【力扣】787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班加权——有向图最短路径
前言
我感觉这题比较有代表性,所以记录一下,这题是加权有向图中求最短路径的问题。
题目
动态规划
假设有一条路径是[src, i, ..., j, dst],解法一子问题的定义是[src, i, ..., j],解法二子问题的定义是[i, ..., j, dst]。
解法一需要知道哪些节点指向dst,需要求入度。
解法二需要知道src指向哪些节点,需要求出度。
解法一
如下图所示,想要求src到dst的最短路径,如果知道了src到s1和src到s2的最短路径,那么问题就好解决了。
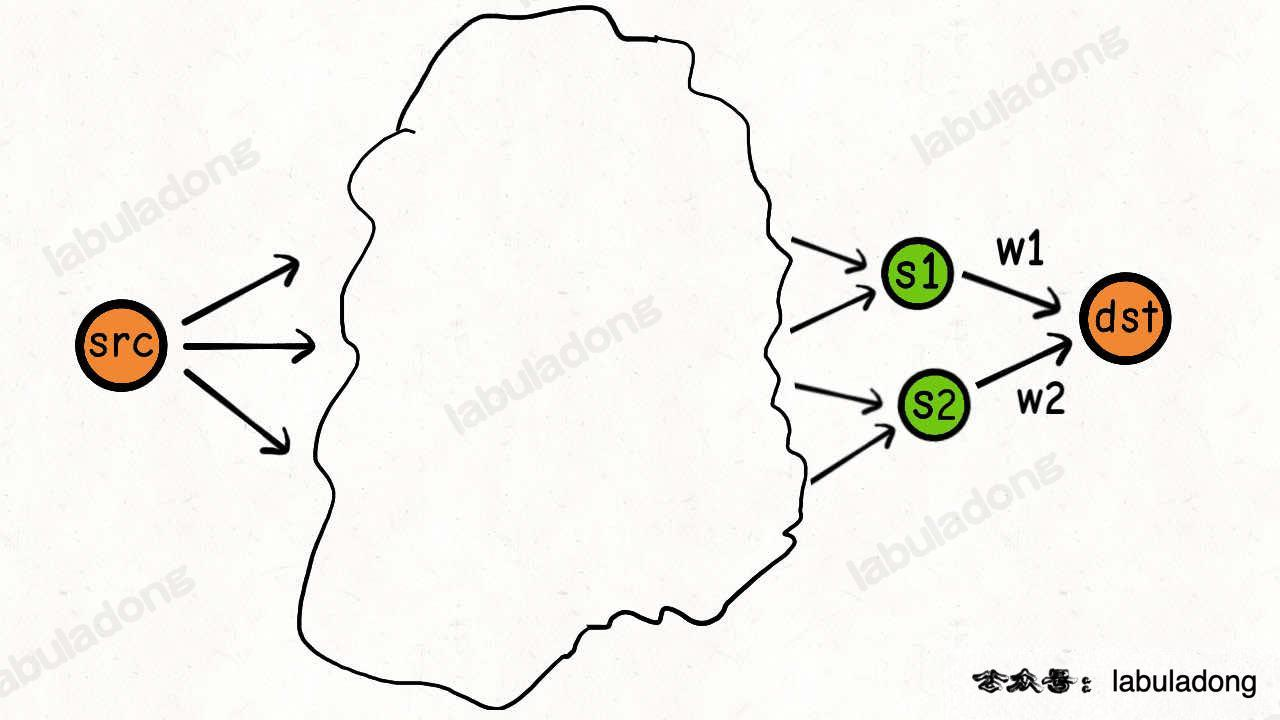
加上s1和s2到dst的花费取最小值即可,伪代码如下
minPrice(dst, k) =
min(minPrice(s1, k - 1) + w1,
minPrice(s2, k - 1) + w2)
最终代码
class Solution {
int n, src, dst;
int[][] flights;
int[][] memo;
HashMap<Integer, List<int[]>> indegree = new HashMap<>();
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
this.n = n;
this.flights = flights;
this.src = src;
this.dst = dst;
// 求入度
for(int[] flight : flights){
int from = flight[0], to = flight[1], price = flight[2];
indegree.putIfAbsent(to, new ArrayList<>());
indegree.get(to).add(new int[]{from, price});
}
memo = new int[n][k + 1];
for(int[] arr : memo){
Arrays.fill(arr, -2);
}
return dp(dst, k);
}
int dp(int dst, int k){
if(src == dst){
return 0;
}
if(k < 0){
return -1;
}
if(memo[dst][k] != -2){
return memo[dst][k];
}
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(indegree.containsKey(dst)){
for(int[] v : indegree.get(dst)){
int subProblem = dp(v[0], k - 1);
if(subProblem == -1) continue;
res = Math.min(res, subProblem + v[1]);
}
}
memo[dst][k] = res == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : res;
return memo[dst][k];
}
}
解法二
如下图所示,想要求src到dst的最短路径,如果知道了s1到dst和s2到dst的最短路径,那么问题就好解决了。

加上src到s1和s2的花费取最小值即可,伪代码如下
minPrice(src, k) =
min(minPrice(s1, k - 1) + w1,
minPrice(s2, k - 1) + w2)
最终代码
class Solution {
int n, src, dst;
int[][] flights;
int[][] memo;
HashMap<Integer, List<int[]>> outdegree = new HashMap<>();
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
this.n = n;
this.flights = flights;
this.src = src;
this.dst = dst;
// 求出度
for(int[] flight : flights){
int from = flight[0], to = flight[1], price = flight[2];
outdegree.putIfAbsent(from, new ArrayList<>());
outdegree.get(from).add(new int[]{to, price});
}
memo = new int[n][k + 1];
for(int[] arr : memo){
Arrays.fill(arr, -2);
}
return dp(src, k);
}
int dp(int src, int k){
if(src == dst){
return 0;
}
if(k < 0){
return -1;
}
if(memo[src][k] != -2){
return memo[src][k];
}
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(outdegree.containsKey(src)){
for(int[] v : outdegree.get(src)){
int subProblem = dp(v[0], k - 1);
if(subProblem == -1) continue;
res = Math.min(res, subProblem + v[1]);
}
}
memo[src][k] = res == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : res;
return memo[src][k];
}
}
小结
两种解法代码非常相似,具有对称性。对于有向图最短路径问题,常规思路都是 Dijkstra 等图论经典算法,没想到动态规划也可以,很奇妙。这也是我想记录这道题的原因吧。
BFS 算法思路
Dijkstra 算法
public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int K) {
List<int[]>[] graph = new LinkedList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
for (int[] edge : flights) {
int from = edge[0];
int to = edge[1];
int price = edge[2];
graph[from].add(new int[]{to, price});
}
// 启动 dijkstra 算法
// 计算以 src 为起点在 k 次中转到达 dst 的最短路径
K++;
return dijkstra(graph, src, K, dst);
}
class State {
// 图节点的 id
int id;
// 从 src 节点到当前节点的花费
int costFromSrc;
// 从 src 节点到当前节点经过的节点个数
int nodeNumFromSrc;
State(int id, int costFromSrc, int nodeNumFromSrc) {
this.id = id;
this.costFromSrc = costFromSrc;
this.nodeNumFromSrc = nodeNumFromSrc;
}
}
// 输入一个起点 src,计算从 src 到其他节点的最短距离
int dijkstra(List<int[]>[] graph, int src, int k, int dst) {
// 定义:从起点 src 到达节点 i 的最短路径权重为 distTo[i]
int[] distTo = new int[graph.length];
// 定义:从起点 src 到达节点 i 的最小权重路径至少要经过 nodeNumTo[i] 个节点
int[] nodeNumTo = new int[graph.length];
Arrays.fill(distTo, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
Arrays.fill(nodeNumTo, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// base case
distTo[src] = 0;
nodeNumTo[src] = 0;
// 优先级队列,costFromSrc 较小的排在前面
Queue<State> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> {
return a.costFromSrc - b.costFromSrc;
});
// 从起点 src 开始进行 BFS
pq.offer(new State(src, 0, 0));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
State curState = pq.poll();
int curNodeID = curState.id;
int costFromSrc = curState.costFromSrc;
int curNodeNumFromSrc = curState.nodeNumFromSrc;
if (curNodeID == dst) {
// 找到最短路径
return costFromSrc;
}
if (curNodeNumFromSrc == k) {
// 中转次数耗尽
continue;
}
// 将 curNode 的相邻节点装入队列
for (int[] neighbor : graph[curNodeID]) {
int nextNodeID = neighbor[0];
int costToNextNode = costFromSrc + neighbor[1];
// 中转次数消耗 1
int nextNodeNumFromSrc = curNodeNumFromSrc + 1;
// 更新 dp table
if (distTo[nextNodeID] > costToNextNode) {
distTo[nextNodeID] = costToNextNode;
nodeNumTo[nextNodeID] = nextNodeNumFromSrc;
}
// 剪枝,如果中转次数更多,花费还更大,那必然不会是最短路径
if (costToNextNode > distTo[nextNodeID]
&& nextNodeNumFromSrc > nodeNumTo[nextNodeID]) {
continue;
}
pq.offer(new State(nextNodeID, costToNextNode, nextNodeNumFromSrc));
}
}
return -1;
}
参考资料
【力扣】787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班加权——有向图最短路径的更多相关文章
- Java实现 LeetCode 787 K 站中转内最便宜的航班(两种DP)
787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班 有 n 个城市通过 m 个航班连接.每个航班都从城市 u 开始,以价格 w 抵达 v. 现在给定所有的城市和航班,以及出发城市 src 和目的地 dst,你的任务是 ...
- 【力扣leetcode】-787. K站中转内最便宜的航班
题目描述: 有 n 个城市通过一些航班连接.给你一个数组 flights ,其中 flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei] ,表示该航班都从城市 fromi 开始,以价格 p ...
- LeetCode——787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班
有 n 个城市通过 m 个航班连接.每个航班都从城市 u 开始,以价格 w 抵达 v. 现在给定所有的城市和航班,以及出发城市 src 和目的地 dst,你的任务是找到从 src 到 dst 最多经过 ...
- leetcode 787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班
问题描述 有 n 个城市通过 m 个航班连接.每个航班都从城市 u 开始,以价格 w 抵达 v. 现在给定所有的城市和航班,以及出发城市 src 和目的地 dst,你的任务是找到从 src 到 dst ...
- [Swift]LeetCode787. K 站中转内最便宜的航班 | Cheapest Flights Within K Stops
There are n cities connected by m flights. Each fight starts from city u and arrives at v with a pri ...
- leetcode_787【K 站中转内最便宜的航班】
有 n 个城市通过 m 个航班连接.每个航班都从城市 u 开始,以价格 w 抵达 v. 现在给定所有的城市和航班,以及出发城市 src 和目的地 dst,你的任务是找到从 src 到 dst 最多经过 ...
- 刷题-力扣-1011. 在 D 天内送达包裹的能力
1011. 在 D 天内送达包裹的能力 题目链接 来源:力扣(LeetCode) 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/capacity-to-ship-packag ...
- 力扣992.K个不同整数的子数组-C语言实现
题目 原题链接 给定一个正整数数组 A,如果 A 的某个子数组中不同整数的个数恰好为 K,则称 A 的这个连续.不一定独立的子数组为好子数组. (例如,[1,2,3,1,2] 中有 3 个不同的整数: ...
- 力扣——Reverse Nodes in k-Group(K 个一组翻转链表) python实现
题目描述: 中文: 给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表. k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度. 如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序 ...
随机推荐
- rabbitmq原理和应用
0.1.索引 https://blog.waterflow.link/articles/1663772504649 RabbitMQ 是一个轻量级且易于部署的消息队列.它支持开箱即用的多种消息传递协议 ...
- django 生产环境部署手册
Django 是 python 的 web 框架,以下是其部署到生产环境的详细步骤,包含 Apache 和 nginx 版本. 部署环境 操作系统:centeros7.3 数据库:MySQL5.6.5 ...
- SQL--存储过程的使用
存储过程的概念 存储过程类似一个函数,可以执行一条或者多条SQL语句,可带参数,可返回值 为了简化操作,方便更改和扩展,将一个事件的处理封装在一个单元中供使用. 创建存储过程 --创建存储过程(不带参 ...
- Golang Gorm time 时间字段格式化模型类 重写
问题: 在使用GORM中 如果我们使用到了CreateAt 和UpdateAt 就会发现 这个时间的类型是time.Time 而其数据是 "2022-10-13T10:14:02.97352 ...
- 将java装进u盘指南
将java装入u盘指南 idea 将下载好的idea的文件夹移动到u盘中.在idea的bin目录里找到idea.properties文件,在最后添加以下两行 idea.config.path=U:/I ...
- Pycharm自定义实时模板
pycharm添加模板 添加装饰器模板 # 1.file-->Setting-->Editor-->Code Style -->Live Templates# 2." ...
- pycharm系列---基本配置
自动加入头文件 # _*_ coding: utf-8 _*_ # @Time : ${DATE} ${TIME} # @Author : xiechunhui # @Version:V 0.1 # ...
- 详解从浏览器地址栏输入URL到页面显示的步骤
版本1(基础版本) 步骤1:浏览器根据请求的 URL 交给 DNS 域名解析,找到真实 IP ,向服务器发起请求: 步骤2:服务器交给后台处理完成后返回数据,浏览器接收⽂件( HTML.JS.CSS ...
- 【Java并发007】原理层面:ReentrantLock中lock()、unlock()全解析
一.前言 Java线程同步两种方式,synchronized关键字和Lock锁机制,其中,AQS队列就是Lock锁实现公平加锁的底层支持. 二.AQS源码对于lock.lock()的实现 2.1 AQ ...
- MSP430中断小实验——通过按键改变小灯闪烁频率
本小实验基于MSP430f5529,不同的型号可能管脚和中断配置有所不同. 实现的功能为: 第一次按下按键后,系统以每 2 秒钟,指示灯暗 1 秒,亮 1 秒的方式闪烁.程序采用默认时钟配置: 第二次 ...
