python之 栈与队列
忍不住想报一句粗口“卧槽”这尼玛python的数据结构也太特么方便了吧
想到当初学c语言的数据结构的时候,真的是一笔一划都要自己写出来,这python尼玛直接一个模块就ok
真的是没有对比就没有伤害啊,之前试着用类来模拟栈与队列的时候就感觉,我擦这还挺方便的。
现在直接就可以import了,直接使用函数了,唉,这这这现在只想说一声,
人生苦短,我用python
当然栈好像没有这个库
.栈(stacks)是一种只能通过访问其一端来实现数据存储与检索的线性数据结构,具有后进先出(last in first out,LIFO)的特征
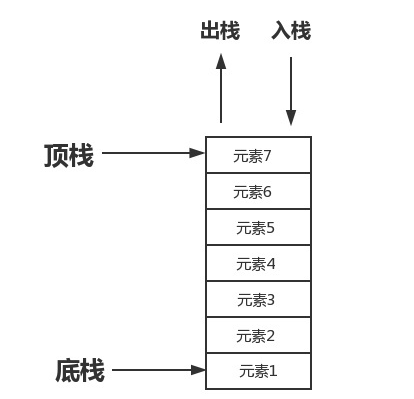
我们可以用这张图来说明栈的应用,那么栈呢有以下功能
- def push(self, num):
- # 把一个元素添加到栈的最顶层
- def pop(self):
- # 删除栈最顶层的元素,并返回这个元素
- def peek(self):
- # 返回最顶层的元素,并不删除它
- def isEmpty(self):
- # 判断栈是否为空
- def size(self):
- # 返回栈中元素的个数
我们这里用顺序来实现栈的功能
- class Stack(object):
- def __init__(self):
- self.__Stack = []
- def push(self, num):
- # 把一个元素添加到栈的最顶层
- self.__Stack.append(num)
- def pop(self):
- # 删除栈最顶层的元素,并返回这个元素
- return self.__Stack.pop()
- def peek(self):
- return self.__Stack[len(self.__Stack)-1]
- # 返回最顶层的元素,并不删除它
- def isEmpty(self):
- return self.__Stack == []
- # 判断栈是否为空
- def size(self):
- return len(self.__Stack)
- # 返回栈中元素的个数
- s = Stack()
当然如果你愿意的话同样可以构成一个链式的栈
队列(queue·)我操,这个就厉害了直接导入一个函数就ok了
- import queue
我们不妨大胆的help一下 help(queue)
就有了这样的东西
我们只需要关注 queue 和lifoqueue(先进先出队列),priorityqueue(优先级队列)
当然一般的queue都是先进后出啦,
- empty(self)
- | Return True if the queue is empty, False otherwise (not
- reliable!).
- |
- | This method is likely to be removed at some point. Use
- qsize() == 0
- | as a direct substitute, but be aware that either approach
- risks a race
- | condition where a queue can grow before the result of
- empty() or
- | qsize() can be used.
- |
- | To create code that needs to wait for all queued tasks to
- be
- | completed, the preferred technique is to use the join()
- method.
- |
- | full(self)
- | Return True if the queue is full, False otherwise (not
- reliable!).
- |
- | This method is likely to be removed at some point. Use
- qsize() >= n
- | as a direct substitute, but be aware that either approach
- risks a race
- | condition where a queue can shrink before the result of
- full() or
- | qsize() can be used.
- |
- | get(self, block=True, timeout=None)
- | Remove and return an item from the queue.
- |
- | If optional args 'block' is true and 'timeout' is None (the
- default),
- | block if necessary until an item is available. If 'timeout' is
- | a non-negative number, it blocks at most 'timeout'
- seconds and raises
- | the Empty exception if no item was available within that
- time.
- | Otherwise ('block' is false), return an item if one is
- immediately
- | available, else raise the Empty exception ('timeout' is
- ignored
- | in that case).
- |
- | get_nowait(self)
- | Remove and return an item from the queue without
- blocking.
- |
- | Only get an item if one is immediately available.
- Otherwise
- | raise the Empty exception.
- |
- | join(self)
- | Blocks until all items in the Queue have been gotten and
- processed.
- |
- | The count of unfinished tasks goes up whenever an item
- is added to the
- | queue. The count goes down whenever a consumer
- thread calls task_done()
- | to indicate the item was retrieved and all work on it is
- complete.
- |
- | When the count of unfinished tasks drops to zero, join()
- unblocks.
- |
- | put(self, item, block=True, timeout=None)
- | Put an item into the queue.
- |
- | If optional args 'block' is true and 'timeout' is None (the
- default),
- | block if necessary until a free slot is available. If 'timeout'
- is
- | a non-negative number, it blocks at most 'timeout'
- seconds and raises
- | the Full exception if no free slot was available within that
- time.
- | Otherwise ('block' is false), put an item on the queue if a
- free slot
- | is immediately available, else raise the Full exception
- ('timeout'
- | is ignored in that case).
- |
- | put_nowait(self, item)
- | Put an item into the queue without blocking.
- |
- | Only enqueue the item if a free slot is immediately
- available.
- | Otherwise raise the Full exception.
- |
- | qsize(self)
- | Return the approximate size of the queue (not reliable!).
- |
- | task_done(self)
- | Indicate that a formerly enqueued task is complete.
- |
- | Used by Queue consumer threads. For each get() used
- to fetch a task,
- | a subsequent call to task_done() tells the queue that the
- processing
- | on the task is complete.
- |
- | If a join() is currently blocking, it will resume when all
- items
- | have been processed (meaning that a task_done() call
- was received
- | for every item that had been put() into the queue).
- |
- | Raises a ValueError if called more times than there were
- items
- | placed in the queue.
好啦这是直接help出来的,总结一下就是
get(self, block=True, timeout=None) # 出队列
put(self, item, block=True, timeout=None) # 进队列 block是堵塞的意思,如果等于false则报错,
task_done(self) # 指示以前加入队列的任务已完成
python之 栈与队列的更多相关文章
- 【DataStructure In Python】Python模拟栈和队列
用Python模拟栈和队列主要是利用List,当然也可以使用collection的deque.以下内容为栈: #! /usr/bin/env python # DataStructure Stack ...
- 使用python实现栈和队列
1.使用python实现栈: class stack(): def __init__(self): self.stack = [] def empty(self): return self.stack ...
- Python实现栈、队列
目录 1. 栈的Python实现 1.1 以列表的形式简单实现栈 1.2 以单链表形式实现栈 2. 队列的Python实现 2.1 以列表实现简单队列 2.2 以单链表形式实现队列 本文将使用py ...
- python之栈与队列
这个在官网中list支持,有实现. 补充一下栈,队列的特性: 1.栈(stacks)是一种只能通过访问其一端来实现数据存储与检索的线性数据结构,具有后进先出(last in first out,LIF ...
- Python 实现栈与队列
#基于Python2.7 #基于顺序表实现 #发现用Python写题时,没有像写C++时方便的STL可用,不过查阅资料之后发现用class实现也很简洁,不过效率应该不是很高 Python实现栈并使用: ...
- python之栈和队列
1. 栈 1.1 示例 #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- codinfg:utf-8 -*- ''' @author: Jeff LEE @file: .py @time: 20 ...
- Python数据结构——栈、队列的实现(二)
1. 一个列表实现两个栈 class Twostacks(object): def __init__(self): self.stack=[] self.a_size=0 self.b_size=0 ...
- Python数据结构——栈、队列的实现(一)
1. 栈 栈(Stack)是限制插入和删除操作只能在一个位置进行的表,该位置是表的末端,称为栈的顶(top).栈的基本操作有PUSH(入栈)和POP(出栈).栈又被称为LIFO(后入先出)表. 1.1 ...
- Python的栈和队列实现
栈 class Node: def __init__(self, data=None): self.next = None self.data = data class Stack: def __in ...
随机推荐
- v-model数据绑定分析
v-model数据绑定分析 v-model是Vue提供的指令,其主要作用是可以实现在表单<input>.<textarea>及<select>等元素以及组件上创建双 ...
- zookeeper动态添加/删除集群中实例(zookeeper 3.6)
一,用来作为demo操作的zookeeper集群中的实例: 机器名:zk1 server.1=172.18.1.1:2888:3888 机器名:zk2 server.2=172.18.1.2:2888 ...
- oracle统计同一字段0和1
SELECT 班级表.班级编号,班级表.班级名称,SUM(DECODE(性别, '1', 1)) 女生人数,SUM(DECODE(性别, '0', 1)) 男生人数FROM 学生表, 班级表WHERE ...
- 五分钟详解MySQL并发控制及事务原理
在如今互联网业务中使用范围最广的数据库无疑还是关系型数据库MySQL,之所以用"还是"这个词,是因为最近几年国内数据库领域也取得了一些长足进步,例如以TIDB.OceanBase等 ...
- Helium文档15-WebUI自动化-chromedriver问题
前言 helium库是自带chromedriver的,我们怎么来查看在哪里呢? 目录介绍 用我的电脑上的路径打比方如下: D:\Program Files (x86)\Python38\Lib\sit ...
- 记录Spring Boot 2.3.4.RELEASE版注解方式实现AOP和通知的执行顺序
1.advice 按照以下的顺序执行 输出结果:(正常和异常) 说明:Spring boot 2.3.4.RELEASE 版本使用的AOP是spring-aop-5.2.9.RELEASE,AOP的通 ...
- xUtils简介和使用方法
xUtils简介 xUtils 包含了很多实用的android工具. xUtils 最初源于Afinal框架,进行了大量重构,使得xUtils支持大文件上传,更全面的http请求协议支持(10种谓词) ...
- Redis学习笔记(三)——数据结构之字符串(String)
一.介绍 String类型,是二进制安全的,存入和获取的数据相同,value最多可以容纳的数据长度是512M,可以存放json数据,图像数据等等. 存储String常用命令: 赋值(set) 取值(g ...
- 2020年Android开发最新整理阿里巴巴、字节跳动、小米面经,你不看看吗?
前言 2020年是转折的一年,上半年疫情原因,很多学android开发的小伙伴失业了,虽找到了一份工作,但高不成低不就,下半年金九银十有想法更换一份工作,很多需要大厂面试经验和大厂面试真题的小伙伴,想 ...
- git 上传代码报错eslint --fix found some errors. Please fix them and try committing again.
在提交时用下面这句 git commit --no-verify -m "提交时的注释"
