深度学习面试题26:GoogLeNet(Inception V2)
目录
第一层卷积换为分离卷积
一些层的卷积核的个数发生了变化
多个小卷积核代替大卷积核
一些最大值池化换为了平均值池化
完整代码
参考资料
|
第一层卷积换为分离卷积 |

net = slim.separable_conv2d(
inputs,
depth(64), [7, 7],
depth_multiplier=depthwise_multiplier,
stride=2,
padding='SAME',
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(1.0),
scope=end_point)
|
一些层的卷积核的个数发生了变化 |
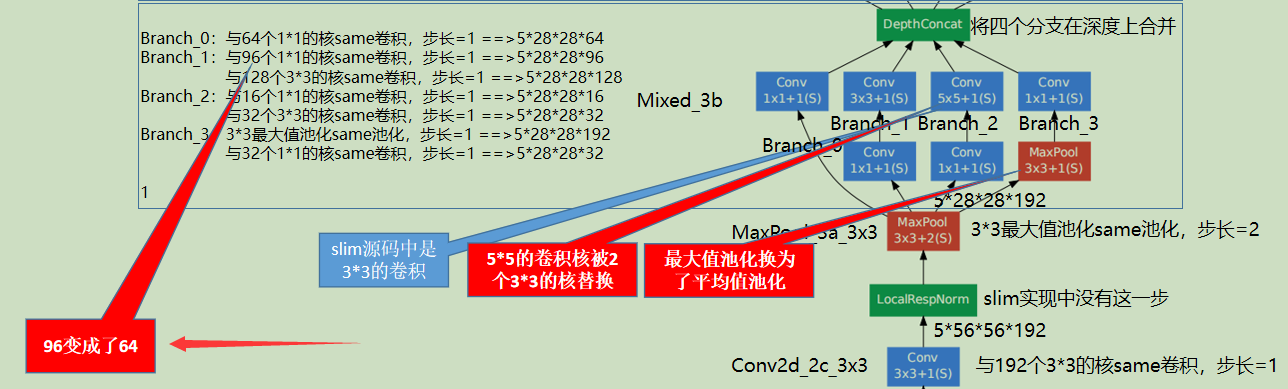
|
多个小卷积核代替大卷积核 |
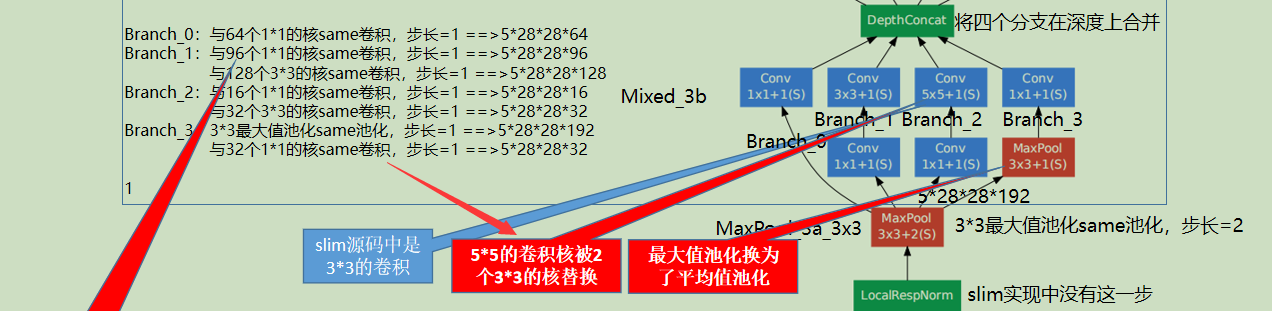
|
一些最大值池化换为了平均值池化 |

branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3')
|
完整代码 |
# Copyright 2016 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
"""Contains the definition for inception v2 classification network.""" from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function import tensorflow as tf from nets import inception_utils slim = tf.contrib.slim
trunc_normal = lambda stddev: tf.truncated_normal_initializer(0.0, stddev) def inception_v2_base(inputs,
final_endpoint='Mixed_5c',
min_depth=16,
depth_multiplier=1.0,
use_separable_conv=True,
data_format='NHWC',
include_root_block=True,
scope=None):
"""Inception v2 (6a2). Constructs an Inception v2 network from inputs to the given final endpoint.
This method can construct the network up to the layer inception(5b) as
described in http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03167. Args:
inputs: a tensor of shape [batch_size, height, width, channels].
final_endpoint: specifies the endpoint to construct the network up to. It
can be one of ['Conv2d_1a_7x7', 'MaxPool_2a_3x3', 'Conv2d_2b_1x1',
'Conv2d_2c_3x3', 'MaxPool_3a_3x3', 'Mixed_3b', 'Mixed_3c', 'Mixed_4a',
'Mixed_4b', 'Mixed_4c', 'Mixed_4d', 'Mixed_4e', 'Mixed_5a', 'Mixed_5b',
'Mixed_5c']. If include_root_block is False, ['Conv2d_1a_7x7',
'MaxPool_2a_3x3', 'Conv2d_2b_1x1', 'Conv2d_2c_3x3', 'MaxPool_3a_3x3'] will
not be available.
min_depth: Minimum depth value (number of channels) for all convolution ops.
Enforced when depth_multiplier < 1, and not an active constraint when
depth_multiplier >= 1.
depth_multiplier: Float multiplier for the depth (number of channels)
for all convolution ops. The value must be greater than zero. Typical
usage will be to set this value in (0, 1) to reduce the number of
parameters or computation cost of the model.
use_separable_conv: Use a separable convolution for the first layer
Conv2d_1a_7x7. If this is False, use a normal convolution instead.
data_format: Data format of the activations ('NHWC' or 'NCHW').
include_root_block: If True, include the convolution and max-pooling layers
before the inception modules. If False, excludes those layers.
scope: Optional variable_scope. Returns:
tensor_out: output tensor corresponding to the final_endpoint.
end_points: a set of activations for external use, for example summaries or
losses. Raises:
ValueError: if final_endpoint is not set to one of the predefined values,
or depth_multiplier <= 0
""" # end_points will collect relevant activations for external use, for example
# summaries or losses.
end_points = {} # Used to find thinned depths for each layer.
if depth_multiplier <= 0:
raise ValueError('depth_multiplier is not greater than zero.')
depth = lambda d: max(int(d * depth_multiplier), min_depth) if data_format != 'NHWC' and data_format != 'NCHW':
raise ValueError('data_format must be either NHWC or NCHW.')
if data_format == 'NCHW' and use_separable_conv:
raise ValueError(
'separable convolution only supports NHWC layout. NCHW data format can'
' only be used when use_separable_conv is False.'
) concat_dim = 3 if data_format == 'NHWC' else 1
with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'InceptionV2', [inputs]):
with slim.arg_scope(
[slim.conv2d, slim.max_pool2d, slim.avg_pool2d],
stride=1,
padding='SAME',
data_format=data_format): net = inputs
if include_root_block:
# Note that sizes in the comments below assume an input spatial size of
# 224x224, however, the inputs can be of any size greater 32x32. # 224 x 224 x 3
end_point = 'Conv2d_1a_7x7' if use_separable_conv:
# depthwise_multiplier here is different from depth_multiplier.
# depthwise_multiplier determines the output channels of the initial
# depthwise conv (see docs for tf.nn.separable_conv2d), while
# depth_multiplier controls the # channels of the subsequent 1x1
# convolution. Must have
# in_channels * depthwise_multipler <= out_channels
# so that the separable convolution is not overparameterized.
depthwise_multiplier = min(int(depth(64) / 3), 8)
net = slim.separable_conv2d(
inputs,
depth(64), [7, 7],
depth_multiplier=depthwise_multiplier,
stride=2,
padding='SAME',
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(1.0),
scope=end_point)
else:
# Use a normal convolution instead of a separable convolution.
net = slim.conv2d(
inputs,
depth(64), [7, 7],
stride=2,
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(1.0),
scope=end_point)
end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint:
return net, end_points
# 112 x 112 x 64
end_point = 'MaxPool_2a_3x3'
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope=end_point, stride=2)
end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint:
return net, end_points
# 56 x 56 x 64
end_point = 'Conv2d_2b_1x1'
net = slim.conv2d(
net,
depth(64), [1, 1],
scope=end_point,
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.1))
end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint:
return net, end_points
# 56 x 56 x 64
end_point = 'Conv2d_2c_3x3'
net = slim.conv2d(net, depth(192), [3, 3], scope=end_point)
end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint:
return net, end_points
# 56 x 56 x 192
end_point = 'MaxPool_3a_3x3'
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope=end_point, stride=2)
end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint:
return net, end_points # 28 x 28 x 192
# Inception module.
end_point = 'Mixed_3b'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, depth(64), [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(64), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, depth(64), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(64), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(96), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(96), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0c_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3')
branch_3 = slim.conv2d(
branch_3, depth(32), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.1),
scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1')
net = tf.concat(
axis=concat_dim, values=[branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3])
end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint: return net, end_points
# 28 x 28 x 256
end_point = 'Mixed_3c'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, depth(64), [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(64), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, depth(96), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(64), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(96), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(96), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0c_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3')
branch_3 = slim.conv2d(
branch_3, depth(64), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.1),
scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1')
net = tf.concat(
axis=concat_dim, values=[branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3])
end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint: return net, end_points
# 28 x 28 x 320
end_point = 'Mixed_4a'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
branch_0 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(128), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_0 = slim.conv2d(branch_0, depth(160), [3, 3], stride=2,
scope='Conv2d_1a_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(64), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(
branch_1, depth(96), [3, 3], scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(
branch_1, depth(96), [3, 3], stride=2, scope='Conv2d_1a_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
branch_2 = slim.max_pool2d(
net, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='MaxPool_1a_3x3')
net = tf.concat(axis=concat_dim, values=[branch_0, branch_1, branch_2])
end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint: return net, end_points
# 14 x 14 x 576
end_point = 'Mixed_4b'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, depth(224), [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(64), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(
branch_1, depth(96), [3, 3], scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(96), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(128), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(128), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0c_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3')
branch_3 = slim.conv2d(
branch_3, depth(128), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.1),
scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1')
net = tf.concat(
axis=concat_dim, values=[branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3])
end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint: return net, end_points
# 14 x 14 x 576
end_point = 'Mixed_4c'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, depth(192), [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(96), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, depth(128), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(96), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(128), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(128), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0c_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3')
branch_3 = slim.conv2d(
branch_3, depth(128), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.1),
scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1')
net = tf.concat(
axis=concat_dim, values=[branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3])
end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint: return net, end_points
# 14 x 14 x 576
end_point = 'Mixed_4d'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, depth(160), [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(128), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, depth(160), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(128), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(160), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(160), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0c_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3')
branch_3 = slim.conv2d(
branch_3, depth(96), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.1),
scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1')
net = tf.concat(
axis=concat_dim, values=[branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3])
end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint: return net, end_points
# 14 x 14 x 576
end_point = 'Mixed_4e'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, depth(96), [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(128), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, depth(192), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(160), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(192), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(192), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0c_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3')
branch_3 = slim.conv2d(
branch_3, depth(96), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.1),
scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1')
net = tf.concat(
axis=concat_dim, values=[branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3])
end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint: return net, end_points
# 14 x 14 x 576
end_point = 'Mixed_5a'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
branch_0 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(128), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_0 = slim.conv2d(branch_0, depth(192), [3, 3], stride=2,
scope='Conv2d_1a_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(192), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, depth(256), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, depth(256), [3, 3], stride=2,
scope='Conv2d_1a_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
branch_2 = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=2,
scope='MaxPool_1a_3x3')
net = tf.concat(
axis=concat_dim, values=[branch_0, branch_1, branch_2])
end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint: return net, end_points
# 7 x 7 x 1024
end_point = 'Mixed_5b'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, depth(352), [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(192), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, depth(320), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(160), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(224), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(224), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0c_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3')
branch_3 = slim.conv2d(
branch_3, depth(128), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.1),
scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1')
net = tf.concat(
axis=concat_dim, values=[branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3])
end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint: return net, end_points
# 7 x 7 x 1024
end_point = 'Mixed_5c'
with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, depth(352), [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(192), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, depth(320), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(
net, depth(192), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.09),
scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(224), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3')
branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, depth(224), [3, 3],
scope='Conv2d_0c_3x3')
with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
branch_3 = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='MaxPool_0a_3x3')
branch_3 = slim.conv2d(
branch_3, depth(128), [1, 1],
weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.1),
scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1')
net = tf.concat(
axis=concat_dim, values=[branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3])
end_points[end_point] = net
if end_point == final_endpoint: return net, end_points
raise ValueError('Unknown final endpoint %s' % final_endpoint) def inception_v2(inputs,
num_classes=1000,
is_training=True,
dropout_keep_prob=0.8,
min_depth=16,
depth_multiplier=1.0,
prediction_fn=slim.softmax,
spatial_squeeze=True,
reuse=None,
scope='InceptionV2',
global_pool=False):
"""Inception v2 model for classification. Constructs an Inception v2 network for classification as described in
http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03167. The default image size used to train this network is 224x224. Args:
inputs: a tensor of shape [batch_size, height, width, channels].
num_classes: number of predicted classes. If 0 or None, the logits layer
is omitted and the input features to the logits layer (before dropout)
are returned instead.
is_training: whether is training or not.
dropout_keep_prob: the percentage of activation values that are retained.
min_depth: Minimum depth value (number of channels) for all convolution ops.
Enforced when depth_multiplier < 1, and not an active constraint when
depth_multiplier >= 1.
depth_multiplier: Float multiplier for the depth (number of channels)
for all convolution ops. The value must be greater than zero. Typical
usage will be to set this value in (0, 1) to reduce the number of
parameters or computation cost of the model.
prediction_fn: a function to get predictions out of logits.
spatial_squeeze: if True, logits is of shape [B, C], if false logits is of
shape [B, 1, 1, C], where B is batch_size and C is number of classes.
reuse: whether or not the network and its variables should be reused. To be
able to reuse 'scope' must be given.
scope: Optional variable_scope.
global_pool: Optional boolean flag to control the avgpooling before the
logits layer. If false or unset, pooling is done with a fixed window
that reduces default-sized inputs to 1x1, while larger inputs lead to
larger outputs. If true, any input size is pooled down to 1x1. Returns:
net: a Tensor with the logits (pre-softmax activations) if num_classes
is a non-zero integer, or the non-dropped-out input to the logits layer
if num_classes is 0 or None.
end_points: a dictionary from components of the network to the corresponding
activation. Raises:
ValueError: if final_endpoint is not set to one of the predefined values,
or depth_multiplier <= 0
"""
if depth_multiplier <= 0:
raise ValueError('depth_multiplier is not greater than zero.') # Final pooling and prediction
with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'InceptionV2', [inputs], reuse=reuse) as scope:
with slim.arg_scope([slim.batch_norm, slim.dropout],
is_training=is_training):
net, end_points = inception_v2_base(
inputs, scope=scope, min_depth=min_depth,
depth_multiplier=depth_multiplier)
with tf.variable_scope('Logits'):
if global_pool:
# Global average pooling.
net = tf.reduce_mean(net, [1, 2], keep_dims=True, name='global_pool')
end_points['global_pool'] = net
else:
# Pooling with a fixed kernel size.
kernel_size = _reduced_kernel_size_for_small_input(net, [7, 7])
net = slim.avg_pool2d(net, kernel_size, padding='VALID',
scope='AvgPool_1a_{}x{}'.format(*kernel_size))
end_points['AvgPool_1a'] = net
if not num_classes:
return net, end_points
# 1 x 1 x 1024
net = slim.dropout(net, keep_prob=dropout_keep_prob, scope='Dropout_1b')
logits = slim.conv2d(net, num_classes, [1, 1], activation_fn=None,
normalizer_fn=None, scope='Conv2d_1c_1x1')
if spatial_squeeze:
logits = tf.squeeze(logits, [1, 2], name='SpatialSqueeze')
end_points['Logits'] = logits
end_points['Predictions'] = prediction_fn(logits, scope='Predictions')
return logits, end_points
inception_v2.default_image_size = 224 def _reduced_kernel_size_for_small_input(input_tensor, kernel_size):
"""Define kernel size which is automatically reduced for small input. If the shape of the input images is unknown at graph construction time this
function assumes that the input images are is large enough. Args:
input_tensor: input tensor of size [batch_size, height, width, channels].
kernel_size: desired kernel size of length 2: [kernel_height, kernel_width] Returns:
a tensor with the kernel size. TODO(jrru): Make this function work with unknown shapes. Theoretically, this
can be done with the code below. Problems are two-fold: (1) If the shape was
known, it will be lost. (2) inception.slim.ops._two_element_tuple cannot
handle tensors that define the kernel size.
shape = tf.shape(input_tensor)
return = tf.stack([tf.minimum(shape[1], kernel_size[0]),
tf.minimum(shape[2], kernel_size[1])]) """
shape = input_tensor.get_shape().as_list()
if shape[1] is None or shape[2] is None:
kernel_size_out = kernel_size
else:
kernel_size_out = [min(shape[1], kernel_size[0]),
min(shape[2], kernel_size[1])]
return kernel_size_out inception_v2_arg_scope = inception_utils.inception_arg_scope
|
参考资料 |
《图解深度学习与神经网络:从张量到TensorFlow实现》_张平
Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision
深度学习面试题26:GoogLeNet(Inception V2)的更多相关文章
- 深度学习面试题29:GoogLeNet(Inception V3)
目录 使用非对称卷积分解大filters 重新设计pooling层 辅助构造器 使用标签平滑 参考资料 在<深度学习面试题20:GoogLeNet(Inception V1)>和<深 ...
- 深度学习(十) GoogleNet
GoogLeNet Incepetion V1 这是GoogLeNet的最早版本,出现在2014年的<Going deeper with convolutions>.之所以名为“GoogL ...
- 深度学习面试题27:非对称卷积(Asymmetric Convolutions)
目录 产生背景 举例 参考资料 产生背景 之前在深度学习面试题16:小卷积核级联卷积VS大卷积核卷积中介绍过小卷积核的三个优势: ①整合了三个非线性激活层,代替单一非线性激活层,增加了判别能力. ②减 ...
- 深度学习面试题13:AlexNet(1000类图像分类)
目录 网络结构 两大创新点 参考资料 第一个典型的CNN是LeNet5网络结构,但是第一个引起大家注意的网络却是AlexNet,Alex Krizhevsky其实是Hinton的学生,这个团队领导者是 ...
- 深度学习面试题20:GoogLeNet(Inception V1)
目录 简介 网络结构 对应代码 网络说明 参考资料 简介 2014年,GoogLeNet和VGG是当年ImageNet挑战赛(ILSVRC14)的双雄,GoogLeNet获得了第一名.VGG获得了第二 ...
- 深度学习面试题21:批量归一化(Batch Normalization,BN)
目录 BN的由来 BN的作用 BN的操作阶段 BN的操作流程 BN可以防止梯度消失吗 为什么归一化后还要放缩和平移 BN在GoogLeNet中的应用 参考资料 BN的由来 BN是由Google于201 ...
- 深度学习面试题18:网中网结构(Network in Network)
目录 举例 参考资料 网中网结构通过多个分支的运算(卷积或池化),将分支上的运算结果在深度上连接 举例 一个3*3*2的张量, 与3个1*1*2的卷积核分别same卷积,步长=1, 与2个2*2*2的 ...
- 深度学习面试题24:在每个深度上分别卷积(depthwise卷积)
目录 举例 单个张量与多个卷积核在深度上分别卷积 参考资料 举例 如下张量x和卷积核K进行depthwise_conv2d卷积 结果为: depthwise_conv2d和conv2d的不同之处在于c ...
- 深度学习面试题17:VGGNet(1000类图像分类)
目录 VGGNet网络结构 论文中还讨论了其他结构 参考资料 2014年,牛津大学计算机视觉组(Visual Geometry Group)和Google DeepMind公司的研究员一起研发出了新的 ...
随机推荐
- UCOSIII等待多个内核对象
内核对象 内核对象包括信号量.互斥信号量.消息队列和事件标志组 UCOSIII中允许任务同时等待多个信号量和多个消息队列 主结构体 typedef struct os_pend_data OS_PEN ...
- CRM-Q模糊查询
Q查询-模糊查询 示例一 q=Q() # 实例化一个Q的对象q,我们可以给它加条件 q.children.append(("name","xxx")) # 添加 ...
- grpc的简单用例 (golang实现)
这个用例的逻辑很简单, 服务器运行一个管理个人信息的服务, 提供如下的四个服务: (1) 添加一个个人信息 注: 对应于Unary RPCs, 客户端发送单一消息给服务器, 服务器返回单一消息 (2) ...
- visual studio故障修复
如果没有安装程序,直接在控制面板——>程序和功能,在列表中找到您安装的vs,右键选择更改,然后程序会启动,做一些准备.然后又三个选项,可以选择修复.
- Luogu P1196 银河英雄传说
Luogu P1196 银河英雄传说 我们考虑用并查集来维护战舰的情况. 同时,我们用一个$d$数组来记录$x$与$fa[x]$之间的距离.再用$size$数组记录战舰当前所在列的战舰数. 易知两艘在 ...
- gdb调试(二)
继续研究gdb相关的调试技巧,话不多说进入正题: 查看运行时数据: 这个上节中已经用过了,这里就不多说了,比较简单 还是有上节中的simple.c例子,不过得稍微做一些修改为了使用这些命令: simp ...
- selenium常用的API(一)截屏
我们在使用selenium测试过程中,可使用截屏功能将用例执行失败的画面截图保存,方便测试执行结束后查看并定位问题. 以下介绍两种截屏方法: 对当前浏览器窗口截屏 使用selenium自带的get_s ...
- JavaScript和JQuery之战再续
之前写过关于JavaScript和Jquery的之间的比较,现在再看比较偏向于理论知识,还不是很理解.经过这一段时间的项目的锻炼,对JQuery有了新的认识. 原生JavaScript和jQuery的 ...
- 十四.Protobuf3扩展
在您发布使用Protocol Buffer区的代码后,您迟早会因为业务需求变更想要“改进”Protocol Buffer的定义.如果你想让你的新Protocol Buffer向后兼容,让你的旧Prot ...
- vue中超简单的方法实现点击一个按钮出现弹框,点击弹框外关闭弹框
效果图展示: View层 <template> <div> <div class="mask" v-if="showModal" ...
