springboot web开发【转】【补】
pom.xml引入webjars的官网
https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html
静态资源映射规则
静态资源就是不经过servlet 或者说不通过controller绕业务代码 中的文件。
静态资源自动配置类 WebMvcAuotConfiguration.java
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
Integer cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCachePeriod();
//jar包中静态资源文件夹映射
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(
registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**")
.addResourceLocations(
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/")
.setCachePeriod(cachePeriod));
}
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
//静态资源文件夹映射
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(
registry.addResourceHandler(staticPathPattern)
.addResourceLocations(
this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations())
.setCachePeriod(cachePeriod));
}
}
静态资源目录
在springboot默认的静态资源目录有
- "classpath:/META-INF/resources/", (推荐)
- "classpath:/resources/", (不推荐使用)
- "classpath:/static/", (推荐)
- "classpath:/public/"
- "/":当前项目的根路径
所以当访问以上5个目录中的文件时,都会直接获取,比如访问 http://localhost:8080/springbootdemo/abc.html , 另外静态资源目录下的index.html和favicon.ico也是默认静态文件可直接访问。
webjars静态资源目录
除了以上5个目录, 还有一个特殊的目录 "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/" , 用于访问jar包的方式引入静态资源 。
比如我们想访问jquery-3.3.1.jar中的jquery.js那么使用以下两个路径都可以直接访问到,
http://localhost:8080/springbootdemo/webjars/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.js
http://localhost:8080/springbootdemo/webjars/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.min.js
至于为什么不是.../jquery.js/jquery.min.js的形式访问目前暂不研究。
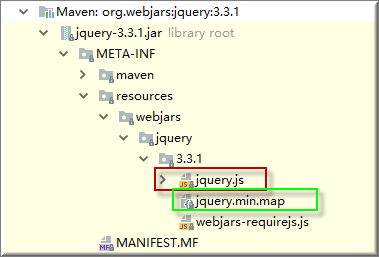
引静态jar
<dependency>
<!-- 前端jquery包 -->
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>3.3.1</version>
</dependency> <dependency>
<!-- 前端bootstrap包 -->
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>bootstrap</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
静态资源属性配置类 ResourceProperties.java
可以设置静态资源目录, 静态资源缓存时间等等
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.resources", ignoreUnknownFields = false)
public class ResourceProperties implements ResourceLoaderAware {
//可以设置和静态资源有关的参数,缓存时间等
在application.properties中对应配置如下, 我自己项目暂未启用,位于application-static-cache.properties中
#配置静态资源映射
spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/static/** #也可以自己指定静态资源, 这会使默认的静态资源失效
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/mystatic,classpath:/yourstatic # 资源缓存时间,单位秒,30天
spring.resources.cache-period=2592000 # 开启gzip压缩
spring.resources.chain.gzipped=true # 启用缓存
spring.resources.chain.cache=true # Enable the Spring Resource Handling chain. Disabled by default unless at least one strategy has been enabled.
spring.resources.chain.enabled=true # 开启版本控制策略,默认为false
spring.resources.chain.strategy.content.enabled=true # 指定要应用的版本的路径,多个以逗号分隔,默认为:[/**]
spring.resources.chain.strategy.content.paths=/** # 设定Session的追踪模式(cookie, url, ssl)
server.session.tracking-modes=cookie
thymeleaf模板
https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html
1、引入thymeleaf依赖
<!-- 切换thymeleaf版本 -->
<properties>
<thymeleaf.version>3.0.9.RELEASE</thymeleaf.version>
<!-- 布局功能的支持程序 thymeleaf3适配layout2以上版本 , thymeleaf2 适配 layout1版本 -->
<thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>2.2.2</thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>
</properties> <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、Thymeleaf使用
配置属性类
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.thymeleaf")
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
private static final MimeType DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE = MimeType.valueOf("text/html");
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
...
日期格式化配置
日期格式化配置的地方有很
请求时--仅当前Controller接收指定格式的日期字符串
@RequestMapping("/MyMybatisController")
@Controller
public class MyMybatisController {
/**
* web数据绑定器,在获取到数据前,做一些预处理,仅对当前Controller有效。
*
* @param binder
* @throws Exception
*/
@InitBinder
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder binder) throws Exception {
//允许Long类型为空
binder.registerCustomEditor(Long.class, new CustomNumberEditor(Long.class, true));
//设置接收的日期,把默认的yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss格式改成yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
binder.registerCustomEditor(java.util.Date.class, new CustomDateEditor(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"), true));
}
}
请求时--application.properties统一配置接收指定日期格式字符串
对所有Controller都有效
spring.mvc.date-format=yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
返回时--所有@ResponseBody返回时格式化Date类型成字符串
@Configuration//指明当前类是一个配置类;就是来替代之前的Spring配置文件
public class MyConfiguration {
/**
* 对@ResponseBody返回的Object类中的各对象对特殊处理
* @return
*/
@Bean
public ObjectMapper getObjectMapper() {
//返回时把日期从默认的long类似必成yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss返回
return new ObjectMapper().setDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss"));
}
}
返回时--thymeleaf中格式化Date类型成字符串
<td th:text="${#dates.format(emp.birth,'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss') }"></td>
1. Spring MVC auto-configuration (了解不够)
Spring Boot 自动配置好了SpringMVC
以下是SpringBoot对SpringMVC的默认配置:(WebMvcAutoConfiguration)
Inclusion of
ContentNegotiatingViewResolverandBeanNameViewResolverbeans.自动配置了ViewResolver(视图解析器:根据方法的返回值得到视图对象(View),视图对象决定如何渲染(转发?重定向?))
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver:组合所有的视图解析器的;
如何定制:我们可以自己给容器中添加一个视图解析器;自动的将其组合进来;
Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars (see below).静态资源文件夹路径,webjars
Static
index.htmlsupport. 静态首页访问Custom
Faviconsupport (see below). favicon.ico自动注册了 of
Converter,GenericConverter,Formatterbeans.Converter:转换器; public String hello(User user):类型转换使用Converter
Formatter格式化器; 2017.12.17===Date;
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc", name = "date-format")//在文件中配置日期格式化的规则
public Formatter<Date> dateFormatter() {
return new DateFormatter(this.mvcProperties.getDateFormat());//日期格式化组件
}
自己添加的格式化器转换器,我们只需要放在容器中即可
Support for
HttpMessageConverters(see below).HttpMessageConverter:SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应的;User---Json;
HttpMessageConverters是从容器中确定;获取所有的HttpMessageConverter;自己给容器中添加HttpMessageConverter,只需要将自己的组件注册容器中(@Bean,@Component)
Automatic registration of
MessageCodesResolver(see below).定义错误代码生成规则Automatic use of a
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializerbean (see below).我们可以配置一个ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer来替换默认的;(添加到容器)
初始化WebDataBinder;
请求数据=====JavaBean;
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web:web的所有自动场景;
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features, and you just want to add additional MVC configuration (interceptors, formatters, view controllers etc.) you can add your own @Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurerAdapter, but without @EnableWebMvc. If you wish to provide custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance providing such components.
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
扩展SpringMVC(了解不够)
比如我们需要扩展SpringMVC中的视图跳转功能
<mvc:view-controller path="/hello" view-name="success"/>
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/hello"/>
<bean></bean>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
在SpringBoot中只需编写一个配置类(@Configuration)继承 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter类型;不能标注@EnableWebMvc; 既保留了所有的自动配置,也能用我们扩展的配置;
//使用WebMvcConfigurerAdapter可以来扩展SpringMVC的功能
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { @Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// super.addViewControllers(registry);
//浏览器发送 /atguigu 请求来到 success
registry.addViewController("/atguigu").setViewName("success");
}
}
原理:
1)、WebMvcAutoConfiguration是SpringMVC的自动配置类
2)、在做其他自动配置时会导入;@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
@Configuration
public static class EnableWebMvcConfiguration extends DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration {
private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite(); //从容器中获取所有的WebMvcConfigurer
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
//一个参考实现;将所有的WebMvcConfigurer相关配置都来一起调用;
@Override
// public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// for (WebMvcConfigurer delegate : this.delegates) {
// delegate.addViewControllers(registry);
// }
}
}
}
3)、容器中所有的WebMvcConfigurer都会一起起作用;
4)、我们的配置类也会被调用;
效果:SpringMVC的自动配置和我们的扩展配置都会起作用;
3、全面接管SpringMVC
SpringBoot对SpringMVC的自动配置不需要了,所有都是我们自己配置;所有的SpringMVC的自动配置都失效了
我们需要在配置类中添加@EnableWebMvc即可;
//使用WebMvcConfigurerAdapter可以来扩展SpringMVC的功能
@EnableWebMvc
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { @Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
// super.addViewControllers(registry);
//浏览器发送 /atguigu 请求来到 success
registry.addViewController("/atguigu").setViewName("success");
}
}
这会让SpringBoot的WebMvcAutoConfiguration.java中各种自动配置Bean无效,在控制台也也就再打印如HiddenHttpMethodFilter等信息 , 且静态资源目录也失效,极不推荐做全面 接管。
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = "";
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(HiddenHttpMethodFilter.class)
public OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter() {
return new OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter();
}
........
原理:
为什么@EnableWebMvc后SpringBoot的自动配置就失效了;
1)@EnableWebMvc
导入了DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration 类
@Import(DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableWebMvc {
2)、DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration
继承了WebMvcConfigurationSupport
@Configuration
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
3)、WebMvcAutoConfiguration
@ConditionalOnMissingBean 容器中没有这个组件才会生效, 而上面就是导入了这个组件,所以 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 无效了.
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
@ConditionalOnClass({Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurerAdapter.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)//容器中没有这个组件的时候,这个自动配置类才生效
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, ValidationAutoConfiguration.class})
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
4)、@EnableWebMvc将WebMvcConfigurationSupport组件导入进来;
5)、导入的WebMvcConfigurationSupport只是SpringMVC最基本的功能;
5、如何修改SpringBoot的默认配置
模式:
1)、SpringBoot在自动配置很多组件的时候,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(@Bean、@Component)如果有就用用户配置的,如果没有,才自动配置;如果有些组件可以有多个(ViewResolver)将用户配置的和自己默认的组合起来;
2)、在SpringBoot中会有非常多的xxxConfigurer帮助我们进行扩展配置
3)、在SpringBoot中会有很多的xxxCustomizer帮助我们进行定制配置
国际化
1)、指定国际化配置文件位置
在application.properties中配置如下, 如果不配置,则默认文件为classpath:messages.properties / messages_zh_CN.properties
spring.messages.basename=i18n.international
2)、编写国际化配置文件,抽取页面需要显示的国际化消息
\src\main\resources\i18n\international.properties
# default location is "classpath:message.properties", changed in application.properties , add "spring.messages.basename=i18n.international" to specified internationalResource here
login.btn=登陆~
login.password=密码~
login.rememberMe=记住我~
login.tip=请登陆~
login.username=用户名~
\src\main\resources\i18n\international_en_US.properties
login.btn=Sign In
login.password=Password
login.rememberMe=Remember Me
login.tip=Please sign in
login.username=UserName
\src\main\resources\i18n\international_zh_CN.properties
login.btn=登录
login.password=密码
login.rememberMe=记住我
login.tip=请登录
login.username=用户名
springboot资源国际化自动化配置组件
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.messages")
public class MessageSourceAutoConfiguration { /**
* Comma-separated list of basenames (essentially a fully-qualified classpath
* location), each following the ResourceBundle convention with relaxed support for
* slash based locations. If it doesn't contain a package qualifier (such as
* "org.mypackage"), it will be resolved from the classpath root.
*/
private String basename = "messages";
//我们的配置文件可以直接放在类路径下叫messages.properties; @Bean
public MessageSource messageSource() {
ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.basename)) {
//设置国际化资源文件的基础名(去掉语言国家代码的)
messageSource.setBasenames(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(
StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(this.basename)));
}
if (this.encoding != null) {
messageSource.setDefaultEncoding(this.encoding.name());
}
messageSource.setFallbackToSystemLocale(this.fallbackToSystemLocale);
messageSource.setCacheSeconds(this.cacheSeconds);
messageSource.setAlwaysUseMessageFormat(this.alwaysUseMessageFormat);
return messageSource;
}
3)、idea配置properties防乱码
idea的properties中内容在页面中展示乱码解决方法==>https://www.cnblogs.com/whatlonelytear/articles/9430768.html
4)、html中引用
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<body>
<h1 th:text="#{login.tip}">Please sign in</h1>
<input type="checkbox" value="remember-me"/> [[#{login.rememberMe}]]
</body>
</html>
通过手动点击切换国际化资源
springboot自动化配置国际化的解析器为localeResolver()方法
国际化Locale(区域信息对象);LocaleResolver(获取区域信息对象);
WebMvcAutoConfiguration.java 的自动化配置bean
当ConditionalOnMissingBean即LocaleResolver不存在时,本自动化配置Bean才有效, 所以我们可以自定义一个MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver来替换当前自动化配置
//在WebMvcAutoConfiguration.java中配有bean如下, 当ConditionalOnMissingBean即LocaleResolver不存在时,本自动化配置Bean才有效,
//所以我们可以自定义一个MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver来替换当前自动化配置
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc", name = "locale")
public LocaleResolver localeResolver() {
if (this.mvcProperties.getLocaleResolver() == WebMvcProperties.LocaleResolver.FIXED) {
return new FixedLocaleResolver(this.mvcProperties.getLocale());
}
//默认的就是根据请求头带来的区域信息获取Locale进行国际化
AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver localeResolver = new AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver();
localeResolver.setDefaultLocale(this.mvcProperties.getLocale());
return localeResolver;
}
自定义MyLocaleResolver.java
/**
* 可以在连接上携带区域信息
*/
public class MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver { /**
* 如果带了lang=zh_CN或lang=en_US形式的参数,则设置成lang的本地化,不然设置默认的
* @param request
* @return
*/
@Override
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
String l = request.getParameter("lang");
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();
if (l != null && !"".equals(l)) {
String[] split = l.split("_");
locale = new Locale(split[0], split[1]);
}
return locale;
} @Override
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) { }
}
在任意一个@Configuration添加MyLocalResolver.java
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
}
SpringBoot默认的错误处理机制
默认效果
浏览器返回Error Page页面 , 是因为请求时Header头Accept指定了明确的接收类型text/html ,SpringBoot后台做了特殊处理
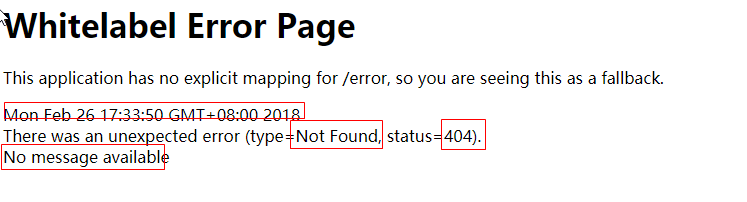

postman返回的是json报文,是因为请求时Header头Accept没有指定明确的接收类型 ,SpringBoot后台做了特殊处理

基本流程
一但系统出现4xx或者5xx之类的错误;ErrorPageCustomizer就会生效(定制错误的响应规则);就会来到 /error 请求;就会被BasicErrorController处理;
参照ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration配置类;它给容器中添加了以下错误处理的相关组件。
1、ErrorPageCustomizer.java (注册错误页)
该bean用于注册错误页面, 配置系统出现错误后跳转到哪
private static class ErrorPageCustomizer implements ErrorPageRegistrar, Ordered {
.....
@Override
public void registerErrorPages(ErrorPageRegistry errorPageRegistry) {
ErrorPage errorPage = new ErrorPage(this.properties.getServletPrefix()
+ this.properties.getError().getPath());
errorPageRegistry.addErrorPages(errorPage);
}
.....
}
其中getPath()内部其实使用了 "/error" , ${error.path:/error}的意思是如果没有error.path配置属性, 则取"/error"值
@Value("${error.path:/error}")
private String path = "/error"; 系统出现错误以后来到/error请求进行处理;(web.xml注册的错误页面规则)
2、BasicErrorController (处理"/error"错误请求)
@Controller
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
... @Override
public String getErrorPath() {
return this.errorProperties.getPath();
} @RequestMapping(produces = "text/html")//产生html类型的数据;浏览器发送的请求来到这个方法处理
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
//获取错误信息 , 而错误信息都在共享区的 DefaultErrorAttributes中
Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(
request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
//去哪个页面作为错误页面;包含页面地址和页面内容
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return (modelAndView != null ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model));
} @RequestMapping
@ResponseBody//产生json数据,其他客户端来到这个方法处理;postman,java代码调用等场景
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request,
isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL));
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
return new ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>>(body, status);
}
... }
resolveErrorView(...)方法内容
遍历所有ErrorViewResolver ,而接下来的DefaultErrorViewResolver这个在Configuration中注册的Bean就继承自ErrorViewResolver (在该类上Ctrl + T , 直接跳转到唯一实现类DefaultErrorViewResolver.java)
protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {
//遍历所有ErrorViewResolver ,而接下来的DefaultErrorViewResolver这个在Configuration中注册的Bean就继承自ErrorViewResolver
for (ErrorViewResolver resolver : this.errorViewResolvers) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model);
if (modelAndView != null) {
return modelAndView;
}
}
return null;
}
4、DefaultErrorViewResolver(默认的错误视图处理解析器)
根据resolve(...)方法可知thymeleaf模板引擎可用时, 去resources/templates/error/4xx.html或404.html中找, 如果模板引擎不可用, 则去静态资源文件夹 resources/static/4xx.html或400.html中找
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status,
Map<String, Object> model) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status), model);
if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
return modelAndView;
} private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
//默认SpringBoot可以去找到一个页面? error/404
String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName; //试着获取模板引擎
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders
.getProvider(errorViewName, this.applicationContext);
if (provider != null) {
//如果模板引擎可用,则返回到errorViewName指定的视图地址
return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model);
}
//模板引擎不可用,就在静态资源文件夹下找errorViewName对应的页面 error/404.html
return resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
}
4、DefaultErrorAttributes (页面错误共享信息对象)
DefaultErrorAttributes.java
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
public class DefaultErrorAttributes
implements ErrorAttributes, HandlerExceptionResolver, Ordered {
...
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(RequestAttributes requestAttributes,
boolean includeStackTrace) {
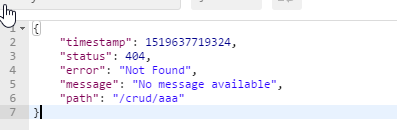
Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>();
errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date());
addStatus(errorAttributes, requestAttributes);
addErrorDetails(errorAttributes, requestAttributes, includeStackTrace);
addPath(errorAttributes, requestAttributes);
return errorAttributes;
}
...
}
如何定制错误响应
1)、如何定制错误的页面;
1. 有模板引擎的情况下;error/状态码; 【将错误页面命名为 错误状态码.html 放在模板引擎文件夹里面的 error文件夹下】,发生此状态码的错误就会来到 对应的页面;
我们可以使用4xx和5xx作为错误页面的文件名来匹配这种类型的所有错误,精确优先(优先寻找精确的状态码.html);
页面能获取的信息;
timestamp:时间戳
path: 请求路径
status:状态码
error:错误提示
exception:异常对象
message:异常消息
errors:JSR303数据校验的错误都在这里
2. 没有模板引擎(模板引擎找不到这个错误页面),静态资源文件夹下找;
3. 以上都没有错误页面,就是默认来到SpringBoot默认的错误提示页面
public class ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration {
...
@Configuration
...
protected static class WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration {
private final ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.SpelView defaultErrorView = new ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.SpelView("<html><body><h1>Whitelabel Error Page</h1><p>This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.</p><div id='created'>${timestamp}</div><div>There was an unexpected error (type=${error}, status=${status}).</div><div>${message}</div></body></html>");
...
}
4. 4xx.html / 5xx.html / 400.html / 500.html修改
所以在templates/error/4xx.html中可以自由改造默认的属性了
<p th:text="${error}"></p>
2)、如何定制错误的json数据;
1)、自定义异常处理器 MyExceptionAdvice.java , 但是这种模式没有自适应性, 会导致浏览器访问也统一返回json
@ControllerAdvice//自定义异常拦截处理器
public class MyExceptionHandler {
@ResponseBody//返回转成json
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)//自定义异常
public Map<String,Object> handleException(Exception e){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code","user.notexist");
map.put("message",e.getMessage());
return map;
}
}
2)、转发到/error进行自适应响应效果处理
自定义异常处理器 MyExceptionAdvice.java
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionAdvice {
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)
public String handleException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//传入我们自己的错误状态码 4xx 5xx,否则就不会进入定制错误页面的解析流程
/**
* Integer statusCode = (Integer) request
.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code");
*/
request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code",500);
map.put("code","user.notexist");
map.put("message",e.getMessage());
//转发到/error
return "forward:/error";
}
}
3)、将我们的定制数据携带出去;
自定义异常处理器 MyExceptionAdvice.java
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionAdvice {
/**
* 自定义异常处理&返回定制json数据 , 但是这种模式有自适应性, 浏览器返回网页, postman返回json
* 此种方式的跳转,不能将自定义参数携带出去
*/
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotFoundException.class)
public String satifiedHandleException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); //传入我们自己的错误状态码 4xx 5xx,否则就不会进入定制错误页面的解析流程,
// 因为在BasicErrorController的父类AbstractErrorController方法getStatus(HttpServletRequest request)中Integer statusCode = (Integer) request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code");默认获取的是200,
// 导致不会进入/error拦截界面.
//而此处设置400,500目的正是为了跳到对应的error/400.html, error/500.html中去
request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code",500); //但是此种方式的跳转,不能将自定义参数携带出去
map.put("extInfo1","info1");
map.put("extInfo2",e.getMessage());
request.setAttribute("extInfo",map);//在自定义的MyErrorAttribute.java中获取
//注意,转发到"/error"
return "forward:/error";
}
}
出现错误以后,会来到/error请求,会被BasicErrorController处理,响应出去可以获取的数据是由getErrorAttributes得到的(是AbstractErrorController(ErrorController)规定的方法);
方式1(不推荐)、完全来编写一个ErrorController的实现类【或者是编写AbstractErrorController的子类】,放在容器中;
方式2(推荐)、页面上能用的数据,或者是json返回能用的数据都是通过ErrorAttributes.getErrorAttributes()得到;所以我们可以自定义一个ErrorAttributes
//给容器中加入我们自己定义的ErrorAttributes
@Component
public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(RequestAttributes requestAttributes, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map<String, Object> map = super.getErrorAttributes(requestAttributes, includeStackTrace);
map.put("company","atguigu");
return map;
}
}
那这个自定义的bean是如何替换原来的呢,重点在于@ConditionalOnMissingBean(...)
public class ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration {
...
@Bean
//表示如果ErrorAttributes.class或其子类一开始全不存在, 才会创建本bean, 而当我们自定义的MyErrorAttributes正是继承自DefaultErrorAttributes(继承自ErrorAttributes)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = {ErrorAttributes.class},search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT )
public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {
return new DefaultErrorAttributes();
}
...
}
最终的效果:响应是自适应的,通过定制ErrorAttributes改变需要返回的内容如下图
{
"timestamp": "2019年05月10日 14:01:23",
"status": 500,
"error": "Internal Server Error",
"exception": "com.example.demo.bean.exception.UserNotFoundException",
"message": "abc",
"path": "/springbootdemo/ThymeleafController/thymeleaf",
"company": "KingCompany",
"extInfo": {
"extInfo1": "info1",
"extInfo2": "abc"
}
}
8、配置嵌入式Servlet容器
方式1、修改和server有关的配置(ServerProperties【也是EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer】);
server.port=8081
server.context-path=/crud server.tomcat.uri-encoding=UTF-8 #通用的Servlet容器设置
server.xxx
#Tomcat的设置
server.tomcat.xxx
方式2、编写一个EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer:嵌入式的Servlet容器的定制器;来修改Servlet容器的配置
@Bean //一定要将这个定制器加入到容器中
public EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer embeddedServletContainerCustomizer(){
return new EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer() { //定制嵌入式的Servlet容器相关的规则
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer container) {
container.setPort(8083);
}
};
}
Servlet三大组件配置【Servlet、Filter、Listener】
MyServlet.java--ServletRegistrationBean
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException; public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
String ret = "MyServlet visited";
System.err.println(ret);
resp.getWriter().write(ret);
} @Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.err.println("MyServlet visited");
doGet(req,resp);
}
}
MyFilter.java--FilterRegistrationBean
import javax.servlet.*;
import java.io.IOException; public class MyFilter implements Filter { @Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
System.err.println("MyFilter init");
} @Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.err.println("MyFilter visited");
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} @Override
public void destroy() {
System.err.println("MyFilter destroy");
}
}
MyListener.java--ServletListenerRegistrationBean
listener分很多种类型, 以ServletContextListener为例
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException; public class MyListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.err.println("ServletContextListener contextInitialized");
} @Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
System.err.println("ServletContextListener contextDestroyed");
}
}
最后把以上三大组合直接放在一个@Configuration中
import com.example.demo.bean.Student;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletListenerRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Arrays; @Configuration//指明当前类是一个配置类;就是来替代之前的Spring配置文件
public class MyServletFilterListenerConfiguration { // http://localhost:8080/springbootdemo/MyServlet2
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean myServlet(){
ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new MyServlet(),"/MyServlet2");
return registrationBean;
} @Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean myFilter(){
FilterRegistrationBean registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
registrationBean.setFilter(new MyFilter());
registrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/MyServlet2","/myServlet3"));
return registrationBean;
} @Bean
public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myListener(){
ServletListenerRegistrationBean<MyListener> registrationBean = new ServletListenerRegistrationBean<MyListener>(new MyListener());
return registrationBean;
} }
于是可以理解SpringBoot默认的Servlet配置
默认拦的就是所有请求
@AutoConfigureOrder(-2147483648)
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
@ConditionalOnClass({DispatcherServlet.class})
@AutoConfigureAfter({EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration.class})
public class DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration {
...
@Configuration
...
protected static class DispatcherServletRegistrationConfiguration {
...
@Bean(name = {"dispatcherServletRegistration"})
@ConditionalOnBean(value = {DispatcherServlet.class},name = {"dispatcherServlet"})
public ServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServletRegistration(DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet) {
//默认拦截: / 所有请求;包静态资源,但是不拦截jsp请求; /*会拦截jsp
//可以通过server.servletPath来修改SpringMVC前端控制器默认拦截的请求路径
ServletRegistrationBean registration = new ServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet, new String[]{this.serverProperties.getServletMapping()});
registration.setName("dispatcherServlet");
registration.setLoadOnStartup(this.webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup());
if (this.multipartConfig != null) {
registration.setMultipartConfig(this.multipartConfig);
}
return registration;
}
}
}
替换为其他嵌入式Servlet容器
Tomcat(默认使用)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
引入web模块默认就是使用嵌入式的Tomcat作为Servlet容器;
</dependency>
Jetty
<!-- 引入web模块 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--引入其他的Servlet容器-->
<dependency>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</dependency>
Undertow
<!-- 引入web模块 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!--引入其他的Servlet容器-->
<dependency>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-undertow</artifactId>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
</dependency>
嵌入式Servlet容器自动配置原理
步骤:
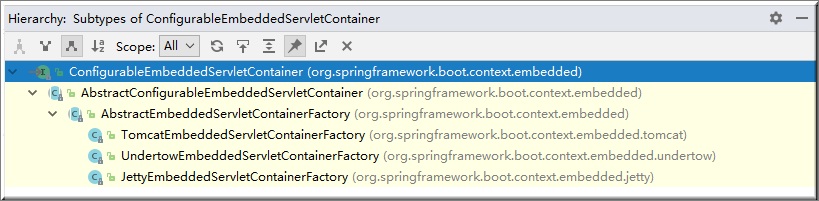
1)、SpringBoot根据EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration导入的依赖情况,给容器中添加相应的EmbeddedServletContainerFactory【TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory】
2)、容器中某个组件要创建对象就会触发后置处理器EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor;只要是嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂,后置处理器就工作;
3)、后置处理器,从容器中获取所有的EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer,调用定制器的定制方法customize(ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer container) 给容器配置属性
EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration.java 嵌入式的Servlet容器自动配置
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
//导入BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar,给容器中导入一些组件, 比较重要的有 EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor,它是一个后置处理器,用于在bean初始化前后(创建完对象,还没赋值赋值)执行初始化工作
@Import(BeanPostProcessorsRegistrar.class)
public class EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration { @Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Tomcat.class })//判断当前是否引入了Tomcat依赖;
//判断当前容器没有用户自己定义EmbeddedServletContainerFactory:嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂(作用:创建嵌入式的Servlet容器)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EmbeddedServletContainerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public static class EmbeddedTomcat {
@Bean
public TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory tomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory() {
return new TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory();
}
} /**
* Nested configuration if Jetty is being used.
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, Server.class, Loader.class,WebAppContext.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = EmbeddedServletContainerFactory.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public static class EmbeddedJetty {
@Bean
public JettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory jettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory() {
return new JettyEmbeddedServletContainerFactory();
}
}
...
EmbeddedServletContainerFactory(嵌入式Servlet容器工厂)和 EmbeddedServletContainer(嵌入式的Servlet容器)
public class TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory extends AbstractEmbeddedServletContainerFactory implements ResourceLoaderAware
public interface EmbeddedServletContainerFactory {
//获取嵌入式的Servlet容器
EmbeddedServletContainer getEmbeddedServletContainer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers);
}
TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory.java
该Factory通过ServerProperties(本身就是EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer子类)、EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer 定制化Servlet容器配置 , 而EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer 又是通过EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor后置处理器配置的
public class TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory extends AbstractEmbeddedServletContainerFactory implements ResourceLoaderAware {
...
@Override
public EmbeddedServletContainer getEmbeddedServletContainer(
ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
//创建一个Tomcat
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
//配置Tomcat的基本环节
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null ? this.baseDirectory
: createTempDir("tomcat"));
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
//将配置好的Tomcat传入进去,返回一个EmbeddedServletContainer;并且启动Tomcat服务器
return getTomcatEmbeddedServletContainer(tomcat);
}
...
}
EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor.java 后置处理器
public class EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizerBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware {
//初始化之前
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//如果当前初始化的是一个ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer类型的组件
if (bean instanceof ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer) {
postProcessBeforeInitialization((ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer) bean);
}
return bean;
}
private void postProcessBeforeInitialization(ConfigurableEmbeddedServletContainer bean) {
//获取所有的定制器,调用每一个定制器的customize方法来给Servlet容器进行属性赋值;
for (EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer customizer : getCustomizers()) {
customizer.customize(bean);
}
}
private Collection<EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer> getCustomizers() {
if (this.customizers == null) {
this.customizers = new ArrayList<EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer>(
//从容器中获取所有这个类型的组件:EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer
this.beanFactory.getBeansOfType(EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer.class,false, false).values());
Collections.sort(this.customizers, AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
this.customizers = Collections.unmodifiableList(this.customizers);
}
return this.customizers;
}
}
嵌入式Servlet容器启动原理
什么时候创建嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂?什么时候获取嵌入式的Servlet容器并启动Tomcat;
获取嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂:
1)、SpringBoot应用启动运行run(xxx.class, arg)方法
2)、refreshContext(context);SpringBoot刷新IOC容器【创建IOC容器对象,并初始化容器,创建容器中的每一个组件】;如果是web应用创建AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext,否则:AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
3)、refresh(context);刷新刚才创建好的ioc容器;
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
4)、onRefresh(); web的ioc容器重写了onRefresh方法
5)、web ioc容器会创建嵌入式的Servlet容器;createEmbeddedServletContainer();
6)、获取嵌入式的Servlet容器工厂:
EmbeddedServletContainerFactory containerFactory = getEmbeddedServletContainerFactory();
从ioc容器中获取EmbeddedServletContainerFactory 组件;TomcatEmbeddedServletContainerFactory创建对象,后置处理器一看是这个对象,就获取所有的定制器来先定制Servlet容器的相关配置;
7)、使用容器工厂获取嵌入式的Servlet容器:this.embeddedServletContainer = containerFactory.getEmbeddedServletContainer(getSelfInitializer());
8)、嵌入式的Servlet容器创建对象并启动Servlet容器;
先启动嵌入式的Servlet容器,再将ioc容器中剩下没有创建出的对象获取出来;
IOC容器启动创建嵌入式的Servlet容器
IOC容器是什么? Spring框架IOC容器和AOP解析==>https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxing/p/5836835.html
使用外置Servlet容器
步骤
1. 创建打war包项目 , 非打 jar包项目
如果使用idea创建SpringBoot的war项目,则一开始就会自动创建SpringBootServletInitializer.java , 这是使用外围容器初始化必要的类。
//类名随意,只要继承SpringBootServletInitializer即可
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(SpringBootOuterContainerApplication.class);
}
}
2. pom.xml中明确指定Tomcat的<scoper>为provided;
provided意为目标环境已经提供了, 打包时就不需要打进去了。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
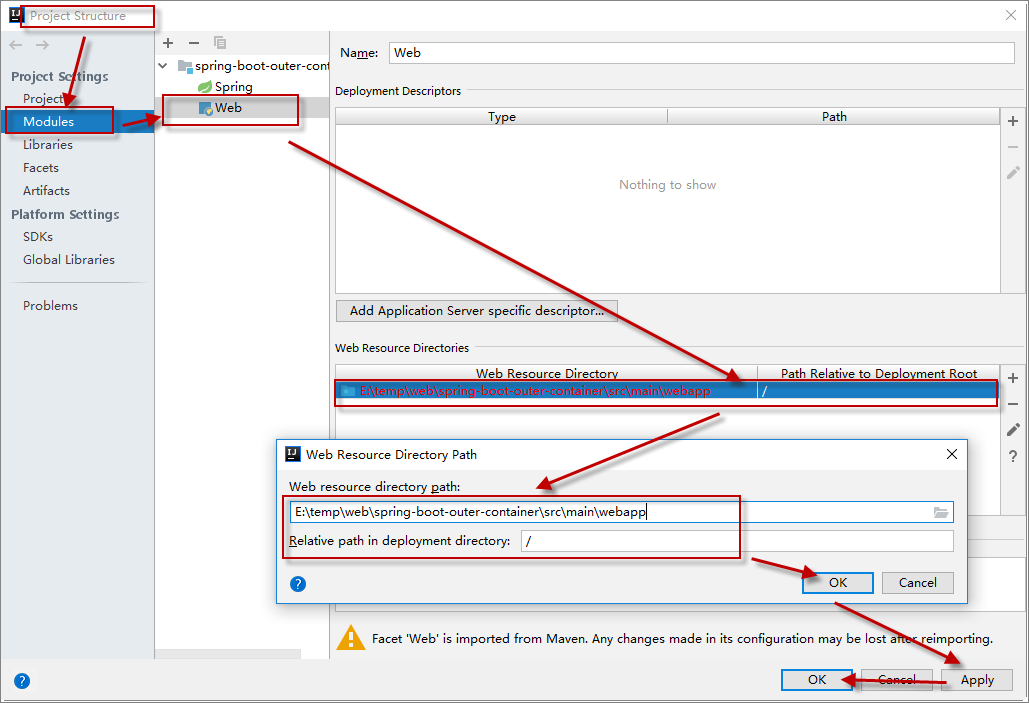
3. 配置webapp目录及web.xml
idea中默认不会有该目录, 需要在Project Structure的Modules的Web模块中手动配置上下文根目录和web.xml
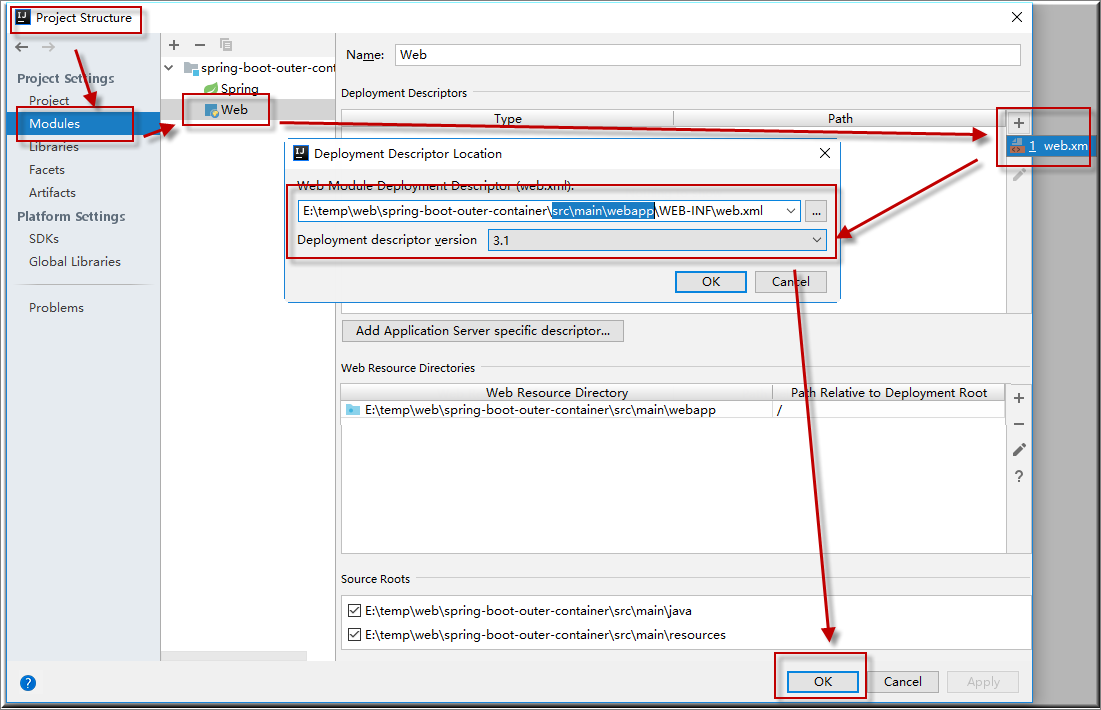
Project Structure | Modules | Web | 配置上下文路径(一开始该路径不存在)
Project Structure | Modules | Web | 配置web.xml (一开始该文件不存在, 注意添加时手动加上src\main\webapp路径)
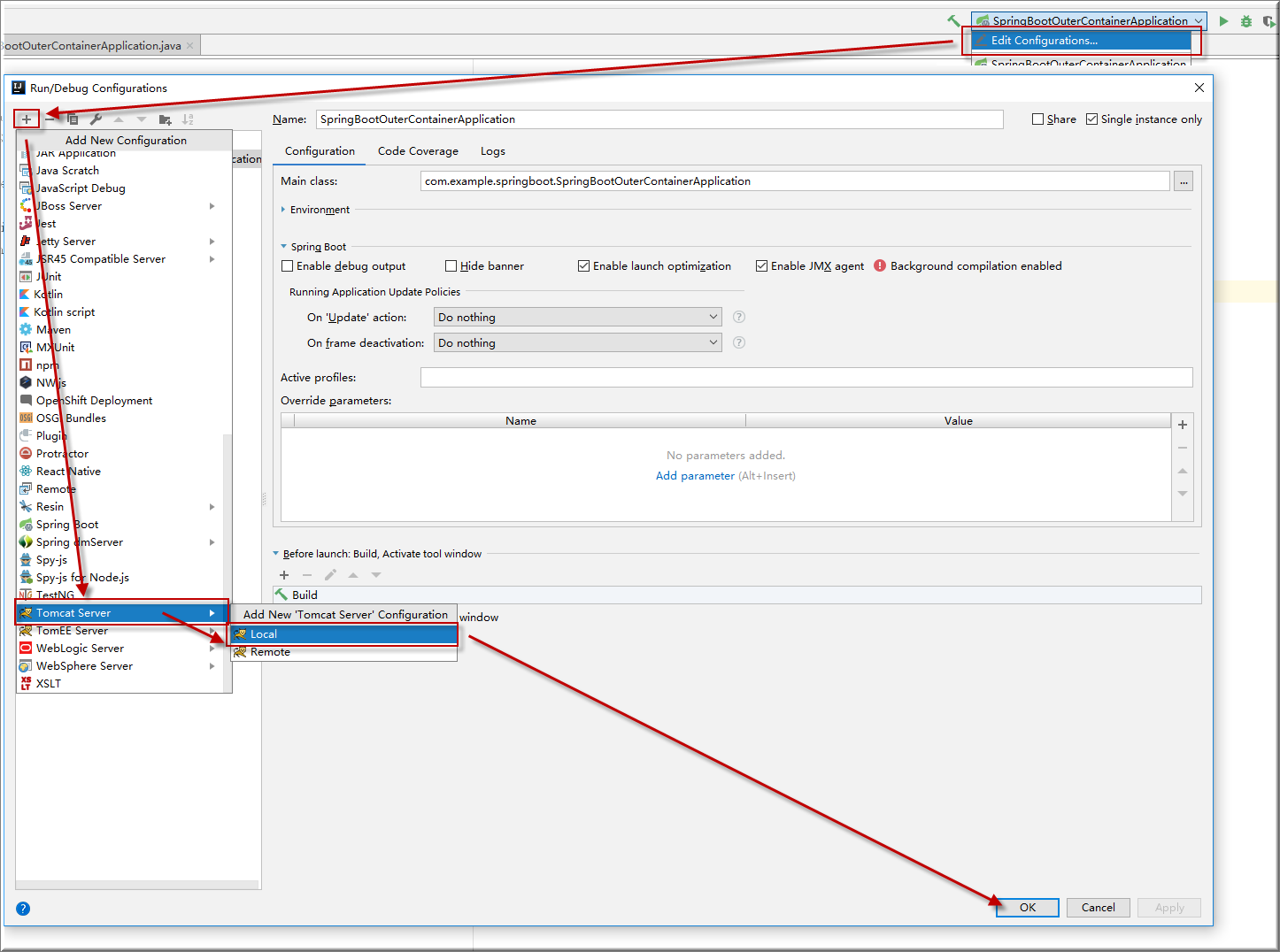
4. 添加外置tomcat
右上 Edit Configurations | 添加tomcat配置 | Tomcat Server | Local | OK
Run/Debug Configurations | Tomcat Server | 取tomcat服务名 mytomcat8 | Server选项卡 | Configure | 配置Tomcat8路径 | OK
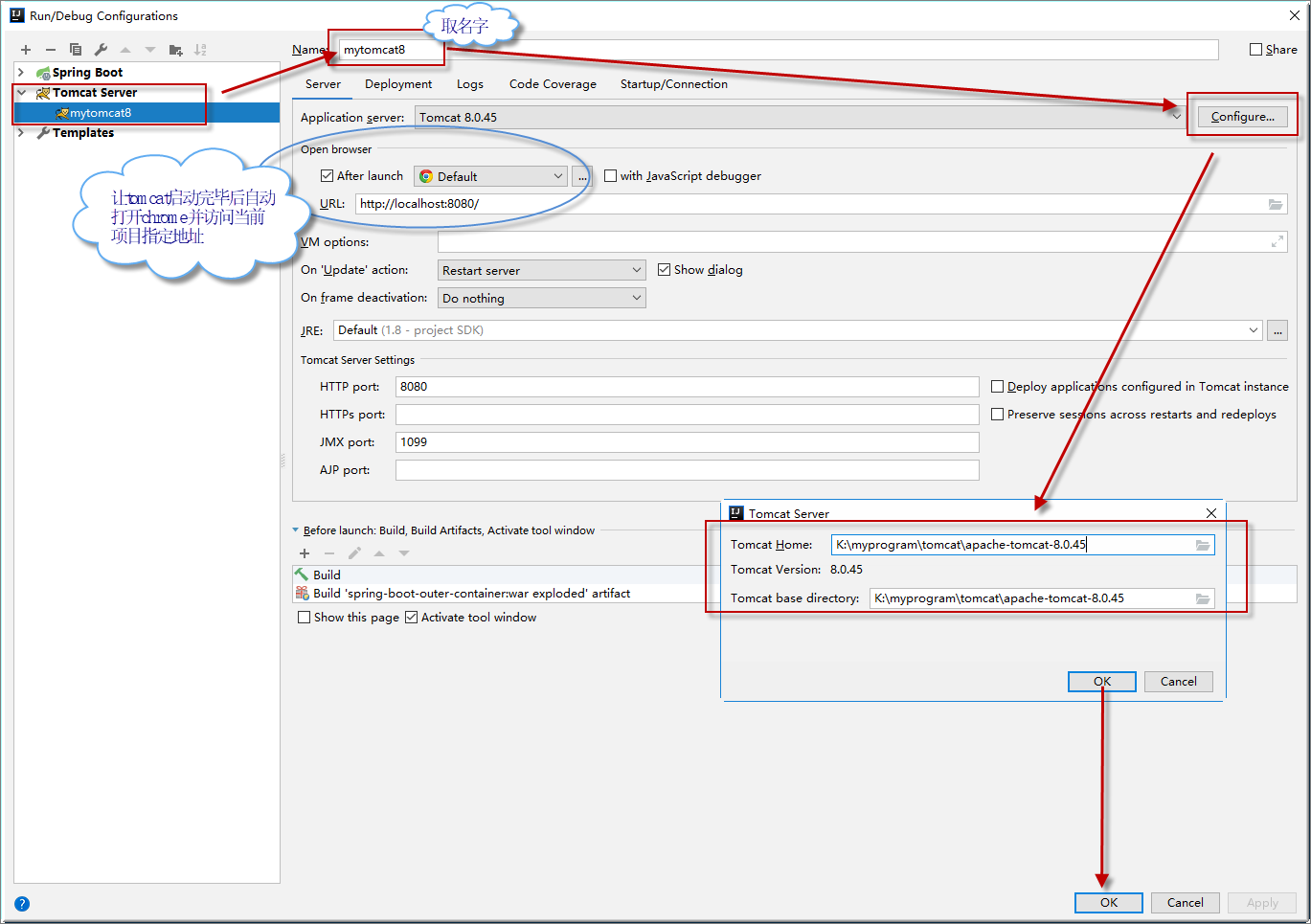
Run/Debug Configurations | Tomcat Server | 取tomcat服务名 mytomcat8 | Deployment选项卡 |添加需要布署的war包| OK

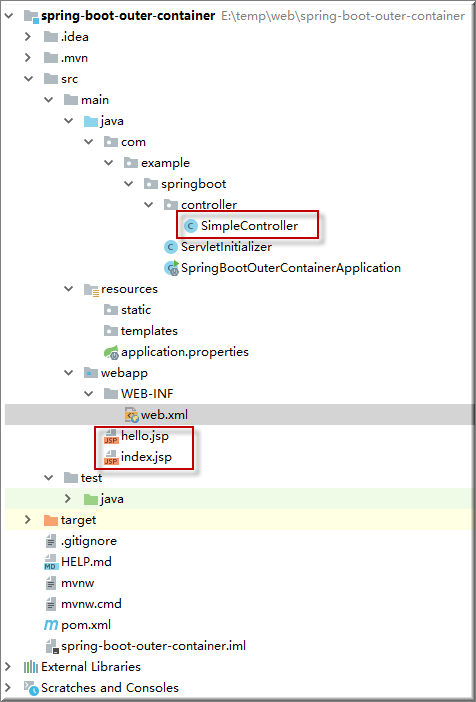
5. 做一些测试用jsp和Controller
6. 启动服务器
将会自动打开chrome浏览器并自动访问http://localhost:8080/ (因为没有指定context上下文,默认即是/)
外部Servlet容器原理
- jar包:执行SpringBoot主类的main方法 --> 启动ioc容器 --> 创建嵌入式的Servlet容器;
- war包:启动服务器,服务器启动SpringBoot应用【SpringBootServletInitializer】,启动ioc容器;
servlet3.0(Spring注解版): 8.2.4 Shared libraries / runtimes pluggability:
规则:
1)、服务器启动(web应用启动)会创建当前web应用里面每一个jar包里面ServletContainerInitializer实例:
2)、ServletContainerInitializer的实现放在jar包的META-INF/services文件夹下,有一个名为javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer的文件,内容就是ServletContainerInitializer的实现类的全类名 (spring-web-5.1.6.RELEASE.jar里面有一个)
3)、还可以使用@HandlesTypes,在应用启动的时候加载我们感兴趣的类;
流程:
1)、启动Tomcat
2)、org\springframework\spring-web\4.3.14.RELEASE\spring-web-4.3.14.RELEASE.jar!\META-INF\services\javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer:
Spring的web模块里面有这个文件:org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer
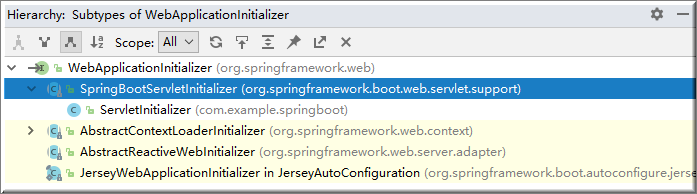
3)、SpringServletContainerInitializer上的注解@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class) 标注的所有这个类型的类都传入到onStartup方法的Set<Class<?>>;为这些WebApplicationInitializer类型的类创建实例;
而WebApplicationInitializer是接口, 其实现类如下图
4)、每一个WebApplicationInitializer都调用自己的onStartup;
5)、相当于我们的SpringBootServletInitializer的类会被创建对象,并执行onStartup方法 ,而自定义类ServletInitializer 正是SpringBootServletInitializer的子类,即WebApplicationInitializer 的子孙类。
6)、SpringBootServletInitializer实例(自定义类Servletinitializer)执行onStartup的时候会createRootApplicationContext;创建容器
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext(
ServletContext servletContext) {
//1、创建SpringApplicationBuilder
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = createSpringApplicationBuilder();
StandardServletEnvironment environment = new StandardServletEnvironment();
environment.initPropertySources(servletContext, null);
builder.environment(environment);
builder.main(getClass());
ApplicationContext parent = getExistingRootWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
if (parent != null) {
this.logger.info("Root context already created (using as parent).");
servletContext.setAttribute(
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, null);
builder.initializers(new ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer(parent));
}
builder.initializers(
new ServletContextApplicationContextInitializer(servletContext));
builder.contextClass(AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext.class); //调用configure方法,子类重写了这个方法,将SpringBoot的主程序类传入了进来
builder = configure(builder); //使用builder创建一个Spring应用
SpringApplication application = builder.build();
if (application.getSources().isEmpty() && AnnotationUtils
.findAnnotation(getClass(), Configuration.class) != null) {
application.getSources().add(getClass());
}
Assert.state(!application.getSources().isEmpty(),
"No SpringApplication sources have been defined. Either override the "
+ "configure method or add an @Configuration annotation");
// Ensure error pages are registered
if (this.registerErrorPageFilter) {
application.getSources().add(ErrorPageFilterConfiguration.class);
}
//启动Spring应用
return run(application);
}
7)、Spring的应用就启动并且创建IOC容器
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
analyzers = new FailureAnalyzers(context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
//刷新IOC容器
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
listeners.finished(context, null);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
return context;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, listeners, analyzers, ex);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}
启动Servlet容器,再启动SpringBoot应用
样例下载地址: https://files.cnblogs.com/files/whatlonelytear/spring-boot-outer-container.zip
参考
Thymeleaf入门(一)——入门与基本概述==>https://www.cnblogs.com/jiangbei/p/8462294.html
springboot web开发【转】【补】的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot Web开发(5) 开发页面国际化+登录拦截
SpringBoot Web开发(5) 开发页面国际化+登录拦截 一.页面国际化 页面国际化目的:根据浏览器语言设置的信息对页面信息进行切换,或者用户点击链接自行对页面语言信息进行切换. **效果演示 ...
- SpringBoot Web开发(4) Thymeleaf模板与freemaker
SpringBoot Web开发(4) Thymeleaf模板与freemaker 一.模板引擎 常用得模板引擎有JSP.Velocity.Freemarker.Thymeleaf SpringBoo ...
- 【SpringBoot】SpringBoot Web开发(八)
本周介绍SpringBoot项目Web开发的项目内容,及常用的CRUD操作,阅读本章前请阅读[SpringBoot]SpringBoot与Thymeleaf模版(六)的相关内容 Web开发 项目搭建 ...
- SpringBoot(四): SpringBoot web开发 SpringBoot使用jsp
1.在SpringBoot中使用jsp,需要在pom.xml文件中添加依赖 <!--引入Spring Boot内嵌的Tomcat对JSP的解析包--> <dependency> ...
- Spring-boot -Web开发
1).创建SpringBoot应用,选中我们需要的模块: 2).SpringBoot已经默认将这些场景配置好了,只需要在配置文件中指定少量配置就可以运行起来 3).自己编写业务代码: 文件名的功能 x ...
- SpringBoot Web开发(3) WebMvcConfigurerAdapter过期替代方案
springboot2.0中 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter过期替代方案 最近在学习尚硅谷的<springboot核心技术篇>,项目中用到SpringMVC的自动配置和扩展 ...
- SpringBoot——Web开发(静态资源映射)
静态资源映射 SpringBoot对于SpringMVC的自动化配置都在WebMVCAutoConfiguration类中. 其中一个静态内部类WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapt ...
- [SpringBoot——Web开发(使用Thymeleaf模板引擎)]
[文字只能描述片段信息,具体细节参考代码] https://github.com/HCJ-shadow/SpringBootPlus 引入POM依赖 <properties> <ja ...
- web开发-CORS支持
一.简介 Web 开发经常会遇到跨域问题,解决方案有:jsonp,iframe,CORS 等等 1.1.CORS与JSONP相比 1.JSONP只能实现GET请求,而CORS支持所有类型的HTTP请求 ...
随机推荐
- springmvc:入门环境搭建
引入依赖(pom.xml): <!-- 版本锁定 --> <properties> <spring.version>5.0.2.RELEASE</spring ...
- CentOS + Nginx 的常用操作指令总结
CentOS + Nginx 的常用操作指令总结 一. 关于CentOS 查看 yum 源是否存在 yum list | grep nginx 如果不存在 或者 不是自己想要的版本 可以自己设置Ngi ...
- php连接数据库查询方法(还少一种pdo方法)
<?php header("content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8"); $conn = mysql_connect("local ...
- 【Scala学习笔记】一、函数式编程的思想
1. 函数是头等值. 在函数编程中,函数也是值,与整数和字符串处于同一地位.函数可以像变量一样被创建,修改,并当成变量一样传递,返回或是在函数中嵌套函数. 函数可以当做参数传递给其他函数. ...
- Javaweb Form表单查询
1.表单(form),是一种可以由用户输入,并提交给服务器端的一个图形界面,有如下性质: (1)表单中可以输入一些内容,这些输入功能由控件提供,叫做表单元素 (2)表单中一般都有一个按钮负责提交 (3 ...
- beego应用做纯API后端如何使用jwt实现无状态权限验证
jwt是什么,可以百度下其它文章,我原来看到一个讲的详细的,现在找不到了.先简单介绍下我个人的理解,就是一个token,只不过通过加密解密的手段,能让这一串字符带有一些简单的信息.这样解密jwt后不用 ...
- 直接删除mysql的日志导致mysql无法启动
--02T08::.750000Z [Warning] [MY-] [Server] 'NO_ZERO_DATE', 'NO_ZERO_IN_DATE' and 'ERROR_FOR_DIVISION ...
- oracle-约束-序列
概要图 一 约束 --问题:往表中插入数据的时候,可能出现一些问题,比如:重复插入数据,内容不对(性别) --如何保证数据库表中数据的完整性和一致性呢? 约束是强加在表上的规则或条件,确保数据库满足业 ...
- php require_once的使用方法
学习笔记 require_once 语句和 require 语句完全相同,唯一区别是 PHP 会检查该文件是否已经被包含过,如果是则不会再次包含. equire_once() 为了避免重复加载文件. ...
- C#中的事件注册和注销
C#中的事件注册和注销 由于.NET框架对消息循环机制进行了很好的封装,开发人员不再需要深入的了解Windows事件/消息实现的具体机制,也无需创建复杂的事件结构体和所谓的消息句柄.我们所要做的无非就 ...
