Java 树结构实际应用 三(二叉排序树)


- package com.lin.binarysorttree_0314;
- public class BinarySortTreeTest {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
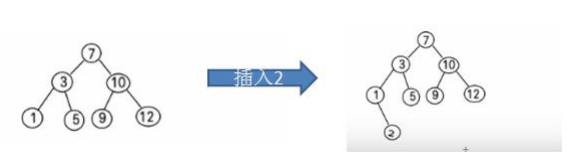
- int[] arr = {7, 3, 10, 12, 5, 1, 9};
- BinarySortTree binarySortTree = new BinarySortTree();
- for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
- binarySortTree.add(new SNode(arr[i]));
- }
- binarySortTree.add(new SNode(2));
- binarySortTree.infixOrder();
- // 删除
- System.out.println("***********");
- binarySortTree.delNode(2);
- binarySortTree.delNode(3);
- binarySortTree.delNode(5);
- binarySortTree.delNode(7);
- binarySortTree.delNode(9);
- binarySortTree.delNode(12);
- System.out.println("root:" + binarySortTree.getRoot());
- binarySortTree.infixOrder();
- }
- }
- class BinarySortTree{
- private SNode root;
- // 查找要删除的节点
- public SNode getRoot() {
- return root;
- }
- public SNode searchDelNode(int value) {
- if(root == null) {
- return null;
- } else {
- return root.searchDelNode(value);
- }
- }
- // 查找要删除节点的父节点
- public SNode searchParent(int value) {
- if(root == null) {
- return null;
- } else {
- return root.searchParent(value);
- }
- }
- /**
- * @param node 传入的节点(当作二叉排序树的根节点)
- * @return 返回的以node为根节点的二叉排序树的最小节点的值
- */
- public int delRightTreeMin(SNode node) {
- SNode target = node;
- // 循环地查找左节点,就会找到最小值
- while(target.left != null) {
- target = target.left;
- }
- delNode(target.value);// !!!!
- return target.value;// !!!!!
- }
- // 删除节点
- public void delNode(int value) {
- if(root == null) {
- return;
- } else {
- // 找删除节点
- SNode targetNode = searchDelNode(value);
- // 没有找到
- if(targetNode == null) {
- return;
- }
- // 如果发现当前这棵二叉树只有一个节点
- if(root.left == null && root.right == null) {
- root = null;
- return;
- }
- // 去找到targetNode的父节点
- SNode parent = searchParent(value);
- // 如果删除的节点是叶子节点
- if(targetNode.left == null && targetNode.right == null) {
- // 判断targetNode是父节点的左子节点还是右子节点
- if(parent.left != null && parent.left.value == value) {
- parent.left = null;
- } else if(parent.right != null && parent.right.value == value) {
- parent.right = null;
- }
- } else if(targetNode.left != null && targetNode.right != null) { // 有左右子节点
- int delRightTreeMin = delRightTreeMin(targetNode.right);
- targetNode.value = delRightTreeMin;
- } else {// 只有一个子节点
- // 要删除的节点只有左节点
- if(targetNode.left != null) {
- if(parent != null) {
- // 如果targetNode是parent的左子节点
- if(parent.left.value == value) {
- parent.left = targetNode.left;
- } else {
- parent.right = targetNode.left;
- }
- } else {
- root = targetNode.left;
- }
- } else {// 要删除的节点有右子节点
- if(parent != null) {
- if(parent.left.value == value) {
- parent.left = targetNode.right;
- } else {
- parent.right = targetNode.right;
- }
- } else {
- root = targetNode.right;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- // 中序遍历
- public void infixOrder() {
- if(root == null) {
- System.out.println("空树!");
- } else {
- root.infixOrder();
- }
- }
- // 添加
- public void add(SNode node) {
- if(root == null) {
- root = node;
- } else {
- root.add(node);
- }
- }
- }
- class SNode{
- protected int value;
- protected SNode left;
- protected SNode right;
- public SNode(int value) {
- // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
- this.value = value;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- return "Node = [value = " + value + "]";
- }
- // 添加节点
- public void add(SNode node) {
- if(node == null) {
- return;
- }
- if(node.value < this.value) {
- if(this.left == null) {
- this.left = node;
- } else {
- this.left.add(node);
- }
- } else {
- if(this.right == null) {
- this.right = node;
- } else {
- this.right.add(node);
- }
- }
- }
- // 中序遍历
- public void infixOrder() {
- if(this.left != null) {
- this.left.infixOrder();
- }
- System.out.println(this);
- if(this.right != null) {
- this.right.infixOrder();
- }
- }
- // 查找要删除的节点
- public SNode searchDelNode(int value) {
- if(this.value == value) {
- return this;
- } else if(this.value > value) {
- // 如果左子节点为空
- if(this.left == null) {
- return null;
- }
- return this.left.searchDelNode(value);
- } else {
- if(this.right == null) {
- return null;
- }
- return this.right.searchDelNode(value);
- }
- }
- // 查找要删除节点的父节点, 如果没有则返回null
- public SNode searchParent(int value) {
- if(( this.left != null && this.left.value == value)
- || ( this.right != null && this.right.value == value )) {
- return this;
- } else {
- // 如果查找的值小于当前节点的值,并且当前节点的左子节点不为空
- if(value < this.value && this.left != null) {
- return this.left.searchParent(value);
- } else if(value >= this.value && this.right != null) {
- return this.right.searchParent(value);
- } else {
- return null;
- }
- }
- }
- }

仅供参考,有错误还请指出!
有什么想法,评论区留言,互相指教指教。
觉得不错的可以点一下右边的推荐哟
Java 树结构实际应用 三(二叉排序树)的更多相关文章
- Java 处理 XML 的三种主流技术及介绍
Java 处理 XML 的三种主流技术及介绍 原文地址:https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/xml/dm-1208gub/ XML (eXtensible Ma ...
- java解析xml的三种方法
java解析XML的三种方法 1.SAX事件解析 package com.wzh.sax; import org.xml.sax.Attributes; import org.xml.sax.SAXE ...
- 20145213《Java程序设计》实验三敏捷开发与XP实践
20145213<Java程序设计>实验三敏捷开发与XP实践 实验要求 1.XP基础 2.XP核心实践 3.相关工具 实验内容 1.敏捷开发与XP 软件工程是把系统的.有序的.可量化的方法 ...
- 20145213《Java程序设计》第三周学习总结
20145213<Java程序设计>第三周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 正所谓距离产生美,上周我还倾心于Java表面的基础语法.其简单的流程结构,屈指可数的基本类型分类,早已烂熟于心的运算符 ...
- 20145206《Java程序设计》实验三实验报告
20145206<Java程序设计>实验三实验报告 实验内容 XP基础 XP核心实践 相关工具 实验步骤 (一)敏捷开发与XP 软件工程是把系统的.有序的.可量化的方法应用到软件的开发.运 ...
- 20145308刘昊阳 《Java程序设计》实验三 敏捷开发与XP实践 实验报告
20145308刘昊阳 <Java程序设计>实验三 敏捷开发与XP实践 实验报告 实验名称 敏捷开发与XP实践 实验内容 XP基础 XP核心实践 相关工具 统计的PSP(Personal ...
- 20145330《Java程序设计》第三周学习总结
20145330 <Java程序设计>第三周学习总结 第三周知识的难度已经逐步上升,并且一周学习两章学习压力也逐渐加大,需要更高效率的来完成学习内容,合理安排时间. 类与对象 对象(Obj ...
- 20145337《Java程序设计》第三周学习总结
20145337 <Java程序设计>第三周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 类与对象 类与对象的关系:要产生对象必须先定义类,类是对象的设计图,对象是类的实例.我觉得在视频中对类与对象关系的描 ...
- 20145320《Java程序设计》第三次实验报告
20145320<Java程序设计>第三次实验报告 北京电子科技学院(BESTI)实验报告 课程:Java程序设计 班级:1453 指导教师:娄嘉鹏 实验日期:2016.04.22 15: ...
随机推荐
- select(),fd_set(),fd_isset()
1. select函数 1. 用途 在编程的过程中,经常会遇到许多阻塞的函数,好像read和网络编程时使用的recv, recvfrom函数都是阻塞的函数,当函数不能成功执行的时候,程序就会一直阻塞在 ...
- POJ - 3665 icow
Fatigued by the endless toils of farming, Farmer John has decided to try his hand in the MP3 player ...
- HDU 4336 Card Collector(状压 + 概率DP 期望)题解
题意:每包干脆面可能开出卡或者什么都没有,一共n种卡,每种卡每包爆率pi,问收齐n种卡的期望 思路:期望求解公式为:$E(x) = \sum_{i=1}^{k}pi * xi + (1 - \sum_ ...
- React Refs All In One
React Refs All In One https://reactjs.org/docs/react-api.html#refs Ref https://reactjs.org/docs/refs ...
- 如何配置 webpack 支持 preload, prefetch, dns-prefetch
如何配置 webpack 支持 preload, prefetch, dns-prefetch webpack , preload, prefetch https://webpack.js.org/p ...
- React Native Apps
React Native Apps https://github.com/ReactNativeNews/React-Native-Apps github app https://github.com ...
- taro defaultProps
taro defaultProps https://nervjs.github.io/taro/docs/best-practice.html#给组件设置-defaultprops import Ta ...
- py django
创建项目 $ django-admin startproject server 运行项目 $ cd server $ python manage.py runserver 创建一个模块 $ pytho ...
- vue农历日历
<template> <div class="calendar-main"> <div class="choose_year"&g ...
- c++ string与wstring转换
wchar_t to char #include <comdef.h> const wchar_t* exepath = L"d:\\中文 路径\\中文 路径.exe" ...
