MyBatis 结果映射总结
前言
结果映射指的是将数据表中的字段与实体类中的属性关联起来,这样 MyBatis 就可以根据查询到的数据来填充实体对象的属性,帮助我们完成赋值操作。其实 MyBatis 的官方文档对映射规则的讲解还是非常清楚的,但考虑到自己马上就会成为一名 SQL Boy,以后免不了经常跟 SQL 打交道(公司使用的也是 MyBatis),所以希望用更加通俗的语言对官方文档所介绍的常用映射规则做一个总结,既为刚入门的同学提供一个参考,也方便自己以后查阅。本文会结合一些常见的应用场景,并通过简单的示例来介绍不同的映射方法。如有理解错误,还请大家批评指正!
简单字段映射
MyBatis 中的 resultType 和 resultMap 均支持结果映射,对于一些简单的映射操作,我们可以直接使用 resultType 来完成。但如果实体类中的属性为复杂类型,或者属性名和字段名无法对应,那么我们就需要使用 resultMap 来创建自定义的映射关系。下面用一个示例来演示 resultType 和 resultMap 的使用方法。
首先创建实体类 User:
@Data
public class User {
private int id;
private String userName;
private int age;
private String address;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
}
然后创建 user 表:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NOT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`address` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_create` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_modified` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 16 CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
接着向 user 表中插入数据:

配置 MyBatis,启用别名和驼峰式命名映射:
#application.yaml
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/* # 指定 mapper.xml 文件的路径,该文件用于编写 SQL 语句
type-aliases-package: com.example.entity # 设置别名,它的作用是告诉 MyBatis 需要设置别名的实体类的所在的包。默认情况下,MyBatis 会使用实体类的非限定类名来作为它的别名,如将 com.example.entity.User 的别名设置为 User 或 user(别名不区分大小写)
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true # 开启驼峰命名自动映射,如将数据表中的字段 user_name 映射到实体对象的属性 userName
创建 mapper 文件,其内容如下:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="UserMap">
select
id,
user_name,
age,
address,
gmt_create,
gmt_modified
from user
where id = #{id}
</select>
上述代码中,我们使用 resultMap 来指定 SQL 语句的出参类型。默认情况下,如果数据表的字段名与实体类的属性名完全相同(如 id 对应 id),或者二者符合驼峰式命名映射的规则(如 user_name 对应 userName),那么 MyBatis 可以直接完成赋值操作。但 gmt_create 和 gmt_modified 不会映射为 createTime 和 updateTime,因此我们需要使用 resultMap 来创建新的映射关系。如果将 user 表的字段 gmt_create 和 gmt_modified 分别改为 create_time 和 update_time,那么就可以使用 resulType="User" 或 resulType="user" 来替换 resultMap="UserMap"。
调用 findUserById(参数 id 等于 1)查询用户信息,可得到如下结果:
{
"address":"BUPT",
"age":24,
"createTime":1637164800000,
"id":1,
"updateTime":1637164800000,
"userName":"John同学"
}
利用 constructor 指定构造方法
MyBatis 查询出数据后,会调用实体类的无参构造方法创建实体对象,然后为该对象的属性赋值。有时候我们会在实体类中重载多个构造方法,例如在不同的构造方法中执行不同的初始化操作,这种情况下我们希望 MyBatis 能够调用指定的构造方法来初始化对象。此外,如果实体类中仅有带参的构造方法,那么也需要通知 MyBatis 调用指定的构造方法。对于这两个问题,我们可以使用 MyBatis 提供的 constructor 元素来解决。
MyBatis 官方文档在介绍
constructor时有提到,constructor允许我们在始化对象时就为对象的属性赋值,这样可以不用暴露出公有方法。
首先在 User 类中添加带参的构造方法:
public User(String userName, int age) {
this.userName = userName;
this.age = age;
}
然后将 mapper 文件修改为:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<constructor>
<arg column="user_name" javaType="String" />
<arg column="age" javaType="_int"/>
</constructor>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="UserMap">
select
id,
user_name,
age,
address,
gmt_create,
gmt_modified
from user
where id = #{id}
</select>
注意,<arg> 标签的定义顺序必须与构造方法中的参数顺序相同,因为 MyBatis 是根据 <constructor> 标签中的参数类型列表来匹配实体类的构造方法的,例如在本例中,匹配的构造方法为 User.<init>(java.lang.String, int)。如果将 xml 文件中的两个 <arg> 标签互换位置,那么 User 对象将不会被实例化成功,因为 User 类中并没有参数类型列表为 (int, java.lang.String) 的构造方法。如果我们不指定 javaType 属性的值,那么 MyBatis 默认将其置为 Object,此时构造方法中对应的参数类型也必须为 Object。
MyBatis 中的 _int 类型对应 Java 中的 int 类型,int 类型对应 Integer 类型。
经过上述配置,MyBatis 在实例化对象的时候就会调用我们指定的构造方法。另外,MyBatis 也支持跟据参数名称来匹配构造方法:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<constructor>
<arg column="age" name="age" javaType="_int"/>
<arg column="user_name" name="userName" javaType="String"/>
</constructor>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
</resultMap>
<arg> 标签中的 name 属性用于设置构造方法的参数名称,如果我们设置了 name 的值,那么 MyBatis 会根据该属性匹配对应的构造方法,且 <arg> 标签的位置可以随意放置。上述代码中,我们将两个 <arg> 标签互换位置,然后调用 findUserById,仍然可以查询出用户的信息。
利用 association 关联一个复杂类型
博客系统中,每个用户都担任着某种角色,如普通用户、管理员、版主等。为了更好地描述用户信息,我们需要为 User 类添加一个 Role 类型的成员变量,记录当前用户所属的角色。但 Role 类型与 String、int 等类型不同,Role 对象本身也存储了一些特定的属性,如 id、roleName 等,默认情况下 MyBatis 无法为这些属性赋值。为了能够正确初始化 Role 变量,我们需要使用 association 元素将查询到的结果与 Role 对象的属性关联起来。
首先修改 User 类/创建 Role 类:
@Data
public class User {
// 省略部分属性
private Role role;
}
@Data
public class Role {
private int id;
private String roleName;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
}
然后创建 role 表(存储角色信息)和 user_roles 表(存储用户和角色的关联信息):
# 创建 `role` 表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `role`;
CREATE TABLE `role` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`role_name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_create` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_modified` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 3 CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
# 创建 `user_roles` 表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user_roles`;
CREATE TABLE `user_roles` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`user_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`role_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_create` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_modified` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
接着向 role 表和 user_roles 表中插入数据:

MyBatis 为我们提供了三种处理子对象(如 Role 对象)的方式,分别为 嵌套结果映射、嵌套查询 和 关联多个结果集。
1. 嵌套结果映射
嵌套结果映射 指的是在 resultMap 中嵌套一个映射关系,mapper 文件的内容如下:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
<association property="role" javaType="Role">
<id column="role_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="role_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="roleName"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="UserMap">
select
u.id,
u.user_name,
u.age,
u.address,
u.gmt_create,
u.gmt_modified,
r.id as 'role_id',
r.role_name
from user as u
left join user_roles as ur on ur.user_id = u.id
left join role as r on ur.role_id = r.id
where u.id = #{id}
</select>
上述代码中,我们将查询到的 role_id 和 role_name 分别映射到 Role 对象(User 对象的属性)的 id 和 roleName。
调用 findUserById 查询用户信息,可得到如下结果:
{
"address":"BUPT",
"age":24,
"createTime":1637164800000,
"id":1,
"role":{
"id":1,
"roleName":"管理员"
},
"updateTime":1637164800000,
"userName":"John同学"
}
我们也可以将 association 中的映射关系独立出来,改写为如下形式,方便复用:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
<association property="role" column="role_id" javaType="Role" resultMap="RoleMap"/>
</resultMap>
<resultMap id="RoleMap" type="Role">
<id column="role_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="role_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="roleName"/>
</resultMap>
2. 嵌套查询
嵌套查询 指的是在 resultMap 中嵌套一个查询语句,mapper 文件的内容如下:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
<association property="role" javaType="Role" column="{user_id=id}" select="selectUserRole"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectUserRole" parameterType="Map" resultType="Role">
select
r.id,
r.role_name
from user_roles as ur
left join role as r on ur.role_id = r.id
where ur.user_id = #{user_id}
</select>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="UserMap">
select
id,
user_name,
age,
address,
gmt_create,
gmt_modified
from user
where id = #{id}
</select>
resultMap 中嵌套了一个子查询 selectUserRole,MyBatis 首先从 user 表中查询出 id、user_name 等信息,然后将 user_id 作为参数传递给 selectUserRole,selectUserRole 负责从 role 表和 user_roles 表中查询出当前用户的角色信息。column="{user_id=id}" 指的是将查询到的 id 赋值给变量 user_id,然后将 user_id 作为子查询的入参(如果直接将 id 作为入参,那么 User 对象的 id 属性将不会被赋值),如果需要传入多个参数,那么可以使用一个复合属性,如 column="{param1=value1, param2=value2}"。注意,嵌套子查询时,子查询中的 parameterType 必须设置为 Map 或省略不写。
3. 关联多个结果集
关联多个结果集 指的是一次性执行多个查询语句,并得到多个结果集,然后利用某个结果集的数据来填充对象的属性。
首先在 MySQL 数据库中创建存储过程 findUserAndRole:
-- 将结束标志符更改为 $$
delimiter $$
create procedure findUserAndRole(in user_id int)
begin
select
id,
user_name,
age,
address,
gmt_create,
gmt_modified
from user
where id = user_id;
select
r.id as role_id,
r.role_name as role_name,
ur.user_id as user_id
from user_roles as ur
left join role as r
on ur.role_id = r.id;
end $$
-- 将结束标志符改回 ;
delimiter ;
然后修改 mapper 文件的内容:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
<association property="role" javaType="Role" resultSet="role" column="id" foreignColumn="user_id">
<id column="role_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="role_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="roleName"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultSets="user,role" resultMap="UserMap" statementType="CALLABLE">
{call findUserAndRole(#{user_id,jdbcType=INTEGER,mode=IN})}
</select>
解释一下上述操作的含义,我们在存储过程 findUserAndRole 中定义了两条 SQL 语句,第一条的执行逻辑是利用 user_id 从 user 表中查询出当前用户的 id,user_name 等信息;第二条的执行逻辑是利用关联查询从 role 表和 user_roles 表中查询出 user_id、role_id 以及 role_name 等信息。我们将两次查询得到的结果集分别表示为 user 和 role,即 resultSets="user,role",然后通过 association 将结果集 role 中的 role_id 和 role_name 分别映射到 Role 对象的 id 和 roleName 属性。column="id" foreignColumn="user_id" 用于关联两个结果集中的数据,因为结果集 role 中包含了所有用户的角色信息(虽然本例中我们只设置了一个用户,但实际上结果集 role 中包含着所有用户的信息),因此在进行属性填充之前,我们需要指明利用哪一个角色信息进行属性填充,column="id" foreignColumn="user_id" 的作用就是从结果集 role 中筛选出 user_id 为 id 的角色信息。
resultSets 中不同的结果集之间用逗号分隔,中间千万不能加空格!
利用 collection 关联多个复杂类型
上文中我们分析了一个用户担任一种角色的情况,然而在实际开发中,每个用户都有可能同时担任多种角色,例如 "John同学" 既可以是管理员,又可以是版主。此时使用 association 无法正确查询出用户的角色信息,因为 association 处理的是一对一的映射关系。当需要关联多个对象时,我们需要使用 collection 元素。
首先修改实体类:
@Data
public class User {
// 省略部分属性
private List<Role> roles;
}
然后在 user_roles 表中插入一条记录:
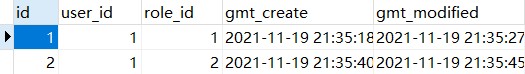
collection 的使用方法和 association 非常相似,在上文中介绍的三种方法中,我们只需要做一些简单的修改,就可以查询出用户的所有角色信息。
1. 嵌套结果映射
mapper 文件的内容如下:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
<collection property="roles" ofType="Role">
<id column="role_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="role_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="roleName"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="UserMap">
select
u.id,
u.user_name,
u.age,
u.address,
u.gmt_create,
u.gmt_modified,
r.id as 'role_id',
r.role_name
from user as u
left join user_roles as ur on ur.user_id = u.id
left join role as r on ur.role_id = r.id
where u.id = #{id}
</select>
与上文中使用 association 嵌套结果映射的区别在于,我们将 javaType 替换为了 ofType,以此来指定 Java 集合中的泛型类型。
调用 findUserById 查询用户信息,可得到如下结果:
{
"address":"BUPT",
"age":24,
"createTime":1637164800000,
"id":1,
"roles":[
{
"id":1,
"roleName":"管理员"
},
{
"id":2,
"roleName":"版主"
}
],
"updateTime":1637164800000,
"userName":"John同学"
}
2. 嵌套查询语句
mapper 文件的内容如下:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
<collection property="roles" ofType="Role" column="user_id=id" select="selectUserRole"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectUserRole" parameterType="Map" resultType="Role">
select
r.id,
r.role_name
from user_roles as ur
left join role as r on ur.role_id = r.id
where ur.user_id = #{user_id}
</select>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="UserMap">
select
id,
user_name,
age,
address,
gmt_create,
gmt_modified
from user
where id = #{id}
</select>
同样地,我们将 javaType 改为 ofType。
3. 关联多个结果集
mapper 文件的内容如下:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
<collection property="roles" ofType="Role" resultSet="roles" column="id" foreignColumn="user_id">
<id column="role_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="role_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="roleName"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultSets="user,roles" resultMap="UserMap" statementType="CALLABLE">
{call findUserAndRole(#{user_id,jdbcType=INTEGER,mode=IN})}
</select>
同理,存储过程中的执行逻辑保持不变,只需将 javaType 改为 ofType。
改用
collection后,还要注意将 property 由 role 改为 roles。当然,这个名称可自由定义。
查询具有树形结构的数据
树形结构数据在实际开发中非常常见,比较典型的就是菜单表,每个父菜单都可能包含一个或多个子菜单,而每个子菜单也可能包含孙子菜单。有时候我们希望查询出某个菜单下的所有子菜单,并分级展示,这种情况应该如何处理呢?其实上文中介绍的三种方法均支持多级结果映射,我们只需要在 mapper 文件中做一些简单的处理。
首先创建 Menu 类:
@Data
public class Menu {
private long id;
private String name;
private long parentId;
private List<Menu> childMenus;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
}
然后创建 menu 表:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `menu`;
CREATE TABLE `menu` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`parent_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_create` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_modified` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
接着向 menu 表中插入数据:
为了更直观地展示各层级菜单之间的关系,我们将数据整理在下面的表格中:
| id | name | parent_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 文章 | 0 |
| 11 | 所有文章 | 1 |
| 12 | 写文章 | 1 |
| 121 | 载入草稿 | 12 |
| 2 | 用户 | 0 |
| 21 | 个人资料 | 2 |
| 3 | 附件 | 0 |
可以看到,菜单表总共有三个层级(不包含第 0 级),第一级的 "所有文章" 下有子菜单 "写文章",第二级的 "写文章" 下有子菜单 "载入草稿"。每个层级的菜单都可能有零个、一个或多个子菜单,为了将所有的菜单查询出来,我们既要修改 SQL 语句,又要修改 resultMap 中的映射关系,下面介绍三种查询方式。
1. 嵌套结果映射
mapper 文件的内容如下:
<resultMap id="menuMap" type="Menu">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="parent_id" property="parentId"/>
<collection property="childMenus" ofType="Menu">
<id column="id2" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="name2" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name"/>
<result column="parent_id2" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="parentId"/>
<collection property="childMenus" ofType="Menu">
<id column="id3" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="name3" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name"/>
<result column="parent_id3" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="parentId"/>
</collection>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findMenus" parameterType="Map" resultMap="menuMap">
select
m1.id as id,
m1.name as name,
m1.parent_id as parent_id,
m2.id as id2,
m2.name as name2,
m2.parent_id as parent_id2,
m3.id as id3,
m3.name as name3,
m3.parent_id as parent_id3
from
menu as m1
left join menu as m2 on m1.id = m2.parent_id
left join menu as m3 on m2.id = m3.parent_id
where m1.parent_id = #{menu_id}
</select>
因为菜单表中最多有三个层级,所以我们在 SQL 语句中使用了三表联查,分别从表 m1、m2、m3(均为 menu 表)中查询出各个级别(从上到下)的菜单,然后在 collection 中新增一个嵌套,表 m2 和表 m3 中查出的数据均用于填充前一级别的 childMenus 属性。
调用 findMenus(参数 menu_id 等于 0)查询菜单信息,可得到如下结果:
[
{
"childMenus":[
{
"childMenus":[
{
"id":121,
"name":"载入草稿",
"parentId":12
}
],
"id":12,
"name":"写文章",
"parentId":1
},
{
"childMenus":[
],
"id":11,
"name":"所有文章",
"parentId":1
}
],
"id":1,
"name":"文章",
"parentId":0
},
{
"childMenus":[
{
"childMenus":[
],
"id":21,
"name":"个人资料",
"parentId":2
}
],
"id":2,
"name":"用户",
"parentId":0
},
{
"childMenus":[
],
"id":3,
"name":"附件",
"parentId":0
}
]
注意,嵌套结果映射 的方式不具备通用性,因为菜单表的结构可能不止三层。如果有多个层级的菜单,那么我们就需要继续修改 SQL 语句并新增嵌套。
2. 嵌套查询
mapper 文件的内容如下:
<resultMap id="menuMap" type="Menu">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="parent_id" property="parentId"/>
<collection column="{menu_id=id}" property="childMenus" ofType="Menu" select="findMenus"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="findMenus" parameterType="Map" resultMap="menuMap">
select
id,
name,
parent_id
from
menu
where parent_id = #{menu_id}
</select>
上述代码中,我们将嵌套的子查询设置为 findMenus 本身,MyBatis 首先调用 findMenus 查询出 parent_id 为 menu_id 的菜单,然后将查询出的菜单的 id 赋值给 menu_id,继续调用 findMenus 查询出下一层级的菜单。此种方式可以递归的查询出所有菜单,无论菜单表有多少个层级。
3. 关联多个结果集
首先创建存储过程 findMenu:
delimiter $$
create procedure findMenu(in menu_id int)
begin
select
id as id1,
name as name1,
parent_id as parent_id1
from menu
where parent_id = menu_id;
select
id as id2,
name as name2,
parent_id as parent_id2
from menu;
select
id as id3,
name as name3,
parent_id as parent_id3
from menu;
end $$
-- 将结束标志符改回 ;
delimiter ;
然后将 mapper 文件的内容修改为:
<resultMap id="MenuMap" type="Menu">
<id column="id1" property="id"/>
<result column="name1" property="name"/>
<result column="parent_id1" property="parentId"/>
<collection property="childMenus" ofType="Menu" resultSet="menu2" column="id1" foreignColumn="parent_id2">
<id column="id2" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="name2" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name"/>
<result column="parent_id2" property="parentId"/>
<collection property="childMenus" ofType="Menu" resultSet="menu3" column="id2" foreignColumn="parent_id3">
<id column="id3" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="name3" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name"/>
<result column="parent_id3" property="parentId"/>
</collection>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findMenus" parameterType="Map" resultSets="menu1,menu2,menu3" resultMap="MenuMap" statementType="CALLABLE">
{call findMenu(#{menu_id,jdbcType=INTEGER,mode=IN})}
</select>
findMenu 中定义了三条 SQL 语句,第一条的执行逻辑是从 menu 表中查询出 parent_id 为 menu_id 的菜单,其它两条的执行逻辑是从 menu 表中查询出所有的菜单。我们将三条查询返回的结果集分别表示为 menu1、menu2 和 menu3,然后利用 menu2 和 menu3 中的数据分别填充子菜单和孙子菜单的属性。
关联多个结果集 和 嵌套结果映射 一样,在查询树形结构数据时不具备通用性。若菜单表的层级大于 3,那么我们就需要修改存储过程和映射关系。
参考资料
MyBatis 官方文档
Mybatis 中强大的 resultMap
MyBatis 结果映射总结的更多相关文章
- 【Mybatis高级映射】一对一映射、一对多映射、多对多映射
前言 当我们学习heribnate的时候,也就是SSH框架的网上商城的时候,我们就学习过它对应的高级映射,一对一映射,一对多映射,多对多映射.对于SSM的Mybatis来说,肯定也是差不多的.既然开了 ...
- MyBatis 关系映射XML配置
关系映射 在我看来这些实体类就没啥太大关联关系,不就是一个sql语句解决的问题,直接多表查询就完事,程序将它设置关联就好 xml里面配置也是配置了sql语句,下面给出几个关系的小毛驴(xml) 一对多 ...
- mybatis高级映射(一对一,一对多)
mybatis高级映射 一对一关联映射 需求:查询订单信息,关联查询用户信息(一个订单对应一个用户) (1)通过resultType实现 sql语句: select orders.* , USER.u ...
- MyBatis 查询映射自定义枚举
背景 MyBatis查询若想映射枚举类型,则需要从 EnumTypeHandler 或者 EnumOrdinalTypeHandler 中选一个来使用 ...
- Mybatis sql映射文件浅析 Mybatis简介(三)
简介 除了配置相关之外,另一个核心就是SQL映射,MyBatis 的真正强大也在于它的映射语句. Mybatis创建了一套规则以XML为载体映射SQL 之前提到过,各项配置信息将Mybatis应用的整 ...
- Mybatis sql映射文件浅析 Mybatis简介(三) 简介
Mybatis sql映射文件浅析 Mybatis简介(三) 简介 除了配置相关之外,另一个核心就是SQL映射,MyBatis 的真正强大也在于它的映射语句. Mybatis创建了一套规则以XML ...
- Mybatis一对一映射
一.Mybatis一对一映射 本例讲述使用mybatis开发过程中常见的一对一映射查询案例.只抽取关键代码和mapper文件中的关键sql和配置,详细的工程搭建和Mybatis详细的流程代码可参见&l ...
- (十一)mybatis之映射器(select)
映射器 映射器的主要元素有八种: 元素名称 描述 select 查询语句,可自定义参数 insert 插入语句,执行后返回插入的条数 update 更新语句,执行后返回更新的条数 delete 删除语 ...
- Mybatis输入输出映射_动态sql_关联关系(一对一、一对多、多对多)
Mybatis输入输出映射_动态sql_关联关系(一对一.一对多.多对多)输入输出映射parameterType完成输入映射parameterType可以传入的参数有,基本数据类型(根据id查询用户的 ...
- mybatis中映射文件和实体类的关联性
mybatis的映射文件写法多种多样,不同的写法和用法,在实际开发过程中所消耗的开发时间.维护时间有很大差别,今天我就把我认为比较简单的一种映射文件写法记录下来,供大家修改建议,争取找到一个最优写法~ ...
随机推荐
- 【HTML5版】导出Table数据并保存为Excel
首发我的博客 http://blog.meathill.com/tech/js/export-table-data-into-a-excel-file.html 最近接到这么个需求,要把<tab ...
- HTML5+CSS3兼容收藏夹
CSS3选择器兼容IE6~8: Selectivizr 使用方法: <!--[if (gte IE 6)&(lte IE 8)]> <script src="htt ...
- 2D骨骼动画工具DragonBones的使用教程
怎样用更少的美术成本创造出更生动的动画效果?今天就为大家介绍一套开源的2D骨骼动画框架和工具--DragonBones,它包含了桌面骨骼动画制作工具DragonBonesPro和一套多语言版本的Dra ...
- 前端面试题整理——webpack相关考点
webpack是开发工具,面试考点重点在配置和使用,原理理解不需要太深. 一.基本配置 1.拆分配置和merge 将公共配置跟dev和prod的配置拆分,然后通过webpack-merge对配置进行整 ...
- Exception Handling Considered Harmful
异常处理被认为存在缺陷 Do, or do not. There is no try. - Yoda, The Empire Strikes Back (George Lucas) by Jason ...
- hbase增删查
代码: package cn.idcast.hbase; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.h ...
- CCF201409-3 字符串匹配
问题描述 给出一个字符串和多行文字,在这些文字中找到字符串出现的那些行.你的程序还需支持大小写敏感选项:当选项打开时,表示同一个字母的大写和小写看作不同的字符:当选项关闭时,表示同一个字母的大写和小写 ...
- Exchange 2013 清空邮箱
在某些应用场景中,需要清空用户邮箱的所有数据.如果使用Outlook web app或者Outlook 的邮件删除方式,对数以千计的邮件来说,实在不是一个好办法.exchange管理员可以使用&quo ...
- js知识梳理6:关于函数的要点梳理(2)(作用域链和闭包)
写在前面 注:这个系列是本人对js知识的一些梳理,其中不少内容来自书籍:Javascript高级程序设计第三版和JavaScript权威指南第六版,感谢它们的作者和译者.有发现什么问题的,欢迎留言指出 ...
- 阿里云申请SSL证书 并部署到SpringBoot项目
前提 有一台阿里云的服务器(安装了java环境) 有已经备案的域名,并且域名绑定上面的服务器 申请SSL证书 申请教程:https://blog.csdn.net/yunweifun/article/ ...
