spring框架学习(二)——注解方式IOC/DI
什么是注解
传统的Spring做法是使用.xml文件来对bean进行注入或者是配置aop、事物,这么做有两个缺点:
1、如果所有的内容都配置在.xml文件中,那么.xml文件将会十分庞大;如果按需求分开.xml文件,那么.xml文件又会非常多。总之这将导致配置文件的可读性与可维护性变得很低
2、在开发中在.java文件和.xml文件之间不断切换,是一件麻烦的事,同时这种思维上的不连贯也会降低开发的效率
为了解决这两个问题,Spring引入了注解 (注解是jdk1.5新特性),通过"@XXX"的方式,让注解与Java Bean紧密结合,既大大减少了配置文件的体积,又增加了Java Bean的可读性与内聚性。
本篇博文将演示如何使用注解的方式完成注入对象的效果
修改applicationContext.xml
1. 在15行添加 <context:annotation-config/> 表示告诉Spring要用注解的方式进行配置
2. 注入对象的21行注释掉,这个行为在后面将使用注解来完成
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <context:annotation-config/>
<bean name="c" class="com.spring.pojo.Category">
<property name="name" value="category 1" />
</bean>
<bean name="p" class="com.spring.pojo.Product">
<property name="name" value="product1" />
<!-- <property name="category" ref="c" /> -->
</bean> </beans>
@Autowired
@Autowired顾名思义,就是自动装配,其作用是为了消除代码Java代码里面的getter/setter与bean属性中的property。当然,getter看个人需求,如果私有属性需要对外提供的话,应当予以保留。
在Product.java的category属性前加上@Autowired注解
@Autowired
private Category category;
除了在属性前加上 @Autowired这种方式外,也可以在setCategory方法前加上@Autowired,这样来达到相同的效果
@Autowired
public void setCategory(Category category)
package com.spring.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class Product {
private int id;
private String name;
@Autowired
private Category category;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Category getCategory() {
return category;
}
//@Autowired加在这里也可以
public void setCategory(Category category) {
this.category = category;
}
}
运行测试
package com.spring.test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.spring.pojo.Product; public class TestSpring { public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] { "applicationContext.xml" });
Product p = (Product) context.getBean("p");
System.out.println(p.getName());
System.out.println(p.getCategory().getName());
}
}
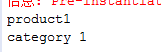
@Resource
除了@Autowired之外,@Resource也是常用的手段,也能得到相同的结果
@Resource(name="c")//默认通过name属性去匹配bean
//Resource(type=Category.class)//找不到再按type去匹配
private Category category;
这是详细一些的用法,说一下@Resource的装配顺序:
1、@Resource后面没有任何内容,默认通过name属性去匹配bean,找不到再按type去匹配
2、指定了name或者type则根据指定的类型去匹配bean
3、指定了name和type则根据指定的name和type去匹配bean,任何一个不匹配都将报错
然后,区分一下@Autowired和@Resource两个注解的区别:
1、@Autowired默认按照byType方式进行bean匹配,@Resource默认按照byName方式进行bean匹配
2、@Autowired是Spring的注解,@Resource是J2EE的注解,这个看一下导入注解的时候这两个注解的包名就一清二楚了
Spring属于第三方的,J2EE是Java自己的东西,因此,建议使用@Resource注解,以减少代码和Spring之间的耦合。
注解@Autowired和@Resource的字段(成员变量)注入和setter注入的区别,请点击此处查看
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
对Bean的注解
上述例子是对注入对象行为的注解,那么bean对象本身,比如Category,Product也可以移出applicationContext.xml配置文件,通过注解进行。
修改applicationContext.xml
什么都去掉,只新增:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.spring.pojo"/>
其作用是告诉Spring,bean都放在com.spring.pojo这个包下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.spring.pojo"/> </beans>
@Component
(@Component注解、@Service注解、@Repository注解、@Controller注解区别,请点击此处查看)
为Product类加上@Component注解,即表明此类是bean
@Component("p")
public class Product {
@Component("c")
public class Category {
另外,因为配置从applicationContext.xml中移出来了,所以属性初始化放在属性声明上进行了。
private String name="product 1";
private String name="category 1";
Product代码:
package com.spring.pojo; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component("p")
public class Product { private int id;
private String name="product 1"; @Autowired
private Category category; public int getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public Category getCategory() {
return category;
} public void setCategory(Category category) {
this.category = category;
}
}
Category代码:
package com.spring.pojo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("c")
public class Category {
private int id;
private String name="category 1";
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
运行TestSpring,可以发现运行结果跟之前是一样的

spring框架学习(二)——注解方式IOC/DI的更多相关文章
- spring框架学习(四)——注解方式AOP
注解配置业务类 使用@Component("s") 注解ProductService 类 package com.how2java.service; import org.spri ...
- Spring框架学习之注解配置与AOP思想
上篇我们介绍了Spring中有关高级依赖关系配置的内容,也可以调用任意方法的返回值作为属性注入的值,它解决了Spring配置文件的动态性不足的缺点.而本篇,我们将介绍Spring的又一大核心 ...
- Spring框架学习(2)IOC学习
内容源自:IOC理解 spring ioc注入的三种方式 ioc工厂bean深入理解 耦合性,在java中表现为类之间的关系,耦合性强说明类之间的依赖关系强: 侵入性:框架对代码的侵入: 在传统 ...
- Spring 框架学习—控制反转(IOC)
Spring是一个开源框架,Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java 开发框架,由Rod Johnson创建. 简单来说,Spring是一个分层的JavaSE/EEfull-st ...
- Spring框架学习(二)
一.依赖注入的三种注入方式 Spring框架为我们提供了三种注入方式:set注入.构造方法注入和接口注入. 1.set注入 规律:无论给什么赋值,配置文件中<property>标签的nam ...
- Android Afinal框架学习(二) FinalActivity 一个IOC框架
框架地址:https://github.com/yangfuhai/afinal 相应的源代码: net.tsz.afinal.annotation.view.* FinalActivity Fina ...
- Spring框架学习总结(上)
目录 1.Spring的概述 2.Spring的入门(IOC) 3.Spring的工厂类 4.Spring的配置 5.Spring的属性注入 6.Spring的分模块开发的配置 @ 1.Spring的 ...
- 深入学习Spring框架(二)- 注解配置
1.为什么要学习Spring的注解配置? 基于注解配置的方式也已经逐渐代替xml.所以我们必须要掌握使用注解的方式配置Spring. 关于实际的开发中到底使用xml还是注解,每家公司有着不同的使用习惯 ...
- Spring框架学习之IOC(二)
Spring框架学习之IOC(二) 接着上一篇的内容,下面开始IOC基于注解装配相关的内容 在 classpath 中扫描组件 <context:component-scan> 特定组件包 ...
随机推荐
- C# .net core 相对路径转绝对路径 (官方示例)
public static string GetAbsolutePath(string relativePath) { FileInfo _dataRoot = new FileInfo(typeof ...
- 微信小程序弹窗
wxml <view class="content"> <button bindtap="popSuccessTest">成功提示弹窗& ...
- 81: luogu3370 hash
hash 模板题 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ULL unsigned long long const UL ...
- 2017.10.1 国庆清北 D1T1 zhx的字符串题
题目背景 2017国庆清北D1T1 题目描述 你是能看到第一题的 friends 呢. ——hja 何大爷对字符串十分有研究,于是天天出字符串题虐杀 zhx.何大爷今天为 字符串定义了新的权值计算方法 ...
- Java后台读取excel表格返回至Web前端
如果是做连接数据库的话,系统难度就降低了不少:这次本人也算是体会到数据库的方便了吧(不过以后云储存好像会更受欢迎些):比如说查询列出所有数据吧:数据库每个表每一列都有列名,正常的做法是遍历数据库表,d ...
- (转载)ranger原理
文章目录 一.业务背景 现状&&需求 二.大数据安全组件介绍与对比 1.Kerberos 2.Apache Sentry 3.Apache Ranger 4.为什么我们选择Ranger ...
- pytorch中tensor数据和numpy数据转换中注意的一个问题
转载自:(pytorch中tensor数据和numpy数据转换中注意的一个问题)[https://blog.csdn.net/nihate/article/details/82791277] 在pyt ...
- K8S从入门到放弃
K8S介绍相关 kubernetes(K8S)集群及Dashboard安装配置 kubernetes(K8S)创建自签TLS证书 K8S Kubernetes 架构 K8S组件 K8S API对象 K ...
- java中&& 的运算优先级高于||
public class First { public static void main(String[] args) { boolean a = false; boolean b = true; b ...
- edusoho上传视频弹出abort之解决方案
错误描述:edusoho上传如avi.mp4等容量大的图片(如100m以上或500m等)弹出abort提示框 原因:是因为web服务器apache默认上传文件有限制导致的 解决办法如下: (1)首先修 ...
