocking functions whose return values indicate the state of the socket.
ASYNCHRONOUS DETECTION
Asynchronous socket state detection means that WinSock DLL will notify the application any time after the asynchronous socket state detection function has been called. Notification is performed via Windows messages. Asynchronous socket state detection is performed using WSAAsyncSelect(). On error this function returns SOCKET_ERROR and WSAGetLastError() can be used to get the specific error. On success, this function returns zero to indicate that:
- The socket is now non-blocking.
- If any the requested events match the current state of the socket, WinSock DLL posts a message for each matched event.
- If any the requested events match the future state of the socket, WinSock DLL posts a message for each matched event, as long as the re-enabling function is called for that event.
- If this socket creates a new socket using accept(), WSAAsyncSelect() will monitor the new socket for the same events requested previously.
WSAAsyncSelect() will remain in effect until WSAAsyncSelect() is called with a different lEvent parameter, or with lEvent equal to zero.
WSAAsyncSelect() is simple to work with. Basically, you tell WSAAsyncSelect() what you want to know about, and the WinSock DLL will tell you about it when it happens. The following diagrams illustrate how WSAAsyncSelect() works for a client that sends data and reads it back, and for the server to which the client connects.
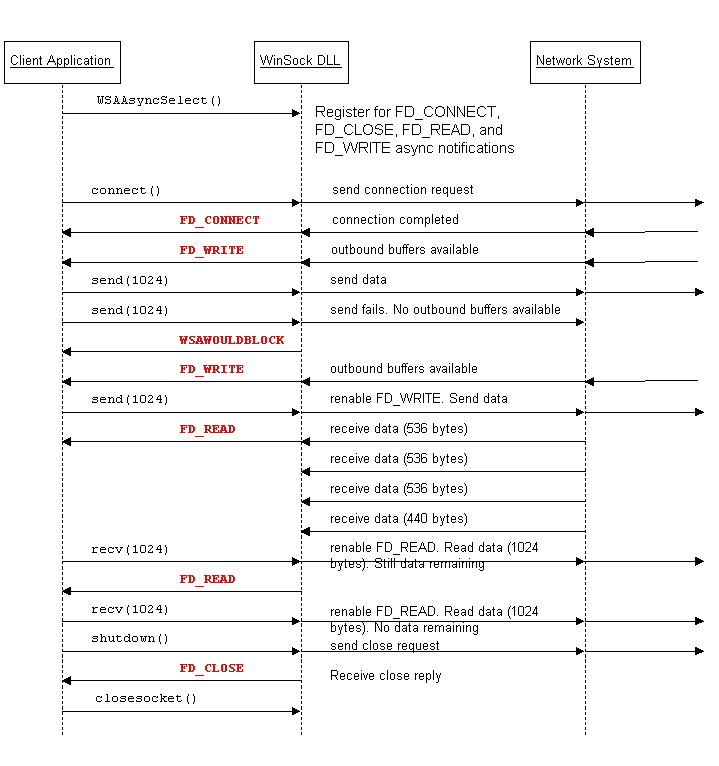
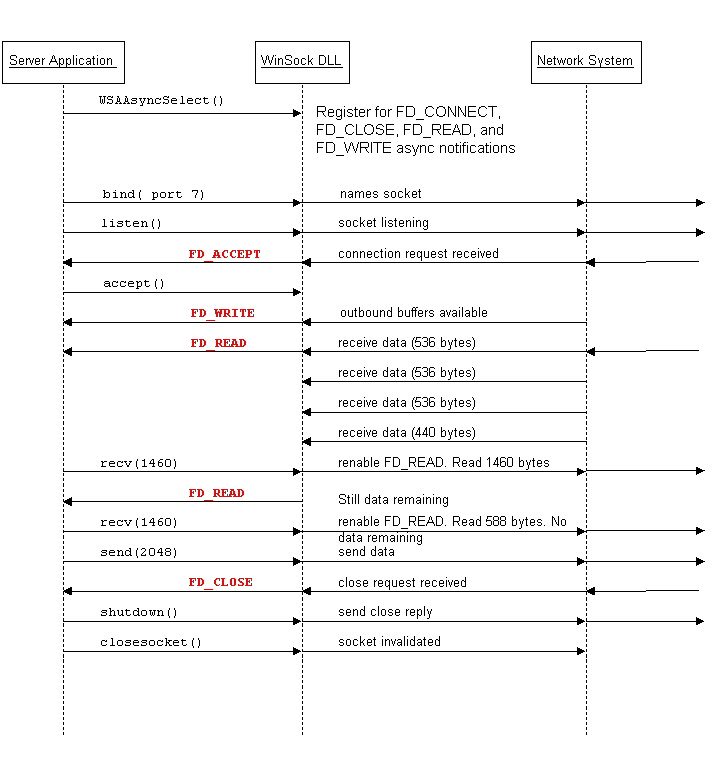
WHAT ARE THE WSAASYNCSELECT EVENTS?
The following table lists the events that WSAAsyncSelect() can detect. Note that each event is equivalent to a socket state
| Event | When It Occurs(Socket State) | Meaning | Re-Enable Function |
| FD_ACCEPT | Connection request received (connection pending) | accept() likely to succeed. Must call accept() to get the socket handle for the new connection. | accept() |
| FD_CLOSE | Connection close received (close pending) | Remote done sending data, though data may remain to be read. Therefore, call recv() to check for any remaining data. closesocket() will complete immediately. | <none> |
| FD_CONNECT | Connection now established (connected) | Association established so sending and receiving on the socket is possible | <none> |
| FD_OOB | Out Of Band data with ready to read | recv() with MSG_OOB will return OOB data. Avoid using OOB at all. | recv() or recvfrom() |
| FD_READ | Data received by network system is ready for application to read (readable) | recv() or recvfrom() likely to succeed. If any data remains after calling recv() or recvfrom(), WinSock will post another FD_READ message. | recv() or recvfrom() |
| FD_WRITE | Network system buffers are available for outgoing data. | send() or sendto() likely to succeed | send() or sendto() |
When a call to WSAAsyncSelect() succeeds, WinSock DLL checks the current state of the socket immediately and posts a message for each requested event that matches the socket state.
WHEN TO CALL WSAASYNCSELECT ()
As a rule of thumb, call WSAAsyncSelect() immediately after you open the socket with socket(). This guarantees that you register for asynchronous event notification before the event can occur.
WHAT ARE RE-ENABLING FUNCTIONS?
Events have re-enabling functions so that WinSock DLL can avoid flooding applications with notification messages. After WinSock DLL posts a notification message, it will not post another until the application calls the enabling function for that message.
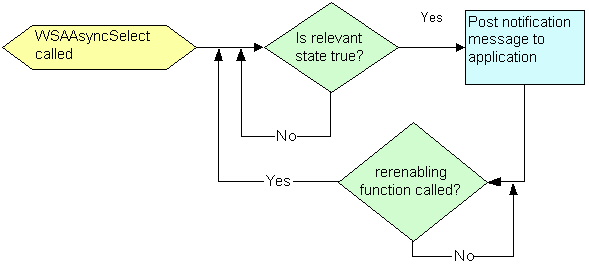
For example, WinSock DLL posts the FD_READ when data first arrives (level trigger), but does not post again as more data arrives. After the application calls recv() – the FD_READ enabling function - WinSock DLL will post another FD_READ message if there is still data available (level-trigger). The following diagram illustrates a flowchart of WSAAsyncSelect() level triggering event notification
WHAT IS IN A NOTIFICATION MESSAGE?
A WinSock DLL notification message is handled very similarly to Windows messages where lParam and wParam are used to hold information
wParam : Socket handle
(LOWORD)lParam : Event value
(HIWORD)lParam : WinSock error value
Always use WSAGETSELECTEVENT to extract the event value from lParam, and WSAGETSELECTERROR to extract the error value from lParam. Never use WSAGetLastError() as the value returned by this function may be different from that returned by WSAGETSELECTERROR macro.
BE PREPARED FOR FAILURE
Between the time WinSock DLL posts an asynchronous notification message to your application, and the time your application acts on it, things may change. Always handle WSAWOULDBLOCK gracefully to avoid serious problems. The WinSock DLL is required to post another notification message since you called the enabling function and the state did not change when the DLL posted the first message.
LOOPING IN RESPONSE
Asynchronous event notification has an inherent latency between the event and the arrival of the event notification message. The only event affected adversely by this latency is FD_READ event. You can offset this effect by calling recv() or recvfrom() more than once in response to each FD_READ event. This will generate extra FD_READ messages each time you call and data still remains. These extra messages will enhance the effect of the looping reads.
To loop safely calling recv() or recvfrom(), you should:
- Limit the number of times you loop (8 or less).
- handle WSAWOULDBLOCK gracefully.
CANCELING ASYNCHRONOUS NOTIFICATION
There are two ways to cancel asynchronous event notifications
- Call WSAAsyncSelect() passing NULL for lEvent parameter.
- Close socket using closesocket().
Note that in both cases, asynchronous notification messages may still be in the queue. Your application should anticipate them and either avoid normal processing, or, be prepared to handle the function failure that may result (failure with WSANOTSOCK error after calling closesocket())
SAMPLE APPLICATION
<TODO>
SELECT()
Like WSAAsyncSelect(), select() is a general purpose state detection and notification function. It can detect all states detected by WSAAsyncSelect(), but does not provide the same resolution; in order to determine some socket states, you must interpret the results of a call to select() in the context of the current socket state.
The select() function operates synchronously. select() is very similar in concept to WaitForMultipleObject() Win32 API. select() takes a set of sockets and blocks until one of the sockets is ‘signalled’ Using select() involves more work in coding than WSAAsyncSelect() which is far more elegant and far more efficient.
PEEKING AT DATA
Some application might require the ability to know how much data is available, or they may need to take a look at the data before they remove it from the incoming buffer.
To detect how much data is available, use ioctlsocket() with FIONREAD flag. To copy incoming data into an application buffer without actually removing the data from the network system buffers, use recv() or recvfrom() with MSG_PEEK flag.
Using these facilities is not recommended as any peek-read is inherently inefficient. It may even cause the application to fail. Your application will work faster, be more portable, and reliable if you simply use recv() or recvfrom() to read data directly into your application.
socket status 的状态变化详解的更多相关文章
- iOS中 HTTP/Socket/TCP/IP通信协议详解
// OSI(开放式系统互联), 由ISO(国际化标准组织)制定 // 1. 应用层 // 2. 表示层 // 3. 会话层 // 4. 传输层 // 5. 网络层 // 6. 数据链接层 // 7. ...
- iOS中 HTTP/Socket/TCP/IP通信协议详解 韩俊强的博客
每日更新关注:http://weibo.com/hanjunqiang 新浪微博 简单介绍: // OSI(开放式系统互联), 由ISO(国际化标准组织)制定 // 1. 应用层 // 2. 表示层 ...
- Mysql show Status常用参数详解
状态名 作用域 详细解释 Aborted_clients Global 由于客户端没有正确关闭连接导致客户端终止而中断的连接数 Aborted_connects Global 试图连接到MySQL服务 ...
- 关于Socket和ServerSocket类详解
Socket类 套接字是网络连接的一个端点.套接字使得一个应用可以从网络中读取和写入数据.放在两个不同计算机上的两个应用可以通过连接发送和接受字节流.为了从你的应用发送一条信息到另一个应用,你需要知道 ...
- Linux系统编程(36)—— socket编程之UDP详解
UDP 是User DatagramProtocol的简称,中文名是用户数据报协议.UDP协议不面向连接,也不保证传输的可靠性,例如: 1.发送端的UDP协议层只管把应用层传来的数据封装成段交给IP协 ...
- Linux系统编程(31)—— socket编程之TCP详解
TCP有源端口号和目的端口号,通讯的双方由IP地址和端口号标识.32位序号.32位确认序号.窗口大小稍后详细解释.4位首部长度和IP协议头类似,表示TCP协议头的长度,以4字节为单位,因此TCP协议头 ...
- TCP/IP、UDP、HTTP、SOCKET详解
文章大纲 网络OSI七层及各层作用 TCP与UDP基本介绍 TCP连接过程详解 SOCKET原理与连接详解 一.网络OSI七层及各层作用 应用层:文件传输,电子邮件,文件服务,虚拟终端 T ...
- MySQL状态变量详解
MySQL状态变量详解 mysql的状态变量(status variables)记录的mysql服务器的运行状态信息.查看语法如下: SHOW [GLOBAL | SESSION] STATUS; S ...
- http服务详解(1)
前言:要熟练掌握一个服务,首先需要非常了解这个服务的工作过程. 跨网络的主机间通讯 在建立通信连接的每一端,进程间的传输要有两个标志: IP地址和端口号,合称为套接字地址 socket address ...
随机推荐
- java基础(9)---静态方法和成员方法
一.方法: 方法的区别: 静态方法:有static方法 成员方法:没有static方法 方法的定义: 方法的调用:类.静态方法,对象.成员方法 一个MyClass类包含静态方法和成员方法: 静态方 ...
- k8s安装之flannel.yaml
收藏一下,以后直接从这里cp过来用的. flannel新版 --- apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: PodSecurityPolicy metadata: n ...
- 神经网络学习中的损失函数及mini-batch学习
# 损失函数(loss function).这个损失函数可以使用任意函数,# 但一般用均方误差(mean squared error)和交叉熵误差(cross entropy error)等一切都在代 ...
- 《你们都是魔鬼吗》团队作业Beta冲刺---第一天
团队作业Beta冲刺 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 任课教师博客主页链接 这个作业的要求在哪里 作业链接地址 团队名称 你们都是魔鬼吗 作业学习目标 (1)掌握软件黑盒测试技术:(2)学会编制软件 ...
- 抖音热门BGM爬虫下载
下午无聊在某网上刷了会儿抖音,发现有些音乐还是挺好听的,可以用来做手机铃声,于是想办法从某网上把歌曲爬下来 附上代码: #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf- ...
- ClickHouse 分布式高可用集群搭建(转载)
一.ClickHouse安装方式: 源码编译安装 Docker安装 RPM包安装 为了方便使用,一般采用RPM包方式安装,其他两种方式这里不做说明. 二.下载安装包 官方没有提供rpm包,但是Alti ...
- HEXO的使用
本文将总结性的介绍如何建立自己的github.io博客,后续会持续补充,进阶.感谢baixin提供的参考文章. 技术选型为github+hexo+idea,首先最简单的阐述下这个东西都干嘛的 1. 技 ...
- BZOJ 2333: [SCOI2011]棘手的操作
题目描述 真的是个很棘手的操作.. 注意每删除一个点,就需要clear一次. #include<complex> #include<cstdio> using namespac ...
- StringSequences
题意: 给出两个长度不超过\(50\)的字符串\(S, T\),每次可以在\(S\)中插入一个字符,把每次操作后的\(S\)写成一个序列,问有多少种不同的序列. 注意到我们可以把\(S\)拆分成一段一 ...
- 36、将RDD转换为DataFrame
一.概述 为什么要将RDD转换为DataFrame? 因为这样的话,我们就可以直接针对HDFS等任何可以构建为RDD的数据,使用Spark SQL进行SQL查询了.这个功能是无比强大的. 想象一下,针 ...
