AtCoder Grand Contest 038 简要题解
从这里开始
Problem A 01 Matrix
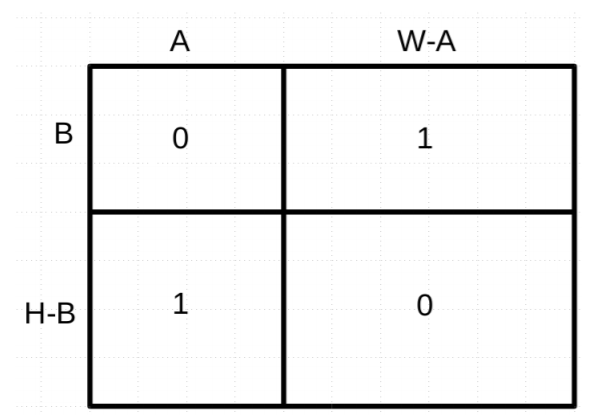
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean; const int N = 1e3 + 5; int W, H, A, B; int main() {
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &W, &H, &A, &B);
for (int i = 0; i < W; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < H; j++) {
putchar('0' ^ (i < B) ^ (j < A));
}
putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}
Problem B Sorting a Segment
如果选择的两个没有交的区间排序后得到的序列相同。那么两次排序都等于什么都没做。
如果有交,那么假设这两个区间分别是$[l_1, r_1]$和$[l_2, r_2]$,$(l_1 < l_2)$。那么$[l_1, l_2)$一定是最小的$(l_2 - l_1)$个数升序排列,$(r_1, r_2]$一定是最大的$(r_2 - r_1)$个数升序排列。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean; const int N = 2e5 + 5; int n, K;
int a[N], Q[N];
boolean ismx[N], ismi[N]; int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &K);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", a + i);
}
int st = 1, ed = 0;
for (int i = n; i; i--) {
while (st <= ed && Q[st] >= i + K)
st++;
while (st <= ed && a[Q[ed]] > a[i])
ed--;
Q[++ed] = i;
ismi[i] = (st == ed);
}
st = 1, ed = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
while (st <= ed && Q[st] <= i - K)
st++;
while (st <= ed && a[Q[ed]] < a[i])
ed--;
Q[++ed] = i;
ismx[i] = (st == ed);
}
int qaq = 0;
for (int i = 1, j = 1; i <= n; i = j) {
++j;
while (a[j] > a[j - 1])
j++;
qaq += (j - i >= K);
}
int ans = n - K + 1 - max(qaq - 1, 0);
for (int i = K + 1; i <= n; i++) {
ans -= ismi[i - K] && ismx[i];
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
Problem C LCMs
基础反演练习题。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean; #define ll long long void exgcd(int a, int b, int& x, int& y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1, y = 0;
} else {
exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y -= (a / b) * x;
}
} int inv(int a, int n) {
int x, y;
exgcd(a, n, x, y);
return (x < 0) ? (x + n) : (x);
} const int Mod = 998244353; template <const int Mod = :: Mod>
class Z {
public:
int v; Z() : v(0) { }
Z(int x) : v(x){ }
Z(ll x) : v(x % Mod) { } Z operator + (Z b) {
int x;
return Z(((x = v + b.v) >= Mod) ? (x - Mod) : (x));
}
Z operator - (Z b) {
int x;
return Z(((x = v - b.v) < 0) ? (x + Mod) : (x));
}
Z operator * (Z b) {
return Z(v * 1ll * b.v);
}
Z operator ~() {
return inv(v, Mod);
}
Z operator - () {
return Z(0) - *this;
}
Z& operator += (Z b) {
return *this = *this + b;
}
Z& operator -= (Z b) {
return *this = *this - b;
}
Z& operator *= (Z b) {
return *this = *this * b;
}
}; Z<> qpow(Z<> a, int p) {
Z<> rt = Z<>(1), pa = a;
for ( ; p; p >>= 1, pa = pa * pa) {
if (p & 1) {
rt = rt * pa;
}
}
return rt;
} typedef Z<> Zi; const int N = 2e5 + 5;
const int V = 1e6 + 5; int n;
Zi f[V];
Zi Inv[V]; int main() {
int m = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
Zi ans = 0;
for (int i = 1, x; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &x);
f[x] += x;
ans -= x;
m = max(m, x);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
for (int j = i + i; j <= m; j += i) {
f[i] += f[j];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
f[i] = f[i] * f[i];
}
for (int i = m; i; i--) {
for (int j = i + i; j <= m; j += i) {
f[i] -= f[j];
}
}
Inv[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= m; i++) {
Inv[i] = (-Inv[Mod % i] * (Mod / i));
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
if (f[i].v) {
ans = ans + f[i] * Inv[i];
}
}
ans = ans * ((Mod + 1) >> 1);
printf("%d\n", ans.v);
return 0;
}
Problem D Unique Path
第一种关系相当于是路径上没有环。
第一种关系显然满足传递性和对称性,可以用并查集维护。
如果第二种关系满足两个点在同一个第一种关系的连通块内,那么无解。
每个连通块至多取出1个点,如果有第二种关系需要特判连通块个数等于2。
最少边数是连成树或者基环树。
最多边数是每个连通块取出一个点,连成完全图。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean; const int N = 1e5 + 5; #define pii pair<int, int>
#define ll long long int n, q;
ll m;
int uf[N];
vector<pii> E0, E1; int find(int x) {
return uf[x] == x ? x : uf[x] = find(uf[x]);
}
boolean unit(int x, int y) {
x = find(x), y = find(y);
if (x ^ y) {
uf[x] = y;
return true;
}
return false;
} void quitf(boolean expression) {
if (expression) {
puts("No");
exit(0);
}
} int main() {
scanf("%d%lld%d", &n, &m, &q);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
uf[i] = i;
for (int i = 1, u, v, opt; i <= q; i++) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v, &opt);
++u, ++v;
if (opt == 0) {
E0.emplace_back(u, v);
} else {
E1.emplace_back(v, u);
}
}
for (auto e : E0)
unit(e.first, e.second);
for (auto e : E1)
quitf(find(e.first) == find(e.second));
int comp = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
comp += find(i) == i;
quitf(E1.size() && comp == 2);
ll mi = ((E1.size()) ? (n) : (n - 1));
ll mx = (n - comp) + (comp * 1ll * (comp - 1) >> 1);
quitf(m < mi || m > mx);
puts("Yes");
return 0;
}
Problem E Gachapon
min-max容斥,考虑把求最小被填满的期望时间转化成填了$k$次都没满的概率,然后dp即可。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean; #define ll long long void exgcd(int a, int b, int& x, int& y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1, y = 0;
} else {
exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y -= (a / b) * x;
}
} int inv(int a, int n) {
int x, y;
exgcd(a, n, x, y);
return (x < 0) ? (x + n) : (x);
} const int Mod = 998244353; template <const int Mod = :: Mod>
class Z {
public:
int v; Z() : v(0) { }
Z(int x) : v(x){ }
Z(ll x) : v(x % Mod) { } Z operator + (Z b) {
int x;
return Z(((x = v + b.v) >= Mod) ? (x - Mod) : (x));
}
Z operator - (Z b) {
int x;
return Z(((x = v - b.v) < 0) ? (x + Mod) : (x));
}
Z operator * (Z b) {
return Z(v * 1ll * b.v);
}
Z operator ~() {
return inv(v, Mod);
}
Z operator - () {
return Z(0) - *this;
}
Z& operator += (Z b) {
return *this = *this + b;
}
Z& operator -= (Z b) {
return *this = *this - b;
}
Z& operator *= (Z b) {
return *this = *this * b;
}
}; Z<> qpow(Z<> a, int p) {
Z<> rt = Z<>(1), pa = a;
for ( ; p; p >>= 1, pa = pa * pa) {
if (p & 1) {
rt = rt * pa;
}
}
return rt;
} typedef Z<> Zi; const int N = 405; int n;
int A[N], B[N];
Zi f[2][N][N];
Zi comb[N][N]; int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
int suma = 0, sumb = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", A + i, B + i);
suma += A[i];
sumb += B[i];
}
comb[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= sumb; i++) {
comb[i][0] = comb[i][i] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
comb[i][j] = comb[i - 1][j - 1] + comb[i - 1][j];
}
}
int cur = 0;
suma = sumb = 0;
f[cur][0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
memset(f[cur ^= 1], 0, sizeof(f[0]));
for (int sa = 0; sa <= suma; sa++) {
for (int sb = 0; sb <= sumb; sb++) {
Zi v = f[cur ^ 1][sa][sb];
if (!v.v) continue;
Zi pw = 1;
f[cur][sa][sb] += v;
for (int j = 0; j < B[i]; j++, pw *= A[i]) {
f[cur][sa + A[i]][sb + j] -= comb[sb + j][j] * pw * v;
}
}
}
suma += A[i];
sumb += B[i];
}
Zi ans = 0;
for (int sa = 1; sa <= suma; sa++) {
Zi inva = ~Zi(sa), pw = 1;
for (int sb = 1; sb <= sumb + 1; sb++, pw *= inva) {
Zi v = f[cur][sa][sb - 1] * pw - f[cur][sa][sb] * (pw * inva);
if (v.v) {
ans -= v * sb * inva * suma;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n", ans.v);
return 0;
}
Problem F Two Permutations
大力讨论$P_i, Q_i, i$的相等或不等关系。考虑最小割建图,把一边属于割集的意义交换一下。然后发现所有代价都可以转化成$i, i', S, T$属于不同割集。具体建图可以见代码。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean; const signed int inf = (signed) (~0u >> 1); template <typename T>
void pfill(T* pst, const T* ped, T val) {
for ( ; pst != ped; *(pst++) = val);
} typedef class Edge {
public:
int ed, nx, r; Edge(int ed = 0, int nx = 0, int r = 0) : ed(ed), nx(nx), r(r) { }
} Edge; typedef class MapManager {
public:
int *h;
vector<Edge> es; MapManager() { }
MapManager(int n) {
h = new int[(n + 1)];
pfill(h, h + n + 1, -1);
}
~MapManager() {
delete[] h;
es.clear();
} void addEdge(int u, int v, int r) {
es.push_back(Edge(v, h[u], r));
h[u] = (signed) es.size() - 1;
} void addArc(int u, int v, int cap) {
addEdge(u, v, cap);
addEdge(v, u, 0);
} Edge& operator [] (int p) {
return es[p];
}
} MapManager; typedef class Network {
public:
int S, T;
int *cur, *div;
MapManager g; Network() { }
Network(int S, int T) : S(S), T(T), g(T + 1) {
cur = new int[(T + 1)];
div = new int[(T + 1)];
}
~Network() {
delete[] cur;
delete[] div;
} boolean bfs() {
static queue<int> que;
pfill(div, div + T + 1, -1);
div[S] = 0;
que.push(S);
while (!que.empty()) {
int e = que.front();
que.pop();
for (int i = g.h[e], eu; ~i; i = g[i].nx) {
// cerr << i << '\n';
if (!g[i].r)
continue;
eu = g[i].ed;
if (!~div[eu]) {
div[eu] = div[e] + 1;
que.push(eu);
}
}
}
return ~div[T];
} int dfs(int p, int minf) {
if (p == T || !minf)
return minf;
int flow = 0, f;
for (int& i = cur[p], e; (~i); i = cur[p], i = g[i].nx) {
e = g[i].ed;
if (div[e] == div[p] + 1 && (f = dfs(e, min(minf, g[i].r))) > 0) {
flow += f;
g[i].r -= f;
g[i ^ 1].r += f;
minf -= f;
if (!minf) {
break;
}
}
}
return flow;
} int dinic() {
int rt = 0;
// cerr << g.h[0] << '\n';
while (bfs()) {
for (int i = 0; i <= T; i++)
cur[i] = g.h[i];
rt += dfs(S, inf);
}
return rt;
}
} Network; const int N = 1e5 + 5; int n, T;
int uf[N << 1];
int P[N], Q[N]; int find(int x) {
return uf[x] == x ? x : (uf[x] = find(uf[x]));
}
void unit(int x, int y) {
x = find(x), y = find(y);
if (x ^ y) {
uf[x] = y;
}
} int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++)
uf[i] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", P + i);
unit(i, ++P[i]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", Q + i);
unit(i + n, ++Q[i] + n);
}
Network network (0, T = 2 * n + 1);
MapManager &g = network.g;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i == P[i] && i == Q[i]) {
continue;
}
ans++;
if (i != P[i] && i != Q[i]) {
g.addArc(find(i), find(i + n), 1);
} else if (i == P[i] && i != Q[i]) {
g.addArc(0, find(i + n), 1);
} else if (i != P[i] && i == Q[i]) {
g.addArc(find(i), T, 1);
}
if (P[i] == Q[i]) {
g.addArc(find(i + n), find(i), 1);
}
}
ans -= network.dinic();
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
AtCoder Grand Contest 038 简要题解的更多相关文章
- AtCoder Grand Contest 031 简要题解
AtCoder Grand Contest 031 Atcoder A - Colorful Subsequence description 求\(s\)中本质不同子序列的个数模\(10^9+7\). ...
- AtCoder Grand Contest 039 简要题解
从这里开始 比赛目录 Problem A Connection and Disconnection 简单讨论即可. Code #include <bits/stdc++.h> using ...
- AtCoder Grand Contest 040 简要题解
从这里开始 比赛目录 A < B < E < D < C = F,心情简单.jpg. Problem A >< 把峰谷都设成 0. Code #include &l ...
- AtCoder Grand Contest 035 简要题解
从这里开始 题目目录 Problem A XOR Circle 你发现,权值的循环节为 $a_0, a_1, a_0\oplus a_1$,然后暴力即可. Code #include <bits ...
- AtCoder Grand Contest 036 简要题解
从这里开始 比赛目录 Problem A Triangle 考虑把三角形移到和坐标轴相交,即 然后能够用坐标比较简单地计算面积,简单构造一下就行了. Code #include <bits/st ...
- AtCoder Grand Contest 037 简要题解
从这里开始 题目目录 Problem A Dividing a String 猜想每段长度不超过2.然后dp即可. 考虑最后一个长度大于等于3的一段,如果划成$1 + 2$会和后面相同,那么划成$2 ...
- AtCoder Grand Contest 038 题解
传送门 这场表现的宛如一个\(zz\) \(A\) 先直接把前\(b\)行全写成\(1\),再把前\(a\)列取反就行 const int N=1005; char mp[N][N];int n,m, ...
- AtCoder Grand Contest 038题解
好久没更了 写点东西吧= = A 01Matrix 简单构造 左上角和右下角染成1其他染成0即可 #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define ll long long ...
- AtCoder Grand Contest 021完整题解
提示:如果公式挂了请多刷新几次,MathJex的公式渲染速度并不是那么理想. 总的来说,还是自己太弱了啊.只做了T1,还WA了两发.今天还有一场CodeForces,晚上0点qwq... 题解还是要好 ...
随机推荐
- tensorflow之tf.stop_gradient
停止梯度计算. 当在一个图中执行时, 这个op按原样输出它的输入张量. 当构建ops来计算梯度时,该op会阻止将其输入贡献考虑在内. 参数: Input: 一个张量. name: 操作的名称(可选) ...
- Visual Studio 定制模板类---详细步骤
1.先定义一个类文件,将要定义的信息写入类文件 比如我每次写一个命令都是这个套路,要继承接口,要写上相应的特性,每次都 是重复的工作: 2.提取类模板 项目=>导出模板 这里你可以导出项目模板和 ...
- Python 学习 第15篇:日期和时间
datetime模块中包含五种基本类型:date.time.datetime.timedelta和tzinfo,tz是time zone的缩写,tzinfo用于表示时区信息. 一,date类型 dat ...
- .NET WebFrom跨时区项目时间问题处理方法
前段时间因为公司的一个 WebFrom 项目设计到跨时区的问题,处理了一段时间,终于解决了,写个博客记录一下,方便以后回顾以及给他人提供一个参考的方法. 本次的项目因为跨越了多个时区,在一些时间上会受 ...
- "初识".Net Winfom
对于“初识”Winform中 初识这两个字的涵义,实际上之前我一直接触的是B/S方面的知识和开发,虽然说不上是熟练,但是大部分时间都是花在B/S上了,例如MVC,如今要从B/S转到C/S了,说实话心里 ...
- springcloud分布式事务Atomikos实例
0.JTA(Java Transaction Manager)的介绍 (1)jta与jdbc 简单的说 jta是多库的事务 jdbc是单库的事务 (2)XA与JTA XA : XA是一个规范或是一个事 ...
- 百度地图API 基本用法
百度地图 百度地图JavaScript API是一套由JavaScript语言编写的应用程序接口,可帮助您在网站中构建功能丰富.交互性强的地图应用,支持PC端和移动端基于浏览器的地图应用开发,且支持H ...
- 小鸟初学Shell编程(三)脚本不同执行方式的影响
执行命令的方式 执行Shell脚本的方式通常有以下四种 方式一:bash ./test.sh 方式二:./test.sh 方式三:source ./test.sh 方式四:. ./test.sh 执行 ...
- 关于javascript,多种函数封装!!
1.获取最终的属性 function getStyleAttr(obj, attr){ if(window.getComputedStyle){ return window.getComputedSt ...
- unity常用的坐标系转换
当调用别人的接口时,经常会有获取位置或向量的接口.遇到这些数据时,先要弄清楚现在获取的数据在哪个坐标系下的. 是否需要进行坐标系变换,一般提供的位置和向量都是在世界坐标系的,此时需要注意: ①对方的坐 ...
