[Python学习笔记-008] 使用双向链表去掉重复的文本行
用Python处理文本文件是极方便的,当文本文件中有较多的重复的行的时候,将那些重复的行数去掉并打印诸如"...<repeats X times>..."有助于更好的浏览文本文件的内容。下面将通过Python打造一个双向链表来实现这一功能。如果你对在Python中实现双向链表感兴趣,不妨花五分钟读一读。Have fun :-)
01 - 定义链表结点
struct node {
int lineno;
char *line;
char *md5;
char *dupcnt; /* duplicated counter */
struct node *prev;
struct node *next;
};
在Python3中,可以使用字典定义这样的结点。例如:
node = {}
node['lineno'] = index + 1
node['line'] = line.strip().rstrip()
node['md5'] = md5txt
node['dupcnt'] = 0
node['prev'] = index - 1
node['next'] = index + 1
由于Python的list本身就是可变数组,这就省力多了,我们不需要从C的角度去考虑链表的建立。
02 - 初始化双向链表
def init_doubly_linked_list(l_in):
l_out = []
index = 0
for text in l_in:
data = text.strip().rstrip()
md5 = hashlib.md5(data.encode(encoding='UTF-8')).hexdigest() d_node = {}
d_node['lineno'] = index + 1
d_node['line'] = data
d_node['md5'] = md5
d_node['dupcnt'] = 0
d_node['prev'] = index - 1
d_node['next'] = index + 1
if index == 0:
d_node['prev'] = None
if index == len(l_in) - 1:
d_node['next'] = None
l_out.append(d_node) index += 1
return l_out
很简单,直接采用尾插法搞定。
03 - 将双向链表中的包含有重复行的结点处理掉
def omit_doubly_linked_list(l_dll):
for curr_node in l_dll:
prev_node_index = curr_node['prev']
next_node_index = curr_node['next'] if prev_node_index is None: # the head node
prev_node = None
continue
else:
prev_node = l_dll[prev_node_index] if next_node_index is None: # the tail node
next_node = None
else:
next_node = l_dll[next_node_index] if curr_node['md5'] != prev_node['md5']:
continue # Update dupcnt of previous node
prev_node['dupcnt'] += 1 # Remove current node
if next_node is not None:
next_node['prev'] = curr_node['prev']
if prev_node is not None:
prev_node['next'] = curr_node['next']
如果当前行的md5跟前一行一样,那说明就重复了。处理的方法如下:
- 将前一个结点的重复计数器(dupcnt)加1;
- 把当前结点从双向链表上摘掉(这里我们只修改前驱结点的next和后继结点的prev, 不做实际的删除,因为没必要)。
也许你会问为什么采用md5比较而不采用直接的文本行比较,个人觉得先把文本行的md5算出后,再使用md5比较会更好一些,尤其是文本行很长的时候,因为md5(占128位)的输出总是32个字符。
04 - 遍历处理后的双向链表
def traverse_doubly_linked_list(l_dll):
l_out = [] node_index = None
if len(l_dll) > 0:
node_index = 0 while (node_index is not None): # <==> p != NULL
curr_node = l_dll[node_index] msg = '%6d\t%s' % (curr_node['lineno'], curr_node['line'])
l_out.append(msg) #
# 1) If dupcnt is 0, it means subsequent lines don't repeat current
# line, just go to visit the next node
# 2) If dupcnt >= 1, it means subsequent lines repeat the current line
# a) If dupcnt is 1, i.e. only one line repeats, just pick it up
# b) else save message like '...<repeats X times>...'
#
if curr_node['dupcnt'] == 0:
node_index = curr_node['next']
continue
elif curr_node['dupcnt'] == 1:
msg = '%6d\t%s' % (curr_node['lineno'] + 1, curr_node['line'])
else: # i.e. curr_node['dupcnt'] > 1
msg = '%s\t...<repeats %d times>...' % (' ' * 6,
curr_node['dupcnt'])
l_out.append(msg) node_index = curr_node['next'] return l_out
- 如果当前结点的dupcnt为0,说明它后面的行与之不同,直接打印;
- 如果当前结点的dupcnt为1,说明它后面的行与之相同,那么打印当前行,再打印下一行,注意行号得加一;
- 如果当前结点的dupcnt为N(>1),说明它后面有N行与之重复了,那么打印当前行并再打印...<repeates N times>...。
注意:头结点的prev和尾结点的next都被定义为None。我们因此可以做类C的遍历。典型的C遍历链表是这样的:
for (p = head; p != NULL; p = p->next)
/* print p->data */
到此为止,在Python中实现一个简单的双向链表就搞定了。其特点是:
- 用None代表NULL;
- 头结点的prev指针的值和尾结点的next指针的值均为None;
- 中间结点的prev指针的值是其前趋结点的下标;
- 中间结点的next指针的值是其后继结点的下标。
完整的代码实现如下:
#!/usr/bin/python3 import sys
import hashlib
import getopt TC_LOG_OUTPUT_RAW = False def init_doubly_linked_list(l_in):
#
# Here is the node definition of the doubly linked list
#
# struct node {
# int lineno;
# char *text;
# char *md5;
# char *dupcnt; /* duplicated counter */
# struct node *prev;
# struct node *next;
# }
#
l_out = []
index = 0
for text in l_in:
data = text.strip().rstrip()
md5 = hashlib.md5(data.encode(encoding='UTF-8')).hexdigest() d_node = {}
d_node['lineno'] = index + 1
d_node['line'] = data
d_node['md5'] = md5
d_node['dupcnt'] = 0
d_node['prev'] = index - 1
d_node['next'] = index + 1
if index == 0:
d_node['prev'] = None
if index == len(l_in) - 1:
d_node['next'] = None
l_out.append(d_node) index += 1
return l_out def omit_doubly_linked_list(l_dll):
#
# Core algorithm to omit repeated lines saved in the doubly linked list
#
# prev_node = curr_node->prev;
# next_node = curr_node->next;
#
# if (curr_node->md5 == prev_node.md5) {
# prev_node.dupcnt++;
#
# /* remove current node */
# next_node->prev = curr_node->prev;
# prev_node->next = curr_node->next;
# }
#
for curr_node in l_dll:
prev_node_index = curr_node['prev']
next_node_index = curr_node['next'] if prev_node_index is None: # the head node
prev_node = None
continue
else:
prev_node = l_dll[prev_node_index] if next_node_index is None: # the tail node
next_node = None
else:
next_node = l_dll[next_node_index] if curr_node['md5'] != prev_node['md5']:
continue # Update dupcnt of previous node
prev_node['dupcnt'] += 1 # Remove current node
if next_node is not None:
next_node['prev'] = curr_node['prev']
if prev_node is not None:
prev_node['next'] = curr_node['next'] def traverse_doubly_linked_list(l_dll):
#
# Core algorithm to traverse the doubly linked list
#
# p = l_dll;
# while (p != NULL) {
# /* print p->lineno and p->text */
#
# if (p->dupcnt == 0) {
# p = p->next;
# continue;
# }
#
# if (p->dupcnt == 1)
# /* print p->lineno + 1 and p->text */
# else /* i.e. > 1 */
# printf("...<repeats %d times>...", p->dupcnt);
#
# p = p->next;
# }
#
l_out = [] node_index = None
if len(l_dll) > 0:
node_index = 0 while (node_index is not None): # <==> p != NULL
curr_node = l_dll[node_index] msg = '%6d\t%s' % (curr_node['lineno'], curr_node['line'])
l_out.append(msg) #
# 1) If dupcnt is 0, it means subsequent lines don't repeat current
# line, just go to visit the next node
# 2) If dupcnt >= 1, it means subsequent lines repeat the current line
# a) If dupcnt is 1, i.e. only one line repeats, just pick it up
# b) else save message like '...<repeats X times>...'
#
if curr_node['dupcnt'] == 0:
node_index = curr_node['next']
continue
elif curr_node['dupcnt'] == 1:
msg = '%6d\t%s' % (curr_node['lineno'] + 1, curr_node['line'])
else: # i.e. curr_node['dupcnt'] > 1
msg = '%s\t...<repeats %d times>...' % (' ' * 6,
curr_node['dupcnt'])
l_out.append(msg) node_index = curr_node['next'] return l_out def print_refined_text(l_lines):
l_dll = init_doubly_linked_list(l_lines)
omit_doubly_linked_list(l_dll)
l_out = traverse_doubly_linked_list(l_dll)
for line in l_out:
print(line) def print_raw_text(l_lines):
lineno = 0
for line in l_lines:
lineno += 1
line = line.strip().rstrip()
print('%6d\t%s' % (lineno, line)) def usage(prog):
sys.stderr.write('Usage: %s [-r] <logfile>\n' % prog) def main(argc, argv):
shortargs = ":r"
longargs = ["raw"]
try:
options, rargv = getopt.getopt(argv[1:], shortargs, longargs)
except getopt.GetoptError as err:
sys.stderr.write("%s\n" % str(err))
usage(argv[0])
return 1 for opt, arg in options:
if opt in ('-r', '--raw'):
global TC_LOG_OUTPUT_RAW
TC_LOG_OUTPUT_RAW = True
else:
usage(argv[0])
return 1 rargc = len(rargv)
if rargc < 1:
usage(argv[0])
return 1 logfile = rargv[0]
with open(logfile, 'r') as file_handle:
if TC_LOG_OUTPUT_RAW:
print_raw_text(file_handle.readlines())
else:
print_refined_text(file_handle.readlines()) return 0 if __name__ == '__main__':
sys.exit(main(len(sys.argv), sys.argv))
测试运行如下:
$ ./foo.py /tmp/a.log > /tmp/a && cat /tmp/a
<<<test_start>>>
tag=dio30 stime=
cmdline="diotest6 -b 65536 -n 100 -i 100 -o 1024000"
contacts=""
analysis=exit
<<<test_output>>>
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TFAIL : diotest6.c:: readv failed, ret =
diotest06 TFAIL : diotest6.c:: Write Direct-child failed
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
...<repeats times>...
diotest06 TFAIL : diotest6.c:: Write with Direct IO, Read without
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TFAIL : diotest6.c:: Write with Direct IO, Read without
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TFAIL : diotest6.c:: Write with Direct IO, Read without
...<repeats times>...
diotest06 TPASS : Read, Write with Direct IO
diotest06 TINFO : / testblocks failed
incrementing stop
<<<execution_status>>>
initiation_status="ok"
duration= termination_type=exited termination_id= corefile=no
cutime= cstime=
<<<test_end>>>
$ ./foo.py -r /tmp/a.log > /tmp/b && cat /tmp/b
<<<test_start>>>
tag=dio30 stime=
cmdline="diotest6 -b 65536 -n 100 -i 100 -o 1024000"
contacts=""
analysis=exit
<<<test_output>>>
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TFAIL : diotest6.c:: readv failed, ret =
diotest06 TFAIL : diotest6.c:: Write Direct-child failed
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TFAIL : diotest6.c:: Write with Direct IO, Read without
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TFAIL : diotest6.c:: Write with Direct IO, Read without
diotest06 TPASS : Read with Direct IO, Write without
diotest06 TFAIL : diotest6.c:: Write with Direct IO, Read without
diotest06 TFAIL : diotest6.c:: Write with Direct IO, Read without
diotest06 TFAIL : diotest6.c:: Write with Direct IO, Read without
diotest06 TPASS : Read, Write with Direct IO
diotest06 TINFO : / testblocks failed
incrementing stop
<<<execution_status>>>
initiation_status="ok"
duration= termination_type=exited termination_id= corefile=no
cutime= cstime=
<<<test_end>>>
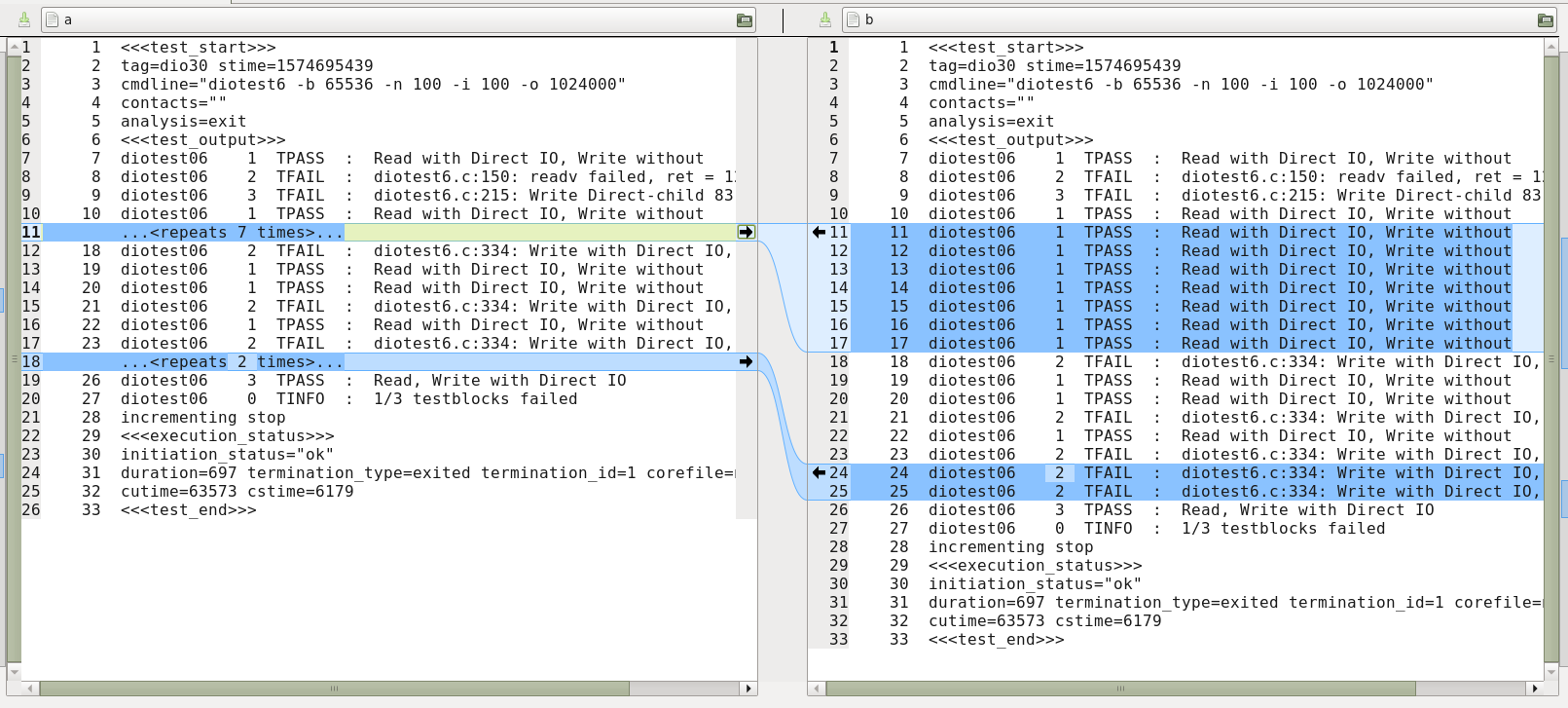
用meld对照/tmp/a和/tmp/b截图如下:
[Python学习笔记-008] 使用双向链表去掉重复的文本行的更多相关文章
- Python学习笔记008
while循环 while 条件 : 执行 num =1 while num<=10: print(num) num+=1 1-100偶数 方法1 num =2 while num& ...
- OpenCV之Python学习笔记
OpenCV之Python学习笔记 直都在用Python+OpenCV做一些算法的原型.本来想留下发布一些文章的,可是整理一下就有点无奈了,都是写零散不成系统的小片段.现在看 到一本国外的新书< ...
- Python学习笔记(四)
Python学习笔记(四) 作业讲解 编码和解码 1. 作业讲解 重复代码瘦身 # 定义地图 nav = {'省略'} # 现在所处的层 current_layer = nav # 记录你去过的地方 ...
- 【python学习笔记】3.字符串使用
[python学习笔记]3.字符串使用 字符串是一种序列,素有标准的序列操作对字符串用样适用,字符串是不可以改变 格式化操作符,%,左侧是格式化字符串,右侧是被格式的值,可以是一个值.元组.字典 数值 ...
- python学习笔记(二)、字符串操作
该一系列python学习笔记都是根据<Python基础教程(第3版)>内容所记录整理的 1.字符串基本操作 所有标准序列操作(索引.切片.乘法.成员资格检查.长度.最小值和最大值)都适用于 ...
- python学习笔记(一)、列表和元祖
该一系列python学习笔记都是根据<Python基础教程(第3版)>内容所记录整理的 1.通用的序列操作 有几种操作适用于所有序列,包括索引.切片.相加.相乘和成员资格检查.另外,Pyt ...
- Deep learning with Python 学习笔记(10)
生成式深度学习 机器学习模型能够对图像.音乐和故事的统计潜在空间(latent space)进行学习,然后从这个空间中采样(sample),创造出与模型在训练数据中所见到的艺术作品具有相似特征的新作品 ...
- Deep learning with Python 学习笔记(9)
神经网络模型的优化 使用 Keras 回调函数 使用 model.fit()或 model.fit_generator() 在一个大型数据集上启动数十轮的训练,有点类似于扔一架纸飞机,一开始给它一点推 ...
- Deep learning with Python 学习笔记(8)
Keras 函数式编程 利用 Keras 函数式 API,你可以构建类图(graph-like)模型.在不同的输入之间共享某一层,并且还可以像使用 Python 函数一样使用 Keras 模型.Ker ...
随机推荐
- C/C++中new的使用规则
本人未重视new与指针的使用,终于,终于在前一天船翻了,而且没有爬上岸: 故此,今特来补全new的用法,及其一些规则: 话不多说 C++提供了一种“动态内存分配”机制,使得程序可以在运行期间,根据实际 ...
- Java自学-I/O 控制台输入流System.in
Java 控制台输入流 System.in和Scanner System.out 是常用的在控制台输出数据的 System.in 可以从控制台输入数据 步骤 1 : System.in package ...
- React的jsx语法,详细介绍和使用方法!
jsx语法 一种混合使用html及javascript语法的代码 在js中 遇到<xx>即开始html语法 遇到</xx>则结束html语法 恢复成js语法 例如: let D ...
- 【入门篇】前端框架Vue.js知识介绍
一.Vue.js介绍 1.什么是MVVM? MVVM(Model-View-ViewModel)是一种软件架构设计模式,它源于MVC(Model-View-Controller)模式,它是一种思想,一 ...
- HeadFirst设计模式---观察者
表达公式 注册者 + 订阅者 = 观察者模式 设计气象站 气象站接口 /** ** 布告板 ** @author lollipop ** @since 2019/11/24 **/ public in ...
- Linux下压缩工具gzip和归档工具tar及其实战shell应用
Linux下压缩工具gzip和归档工具tar及其实战shell应用 第一章:gzip的使用技巧 gzip [option]... file... -d: 解压缩,相当于gunzip; -# ...
- OpenStack Train版 简单部署流程
environment 1.网络平面 management(管理网络)→软件安装,组件通信 provider(提供实例网络)→:提供者网络:直接获取ip地址,实例之间直接互通 自服务网络(私有网络 ...
- git fatal: remote origin already exists错误解决方案
$ git remote add origin git@github.com:AntonioSu/learngitWindows.git 在运行以上代码出现的错误,此错误是因为已经存在了远程分支,只需 ...
- day10_7.10 函数的嵌套等
一.命名关键字参数.(了解) 1.在函数阶段,写在*与** 可变长参数之间的形参称为命名关键字参数. 在给命名关键字参数传值时,只能用关键字为其传值.诸如以下函数的形参 def func(x,y=,* ...
- Ubuntu使用snap安装常用软件
1,snap简介 什么是snap,snap是一种全新的软件包管理方式,它类似一个容器拥有一个应用程序所有的文件和库,各个应用程序之间完全独立.所以使用snap包的好处就是它解决了应用程序之间的依赖问题 ...
