死锁,线程协作(同步,阻塞队列,Condition,管道流)
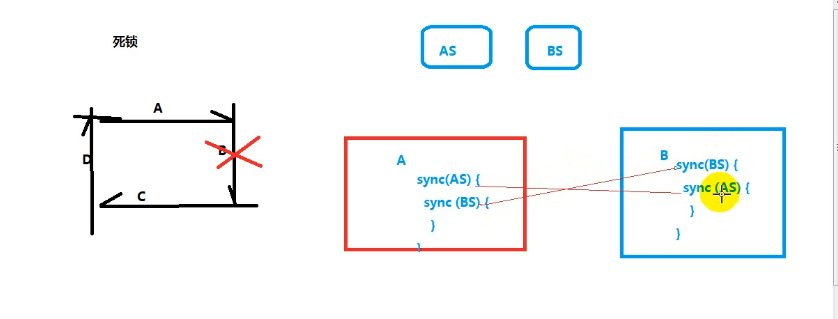
synchronized死锁
package com.thread.demo.deadlock;
public class DeadLock {
private static Object lock1 = new Object();
private static Object lock2 = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建线程1
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (lock1) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获取到lock1这把锁");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "等待lock2锁..........");
synchronized (lock2) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获取到lock2这把锁");
}
}
}
}
}, "A线程").start();
// 创建的线程2
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (lock2) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获取到lock2这把锁");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "等待lock1锁..........");
synchronized (lock1) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获取到lock1这把锁");
}
}
}
}
}, "B线程").start();
}
}
ReentrantLock死锁
package com.thread.demo.deadlock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class ReentrantDeadLock {
private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new MyRunnable(lock), "一线程").start();
new Thread(new MyRunnable(lock), "二线程").start();
} } class MyRunnable implements Runnable { private Lock lock;
private static int count = 0; public MyRunnable(Lock lock) {
this.lock = lock;
} @Override
public void run() {
lock.lock(); try {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) {
count++; if (i == 100000) {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":count=" + count);
} catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
} } }
wait,notify,notifyAll 必须结合synchronized关键字使用
package com.thread.demo.cooperation; /**
* wait,notify,notifyAll 必须结合synchronized关键字使用
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建共享池
Container container = new Container();
new MyThread(container).start();
new MyThread(container).start();
new MyThread(container).start();
new MyThread1(container).start();
new MyThread1(container).start();
new MyThread1(container).start();
}
} class MyThread extends Thread {
private Container container; public MyThread(Container container) {
this.container = container;
} @Override
public void run() {
container.get();
}
} class MyThread1 extends Thread {
private Container container; public MyThread1(Container container) {
this.container = container;
} @Override
public void run() {
container.put();
}
} class Container {
boolean flag = true; public synchronized void put() {
while (true) {
if (!flag) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "放入内容.......");
flag = false;
// 唤醒拿内容线程
notifyAll();
}
} public synchronized void get() {
while (true) {
if (flag) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "拿出内容.......");
flag = true;
notifyAll();
}
}
}
使用synchronized实现生产消费者模式
package com.thread.demo.cooperation; /**
* 使用synchronized实现生产消费者模式
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AppleContainer container = new AppleContainer();
new Thread(new Producer(container),"AA").start();
new Thread(new Consumer(container),"BB").start();
}
} // 生产者
class Producer implements Runnable { private AppleContainer container; public Producer(AppleContainer container) {
this.container = container;
} @Override
public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
System.out.println("生产----------------------苹果:" + (i+1));
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} container.increace();
}
}
} // 消费者
class Consumer implements Runnable { private AppleContainer container; public Consumer(AppleContainer container) {
this.container = container;
} @Override
public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"消费----------------------苹果:" + (i+1));
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
} container.decreace();
} }
} class AppleContainer {
private int apple; public synchronized void increace() {
if (apple == 5) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} }
apple++;
System.out.println("生产有苹果:"+apple);
notifyAll();
} public synchronized void decreace() {
if (apple == 0) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
apple--;
System.out.println("消费有苹果:"+apple);
notifyAll();
}
}
使用阻塞队列实现生产消费者模式
package com.thread.demo.cooperation; import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue; /**
* 使用阻塞队列实现生产消费者模式
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建阻塞队列(先进先出)
BlockingQueue<Integer> proQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(4);
new Thread(new ProducerQueue(proQueue),"AA").start();
new Thread(new ConsumerQueue(proQueue),"BB").start();
}
} class ProducerQueue implements Runnable { private BlockingQueue<Integer> proQueue; public ProducerQueue(BlockingQueue<Integer> proQueue) {
this.proQueue = proQueue;
} @Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("生产了编号为:"+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
proQueue.put(i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} } class ConsumerQueue implements Runnable { private BlockingQueue<Integer> proQueue; public ConsumerQueue(BlockingQueue<Integer> proQueue) {
this.proQueue = proQueue;
} @Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
System.out.println("消费了编号为:"+proQueue.take());
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} }
} }
lock实现生产消费者模式
package com.thread.demo.cooperation; import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Basket b = new Basket();
Product p = new Product(b);
ConsumerCondition c = new ConsumerCondition(b);
ConsumerCondition c1 = new ConsumerCondition(b);
new Thread(p,"生产者1").start();
new Thread(c,"消费者1").start();
new Thread(c1,"消费者2").start();
}
} // 馒头
class ManTou {
int id; public ManTou(int id) {
this.id = id;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "ManTou" + id;
}
} // 装馒头的篮子
class Basket {
int max = 6;
LinkedList<ManTou> manTous = new LinkedList<ManTou>();
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); // 锁对象
Condition full = lock.newCondition(); // 用来监控篮子是否满的Condition实例
Condition empty = lock.newCondition(); // 用来监控篮子是否空的Condition实例
// 往篮子里面放馒头 public void push(ManTou m) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (max == manTous.size()) {
System.out.println("篮子是满的,待会儿再生产...");
full.await(); // wait
}
manTous.add(m);
empty.signalAll(); // notfiy
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} // 往篮子里面取馒头
public ManTou pop() {
ManTou m = null;
lock.lock();
try {
while (manTous.size() == 0) {
System.out.println("篮子是空的,待会儿再吃...");
empty.await();
}
m = manTous.removeFirst();
full.signalAll();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock(); }
return m;
}
} // 生产者
class Product implements Runnable {
Basket basket; public Product(Basket basket) {
this.basket = basket;
} public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
ManTou m = new ManTou(i);
basket.push(m);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"生产了" + m);
try {
Thread.sleep((int) (Math.random() * 2000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} }
}
} // 消费者
class ConsumerCondition implements Runnable {
Basket basket; public ConsumerCondition(Basket basket) {
this.basket = basket;
} public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep((int) (Math.random() * 2000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ManTou m = basket.pop();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"消费了" + m);
}
}
}
管道输入输出流实现生产消费者模式
package com.thread.demo.cooperation; import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PipedInputStream;
import java.io.PipedOutputStream; public class Demo5 { public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 创建管道输出流
*/
PipedOutputStream pos = new PipedOutputStream();
/**
* 创建管道输入流
*/
PipedInputStream pis = new PipedInputStream();
try {
/**
* 将管道输入流与输出流连接 此过程也可通过重载的构造函数来实现
*/
pos.connect(pis);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/**
* 创建生产者线程
*/
PipeProducer p = new PipeProducer(pos, "CCC");
/**
* 创建消费者线程
*/
PipeProducerConsumer c1 = new PipeProducerConsumer(pis, "AAA");
PipeProducerConsumer c2 = new PipeProducerConsumer(pis, "BBB");
/**
* 启动线程
*/
p.start();
c1.start();
c2.start();
}
} /**
* 生产者线程(与一个管道输入流相关联)
*
*/
class PipeProducer extends Thread {
private PipedOutputStream pos; public PipeProducer(PipedOutputStream pos, String name) {
super(name);
this.pos = pos; } public void run() {
int i = 0;
try {
while (true) {
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "product:" + i);
pos.write(i);
i++;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} /**
* 消费者线程(与一个管道输入流相关联)
*
*/
class PipeProducerConsumer extends Thread {
private PipedInputStream pis; public PipeProducerConsumer(PipedInputStream pis, String name) {
super(name);
this.pis = pis;
} public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "consumer1:" + pis.read());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
死锁,线程协作(同步,阻塞队列,Condition,管道流)的更多相关文章
- 一天十道Java面试题----第三天(对线程安全的理解------>线程池中阻塞队列的作用)
这里是参考B站上的大佬做的面试题笔记.大家也可以去看视频讲解!!! 文章目录 21.对线程安全的理解 22.Thread和Runnable的区别 23.说说你对守护线程的理解 24.ThreadLoc ...
- java 线程池线程忙碌且阻塞队列也满了时给一个拒接的详细报告
线程池线程忙碌且阻塞队列也满了时给一个拒接的详细报告.下面是一个自定义的终止策略类,继承了ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy类并覆盖了rejectedExecution方法把 ...
- c++ 同步阻塞队列
参考:<C++11深入应用> 用同步阻塞队列解决生产者消费者问题. 生产者消费者问题: 有一个生产者在生产产品,这些产品将提供给若干个消费者去消费,为了使生产者和消费者能并发执行,在两者之 ...
- 线程高级应用-心得7-java5线程并发库中阻塞队列Condition的应用及案例分析
1.阻塞队列知识点 阻塞队列重要的有以下几个方法,具体用法可以参考帮助文档:区别说的很清楚,第一个种方法不阻塞直接抛异常:第二种方法是boolean型的,阻塞返回flase:第三种方法直接阻塞. 2. ...
- 源码剖析ThreadPoolExecutor线程池及阻塞队列
本文章对ThreadPoolExecutor线程池的底层源码进行分析,线程池如何起到了线程复用.又是如何进行维护我们的线程任务的呢?我们直接进入正题: 首先我们看一下ThreadPoolExecuto ...
- Java:阻塞队列
Java:阻塞队列 本笔记是根据bilibili上 尚硅谷 的课程 Java大厂面试题第二季 而做的笔记 1. 概述 概念 队列 队列就可以想成是一个数组,从一头进入,一头出去,排队买饭 阻塞队列 B ...
- 阻塞队列---ArrayBlockingQueue,LinkedBlockingQueue,DelayQueue源码分析
阻塞队列和非阻塞队列阻塞队列和非阻塞队列的区别:阻塞队列可以自己阻塞,非阻塞队列不能自己阻塞,只能使用队列wait(),notify()进行队列消息传送.而阻塞队列当队列里面没有值时,会阻塞直到有值输 ...
- java高并发系列 - 第25天:掌握JUC中的阻塞队列
这是java高并发系列第25篇文章. 环境:jdk1.8. 本文内容 掌握Queue.BlockingQueue接口中常用的方法 介绍6中阻塞队列,及相关场景示例 重点掌握4种常用的阻塞队列 Queu ...
- 【JUC】阻塞队列&生产者和消费者
阻塞队列 线程1往阻塞队列添加元素[生产者] 线程2从阻塞队列取出元素[消费者] 当队列空时,获取元素的操作会被阻塞 当队列满时,添加元素的操作会被阻塞 阻塞队列的优势:在多线程领域,发生阻塞时,线程 ...
随机推荐
- 第三章 Python函数
函数 如果在开发程序时,需要某块代码多次,但是为了提⾼编写的效率以及代码的重⽤,所以把具有独⽴功能的代码块组织为⼀个⼩模块,这就是函数 函数的定义 函数定义的三种方式:无参函数,有参函数,空函数 #无 ...
- 前端dom操作竟然使得http请求的时间延长了
最近在项目中遇到了一个奇怪的问题:在google浏览器的调试窗口network下看到一个请求的时间一直是2s多,但是当我把这个请求单独拿出来执行的时候发现根本用不了2s,100多毫秒就完成了.最后再不 ...
- zabbix-agent端自定义监控项(free -m)服务器内存使用率
Agent端操作 [root@agent ~]# vim /usr/local/zabbix/etc/zabbix_agentd.conf 末行追加 UserParameter=memory_user ...
- 11、E-commerce in Your Inbox:Product Recommendations at Scale-----产品推荐(prod2vec和user2vec)
一.摘要 本文提出一种方法,将神经语言模型应用在用户购买时间序列上,将产品嵌入到低维向量空间中.结果,具有相似上下文(即,其周围购买)的产品被映射到嵌入空间中附近的向量. 二.模型: 低维项目向量表示 ...
- 小学生绞尽脑汁也学不会的python(面对对象-----成员)
小学生绞尽脑汁也学不会的python(面对对象-----成员) 成员 class Person: def __init__(self, name, num, gender, birthday): # ...
- linux环境下删除包含特殊字符的文件或目录
linux环境下删除包含特殊字符的文件或目录 ls -liUse find command as follows to delete the file if the file has inode nu ...
- tp框架引入第三方sdk的经验总结
tp框架开发常用到第三方的接口,这时候需要引入第三方的sdk.例如:微信扫码支付sdk,阿里大于的淘宝sdk等等 首先到官网上下载对应php的sdk文件,通常会有至少一个实例代码. 1 新建一个控制器 ...
- 数人云CTO解读Docker 1.12和金融业容器化
7月29日 数人云 在上海举办金融沙龙,邀请上交所和近二十家来自银行.保险.证券的IT技术专家一同探讨容器技术在金融业中的最佳实践.数人云CTO肖德时在会上将传统金融行业通过容器可以解决的四大问题做了 ...
- Linux下MySql数据库常用操作
1.显示数据库 show databases; 2.选择数据库 use 数据库名; 3.显示数据库中的表 show tables; 4.显示数据表的结构 describe 表名; 5.显示表中记录 S ...
- vim 跳转指定行
在编辑模式下输入 ngg 或者 nG n为指定的行数(如25) 25gg或者25G 跳转到第25行. 在命令模式下输入行号n : n 如果想打开文件即跳转 vim +n FileName 查看当然光标 ...
