Lindström–Gessel–Viennot lemma定理 行列式板子
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37025443/article/details/86537261 博客
下面是wiki上的讲解,建议耐心地看一遍...虽然看了可能还是不懂
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lindström–Gessel–Viennot_lemma
Lindström–Gessel–Viennot lemma定理是
起点集合A=(a1,a2,a3..an),终点集合B=(b1.b2,b3,..bn)
假定P是从一条从一个点到另一个点的路径,定义w(P)=路径上经过的边的权值积
定义一个n元组P‘=(P1,P2,P3...PN)
Pi: -> 的路径
是{1,2,3,...n}的一种排列(类似于置换群的概念)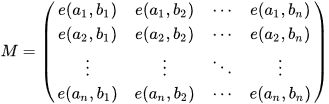
M行列式所求的值代表...(那句话我也不知道怎么翻译直接看原文吧)
下面这句话就是讲我们真正的用处——当所有边的权值都为1,并且 只有一种排列组合是可以的(即ai->bi)
那么M计算出来的值就是ai->bi不相交路径的方案数。此时e(a,b)就是a->b的合法路径的方案数
看了上面你可能还是不懂,其实在实际题目中用一下,你就可以知道他的套路了
Intersection is not allowed!
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 602 Accepted Submission(s): 195
Problem Description
There are K pieces on the chessboard.
The size of the chessboard is N*N.
The pieces are initially placed on the top cells of the board.
A piece located on (r, c) can be moved by one cell right to (r, c + 1) or one cell down to (r+1, c).
Your task is to count how many different ways to move all pieces to the given positions at the bottom of the board.
Furthermore, the paths of the pieces mustn’t intersect each other.
Input
The first line of input contains an integer T-the number of test cases.
Each test case begins with a line containing two integers-N(1<=N<=100000) and K(1<=K<=100) representing the size of the chessboard and the number of pieces respectively.
The second line contains K integers: 1<=a1<a2< …<aK<=N representing the initial positions of the pieces. That is, the pieces are located at (1, a1), (1, a2), …, (1, aK).
Next line contains K integers: 1<=b1<b2<…<bK<=N representing the final positions of the pieces. This means the pieces should be moved to (N, b1), (N, b2), …, (N, bK).
Output
Print consecutive T lines, each of which represents the number of different ways modulo 1000000007.
Sample Input
1
5 2
1 2
3 4
Sample Output
50
题意:
给你一个n*n的矩阵,再第一行一次有k个起点1<=a1<a2<a3<...<ak<=n
最后一行有n个终点1<=b1<b2<b3<...<bk<=n
你只能向右或向下走,问你有多少种路线方案,使得ai->bi i=1...n
答案mod 1e9+7
解析:
e(a,b)是合法路径的方案数,那么我们就先将这个行列式填好
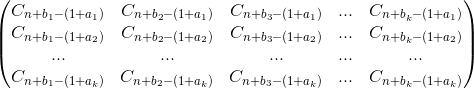
然后我们只需要用高斯消元法求出这个行列式的值就可以得出答案了。
也就是把通过行列式行变换把行列式转换成上(下)三角矩阵,然后将对角线上的元素乘起来就是答案了
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int ll; const int MAXN = 2e5+;
ll jc[MAXN];
ll inv[MAXN]; const ll MOD = 1e9+;
const int N = 1e2+;
ll a[N][N]; ll pow(ll a, ll n, ll p) //快速幂 a^n % p
{
ll ans = ;
while(n){
if(n & ) ans = ans * a % p;
a = a * a % p;
n >>= ;
}
return ans;
} ll niYuan(ll a, ll b) //费马小定理求逆元
{
return pow(a, b - , MOD);
} inline ll C(int a, int b) //计算C(a, b),a下,b上
{
if(b>a) return ;
return jc[a] * inv[b] % MOD
* inv[a-b]%MOD;
} void init()
{
ll p=;
jc[]=;
jc[]=;
inv[]=;
inv[]=;
for(int i=;i<MAXN;i++){
p=(p*i)%MOD;
jc[i]=p;
//inv[i]=inv[MOD%i]*(MOD-MOD/i)%MOD;
} for(int i=;i<MAXN;i++) inv[i]=inv[MOD%i]*(MOD-MOD/i)%MOD; //O(n)求逆元
for(int i=;i<MAXN;i++) inv[i]=inv[i-]*inv[i]%MOD; //扩展到i!的逆元
} ll determinant(int n)
{
//a为方阵
//MOD根据实际情况而定
ll ans=;
for(int k=;k<=n;k++) //将a[k+1..n][k]都变成0
{
ll pos=-;
for(int i=k;i<=n;i++) //找到a[k..n][k]中第一个非0元素
if(a[i][k])
{
pos=i;
break;
}
if(pos==-)return ; //没有的话行列式值为0
if(pos!=k) //将找到的那一行换到第k行,swap(a[k],a[pos])
for(int j=k;j<=n;j++)swap(a[pos][j],a[k][j]);
ll inv=niYuan(a[k][k],MOD);
for(int i=k+;i<=n;i++)
if(a[i][k])
{
ans=ans*inv%MOD; //下面的计算中第i行提高a[k][k]倍,所以答案需要除以a[k][k]才是正解
for(int j=k+;j<=n;j++)
a[i][j]=((a[i][j]*a[k][k]%MOD-a[k][j]*a[i][k]%MOD)%MOD+MOD)%MOD;
a[i][k]=;
}
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
ans=ans*a[i][i]%MOD;
return ans;
} int A[N],B[N]; int main()
{
int t;
init();
scanf("%d",&t);
while (t--)
{
int n,k;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
for(int i=;i<=k;i++) scanf("%d",&A[i]);
for(int i=;i<=k;i++) scanf("%d",&B[i]); for(int i=;i<=k;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<=k;j++)
{
a[i][j]=C(n+B[j]-(+A[i]),n-);
}
}
printf("%lld\n",determinant(k));
}
}
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36368339/article/details/81133921
题意:给你一个矩阵(#表示不可走),两只乌龟从左上角出发到达右下角,中间不能相遇,存在多少种不同的方案,也就是两条不相交的路径的方案数.
分析:
LGV:(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lindstr%C3%B6m%E2%80%93Gessel%E2%80%93Viennot_lemma)
ps:我自己也不是很懂原理,但是知道怎么用,就说一下吧.
给定n个起点,n个终点(一个终点对应一个起点),LGV主要解决n∗nn∗n条路径不相交的方案数.
LGV是一个n阶的行列式,行代表起点,列代表终点,(i, j)表示第i个起点到第j个终点的方案数,最后行列式的值就是n条不相交路径的方案数.
有了LGV,这个题最大的麻烦解决了。两只乌龟同起点同终点,要分离出来,也就等价一只乌龟从(1, 2)出发,到(n - 1, m),另一只从(2, 1)到(n, m - 1),因为路径不相交,不懂得可以仔细想想。
有了起点,有了终点,每个起点对应每个终点的方案数,用DP转移一下行了,然后就套LGV问题解决.
相当于两个起点,两个终点的题,且起点的横坐标都是1,终点的横坐标都是n。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring>
typedef unsigned long long LL; const int MAXN = 3e3 + ;
const int mod = 1e9 + ;
LL dp[MAXN][MAXN];
char ma[MAXN][MAXN]; int main() {
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i) {
getchar();
for(int j = ; j <= m; ++j) {
ma[i][j] = getchar();
}
}
if(ma[][] == '#' || ma[][] == '#') {
puts("");
return ;
}
if(ma[][] != '#') dp[][]++;
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i) {
for(int j = ; j <= m; ++j) {
if(ma[i][j] != '#') dp[i][j] = (dp[i][j] + dp[i - ][j] + dp[i][j - ]) % mod;
}
}
LL ans1 = dp[n - ][m] % mod, ans2 = dp[n][m - ] % mod;
memset(dp, , sizeof(dp));
if(ma[][] != '#') dp[][]++;
for(int i = ; i <= n; ++i) {
for(int j = ; j <= m; ++j) {
if(ma[i][j] != '#') dp[i][j] = (dp[i][j] + dp[i - ][j] + dp[i][j - ]) % mod;
}
}
LL ans3 = dp[n - ][m] % mod, ans4 = dp[n][m - ] % mod;
printf("%lld\n", ((ans4 * ans1) % mod - (ans2 * ans3) % mod + mod) % mod);
return ;
}
https://blog.csdn.net/ftx456789/article/details/81132126
牛客上的一个题。
Lindström–Gessel–Viennot lemma定理 行列式板子的更多相关文章
- Nowcoder Monotonic Matrix ( Lindström–Gessel–Viennot lemma 定理 )
题目链接 题意 : 在一个 n * m 的矩阵中放置 {0, 1, 2} 这三个数字.要求 每个元素 A(i, j) <= A(i+1, j) && A(i, j) <= ...
- 排列组合( Lindström–Gessel–Viennot lemma 定理)
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/139/A来源:牛客网 Monotonic Matrix 时间限制:C/C++ 1秒,其他语言2秒空间限制:C/C++ ...
- 牛客网多校训练第一场 A - Monotonic Matrix(Lindström–Gessel–Viennot lemma)
链接: https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/139/A 题意: 求满足以下条件的n*m矩阵A的数量模(1e9+7):A(i,j) ∈ {0,1,2}, 1≤i≤n ...
- LGV 算法 (Lindström–Gessel–Viennot lemma)
e(ai,bi)为从起点ai到终点bi的方案数.以上矩阵行列式结果就是(a1,a2,...an) 到 (b1,b2,...bn) 的所有不相交路径的种数. 具体证明的话看wiki,比较长.. 这个定理 ...
- Lindström–Gessel–Viennot lemma 应用两则
对于一张无边权的DAG图,给定n个起点和对应的n个终点,这n条不相交路径的方案数为 det() (该矩阵的行列式) 其中e(a,b)为图上a到b的方案数 codeforces 348D [给定一张n* ...
- Codeforces 348 D - Turtles Lindström–Gessel–Viennot lemma
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define y1 y11 #define fi first #define se second ...
- Lindström–Gessel–Viennot lemma
解决不相交路径计数 有两个大小为N的点集A,B A上每一个点对应着B的每一个点 求满足条件的路径集合有多少个 图里面可能还有一些障碍 Codeforces 348 D 有一个N*M的网格图 有两个点 ...
- [自用]数论和组合计数类数学相关(定理&证明&板子)
0 写在前面 本文受 NaVi_Awson 的启发,甚至一些地方直接引用,在此说明. 1 数论 1.0 gcd 1.0.0 gcd $gcd(a,b) = gcd(b,a\;mod\;b)$ 证明:设 ...
- [自用]多项式类数学相关(定理&证明&板子)
写在前面 由于上一篇总结的版面限制,特开此文来记录 \(OI\) 中多项式类数学相关的问题. 该文启发于Miskcoo的博客,甚至一些地方直接引用,在此特别说明:若文章中出现错误,烦请告知. 感谢你的 ...
随机推荐
- unity一些操作汇总
设置父物体高度自适应子物体:父物体添加ContentSizeFitter,设置Horizeontal Fit和Vertical Fit为Preferred Size. ScrollView设置Cone ...
- [Python]find_all函数 2020.2.7
.find_all(name,attrs,recursive,string,**kwargs) name:对标签名称的检索字符串attrs:对标签属性值的检索字符串,可标注属性检索recursive: ...
- Codeforce 25A - IQ test (唯一奇偶)
Bob is preparing to pass IQ test. The most frequent task in this test is to find out which one of th ...
- AI: Uninformed search
What is a search problem: A solution to a search problem is a sequence of actions (a path) from s0 t ...
- gflag的简单入门demo
gflags 一. 下载与安装 这里直接使用包管理器安装: sudo apt install libgflags-dev 二. gflags的简单使用 1. 定义需要的类型 格式: DEFINE_类型 ...
- promise的连缀写法
promise的连缀写法 以上写法相当于写了两个实例 promise.all() 1. promise.all() all这个方法是 promise 构造函数的成员不是实例对象成员,这个方法接受一个参 ...
- Introduction to SQL
目录 SELECTING SELECTing single columns SELECTing multiple columns select all SELECT DISTINCT Learning ...
- 浅析State-Thread
State-Thread(以下简称st),是一个由C语言编写的小巧.简洁却高效的开源协程库.这个库基于单线程运作.不强制占用用户线程,给予了开发者最大程度的轻量级和较低的侵入性.本篇文章中,网易云信音 ...
- .htaccess详解
http://www.cnblogs.com/adforce/archive/2012/11/23/2784664.html .htaccess是什么 .htaccess文件(或者"分布式配 ...
- xrdp---远程桌面连接
xrdp is an Open Source Remote desktop Protocol server, which allows you to RDP to your Linux server ...
