(四)elasticsearch 源码之索引流程分析
1.概览
前面我们讨论了es是如何启动,本文研究下es是如何索引文档的。
下面是启动流程图,我们按照流程图的顺序依次描述。
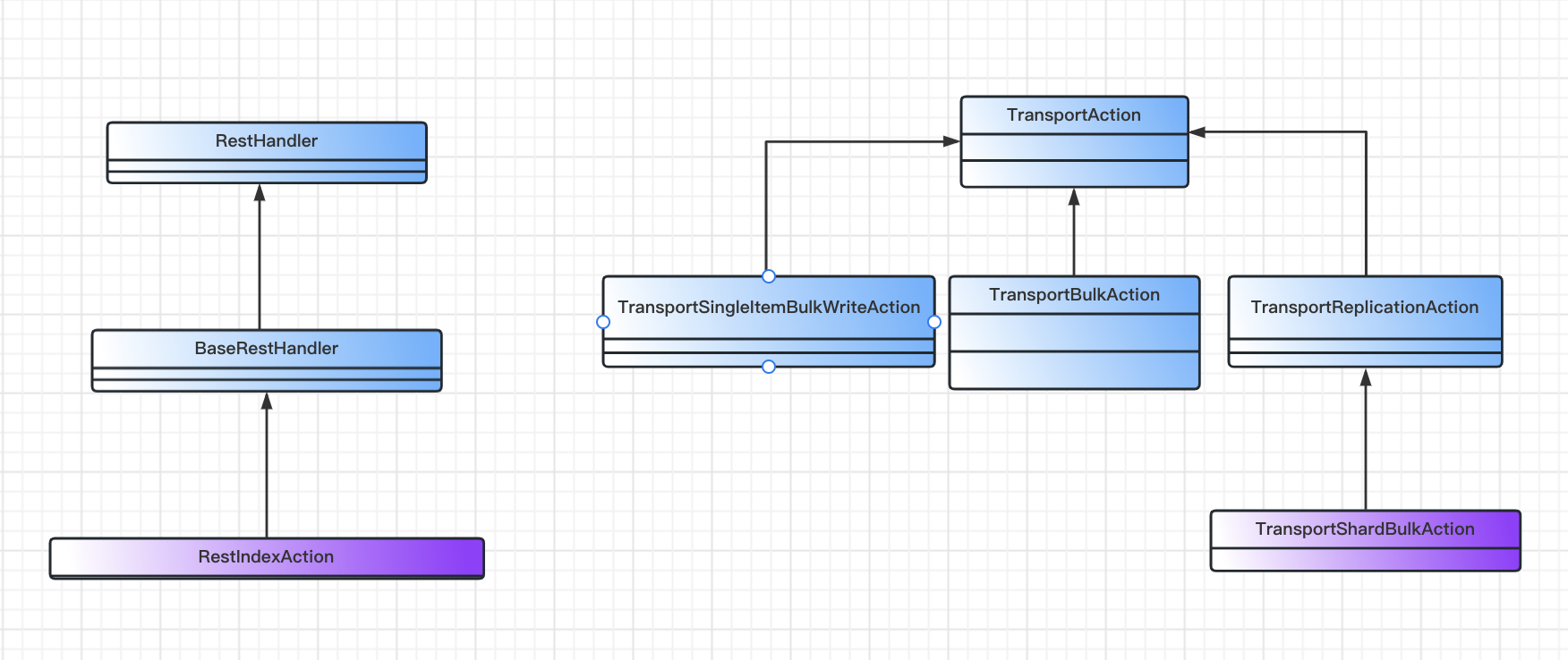
2. 索引流程
我们用postman发送请求,创建一个文档
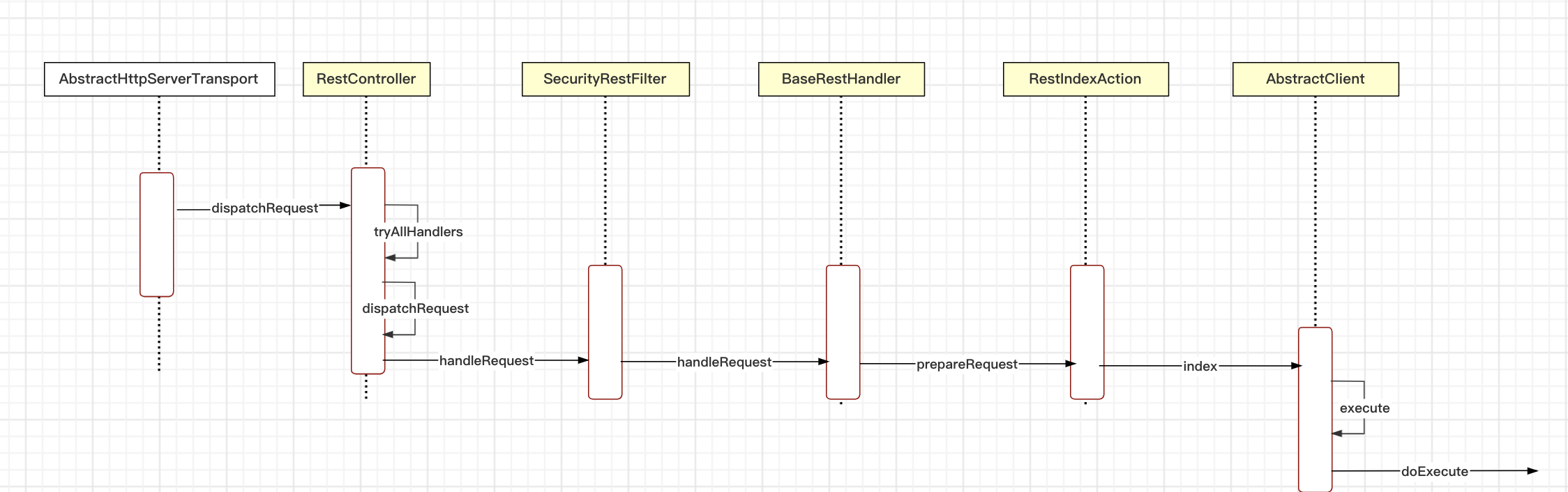
我们发送的是http请求,es也有一套http请求处理逻辑,和spring的mvc类似
// org.elasticsearch.rest.RestController
private void dispatchRequest(RestRequest request, RestChannel channel, RestHandler handler) throws Exception {
final int contentLength = request.content().length();
if (contentLength > 0) {
final XContentType xContentType = request.getXContentType(); // 校验content-type
if (xContentType == null) {
sendContentTypeErrorMessage(request.getAllHeaderValues("Content-Type"), channel);
return;
}
if (handler.supportsContentStream() && xContentType != XContentType.JSON && xContentType != XContentType.SMILE) {
channel.sendResponse(BytesRestResponse.createSimpleErrorResponse(channel, RestStatus.NOT_ACCEPTABLE,
"Content-Type [" + xContentType + "] does not support stream parsing. Use JSON or SMILE instead"));
return;
}
}
RestChannel responseChannel = channel;
try {
if (handler.canTripCircuitBreaker()) {
inFlightRequestsBreaker(circuitBreakerService).addEstimateBytesAndMaybeBreak(contentLength, "<http_request>");
} else {
inFlightRequestsBreaker(circuitBreakerService).addWithoutBreaking(contentLength);
}
// iff we could reserve bytes for the request we need to send the response also over this channel
responseChannel = new ResourceHandlingHttpChannel(channel, circuitBreakerService, contentLength);
handler.handleRequest(request, responseChannel, client);
} catch (Exception e) {
responseChannel.sendResponse(new BytesRestResponse(responseChannel, e));
}
}// org.elasticsearch.rest.BaseRestHandler
@Override
public final void handleRequest(RestRequest request, RestChannel channel, NodeClient client) throws Exception {
// prepare the request for execution; has the side effect of touching the request parameters
final RestChannelConsumer action = prepareRequest(request, client);
// validate unconsumed params, but we must exclude params used to format the response
// use a sorted set so the unconsumed parameters appear in a reliable sorted order
final SortedSet<String> unconsumedParams =
request.unconsumedParams().stream().filter(p -> !responseParams().contains(p)).collect(Collectors.toCollection(TreeSet::new));
// validate the non-response params
if (!unconsumedParams.isEmpty()) {
final Set<String> candidateParams = new HashSet<>();
candidateParams.addAll(request.consumedParams());
candidateParams.addAll(responseParams());
throw new IllegalArgumentException(unrecognized(request, unconsumedParams, candidateParams, "parameter"));
}
if (request.hasContent() && request.isContentConsumed() == false) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("request [" + request.method() + " " + request.path() + "] does not support having a body");
}
usageCount.increment();
// execute the action
action.accept(channel); // 执行action
}// org.elasticsearch.rest.action.document.RestIndexAction
public RestChannelConsumer prepareRequest(final RestRequest request, final NodeClient client) throws IOException {
IndexRequest indexRequest;
final String type = request.param("type");
if (type != null && type.equals(MapperService.SINGLE_MAPPING_NAME) == false) {
deprecationLogger.deprecatedAndMaybeLog("index_with_types", TYPES_DEPRECATION_MESSAGE); // type 已经废弃
indexRequest = new IndexRequest(request.param("index"), type, request.param("id"));
} else {
indexRequest = new IndexRequest(request.param("index"));
indexRequest.id(request.param("id"));
}
indexRequest.routing(request.param("routing"));
indexRequest.setPipeline(request.param("pipeline"));
indexRequest.source(request.requiredContent(), request.getXContentType());
indexRequest.timeout(request.paramAsTime("timeout", IndexRequest.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT));
indexRequest.setRefreshPolicy(request.param("refresh"));
indexRequest.version(RestActions.parseVersion(request));
indexRequest.versionType(VersionType.fromString(request.param("version_type"), indexRequest.versionType()));
indexRequest.setIfSeqNo(request.paramAsLong("if_seq_no", indexRequest.ifSeqNo()));
indexRequest.setIfPrimaryTerm(request.paramAsLong("if_primary_term", indexRequest.ifPrimaryTerm()));
String sOpType = request.param("op_type");
String waitForActiveShards = request.param("wait_for_active_shards");
if (waitForActiveShards != null) {
indexRequest.waitForActiveShards(ActiveShardCount.parseString(waitForActiveShards));
}
if (sOpType != null) {
indexRequest.opType(sOpType);
}
return channel ->
client.index(indexRequest, new RestStatusToXContentListener<>(channel, r -> r.getLocation(indexRequest.routing()))); // 执行index操作的consumer
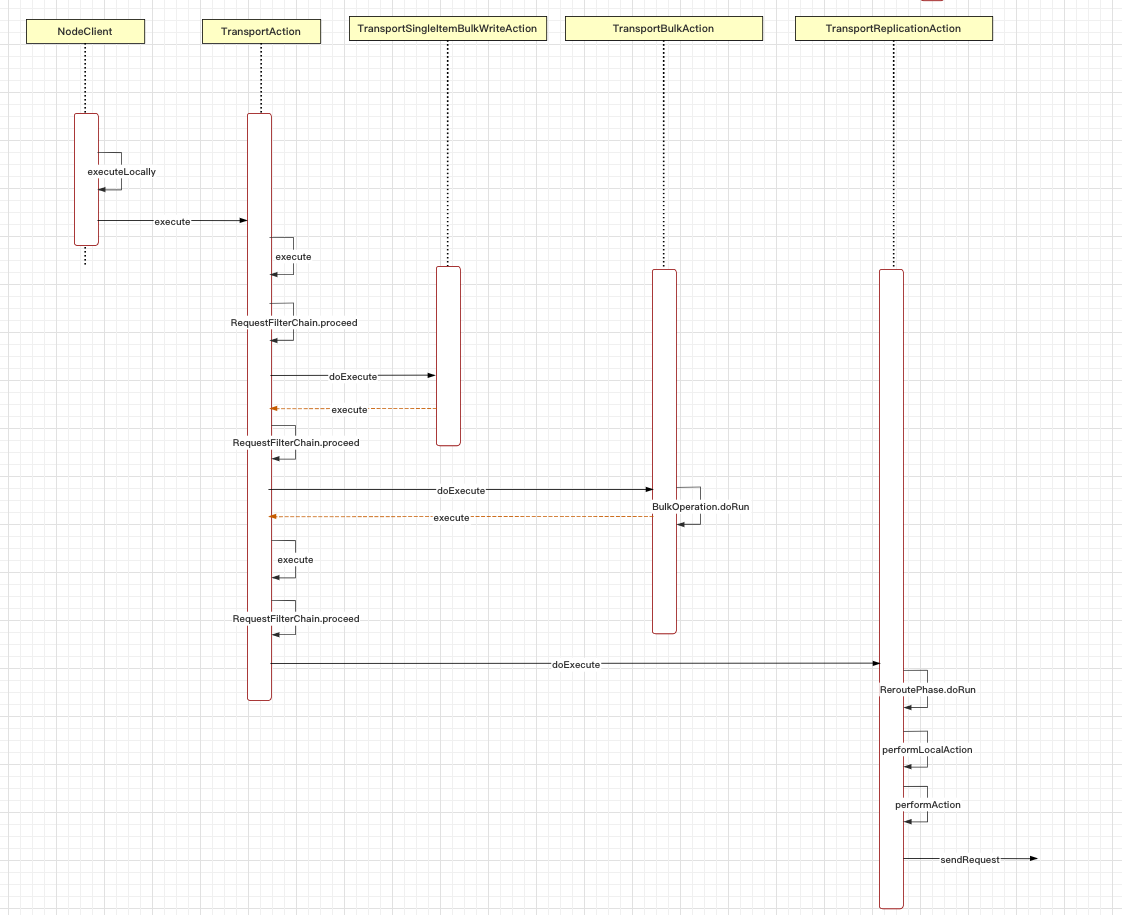
}然后我们来看index操作具体是怎么处理的,主要由TransportAction管理
// org.elasticsearch.action.support.TransportAction
public final Task execute(Request request, ActionListener<Response> listener) {
/*
* While this version of execute could delegate to the TaskListener
* version of execute that'd add yet another layer of wrapping on the
* listener and prevent us from using the listener bare if there isn't a
* task. That just seems like too many objects. Thus the two versions of
* this method.
*/
Task task = taskManager.register("transport", actionName, request); // 注册任务管理器,call -> task
execute(task, request, new ActionListener<Response>() { // ActionListener 封装
@Override
public void onResponse(Response response) {
try {
taskManager.unregister(task);
} finally {
listener.onResponse(response);
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
try {
taskManager.unregister(task);
} finally {
listener.onFailure(e);
}
}
});
return task;
}
...
public final void execute(Task task, Request request, ActionListener<Response> listener) {
ActionRequestValidationException validationException = request.validate();
if (validationException != null) {
listener.onFailure(validationException);
return;
}
if (task != null && request.getShouldStoreResult()) {
listener = new TaskResultStoringActionListener<>(taskManager, task, listener);
}
RequestFilterChain<Request, Response> requestFilterChain = new RequestFilterChain<>(this, logger); // 链式处理
requestFilterChain.proceed(task, actionName, request, listener);
}
...
public void proceed(Task task, String actionName, Request request, ActionListener<Response> listener) {
int i = index.getAndIncrement();
try {
if (i < this.action.filters.length) {
this.action.filters[i].apply(task, actionName, request, listener, this); // 先处理过滤器
} else if (i == this.action.filters.length) {
this.action.doExecute(task, request, listener); // 执行action操作
} else {
listener.onFailure(new IllegalStateException("proceed was called too many times"));
}
} catch(Exception e) {
logger.trace("Error during transport action execution.", e);
listener.onFailure(e);
}
}实际上是TransportBulkAction执行具体操作
// org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.TransportBulkAction
protected void doExecute(Task task, BulkRequest bulkRequest, ActionListener<BulkResponse> listener) {
final long startTime = relativeTime();
final AtomicArray<BulkItemResponse> responses = new AtomicArray<>(bulkRequest.requests.size());
boolean hasIndexRequestsWithPipelines = false;
final MetaData metaData = clusterService.state().getMetaData();
ImmutableOpenMap<String, IndexMetaData> indicesMetaData = metaData.indices();
for (DocWriteRequest<?> actionRequest : bulkRequest.requests) {
IndexRequest indexRequest = getIndexWriteRequest(actionRequest);
if (indexRequest != null) {
// get pipeline from request
String pipeline = indexRequest.getPipeline();
if (pipeline == null) { // 不是管道
// start to look for default pipeline via settings found in the index meta data
IndexMetaData indexMetaData = indicesMetaData.get(actionRequest.index());
// check the alias for the index request (this is how normal index requests are modeled)
if (indexMetaData == null && indexRequest.index() != null) {
AliasOrIndex indexOrAlias = metaData.getAliasAndIndexLookup().get(indexRequest.index()); // 使用别名
if (indexOrAlias != null && indexOrAlias.isAlias()) {
AliasOrIndex.Alias alias = (AliasOrIndex.Alias) indexOrAlias;
indexMetaData = alias.getWriteIndex();
}
}
// check the alias for the action request (this is how upserts are modeled)
if (indexMetaData == null && actionRequest.index() != null) {
AliasOrIndex indexOrAlias = metaData.getAliasAndIndexLookup().get(actionRequest.index());
if (indexOrAlias != null && indexOrAlias.isAlias()) {
AliasOrIndex.Alias alias = (AliasOrIndex.Alias) indexOrAlias;
indexMetaData = alias.getWriteIndex();
}
}
if (indexMetaData != null) {
// Find the default pipeline if one is defined from and existing index.
String defaultPipeline = IndexSettings.DEFAULT_PIPELINE.get(indexMetaData.getSettings());
indexRequest.setPipeline(defaultPipeline);
if (IngestService.NOOP_PIPELINE_NAME.equals(defaultPipeline) == false) {
hasIndexRequestsWithPipelines = true;
}
} else if (indexRequest.index() != null) {
// No index exists yet (and is valid request), so matching index templates to look for a default pipeline
List<IndexTemplateMetaData> templates = MetaDataIndexTemplateService.findTemplates(metaData, indexRequest.index());
assert (templates != null);
String defaultPipeline = IngestService.NOOP_PIPELINE_NAME;
// order of templates are highest order first, break if we find a default_pipeline
for (IndexTemplateMetaData template : templates) {
final Settings settings = template.settings();
if (IndexSettings.DEFAULT_PIPELINE.exists(settings)) {
defaultPipeline = IndexSettings.DEFAULT_PIPELINE.get(settings);
break;
}
}
indexRequest.setPipeline(defaultPipeline);
if (IngestService.NOOP_PIPELINE_NAME.equals(defaultPipeline) == false) {
hasIndexRequestsWithPipelines = true;
}
}
} else if (IngestService.NOOP_PIPELINE_NAME.equals(pipeline) == false) {
hasIndexRequestsWithPipelines = true;
}
}
}
if (hasIndexRequestsWithPipelines) {
// this method (doExecute) will be called again, but with the bulk requests updated from the ingest node processing but
// also with IngestService.NOOP_PIPELINE_NAME on each request. This ensures that this on the second time through this method,
// this path is never taken.
try {
if (clusterService.localNode().isIngestNode()) {
processBulkIndexIngestRequest(task, bulkRequest, listener);
} else {
ingestForwarder.forwardIngestRequest(BulkAction.INSTANCE, bulkRequest, listener);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
listener.onFailure(e);
}
return;
}
if (needToCheck()) { // 根据批量请求自动创建索引,方便后续写入数据
// Attempt to create all the indices that we're going to need during the bulk before we start.
// Step 1: collect all the indices in the request
final Set<String> indices = bulkRequest.requests.stream()
// delete requests should not attempt to create the index (if the index does not
// exists), unless an external versioning is used
.filter(request -> request.opType() != DocWriteRequest.OpType.DELETE
|| request.versionType() == VersionType.EXTERNAL
|| request.versionType() == VersionType.EXTERNAL_GTE)
.map(DocWriteRequest::index)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
/* Step 2: filter that to indices that don't exist and we can create. At the same time build a map of indices we can't create
* that we'll use when we try to run the requests. */
final Map<String, IndexNotFoundException> indicesThatCannotBeCreated = new HashMap<>();
Set<String> autoCreateIndices = new HashSet<>();
ClusterState state = clusterService.state();
for (String index : indices) {
boolean shouldAutoCreate;
try {
shouldAutoCreate = shouldAutoCreate(index, state);
} catch (IndexNotFoundException e) {
shouldAutoCreate = false;
indicesThatCannotBeCreated.put(index, e);
}
if (shouldAutoCreate) {
autoCreateIndices.add(index);
}
}
// Step 3: create all the indices that are missing, if there are any missing. start the bulk after all the creates come back.
if (autoCreateIndices.isEmpty()) {
executeBulk(task, bulkRequest, startTime, listener, responses, indicesThatCannotBeCreated); // 索引
} else {
final AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(autoCreateIndices.size());
for (String index : autoCreateIndices) {
createIndex(index, bulkRequest.timeout(), new ActionListener<CreateIndexResponse>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(CreateIndexResponse result) {
if (counter.decrementAndGet() == 0) {
threadPool.executor(ThreadPool.Names.WRITE).execute(
() -> executeBulk(task, bulkRequest, startTime, listener, responses, indicesThatCannotBeCreated));
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
if (!(ExceptionsHelper.unwrapCause(e) instanceof ResourceAlreadyExistsException)) {
// fail all requests involving this index, if create didn't work
for (int i = 0; i < bulkRequest.requests.size(); i++) {
DocWriteRequest<?> request = bulkRequest.requests.get(i);
if (request != null && setResponseFailureIfIndexMatches(responses, i, request, index, e)) {
bulkRequest.requests.set(i, null);
}
}
}
if (counter.decrementAndGet() == 0) {
executeBulk(task, bulkRequest, startTime, ActionListener.wrap(listener::onResponse, inner -> {
inner.addSuppressed(e);
listener.onFailure(inner);
}), responses, indicesThatCannotBeCreated);
}
}
});
}
}
} else {
executeBulk(task, bulkRequest, startTime, listener, responses, emptyMap());
}
}接下来, BulkOperation将 BulkRequest 转换成 BulkShardRequest,也就是具体在哪个分片上执行操作
// org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.TransportBulkAction
protected void doRun() {
final ClusterState clusterState = observer.setAndGetObservedState();
if (handleBlockExceptions(clusterState)) {
return;
}
final ConcreteIndices concreteIndices = new ConcreteIndices(clusterState, indexNameExpressionResolver);
MetaData metaData = clusterState.metaData();
for (int i = 0; i < bulkRequest.requests.size(); i++) {
DocWriteRequest<?> docWriteRequest = bulkRequest.requests.get(i);
//the request can only be null because we set it to null in the previous step, so it gets ignored
if (docWriteRequest == null) {
continue;
}
if (addFailureIfIndexIsUnavailable(docWriteRequest, i, concreteIndices, metaData)) {
continue;
}
Index concreteIndex = concreteIndices.resolveIfAbsent(docWriteRequest); // 解析索引
try {
switch (docWriteRequest.opType()) {
case CREATE:
case INDEX:
IndexRequest indexRequest = (IndexRequest) docWriteRequest;
final IndexMetaData indexMetaData = metaData.index(concreteIndex);
MappingMetaData mappingMd = indexMetaData.mappingOrDefault();
Version indexCreated = indexMetaData.getCreationVersion();
indexRequest.resolveRouting(metaData);
indexRequest.process(indexCreated, mappingMd, concreteIndex.getName()); // 校验indexRequest,自动生成id
break;
case UPDATE:
TransportUpdateAction.resolveAndValidateRouting(metaData, concreteIndex.getName(),
(UpdateRequest) docWriteRequest);
break;
case DELETE:
docWriteRequest.routing(metaData.resolveWriteIndexRouting(docWriteRequest.routing(), docWriteRequest.index()));
// check if routing is required, if so, throw error if routing wasn't specified
if (docWriteRequest.routing() == null && metaData.routingRequired(concreteIndex.getName())) {
throw new RoutingMissingException(concreteIndex.getName(), docWriteRequest.type(), docWriteRequest.id());
}
break;
default: throw new AssertionError("request type not supported: [" + docWriteRequest.opType() + "]");
}
} catch (ElasticsearchParseException | IllegalArgumentException | RoutingMissingException e) {
BulkItemResponse.Failure failure = new BulkItemResponse.Failure(concreteIndex.getName(), docWriteRequest.type(),
docWriteRequest.id(), e);
BulkItemResponse bulkItemResponse = new BulkItemResponse(i, docWriteRequest.opType(), failure);
responses.set(i, bulkItemResponse);
// make sure the request gets never processed again
bulkRequest.requests.set(i, null);
}
}
// first, go over all the requests and create a ShardId -> Operations mapping
Map<ShardId, List<BulkItemRequest>> requestsByShard = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < bulkRequest.requests.size(); i++) {
DocWriteRequest<?> request = bulkRequest.requests.get(i);
if (request == null) {
continue;
}
String concreteIndex = concreteIndices.getConcreteIndex(request.index()).getName();
ShardId shardId = clusterService.operationRouting().indexShards(clusterState, concreteIndex, request.id(),
request.routing()).shardId();
List<BulkItemRequest> shardRequests = requestsByShard.computeIfAbsent(shardId, shard -> new ArrayList<>());
shardRequests.add(new BulkItemRequest(i, request));
}
if (requestsByShard.isEmpty()) {
listener.onResponse(new BulkResponse(responses.toArray(new BulkItemResponse[responses.length()]),
buildTookInMillis(startTimeNanos)));
return;
}
final AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(requestsByShard.size());
String nodeId = clusterService.localNode().getId();
for (Map.Entry<ShardId, List<BulkItemRequest>> entry : requestsByShard.entrySet()) {
final ShardId shardId = entry.getKey();
final List<BulkItemRequest> requests = entry.getValue();
BulkShardRequest bulkShardRequest = new BulkShardRequest(shardId, bulkRequest.getRefreshPolicy(), // 构建BulkShardRequest
requests.toArray(new BulkItemRequest[requests.size()]));
bulkShardRequest.waitForActiveShards(bulkRequest.waitForActiveShards());
bulkShardRequest.timeout(bulkRequest.timeout());
if (task != null) {
bulkShardRequest.setParentTask(nodeId, task.getId());
}
shardBulkAction.execute(bulkShardRequest, new ActionListener<BulkShardResponse>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(BulkShardResponse bulkShardResponse) {
for (BulkItemResponse bulkItemResponse : bulkShardResponse.getResponses()) {
// we may have no response if item failed
if (bulkItemResponse.getResponse() != null) {
bulkItemResponse.getResponse().setShardInfo(bulkShardResponse.getShardInfo());
}
responses.set(bulkItemResponse.getItemId(), bulkItemResponse);
}
if (counter.decrementAndGet() == 0) {
finishHim();
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
// create failures for all relevant requests
for (BulkItemRequest request : requests) {
final String indexName = concreteIndices.getConcreteIndex(request.index()).getName();
DocWriteRequest<?> docWriteRequest = request.request();
responses.set(request.id(), new BulkItemResponse(request.id(), docWriteRequest.opType(),
new BulkItemResponse.Failure(indexName, docWriteRequest.type(), docWriteRequest.id(), e)));
}
if (counter.decrementAndGet() == 0) {
finishHim();
}
}
private void finishHim() {
listener.onResponse(new BulkResponse(responses.toArray(new BulkItemResponse[responses.length()]),
buildTookInMillis(startTimeNanos)));
}
});
}
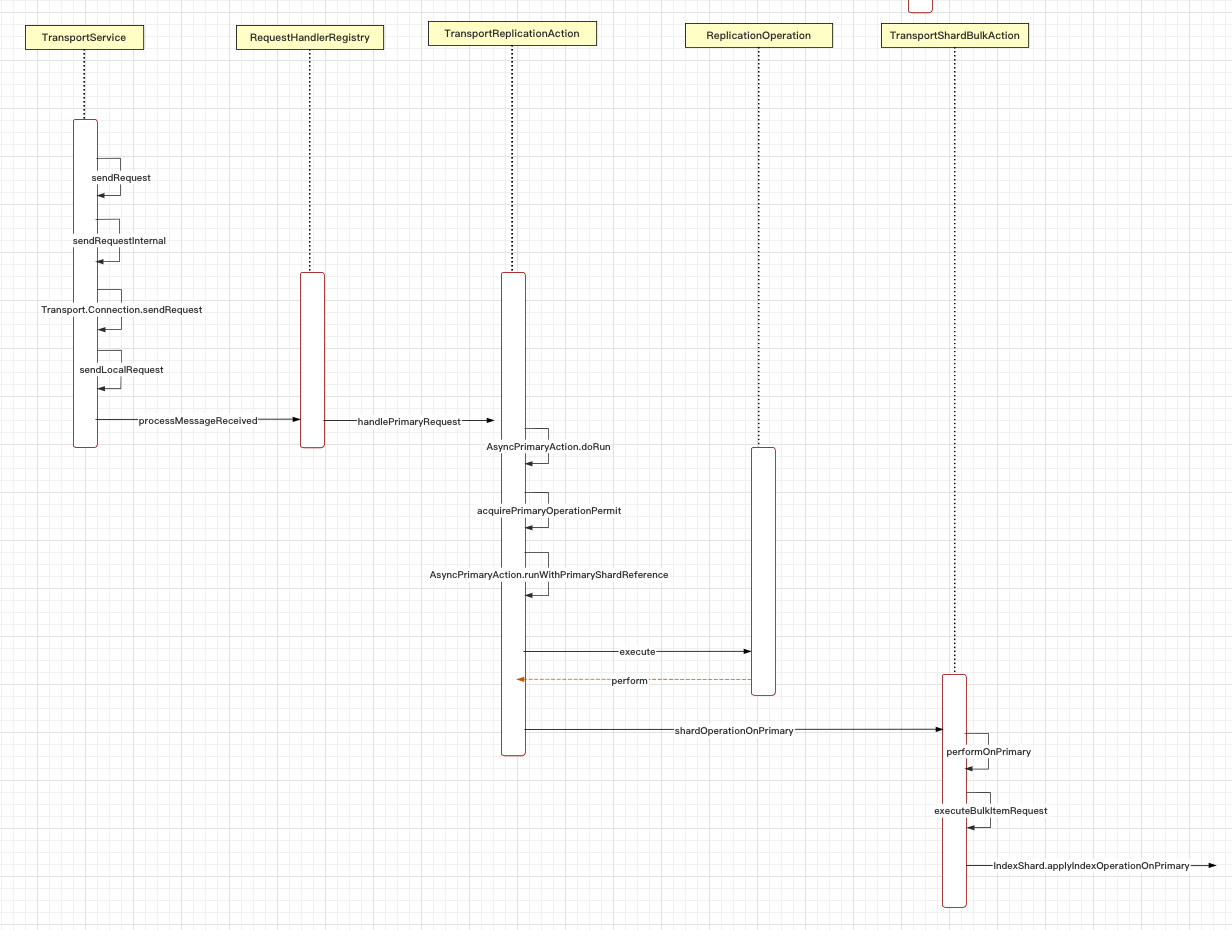
}然后看看此分片是在当前节点,还是远程节点上,现在进入routing阶段。(笔者这里只启动了一个节点,我们就看下本地节点的逻辑)
// org.elasticsearch.action.support.replication.TransportReplicationAction
protected void doRun() {
setPhase(task, "routing");
final ClusterState state = observer.setAndGetObservedState();
final String concreteIndex = concreteIndex(state, request);
final ClusterBlockException blockException = blockExceptions(state, concreteIndex);
if (blockException != null) {
if (blockException.retryable()) {
logger.trace("cluster is blocked, scheduling a retry", blockException);
retry(blockException);
} else {
finishAsFailed(blockException);
}
} else {
// request does not have a shardId yet, we need to pass the concrete index to resolve shardId
final IndexMetaData indexMetaData = state.metaData().index(concreteIndex);
if (indexMetaData == null) {
retry(new IndexNotFoundException(concreteIndex));
return;
}
if (indexMetaData.getState() == IndexMetaData.State.CLOSE) {
throw new IndexClosedException(indexMetaData.getIndex());
}
// resolve all derived request fields, so we can route and apply it
resolveRequest(indexMetaData, request);
assert request.waitForActiveShards() != ActiveShardCount.DEFAULT :
"request waitForActiveShards must be set in resolveRequest";
final ShardRouting primary = primary(state);
if (retryIfUnavailable(state, primary)) {
return;
}
final DiscoveryNode node = state.nodes().get(primary.currentNodeId());
if (primary.currentNodeId().equals(state.nodes().getLocalNodeId())) { // 根据路由确定primary在哪个node上,然后和当前node做比较
performLocalAction(state, primary, node, indexMetaData);
} else {
performRemoteAction(state, primary, node);
}
}
}既然是当前节点,那就是发送内部请求
// org.elasticsearch.transport.TransportService
private <T extends TransportResponse> void sendRequestInternal(final Transport.Connection connection, final String action,
final TransportRequest request,
final TransportRequestOptions options,
TransportResponseHandler<T> handler) {
if (connection == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("can't send request to a null connection");
}
DiscoveryNode node = connection.getNode();
Supplier<ThreadContext.StoredContext> storedContextSupplier = threadPool.getThreadContext().newRestorableContext(true);
ContextRestoreResponseHandler<T> responseHandler = new ContextRestoreResponseHandler<>(storedContextSupplier, handler);
// TODO we can probably fold this entire request ID dance into connection.sendReqeust but it will be a bigger refactoring
final long requestId = responseHandlers.add(new Transport.ResponseContext<>(responseHandler, connection, action));
final TimeoutHandler timeoutHandler;
if (options.timeout() != null) {
timeoutHandler = new TimeoutHandler(requestId, connection.getNode(), action);
responseHandler.setTimeoutHandler(timeoutHandler);
} else {
timeoutHandler = null;
}
try {
if (lifecycle.stoppedOrClosed()) {
/*
* If we are not started the exception handling will remove the request holder again and calls the handler to notify the
* caller. It will only notify if toStop hasn't done the work yet.
*
* Do not edit this exception message, it is currently relied upon in production code!
*/
// TODO: make a dedicated exception for a stopped transport service? cf. ExceptionsHelper#isTransportStoppedForAction
throw new TransportException("TransportService is closed stopped can't send request");
}
if (timeoutHandler != null) {
assert options.timeout() != null;
timeoutHandler.scheduleTimeout(options.timeout());
}
connection.sendRequest(requestId, action, request, options); // local node optimization happens upstream
...
private void sendLocalRequest(long requestId, final String action, final TransportRequest request, TransportRequestOptions options) {
final DirectResponseChannel channel = new DirectResponseChannel(localNode, action, requestId, this, threadPool);
try {
onRequestSent(localNode, requestId, action, request, options);
onRequestReceived(requestId, action);
final RequestHandlerRegistry reg = getRequestHandler(action); // 注册器模式 action -> handler
if (reg == null) {
throw new ActionNotFoundTransportException("Action [" + action + "] not found");
}
final String executor = reg.getExecutor();
if (ThreadPool.Names.SAME.equals(executor)) {
//noinspection unchecked
reg.processMessageReceived(request, channel);
} else {
threadPool.executor(executor).execute(new AbstractRunnable() {
@Override
protected void doRun() throws Exception {
//noinspection unchecked
reg.processMessageReceived(request, channel); // 处理请求
}
@Override
public boolean isForceExecution() {
return reg.isForceExecution();
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
try {
channel.sendResponse(e);
} catch (Exception inner) {
inner.addSuppressed(e);
logger.warn(() -> new ParameterizedMessage(
"failed to notify channel of error message for action [{}]", action), inner);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "processing of [" + requestId + "][" + action + "]: " + request;
}
});
}然后获取在分片上的执行请求许可
// org.elasticsearch.action.support.replication.TransportReplicationAction
protected void doRun() throws Exception {
final ShardId shardId = primaryRequest.getRequest().shardId();
final IndexShard indexShard = getIndexShard(shardId);
final ShardRouting shardRouting = indexShard.routingEntry();
// we may end up here if the cluster state used to route the primary is so stale that the underlying
// index shard was replaced with a replica. For example - in a two node cluster, if the primary fails
// the replica will take over and a replica will be assigned to the first node.
if (shardRouting.primary() == false) {
throw new ReplicationOperation.RetryOnPrimaryException(shardId, "actual shard is not a primary " + shardRouting);
}
final String actualAllocationId = shardRouting.allocationId().getId();
if (actualAllocationId.equals(primaryRequest.getTargetAllocationID()) == false) {
throw new ShardNotFoundException(shardId, "expected allocation id [{}] but found [{}]",
primaryRequest.getTargetAllocationID(), actualAllocationId);
}
final long actualTerm = indexShard.getPendingPrimaryTerm();
if (actualTerm != primaryRequest.getPrimaryTerm()) {
throw new ShardNotFoundException(shardId, "expected allocation id [{}] with term [{}] but found [{}]",
primaryRequest.getTargetAllocationID(), primaryRequest.getPrimaryTerm(), actualTerm);
}
acquirePrimaryOperationPermit( // 获取在primary分片上执行操作的许可
indexShard,
primaryRequest.getRequest(),
ActionListener.wrap(
releasable -> runWithPrimaryShardReference(new PrimaryShardReference(indexShard, releasable)),
e -> {
if (e instanceof ShardNotInPrimaryModeException) {
onFailure(new ReplicationOperation.RetryOnPrimaryException(shardId, "shard is not in primary mode", e));
} else {
onFailure(e);
}
}));
}现在进入primary阶段
// org.elasticsearch.action.support.replication.TransportReplicationAction
setPhase(replicationTask, "primary");
final ActionListener<Response> referenceClosingListener = ActionListener.wrap(response -> {
primaryShardReference.close(); // release shard operation lock before responding to caller
setPhase(replicationTask, "finished");
onCompletionListener.onResponse(response);
}, e -> handleException(primaryShardReference, e));
final ActionListener<Response> globalCheckpointSyncingListener = ActionListener.wrap(response -> {
if (syncGlobalCheckpointAfterOperation) {
final IndexShard shard = primaryShardReference.indexShard;
try {
shard.maybeSyncGlobalCheckpoint("post-operation");
} catch (final Exception e) {
// only log non-closed exceptions
if (ExceptionsHelper.unwrap(
e, AlreadyClosedException.class, IndexShardClosedException.class) == null) {
// intentionally swallow, a missed global checkpoint sync should not fail this operation
logger.info(
new ParameterizedMessage(
"{} failed to execute post-operation global checkpoint sync", shard.shardId()), e);
}
}
}
referenceClosingListener.onResponse(response);
}, referenceClosingListener::onFailure);
new ReplicationOperation<>(primaryRequest.getRequest(), primaryShardReference,
ActionListener.wrap(result -> result.respond(globalCheckpointSyncingListener), referenceClosingListener::onFailure),
newReplicasProxy(), logger, actionName, primaryRequest.getPrimaryTerm()).execute();中间的调用跳转不赘述,最后TransportShardBulkAction 调用索引引引擎
// org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.TransportShardBulkAction
static boolean executeBulkItemRequest(BulkPrimaryExecutionContext context, UpdateHelper updateHelper, LongSupplier nowInMillisSupplier,
MappingUpdatePerformer mappingUpdater, Consumer<ActionListener<Void>> waitForMappingUpdate,
ActionListener<Void> itemDoneListener) throws Exception {
final DocWriteRequest.OpType opType = context.getCurrent().opType();
final UpdateHelper.Result updateResult;
if (opType == DocWriteRequest.OpType.UPDATE) {
final UpdateRequest updateRequest = (UpdateRequest) context.getCurrent();
try {
updateResult = updateHelper.prepare(updateRequest, context.getPrimary(), nowInMillisSupplier);
} catch (Exception failure) {
// we may fail translating a update to index or delete operation
// we use index result to communicate failure while translating update request
final Engine.Result result =
new Engine.IndexResult(failure, updateRequest.version());
context.setRequestToExecute(updateRequest);
context.markOperationAsExecuted(result);
context.markAsCompleted(context.getExecutionResult());
return true;
}
// execute translated update request
switch (updateResult.getResponseResult()) {
case CREATED:
case UPDATED:
IndexRequest indexRequest = updateResult.action();
IndexMetaData metaData = context.getPrimary().indexSettings().getIndexMetaData();
MappingMetaData mappingMd = metaData.mappingOrDefault();
indexRequest.process(metaData.getCreationVersion(), mappingMd, updateRequest.concreteIndex());
context.setRequestToExecute(indexRequest);
break;
case DELETED:
context.setRequestToExecute(updateResult.action());
break;
case NOOP:
context.markOperationAsNoOp(updateResult.action());
context.markAsCompleted(context.getExecutionResult());
return true;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Illegal update operation " + updateResult.getResponseResult());
}
} else {
context.setRequestToExecute(context.getCurrent());
updateResult = null;
}
assert context.getRequestToExecute() != null; // also checks that we're in TRANSLATED state
final IndexShard primary = context.getPrimary();
final long version = context.getRequestToExecute().version();
final boolean isDelete = context.getRequestToExecute().opType() == DocWriteRequest.OpType.DELETE;
final Engine.Result result;
if (isDelete) {
final DeleteRequest request = context.getRequestToExecute();
result = primary.applyDeleteOperationOnPrimary(version, request.type(), request.id(), request.versionType(),
request.ifSeqNo(), request.ifPrimaryTerm());
} else {
final IndexRequest request = context.getRequestToExecute();
result = primary.applyIndexOperationOnPrimary(version, request.versionType(), new SourceToParse( // lucene 执行引擎
request.index(), request.type(), request.id(), request.source(), request.getContentType(), request.routing()),
request.ifSeqNo(), request.ifPrimaryTerm(), request.getAutoGeneratedTimestamp(), request.isRetry());
}3.总结
本文简单描述了es索引流程,包括了http请求是如何解析的,如何确定分片的。但是仍有许多不足,比如没有讨论远程节点是如何处理的,lucene执行引擎的细节,后面博客会继续探讨这些课题。
(四)elasticsearch 源码之索引流程分析的更多相关文章
- 渣渣菜鸡的 ElasticSearch 源码解析 —— 启动流程(下)
关注我 转载请务必注明原创地址为:http://www.54tianzhisheng.cn/2018/08/12/es-code03/ 前提 上篇文章写完了 ES 流程启动的一部分,main 方法都入 ...
- 渣渣菜鸡的 ElasticSearch 源码解析 —— 启动流程(上)
关注我 转载请务必注明原创地址为:http://www.54tianzhisheng.cn/2018/08/11/es-code02/ 前提 上篇文章写了 ElasticSearch 源码解析 -- ...
- Netty 源码学习——客户端流程分析
Netty 源码学习--客户端流程分析 友情提醒: 需要观看者具备一些 NIO 的知识,否则看起来有的地方可能会不明白. 使用版本依赖 <dependency> <groupId&g ...
- Chromium源码--网络请求流程分析
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/fangkm/p/3784660.html 本文探讨一下chromium中加载URL的流程,具体来说是从地址栏输入URL地址到通过URLR ...
- boost.asio源码剖析(三) ---- 流程分析
* 常见流程分析之一(Tcp异步连接) 我们用一个简单的demo分析Tcp异步连接的流程: #include <iostream> #include <boost/asio.hpp& ...
- vue2源码框架和流程分析
vue整体框架和主要流程分析 之前对看过比较多关于vue源码的文章,但是对于整体框架和流程还是有些模糊,最后用chrome debug对vue的源码进行查看整理出这篇文章.... 本文对vue的整体框 ...
- Android4.0源码Launcher启动流程分析【android源码Launcher系列一】
最近研究ICS4.0的Launcher,发现4.0和2.3有稍微点区别,但是区别不是特别大,所以我就先整理一下Launcher启动的大致流程. Launcher其实是贯彻于手机的整个系统的,时时刻刻都 ...
- Elasticsearch源码分析 | 单节点的启动和关闭
本文主要简要介绍Elasticsearch单节点的启动和关闭流程.Elasticsearch版本:6.3.2 相关文章 1.Google Guice 快速入门 2.Elasticsearch 中的 G ...
- elasticsearch源码分析之search模块(server端)
elasticsearch源码分析之search模块(server端) 继续接着上一篇的来说啊,当client端将search的请求发送到某一个node之后,剩下的事情就是server端来处理了,具体 ...
- Elasticsearch源码分析 - 源码构建
原文地址:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU2Njg5Nzk0NQ==&mid=2247483694&idx=1&sn=bd03afe5a ...
随机推荐
- git(新)
Git仓库的工作分区 工作区到暂存区的操作 git init :在当前文件夹创建一个文档库,自动产生一个master分支.当当前文件夹已有文档库时,不会再次创建也不会修改,只会将隐藏的.git文件夹显 ...
- GMOJ3284 [GDOI2013] 重构 题解
Description 给你一个有向图,要求重新建出一张点数相同有向图,使得点的联通关系和原图一致且边数最小. Solution 显然对于图上的一个强连通分量跑个缩点然后把每个强连通分量都变成一个环即 ...
- Spring使用注解开发及使用java类进行配置bean
Spring使用注解开发 说明 在spring4之后,想要使用注解形式,必须得要引入aop的包 在配置文件当中,还得要引入一个context约束 <?xml version="1.0& ...
- composer 报错 The "https://mirrors.aliyun.com/composer/p....json" file could not be downloaded (HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found)
[Composer\Downloader\TransportException] The "https://mirrors.aliyun.com/composer/p/provider-20 ...
- JUC(4)Callable和常用的辅助类
1.Callable 1.可以有返回值 2.可以抛出异常 3.方法不同.run()/call() future Task 细节: 1.有缓存 2.结果可能需要等待,会阻塞 2.常用的辅助类 2.1 C ...
- JUC(1)线程和进程、并发和并行、线程的状态、lock锁、生产者和消费者问题
1.线程和进程 进程:一个程序,微信.qq...程序的集合.(一个进程包含多个线程,至少包含一个线程.java默认有两个线程:主线程(main).垃圾回收线程(GC) 线程:runnable.thre ...
- 【一】ERNIE:飞桨开源开发套件,入门学习,看看行业顶尖持续学习语义理解框架,如何取得世界多个实战的SOTA效果?
参考文章: 深度剖析知识增强语义表示模型--ERNIE_财神Childe的博客-CSDN博客_ernie模型 ERNIE_ERNIE开源开发套件_飞桨 https://github.com/Pad ...
- v-for中key的作用与原理
一.虚拟DOM中key的作用 key是虚拟DOM对象的标识,当数据发生变化时,Vue会根据新数据生成新的虚拟DOM,随后Vue会对新虚拟DOM与旧虚拟DOM的差异进行比较. 二.如何选择key 最好使 ...
- Go语言核心36讲18
你很棒,已经学完了关于Go语言数据类型的全部内容.我相信你不但已经知晓了怎样高效地使用Go语言内建的那些数据类型,还明白了怎样正确地创造自己的数据类型. 对于Go语言的编程知识,你确实已经知道了不少了 ...
- Go语言核心36讲16----接口
你好,我是郝林,今天我们来聊聊接口的相关内容. 前导内容:正确使用接口的基础知识 在Go语言的语境中,当我们在谈论"接口"的时候,一定指的是接口类型.因为接口类型与其他数据类型不同 ...
