JSOI Round 2题解
强行一波题解骗一个访问量好了...
http://blog.csdn.net/yanqval/article/details/51457302
http://absi2011.is-programmer.com/posts/200822.html
http://absi2011.is-programmer.com/posts/200920.html
orz js省队神犇↑
Day1
最佳团队(team)
给一个n+1个点的树,每个点有价值pi和费用si,求一个包含根的大小为m+1的联通块,使价值和/费用和最大。
为什么是n+1和m+1呢?根节点是0,节点从0开始编号。
1<=m<=n<=2500,0<si,pi<=10000。
首先这是一个01分数规划,我们二分答案x之后就变成了每个点权为p-s*x,判断是否存在一个包含根的正权联通块。
其实就是问联通块的最大权值。这个有两种做法。
第一种是暴力树形背包dp,每一次只循环到子树大小,由于这里物品重量都相当于是1,可以证明复杂度是O(n^2)的。
第二种之前写过,一类有依赖的属性背包dp方法。
事实上第二种还更好写~
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
#define SZ 2600
int m,n,s[SZ],p[SZ],fa[SZ],fc[SZ],nc[SZ],siz[SZ],qs[SZ],qn=0;
void dfs(int p)
{
qs[++qn]=p; siz[p]=1;
for(int c=fc[p];c;c=nc[c]) dfs(c), siz[p]+=siz[c];
}
double f[SZ][SZ];
bool ok(double x)
{
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) f[n+2][j]=-20000000000000LL;
for(int i=n+1;i>=1;i--)
{
f[i][0]=0;
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++) f[i][j]=max(f[i+1][j-1]+p[qs[i]]-s[qs[i]]*x,f[i+siz[qs[i]]][j]);
}
return f[1][m]>1e-7;
}
#define FO(x) {freopen(#x".in","r",stdin);freopen(#x".out","w",stdout);}
int main()
{
FO(team)
scanf("%d%d",&m,&n); ++m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",s+i,p+i,fa+i);
nc[i]=fc[fa[i]]; fc[fa[i]]=i;
}
dfs(0);
double l=0,r=10007;
double jd=(1e-5)*3;
while(r-l>jd)
{
double m=(l+r)/2;
if(ok(m)) l=m; else r=m;
}
printf("%.3lf",l);
}
独特的树叶(leaf)
给定一个大小为n的树A和大小为n+1的树B,已知B是由A加上一个叶子并打乱节点编号构成的,求这个叶子。如果有多个输出编号最小的。
1<=n<=10^5
教你hash正确姿势系列
我们首先可以想到,假设我们有一种非常靠谱的hash姿势可以在比较靠谱的时间内求出一棵树以每个点为根的hash值。
这样我们只要枚举每一个叶子,把它的父向边以一种比较靠谱的方式删掉,在map里查一下hash值就行了。
那至于这个“比较靠谱的hash姿势”,其实还比较难想...
吴大爷告诉了我一个比较靠谱的hash方法,我们设dp(i,j)为(i,j)这条边的hash值(别问我为什么要以边为单位定义hash值)
我们让$dp(i,j)={(\sum_{p\not=i}{dp(j,p)}+233)}^{666623333}$模上一个大质数。可以发现这个做法是十分靠谱的。(而且666623333是一个质数)
至于以每个点x为根,只要再统计一下$(\sum_{p}{dp(x,p)}+233)^{666623333}$就行了。
那至于删掉父向边...我们发现我们并不需要真的删掉它,只需要计算这条边的hash值就行了。
//代码等测试过了再补
扭动的回文串(palindrome)
给两个长度为n的字符串A和B,求由A的[i,j]拼接上B的[j,k]组成的最长回文串。
需要注意的是,也可以只由A或B中的一截组成回文串。
首先我们可以用hash或manacher求出A或B的最长回文串,以及以每个位置为中心的极大回文串(就是不能再扩展的那种)。
假设我们现在有一坨A或B中的极大回文串,我们可以发现一个事情,那就是如果经过了这样一个“扭动”的过程,一定是A的一段+A的一个极大回文串+B的一段 或者 A的一段+B的一个极大回文串+B的一段 这种形式。证明就算了。
然后我们hash乱搞一波就行了。
//强行卡常系列
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <memory.h>
using namespace std;
#define SZ 233333
#define UP 200001
typedef long long ll;
int jz=31,cm[SZ];
struct Hasher
{
char s[SZ+1]; int n;
int hash[SZ+1],fhash[SZ+1];
char* str() {return s+1;}
void pre1()
{
n=strlen(s+1);
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--) hash[i]=hash[i+1]+cm[n-i]*(s[i]-'A'+2);
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--) fhash[i]=fhash[i+1]+cm[n-i]*(s[n+1-i]-'A'+2);
}
int ghash(int l,int r)
{
return (hash[l]-hash[r+1])*cm[r];
}
int gfhash(int l,int r)
{
l=n-l+1; r=n-r+1; l^=r; r^=l; l^=r;
return (fhash[l]-fhash[r+1])*cm[r];
}
int hl[SZ],hr[SZ],hs;
Hasher() {hs=0;}
void pre2()
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int l=0,r=min(n-i,i-1);
while(l<r)
{
int m=l+r+1>>1;
if(gfhash(i-m,i)!=ghash(i,i+m)) r=m-1; else l=m;
}
++hs; hl[hs]=i-l; hr[hs]=i+r;
}
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
if(s[i]!=s[i+1]) continue;
int l=0,r=min(n-i+1,i-1);
while(l<r)
{
int m=l+r+1>>1;
if(gfhash(i-m,i)!=ghash(i+1,i+1+m)) r=m-1; else l=m;
}
++hs; hl[hs]=i-l; hr[hs]=i+1+r;
}
}
void pre12()
{
pre1(); pre2();
}
}ha,hb;
#define FO(x) {freopen(#x".in","r",stdin);freopen(#x".out","w",stdout);}
int main()
{
FO(palindrome)
int n;
cm[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=UP;i++) cm[i]=cm[i-1]*jz;
scanf("%d\n",&n);
gets(ha.str());
gets(hb.str());
ha.pre12(); hb.pre12();
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=ha.hs;i++)
{
int l=ha.hl[i],r=ha.hr[i];
int el=0,er=min(l-1,n-r+1);
if(r-l+1+2*er<=ans) continue;
while(el<er)
{
int em=el+er+1>>1;
if(ha.gfhash(l-em,l-1)!=hb.ghash(r,r+em-1)) er=em-1; else el=em;
}
ans=max(ans,r-l+1+2*el);
}
for(int i=1;i<=hb.hs;i++)
{
int l=hb.hl[i],r=hb.hr[i];
int el=0,er=min(l,n-r);
if(r-l+1+2*er<=ans) continue;
while(el<er)
{
int em=el+er+1>>1;
if(ha.gfhash(l-em+1,l)!=hb.ghash(r+1,r+em)) er=em-1; else el=em;
}
ans=max(ans,r-l+1+2*el);
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}
Day2
病毒感染(virus)
原题目简直鬼畜...以下仅作参考,不保证正确性
有n个点排成一排,每个点有一个权值ai。初始时在1号点,在i号点时有三种操作:令ai=0,左移一步,右移一步。每次操作后要付出sigma(ai)的代价。如果经过一个点,没有令这个点的ai=0,并且之后某一步选择往左走,那么必须令这个点的ai=0后才能远离这个点。求令所有ai=0的最小代价。
1<=n<=3000。
因为我还不会做所以还是不要瞎bb比较好...不过听说是个沙茶dp?
反质数序列(prime)
给一个长度为n的序列,要求找出一个长度最长的满足任意两个数加起来均不为质数的最长子序列,输出长度。
1<=n<=3000,1<=ai<=10^5。
可以发现,如果我们把“不为质数”的关系列出来,似乎是叫我们找最大团。
虽然最大团是NP的(虽然可以用一些分支定界搜索之类的奇技淫巧卡过去)但是我们可以发现最大团=补图的最大独立集。
补图?任意两个数加起来均为质数?似乎必然是一奇一偶?
哦好像还有1+1=2,但是我们如果开头把所有的1去成只剩一个1,那么补图必然边都是一奇连一偶。
那么这就是一个二分图拉,最大独立集=n-最大匹配。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <memory.h>
using namespace std;
int n,a[233333];
bool ip[233333];
namespace Matcher
{
#define SZ 666666
#define ES 36000005
int M=1;typedef long long ll;
int fst[SZ],nxt[ES],vb[ES],n1,n2;
bool cap[ES];
void _ad_dl(int a,int b,int c) {++M;nxt[M]=fst[a];fst[a]=M;vb[M]=b;cap[M]=c;}
void ad_dl(int a,int b,int c) {_ad_dl(a,b,c); _ad_dl(b,a,0); /*cout<<a<<"->"<<b<<";\n";*/}
int S,T,q[SZ],d[SZ];
bool bfs()
{
memset(d,-1,sizeof(d));
d[S]=0; q[1]=S; int h=1,t=2;
while(h!=t)
{
int cur=q[h++];
for(int e=fst[cur];e;e=nxt[e])
{
int b=vb[e];
if(d[b]==-1&&cap[e]) d[b]=d[cur]+1, q[t++]=b;
}
}
return d[T]!=-1;
}
int dfs(int x,int f)
{
if(f<=0) return 0;
if(x==T) return f;
int ca=0;
for(int e=fst[x];e;e=nxt[e])
{
int b=vb[e];
if(d[b]!=d[x]+1) continue;
int w=dfs(b,min((int)cap[e],f-ca));
cap[e]-=w; cap[e^1]+=w; ca+=w;
if(ca==f) break;
}
if(!ca) d[x]=-1;
return ca;
}
#define inf 1000000000
int dinic()
{
int ans=0;
while(bfs()) ans+=dfs(S,inf);
return ans;
}
}
#define FO(x) {freopen(#x".in","r",stdin);freopen(#x".out","w",stdout);}
int main()
{
FO(prime)
scanf("%d",&n);
bool yi=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",a+i);
if(a[i]==1)
{
if(!yi) yi=1;
else {--i; --n;}
}
}
for(int i=2;i<=200000;i++)
{
bool np=0;
for(int j=2;j*j<=i;j++)
{
if(i%j==0) {np=1; break;}
}
ip[i]=!np;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(ip[a[i]+a[j]])
{
if(a[i]%2!=0) Matcher::ad_dl(j,i,1);
else Matcher::ad_dl(i,j,1);
}
}
}
Matcher::S=n+1; Matcher::T=n+2;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(a[i]%2==0) Matcher::ad_dl(n+1,i,1);
else Matcher::ad_dl(i,n+2,1);
}
printf("%d\n",n-Matcher::dinic());
}
炸弹攻击2(attack2)
X轴上方有A个a点,X轴下方有B个b点和C个c点。求四元组(ai,bj,ck,cl)的对数,其中k<l且aibj与ckcl相交。保证不存在重点和三点共线。
1<=A,B,C<=800,0<=|x|,|y|<=10^9
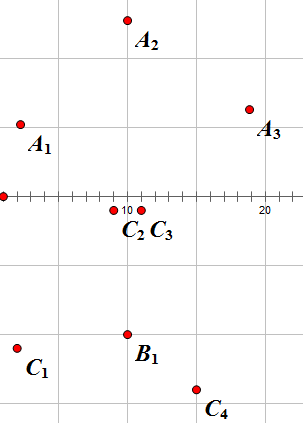
 样例图(为了观察方便,有压缩,实际上A点的y坐标没这么小)
样例图(为了观察方便,有压缩,实际上A点的y坐标没这么小)
一个比较直观的想法是,对于一个b点,我们可以枚举所有的c点对,然后首先连线要在b的上方,那么计入答案的就会是极角序上的一段区间。我们把a和c的极角序排一下,前缀和啥的搞搞,就可以得到一个...O(n^3)的优秀算法了!这样就可以得到50分(虽然性价比不是很高啊,这个东西实际上并不是很好写)
那么我们发现我们对于某一个c点,假设以它作为连线的一端,然后极角序sort完之后,可以发现“连线在b的上方”是从这个c点开始逆时针的一串,所以这个玩意儿是满足二分性质的。
那么我们可以发现对于每一个c点作为一端点另外一头能到哪里了,接下来我们发现这个东西对于中间极角分成的每一段a的贡献大概是像1 2 3 4 5这样的一个等差数列。
我们只要想办法维护一个等差数列啥的就行。
注意到兹磁离线,那么比如要在[2,4]这样弄一个等差数列,那就把[2,4]这个区间+1,[5]这个位置-3,然后求一个前缀和就完事了。
注意到区间加法这种东西离线也是可以兹磁O(1)的,例如[a,b]+1,只要[a]+1,[b+1]-1,前缀和一发就行。
当然这题的等差数列加法更为蛋疼,因为它是环状的...但是认真想想还是能写的。
所以这样我们就可以得到一个非常靠谱的O(n^2logn)的做法啦。
(还好这题没有共线,不然这题写起来简直**)
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
typedef double ld;
ld pi=acos(-1),eps=1e-6;
int pp(ld x)
{
if(x>eps) return 1;
if(x<-eps) return -1;
return 0;
}
ld cl(ld x) //return [0,2pi)
{
while(pp(x)<0) x+=pi*2;
while(pp(x-pi*2)>=0) x-=pi*2;
return x;
}
typedef pair<ld,ld> pnt;
#define _1 first
#define _x first
#define _2 second
#define _y second
ld ang(pnt x) {return cl(atan2(x._y,x._x));}
pnt operator + (pnt a,pnt b) {return pnt(a._x+b._x,a._y+b._y);}
pnt operator - (pnt a,pnt b) {return pnt(a._x-b._x,a._y-b._y);}
#define SZ 666666
int an,bn,cn;
pnt as[SZ],bs[SZ],cs[SZ],mb;
int aid[SZ],cid[SZ];
ld dgci[SZ],dga[SZ],dgc[SZ];
int cnt[SZ],qzh[SZ];
bool cmpa(int a,int b) {return dga[a]<dga[b];}
bool cmpc(int a,int b) {return dgc[a]<dgc[b];}
void add(int l,int r,int x)
{
if(r<0||l>r) return;
qzh[l]+=x; qzh[r+1]-=x;
}
void dj_add(int l,int r) //递减add [l,r)
{
if(l==r) return;
if(l<=r)
{
add(l,r-1,1);
add(l-1,l-1,l-r);
}
else
{
int tot=cn-l+r;
add(0,r-1,1);
add(l,cn-1,1);
add(l-1,l-1,-tot);
add(cn-1,cn-1,r);
}
}
#define FO(x) {freopen(#x".in","r",stdin);freopen(#x".out","w",stdout);}
int main()
{
FO(attack2)
scanf("%d",&an);
for(int i=0;i<an;i++) scanf("%lf%lf",&as[i]._x,&as[i]._y), aid[i]=i;
scanf("%d",&bn);
for(int i=0;i<bn;i++) scanf("%lf%lf",&bs[i]._x,&bs[i]._y);
scanf("%d",&cn);
for(int i=0;i<cn;i++) scanf("%lf%lf",&cs[i]._x,&cs[i]._y), cid[i]=i;
long long ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<bn;i++)
{
mb=bs[i];
for(int j=0;j<an;j++) dga[j]=ang(as[j]-mb);
cnt[cn]=qzh[cn]=0;
for(int j=0;j<cn;j++) dgc[j]=ang(cs[j]-mb), cnt[j]=qzh[j]=0;
sort(aid,aid+an,cmpa);
sort(cid,cid+cn,cmpc);
for(int j=0;j<cn;j++) dgci[j]=dgc[cid[j]];
for(int j=0;j<an;j++)
{
ld x=dga[aid[j]];
int bl=0;
if(x<dgci[0]||x>dgci[cn-1]) bl=cn-1;
else bl=upper_bound(dgci,dgci+cn,x)-dgci-1;
++cnt[bl];
}
for(int j=0;j<cn;j++)
{
ld tg=cl(dgci[j]+pi);
int tp=upper_bound(dgci,dgci+cn,tg)-dgci-1;
tp=(tp%cn+cn)%cn;
dj_add(j,tp);
}
for(int j=1;j<=cn;j++) qzh[j]+=qzh[j-1];
for(int j=cn-1;j>=0;j--) qzh[j]+=qzh[j+1];
for(int j=0;j<cn;j++) ans+=(long long)(qzh[j])*cnt[j];
}
cout<<ans<<"\n";
}
JSOI Round 2题解的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #556 题解
Codeforces Round #556 题解 Div.2 A Stock Arbitraging 傻逼题 Div.2 B Tiling Challenge 傻逼题 Div.1 A Prefix S ...
- LibreOJ β Round #2 题解
LibreOJ β Round #2 题解 模拟只会猜题意 题目: 给定一个长为 \(n\) 的序列,有 \(m\) 次询问,每次问所有长度大于 \(x\) 的区间的元素和的最大值. \(1 \leq ...
- Codeforces Round #569 题解
Codeforces Round #569 题解 CF1179A Valeriy and Deque 有一个双端队列,每次取队首两个值,将较小值移动到队尾,较大值位置不变.多组询问求第\(m\)次操作 ...
- Codeforces Round #557 题解【更完了】
Codeforces Round #557 题解 掉分快乐 CF1161A Hide and Seek Alice和Bob在玩捉♂迷♂藏,有\(n\)个格子,Bob会检查\(k\)次,第\(i\)次检 ...
- CFEducational Codeforces Round 66题解报告
CFEducational Codeforces Round 66题解报告 感觉丧失了唯一一次能在CF上超过wqy的机会QAQ A 不管 B 不能直接累计乘法打\(tag\),要直接跳 C 考虑二分第 ...
- Google kickstart 2022 Round A题解
Speed Typing 题意概述 给出两个字符串I和P,问能否通过删除P中若干个字符得到I?如果能的话,需要删除字符的个数是多少? 数据规模 \[1≤|I|,|P|≤10^5 \] 双指针 设置两个 ...
- Codeforces Beta Round #62 题解【ABCD】
Codeforces Beta Round #62 A Irrational problem 题意 f(x) = x mod p1 mod p2 mod p3 mod p4 问你[a,b]中有多少个数 ...
- “玲珑杯”ACM比赛 Round #12题解&源码
我能说我比较傻么!就只能做一道签到题,没办法,我就先写下A题的题解&源码吧,日后补上剩余题的题解&源码吧! A ...
- “玲珑杯”ACM比赛 Round #19题解&源码【A,规律,B,二分,C,牛顿迭代法,D,平衡树,E,概率dp】
A -- simple math problem Time Limit:2s Memory Limit:128MByte Submissions:1599Solved:270 SAMPLE INPUT ...
随机推荐
- Android Studio Gradle Build Running 特别慢的问题探讨
本文的本本win7 64bit 6G android studio2.1 在运行程序的时候Gradle Build Running 特别慢,一个helloworld都快2min了 1.开启gradle ...
- 三种经典iPhone上网络抓包方法详解
此文章来自:听云博客 很多时候需要网络抓包分析,在iPhone上抓包稍有不同,下面介绍三种常用的方式.分析工具以wireshark为例. 一.最简单的方式:用PC作为热点,在PC上抓包 优点:简单 缺 ...
- 【代码笔记】iOS-时间选择框
一, 效果图. 二,工程图. 三,代码. RootViewController.h #import <UIKit/UIKit.h> @interface RootViewControlle ...
- GCD中的dispatch_barrier_async函数的使用(栅栏函数)
<一>什么是dispatch_barrier_async函数 毫无疑问,dispatch_barrier_async函数的作用与barrier的意思相同,在进程管理中起到一个栅栏的作用,它 ...
- OBST(Optimal Binary Tree最优二叉搜索树)
二叉搜索树 二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree),(又:二叉搜索树,二叉排序树)它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树: 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的 ...
- yii2 rbac权限控制详细操作步骤
作者:白狼 出处:http://www.manks.top/article/yii2_rbac_description本文版权归作者,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出 ...
- Maven基础配置--nexus私服配置
登录nexus私服后台,按照下图1-3的顺序进行添加仓库: 其中步骤3有三种仓库类型(Type)进行选择 1. Hosted Repository:本地仓库,在私服服务器上存放用户自行上传的jar包: ...
- SSIS技巧--优化数据流缓存
问题 我们经常遇到一种情况,在SSMS中运行很慢的一个查询,当把查询转化成从源到目的数据库的SSIS数据流以后,需要花费几倍的时间!源和数据源都没有任何软硬件瓶颈,并且没有大量的格式转换.之前看了很多 ...
- JSON格式互转集合
在工作中我们经常会遇到格式转换的问题,有的时候是将JSON转换成DataTable.DataSet或是List等,也有可能将DataTable.DataSet或是List转换成JSON的,抽了点时间把 ...
- hadoop2.6分布式部署时 livenodes等于1的原因
1.问题描述 在进行hadoop2.x版本的hdfs分布式部署时,遇到了一个奇怪的问题: 使用start-dfs.sh命令启动dfs之后,所有的datanode节点上均能看到datanode进程,然而 ...
