Python 数据结构 树
什么是树
数是一种抽象的数据类型(ADT)或是作这种抽象数据类型的数据结构,用来模拟具有树状结构性质的数据集合,它是由n(n>1)的有限个节点和节点之间的边组成的一个有层次关系的集合。
树的组成元素:
- 根节点:树的最上层的节点,任何非空的树都有一个节点
- 路径:从起始节点到终止节点经历过的路径
- 父节点:除了根节点,每个节点的上一层边连接的节点就是它的父节点
- 子节点:每一节点由边指向的下一层节点
- 兄弟节点:同一父节点且处在同一层的节点
- 子树:每个节点包含它所有的后代组成的子树
- 叶子节点:没有子节点的节点,称为叶子节点
- 树的高度或深度:树中节点的最大层次
树具有以下的特点:
- 每个节点有零个或多个子节点;
- 没有父节点的节点称为根节点;
- 每一个非根节点有且只有一个父节点;
- 除了根节点外,每个子节点可以分为多个不相交的子树。
树的种类
- 无序树:树中的任意节点的子节点之间没有顺序关系,也称为自由树。
- 有序树:树中的任意节点的子节点之间有顺序关系。
- 二叉树:每个节点最多含有两个子树
- 完全二叉树:当一个高度为h的完美二叉树减少到h-1,并且最底层的槽被毫无间隙地从左到右填充,我们就叫它完全二叉树
- 满二叉树:如果每个内部节点(非叶子节点)都有两个子节点,就成为满二叉树
- 完美二叉树:当所有的叶子节点都在同一层就是完美二叉树,毫无间隙填充了h层
如下图所示:
满二叉树:
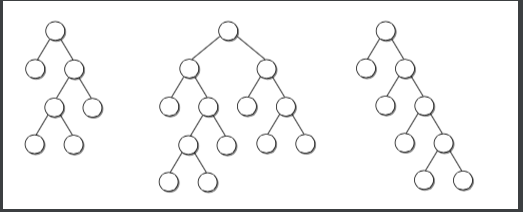
完美二叉树:
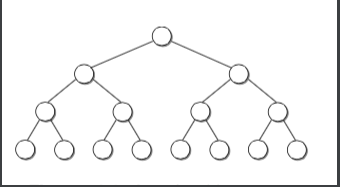
完全二叉树:

数的存储和表示
顺序存储:将数据结构存储在固定的数组中,所以在遍历速度上有一定的优势,同时所占用的空间比较大,是非主流二叉树。二叉树通常以链式方式存储:
如下图所示是简单的顺序存储:
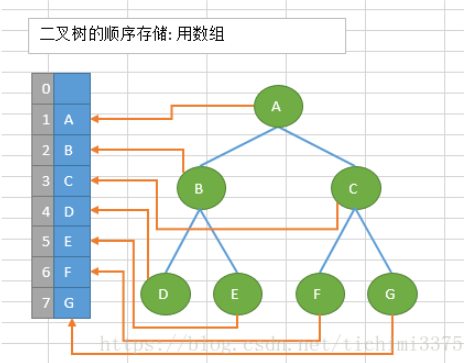
链式存储: 结构采用链表存储二叉树中的数据元素,用链表建立二叉树中节点之间关系,二叉树最常用的链式存储结构是二叉链,每个节点包含三个域,分别是数据元素域data,
左还在链域Child和右孩子链域Child,与单链表头结点和不带头节点的两种情况相似,二叉链存储结构的二叉树也有带头节点和不带头结点两种。

树的常用场景
- xml,html等,那么编写这些东西的解析器的时候,不可避免用到树
- 路由协议就是使用了树的算法
- mysql数据库索引
- 文件系统的目录结构
- 所以很多经典的AI算法其实都是树搜索,此外机器学习中的decision tree也是树结构
二叉树
二叉树的基本概念
二叉树是由n(n>=0)个节点组成的集合,每个节点最多有两个子树的有序树,它或者是空集,或者是一个根和左右子树的两个不相交的二叉树组成。
二叉树的特点:
二叉树是有序树,即使是只有一个子树,也必须区分左右树。
二叉树的每个节点的的度,不能大于2.
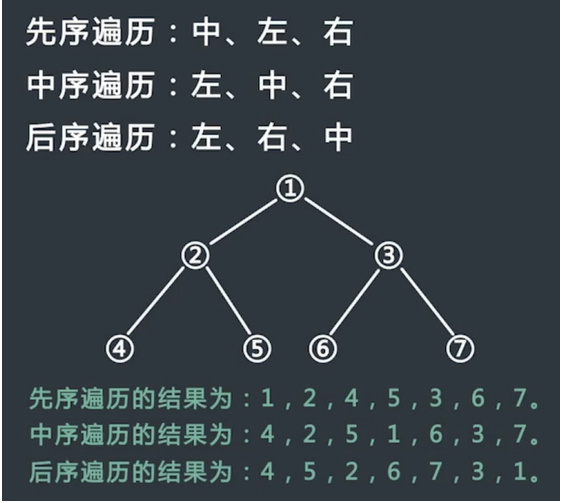
二叉树的遍历
前序遍历:先访问根节点, 然后前序遍历左子树,再前序遍历右子树
中序遍历:中序遍历根节点的左子树,然后再访问根节点,最后遍历右子树
后序遍历:从左到右叶子节点的方式遍历访问左子树,最后访问根节点
层序遍历:从根节点从上往下逐层遍历,在同一层,按从左到右的顺序对节点逐个访问
二叉树实现方式:
# 节点定义
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, value, left_child, right_child):
self._value = value
self._left_child = left_child
self._right_child = right_child @property
def value(self):
return self._value @value.setter
def value(self, value):
self._value = self.value @property
def left_child(self):
return self._left_child @left_child.setter
def left_child(self, value):
self._left_child = value @property
def right_child(self):
return self._right_child @right_child.setter
def right_child(self, value):
self._right_child = value # 树的定义
class Tree(object):
def __init__(self, value):
self._root = Node(value, None, None) @property
def root(self):
return self._root
遍历树的代码实现:以下遍历方式亲测有效
# 递归后续遍历 def pre_order(root):
if not isinstance(root, Node):
return []
pre_order_tmp = []
if root is not None:
pre_order_tmp.append(root.value)
pre_order_tmp += pre_order(root.left_child)
pre_order_tmp += pre_order(root.right_child)
return pre_order_tmp # 非递归后续遍历
def pre_order_not_recursion(root):
if not isinstance(root, Node):
return None
stack = [root]
result = []
while stack:
node = stack.pop(-1)
if node:
if isinstance(node, Node):
result.append(node.value)
stack.append(node.right_child)
stack.append(node.left_child)
else:
result.append(node)
return result # 递归中序遍历
def middle_order(root):
if not isinstance(root, Node):
return []
middle_order_tmp = []
if root is not None:
middle_order_tmp += middle_order(root.left_child)
middle_order_tmp.append(root.value)
middle_order_tmp += middle_order(root.right_child)
return middle_order_tmp # 非递归中序遍历
def middle_order_not_recursion(root):
if not isinstance(root, Node):
return None
stack = [root.right_child, root.value, root.left_child]
result = []
while stack:
node = stack.pop(-1)
if node:
if isinstance(node, Node):
stack.append(node.left_child)
stack.append(node.value)
stack.append(node.right_child)
else:
result.append(node)
return result # 递归后续遍历
def post_order(root):
if not isinstance(root, Node):
return [] post_order_tmp=[]
if root is not None:
post_order_tmp += pre_order(root.left_child)
post_order_tmp += pre_order(root.right_child)
post_order_tmp.append(root.value)
return post_order_tmp # 非递归后续遍历
def post_order_recursion(root):
if not isinstance(root, Node):
return None
stack = [root.value, root.right_child, root.left_child]
result = []
while stack:
node = stack.pop(-1)
if node:
if isinstance(node, Node):
result.append(node.value)
stack.append(node.right_child)
stack.append(node.left_child)
else:
result.append(node)
return result # 分层遍历
def layer_order(root):
if not isinstance(root, Node):
return [] queue = [root.value, root.left_child, root.right_child]
result = []
while queue:
tmp = queue.pop(0)
if tmp:
if isinstance(tmp, Node):
queue.append(tmp.value)
queue.append(tmp.left_child)
queue.append(tmp.right_child)
else:
result.append(tmp)
return result
二叉树的其他方法:
# 递归方式计算节点个数
def node_count(root):
if not isinstance(root, Node):
return None
else:
if root:
return node_count(root.left_child)+node_count(root.right_child)+1
else:
return None # 借用分层遍历实现
def node_count_not_recursion(root):
if not isinstance(root, Node):
return None return len(layer_order(root)) # 计算二叉树深度
def tree_deep(root):
if not isinstance(root, Node):
return None if root:
return 1+max(tree_deep(root.left_child), max(root.right_child))
else:
return 0 # 非递归方式实现
def tree_deep_not_recursion(root):
if not isinstance(root, Node):
return None stack = [(root, 1)]
result = 0
while stack:
tmp_node, tmp_layer = stack.pop(0)
if tmp_node:
stack.append((tmp_node.left_child, tmp_layer+1))
stack.append((tmp_node.ritht_child, tmp_layer+1))
result = tmp_layer+1
return result # 计算第K层节点的个数
def kth_node_count(root, k):
if not isinstance(root, Node):
return None if not root or k <=0:
return 0
if k == 1:
return 1
return kth_node_count(root.left_child, k-1)+kth_node_count(root.right_child, k-1) # 计算二叉树叶子节点的个数
def leaf_account(root):
if not isinstance(root, Node):
return None if not root:
return 0
if not root.left_child and not root.right_child:
return 1
return leaf_account(root.left_child)+leaf_account(root.right_child) # 判断是否为二分查找树BST
# 判断是否为二分查找树BST,递归方式
# 二分查找树的定义搞清楚,二分查找树的中序遍历结果为递增序列
def is_bst_tree(root):
if not isinstance(root, Node):
return [] def is_asc(order):
for i in range(len(order)-1):
if order[i] > order[i+1]:
return False
return True
return is_asc(middle_order_not_recursion(root)) if __name__ == '__main__':
tree = Tree(1)
tree1 = Tree(1)
node7 = Node(5, None,None)
node6 = Node(4, None,None)
node5 = Node(3, None,None)
node4 = Node(2, None,None)
node3 = Node(1, None,None)
node2 = Node(3, node5, node6)
node1 = Node(4, node3, node4) tree.root.left_child = node1
tree.root.right_child = node2
tree1.root.left_child = node2
tree1.root.right_child = node2 print (post_order_recursion(tree.root)) print(is_bst_tree(tree.root))
print(is_bst_tree(tree1.root))
Python 数据结构 树的更多相关文章
- python数据结构树和二叉树简介
一.树的定义 树形结构是一类重要的非线性结构.树形结构是结点之间有分支,并具有层次关系的结构.它非常类似于自然界中的树.树的递归定义:树(Tree)是n(n≥0)个结点的有限集T,T为空时称为空树,否 ...
- Python数据结构--树遍历算法
''' 遍历是访问树的所有节点的过程,也可以打印它们的值. 因为所有节点都通过边(链接)连接,所以始终从根(头)节点开始. 也就是说,我们不能随机访问树中的一个节点. 这里介绍三种方式来遍历一棵树 - ...
- Python数据结构-树与树的遍历
树:是一种抽象的数据类型 树的作用:用来模拟树状结构性质的数据集合 树的特点: 每个节点有零个或者多个节点 没有父节点的节点,叫做根节点 每一个根节点有且只有一个父节点 除了根节点外,每个节点可以分成 ...
- python数据结构之树和二叉树(先序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历)
python数据结构之树和二叉树(先序遍历.中序遍历和后序遍历) 树 树是\(n\)(\(n\ge 0\))个结点的有限集.在任意一棵非空树中,有且只有一个根结点. 二叉树是有限个元素的集合,该集合或 ...
- Python入门篇-数据结构树(tree)的遍历
Python入门篇-数据结构树(tree)的遍历 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.遍历 迭代所有元素一遍. 二.树的遍历 对树中所有元素不重复地访问一遍,也称作扫 ...
- Python入门篇-数据结构树(tree)篇
Python入门篇-数据结构树(tree)篇 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.树概述 1>.树的概念 非线性结构,每个元素可以有多个前躯和后继 树是n(n& ...
- Python数据结构与算法设计总结篇
1.Python数据结构篇 数据结构篇主要是阅读[Problem Solving with Python]( http://interactivepython.org/courselib/static ...
- python数据结构与算法
最近忙着准备各种笔试的东西,主要看什么数据结构啊,算法啦,balahbalah啊,以前一直就没看过这些,就挑了本简单的<啊哈算法>入门,不过里面的数据结构和算法都是用C语言写的,而自己对p ...
- Python数据结构与算法设计(总结篇)
的确,正如偶像Bruce Eckel所说,"Life is short, you need Python"! 如果你正在考虑学Java还是Python的话,那就别想了,选Pytho ...
随机推荐
- apache 二级域名设置完整步骤
步骤如下: 1. 你要拥有一个有泛域名解析的顶级域名,例如:abc.com 在dns服务上设置,域名服务商都提供此服务 www.abc.com 指向服务器IPabc.com ...
- 网络推送通知:及时,相关和准确 (navigator.serviceWorker.register(), window.PushManager, new Notification)
google网络推送通知 https://developers.google.cn/web/fundamentals/push-notifications/ 服务工作线程:简介server worle ...
- .net core 支持apk下载
在 app.UseStaticFiles(); 后面加上 app.UseStaticFiles(new StaticFileOptions { //FileProvider = new Physica ...
- easyui---form表单_validatebox验证框
第一种方式:混合写法 $("#password").validatebox({ }) <td><input type="text" name= ...
- 如何将sql查询出的结果,用符号隔开
晚饭过后,打开QQ圈子,发现QQ群里有人提问了一个问题↓ 数据表中有这样的数据 如何转换为 ,, , 知道写存储过程或者函数可以解决,但是想想能不能用一条sql语句解决...未果... 还是去搜索了下 ...
- ubuntu16.04安装kinetic调用gazebo_control解决方案
解决方案 sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-gazebo-ros-control
- angularjs 在 iframe 里面无法正确显示 src 指定的内容
原 controller : $scope.myURL = URL; 页面: <iframe ng-src='{{myURL}}' class="width-100 height-10 ...
- express 写一个简单的web app
之前写过一个简单的web app, 能够完成注册登录,展示列表,CURD 但是版本好像旧了,今天想写一个简单的API 供移动端调用 1.下载最新的node https://nodejs.org/zh- ...
- MySQL服务器线程数的查看方法详解
本文实例讲述了MySQL服务器线程数的查看方法.分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: mysql重启命令: ? 1 /etc/init.d/mysql restart MySQL服务器的线程数需要在一个合 ...
- js实现数字千分位
/** * * @param num * @param precision * @param separator * @returns {*} *=========================== ...
