cocos2dx[3.2](8) 数学类Vec2/Size/Rect
数学类Vec2、Size、Rect,是cocos2dx中比较常用的类。
比如设置图片位置,设置图片大小,两图片的碰撞检测等等。
比起2.x版本,在3.x中本质上其实没有太大的变化,主要的变化就是将全局宏定义相关的操作封装到各自的类中而已。比如:Vec2的向量运算宏定义ccp***(),现在都已经封装到Vec2类里面去了。
在V2.x中,底层数学库使用的是:Kazmath数学库。
而在 V3.1 中,由于 Sprite3D 需要我们提供更多的API给开发者,这是Kazmath库所不能提供的,而cocos2d-x内部拥有多个数学库是没有意义的。
所以V3.1中,底层选择了新的数学库:GamePlay3D数学库。
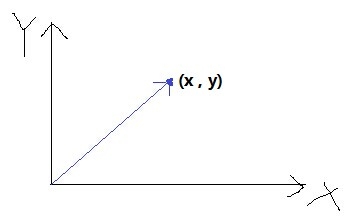
【Vec2】
Vec2原名Point,它既可以表示一个二维坐标点,又可以表示一个二维向量。
同时Vec2对运算符进行了重载,可以很方便的完成Vec2的赋值、加减乘除等操作。另外还有与坐标向量相关的:距离、角度、点积、叉积、投影、标准化等操作。
此外在3.x中,还将2.x里的函数定义ccp***(如ccp,ccpAdd,ccpSub)相关的操作都封装到了这个Vec2的类中,这样就可以更加系统化地管理向量的运算操作了。
此外,除了Vec2。还有两个坐标类:Vec3、Vec4,分别代表了三维、四维坐标向量。
Vec2可以是一个二维坐标点,也可以是一个二维向量。
1、创建方式
///*** Vec2只有两个成员变量x , y*/float x; //X坐标float y; //Y坐标/*** 构造函数*/Vec2(); //(0 , 0)Vec2(float xx, float yy); //(xx , yy)Vec2(const float* array); //(array[0] , array[1])Vec2(const Vec2& copy); //copyVec2(const Vec2& p1, const Vec2& p2); //p2 - p1//
2、设置向量坐标
使用set可以给向量重新设置新坐标值。
//void set(float xx, float yy); //(xx , yy)void set(const float* array); //(array[0] , array[1])void set(const Vec2& v); //vvoid set(const Vec2& p1, const Vec2& p2); //p2 - p1//
3、向量运算
其中包含了一些2.x中的ccp***()宏定义的函数,都全部封装到了Vec2类中。
///*** 向量运算* void : 自身运算 , 值会改变* 有返回值 : 返回运算结果, 值不会改变*/void add(const Vec2& v); //相加( x+v.x , y+v.y )void subtract(const Vec2& v); //相减( x-v.x , y-v.y )void clamp(const Vec2& min, const Vec2& max); //将向量值限制在[min,max]区间内void negate(); //向量取负( -x , -y )void normalize(); //标准化向量. 若为零向量,忽略void scale(float scalar); //x,y坐标同时放缩void scale(const Vec2& scale); //x,y坐标分别放缩void rotate(const Vec2& point, float angle); //绕point点, 旋转angle弧度float dot(const Vec2& v) const; //点积: x*v.x + y*v.yfloat cross(const Vec2& v) const; //叉积: x*v.y - y*v.xVec2 project(const Vec2& v) const; //投影: 向量在v上的投影向量float distance(const Vec2& v) const; //与v的距离.float distanceSquared(const Vec2& v) const; //与v的距离平方.float length() const; //向量长度. 即与原点的距离float lengthSquared() const; //向量长度平方. 即与原点的距离平方Vec2 getNormalized() const; //获取向量的标准化形式. 若为零向量,返回(0,0)inline Vec2 getPerp() const; //逆时针旋转90度. Vec2(-y, x);inline Vec2 getRPerp() const //顺时针旋转90度. Vec2(y, -x);inline float getAngle() const; //与X轴的夹角(弧度)float getAngle(const Vec2& v) const; //与v向量的夹角(弧度)inline Vec2 getMidpoint(const Vec2& v) const; //计算两点间的中点//将向量值限制在[min,max]区间内,返回该点inline Vec2 getClampPoint(const Vec2& min, const Vec2& max) const{return Vec2(clampf(x, min.x, max.x), clampf(y, min.y, max.y));}bool isZero() const; //是否为(0,0)bool isOne() const; //是否为(1,1)//判断target是否在坐标点模糊偏差为var的范围内.//if( (x - var <= target.x && target.x <= x + var) &&// (y - var <= target.y && target.y <= y + var) )// return true;bool fuzzyEquals(const Vec2& target, float variance) const;//以pivot为轴, 逆时针旋转angle度(弧度)Vec2 rotateByAngle(const Vec2& pivot, float angle) const;//绕other向量旋转//返回向量: 角度 this.getAngle() +other.getAngle();// 长度 this.getLength()*other.getLength();inline Vec2 rotate(const Vec2& other) const {return Vec2(x*other.x - y*other.y, x*other.y + y*other.x);};//绕other向量旋转前的向量值//返回向量: 角度 this.getAngle() -other.getAngle();// 长度 this.getLength()*other.getLength();//(这里是不是有点问题,难道不应该是this.getLength()/other.getLength()么?)inline Vec2 unrotate(const Vec2& other) const {return Vec2(x*other.x + y*other.y, y*other.x - x*other.y);};//两个点a和b之间的线性插值//alpha ==0 ? a alpha ==1 ? b 否则为a和b之间的一个值inline Vec2 lerp(const Vec2& other, float alpha) const {return *this * (1.f - alpha) + other * alpha;};//平滑更新向量的当前位置,指向目标向量target.//responseTime定义了平滑时间量,该值越大结果越平滑,相应的延迟时间越长。//如果希望向量紧跟target向量,提供一个相对elapsedTime小很多的responseTime值即可。//参数//target 目标值//elapsedTime 消逝时间//responseTime 响应时间void smooth(const Vec2& target, float elapsedTime, float responseTime);/*** 自定义运算* compOp*///对该点向量形式的各分量进行function参数来指定的运算,//如absf,floorf,ceilf,roundf等,//任何函数拥有如下形式:float func(float)均可。//例如:我们对x,y进行floor运算,则调用方法为p.compOp(floorf);//3.0inline Vec2 compOp(std::function<float(float)> function) const{return Vec2(function(x), function(y));}/*** 兼容代码* 估计是要被抛弃了~(>_<)~*/void setPoint(float xx, float yy); //同set(float xx, float yy)bool equals(const Vec2& target) const; //同==float getLength() const; //同length()float getLengthSq() const; //同lengthSquared()float getDistance(const Vec2& other) const; //同distance(const Vec2& v)float getDistanceSq(const Vec2& other) const; //同distanceSquared(const Vec2& v)//
4、运算符重载
//inline const Vec2 operator+(const Vec2& v) const; //( x+v.x , y+v.y )inline const Vec2 operator-(const Vec2& v) const; //( x-v.x , y-v.y )inline const Vec2 operator*(float s) const; //( x*s , y*s )inline const Vec2 operator/(float s) const; //( x/s , y/s )inline const Vec2 operator-() const; //( -x , -y )inline Vec2& operator+=(const Vec2& v); //(x,y) = ( x+v.x , y+v.y )inline Vec2& operator-=(const Vec2& v); //(x,y) = ( x-v.x , y-v.y )inline Vec2& operator*=(float s); //(x,y) = ( x*s , y*s )inline bool operator<(const Vec2& v) const;inline bool operator==(const Vec2& v) const;inline bool operator!=(const Vec2& v) const;//
5、静态函数与常量
///*** 静态方法*/static void add(const Vec2& v1, const Vec2& v2, Vec2* dst); //dst = v1 + v2static void subtract(const Vec2& v1, const Vec2& v2, Vec2* dst); //dst = v1 - v2static void clamp(const Vec2& v, const Vec2& min, const Vec2& max, Vec2* dst); //将向量v限制在[min,max]区间内,结果存入dststatic float angle(const Vec2& v1, const Vec2& v2); //两向量夹角(弧度)static float dot(const Vec2& v1, const Vec2& v2); //两向量点积static inline Vec2 forAngle(const float a); //返回向量坐标 x=cos(a) , y=sin(a)/*** 静态常量*/static const Vec2 ZERO; //Vec2(0, 0)static const Vec2 ONE; //Vec2(1, 1)static const Vec2 UNIT_X; //Vec2(1, 0)static const Vec2 UNIT_Y; //Vec2(0, 1)static const Vec2 ANCHOR_MIDDLE; //Vec2(0.5, 0.5)static const Vec2 ANCHOR_BOTTOM_LEFT; //Vec2(0, 0)static const Vec2 ANCHOR_TOP_LEFT; //Vec2(0, 1)static const Vec2 ANCHOR_BOTTOM_RIGHT; //Vec2(1, 0)static const Vec2 ANCHOR_TOP_RIGHT; //Vec2(1, 1)static const Vec2 ANCHOR_MIDDLE_RIGHT; //Vec2(1, 0.5)static const Vec2 ANCHOR_MIDDLE_LEFT; //Vec2(0, 0.5)static const Vec2 ANCHOR_MIDDLE_TOP; //Vec2(0.5, 1)static const Vec2 ANCHOR_MIDDLE_BOTTOM; //Vec2(0.5, 0)//
6、线段相交检测
这些用于检测线段相交的函数,也都是静态的成员函数。
///**线段相交检测 v3.0参数:A 为线段L1起点. L1 = (A - B)B 为L1终点 . L1 = (A - B)C 为线段L2起点. L2 = (C - D)D 为L2终点 . L2 = (C - D)S 为L1上计算各点的插值参数,计算方法为:p = A + S*(B - A)T 为L2上计算各点的插值参数,计算方法为:p = C + T*(D - C)*///直线AB与线段CD是否平行static bool isLineParallel(const Vec2& A, const Vec2& B, const Vec2& C, const Vec2& D);//直线AB与线段CD是否重叠static bool isLineOverlap(const Vec2& A, const Vec2& B, const Vec2& C, const Vec2& D);//直线AB与直线CD是否相交static bool isLineIntersect(const Vec2& A, const Vec2& B, const Vec2& C, const Vec2& D,float *S = nullptr, float *T = nullptr);//线段AB与线段CD是否重叠static bool isSegmentOverlap(const Vec2& A, const Vec2& B, const Vec2& C, const Vec2& D,Vec2* S = nullptr, Vec2* E = nullptr);//线段AB与线段CD是否相交static bool isSegmentIntersect(const Vec2& A, const Vec2& B, const Vec2& C, const Vec2& D);//返回直线AB与直线CD的交点static Vec2 getIntersectPoint(const Vec2& A, const Vec2& B, const Vec2& C, const Vec2& D);//
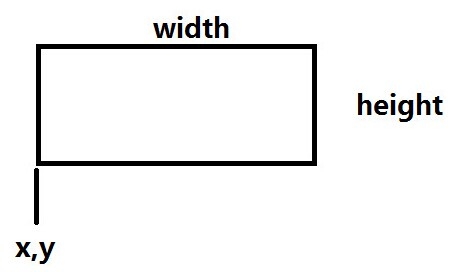
【Size】
Size比较简单,只是一个用来表示尺寸大小的类。宽为width,高为height。
和Vec2一样,也对一些运算符进行了重载。
与2.x相比,没有太大的变化。
PS: 因为和Vec2一样,都只有两个成员变量,所以Size和Vec2之间可以相互转换。
1、主要函数如下
//class CC_DLL Size{/*** Size只有两个成员变量width , height*/float width; //宽float height; //高/*** 构造函数*/Size(); //(0, 0)Size(float width, float height); //(width, height)Size(const Size& other); //otherexplicit Size(const Vec2& point); //(显式)构造函数. 构造时Size size = Size(Vec2&), 而不能Size size = vec2;/*** 相关操作* - setSize* - equals* - Vec2()*/void setSize(float width, float height); //设置尺寸bool equals(const Size& target) const; //判断是否等于target//Size::Vec2()//返回类型为Vec2operator Vec2() const { return Vec2(width, height); }/*** 静态常量*/static const Size ZERO; //(0, 0)/*** 运算符重载*/Size& operator= (const Size& other);Size& operator= (const Vec2& point); //可以用Vec2赋值Size operator+(const Size& right) const;Size operator-(const Size& right) const;Size operator*(float a) const;Size operator/(float a) const;};//
【Rect】
Rect是一个矩形类。包含两个成员属性:起始坐标(左下角)Vec2、矩阵尺寸大小Size。
Rect只对“=”运算符进行了重载。
与2.x相比,多了一个函数unionWithRect,用于合并两个矩形。
值得注意的是Rect类中:
intersectsRect函数,可以用作两个Rect矩形是否相交,即碰撞检测。
containsPoint 函数,可以用作判断点Vec2是否在Rect矩形中。
unionWithRect 函数,可以用做将两矩形进行合并操作。
1、主要函数如下
//class CC_DLL Rect{public:Vec2 origin; //起始坐标: 矩形左下角坐标Size size; //尺寸大小/*** 构造函数*/Rect();Rect(float x, float y, float width, float height);Rect(const Rect& other);/*** 运算符重载* 只重载了 “=” 运算符*/Rect& operator= (const Rect& other);/*** 相关操作* - setRect* - getMinX , getMidX , getMaxX* - getMinY , getMidY , getMaxY* - equals , containsPoint , intersectsRect* - unionWithRect*///设置矩形void setRect(float x, float y, float width, float height);//获取矩形信息float getMinX() const; //origin.xfloat getMidX() const; //origin.x + size.width/2float getMaxX() const; //origin.x + size.widthfloat getMinY() const; //origin.yfloat getMidY() const; //origin.y + size.height/2float getMaxY() const; //origin.y + size.height//判断是否与rect相同. 原点相同,尺寸相同.bool equals(const Rect& rect) const;//判断point是否包含在矩形内或四条边上bool containsPoint(const Vec2& point) const;//判断矩形是否相交. 常常用作碰撞检测.bool intersectsRect(const Rect& rect) const;//与rect矩形合并. 并返回结果. v3.0//不会改变原矩形的值Rect unionWithRect(const Rect & rect) const;/*** 静态常量* Rect::ZERO*/static const Rect ZERO;};//
2、精灵创建中的一种方式
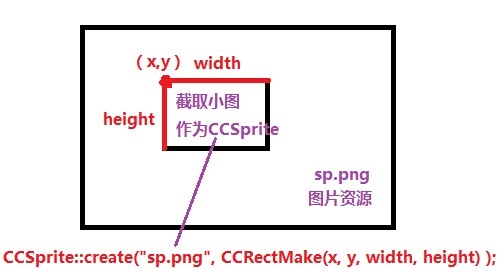
还记得Sprite的几种创建方式吗?里面有一种创建方式如下:
> Sprite::create(const std::string& filename, const Rect& rect)
若用Rect来作为创建Sprite精灵的参数,需要注意,从大图中截取某一区域的图片的Rect rect的构造应该是这样的:
> Rect("小图左上角坐标x", "小图左上角坐标y", 小图宽, 小图高);
使用的是UIKit坐标系,而不是cocos2dx的OpenGL坐标系是不一样的。
如下图所示:
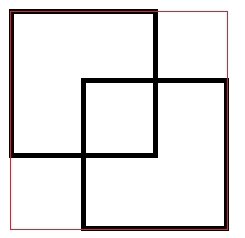
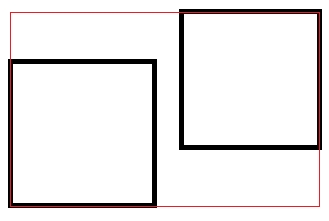
3、矩形合并函数unionWithRect
看几张图,你应该就会明白了。
两个黑色矩形区域,使用unionWithRect合并后,变成红色矩形区域。
cocos2dx[3.2](8) 数学类Vec2/Size/Rect的更多相关文章
- 【转】Cocos2d-x 3.x基础学习: 总结数学类Vec2/Size/Rect
转载:http://www.taikr.com/article/1847 在Cocos2d-x 3.x中,数学类Vec2.Size.Rect,是比较常用的类.比如设置图片位置,图片大小,两图片的碰撞检 ...
- Lua 数学类
数学类主要有Vec2(坐标向量).Size(尺寸).Rect(矩形). 创建 在Lua中创建的 Vec2.Size.Rect 都是一个table类型. 其中只有相应的成员变量,没有相关的函数运算. c ...
- Java:日历类、日期类、数学类、运行时类、随机类、系统类
一:Calendar类 java.util 抽象类Calendar 1.static Calendar getInstance()使用默认时区和语言环境获得一个日历. 2. int get(int ...
- cocos2d-x v3.2 FlappyBird 各个类对象详细代码分析(7)
今天我们介绍最后两个类 GameOverLayer类 GameLayer类 GameLayer类是整个游戏中最重要的类,由于是整个游戏的中央系统,控制着各个类(层)之间的交互,这个类中实现了猪脚小鸟和 ...
- [19/03/18-星期一] 常用类_Math(数学)类&Rondom(随机数)类
一.Math(数学)类(单独一个Java.Math 包中) java.lang.Math提供了一系列静态方法用于科学计算;其方法的参数和返回值类型一般为double型.如果需要更加强大的数学运算能力, ...
- 说说C#的数学类,Math,浮点数(上)
说说C#的数学类,Math,浮点数 C#语言支持下图所看到的的数值类型,各自是整数,浮点数和小数 可能不是非常清楚,可是细致看看还是能看清楚的. 在一个C#程序中,整数(没有小数点的数)被觉得是一个i ...
- Math 数学类
/* Math 数学类, 主要是提供了很多的数学公式. abs(double a) 获取绝对值 ceil(double a) 向上取整 floor(double a) 向下取整 round(float ...
- cocos2dx 3.17.1 导演类
进入导演类的头文件,首先看到的是一些头文件的引用:CCPlatformMacros(适配),CCRef(继承的父类),CCVector(3.0以后的新向量),CCScene(场景),CCMath(数学 ...
- cocos2d-x 的两大基类
cocos2d-x 有两个重要的基类,一个管理引用计数的 Ref,别一个则定义许多基本属性的 Node. 在 cocos2d-x 中的基本概念 说到 create 函数的时候提到 cocos2d-x ...
随机推荐
- Mongodb数据模型
描述表关系的方式: 方式一:嵌入式 > db.person.find({name:'zjf'}).pretty() { "_id" : ObjectId("592f ...
- Java介绍、环境的搭建及结构化程序
一.Java 简介及环境配置: JDK和JRE的区别:JRE(Java Runtime Environment)Java运行时环境有些程序运行需要Java环境,因此JRE只是给客户端使用的. JDK( ...
- Docker从0开始之部署一套2048
创建容器并运行程序 [root@localhost ~]# docker run -d -p 8888:80 daocloud.io/daocloud/dao-2048:master-a2c564e ...
- linux命令详解之ls命令
ls命令概述 ls命令用于显示文件目录列表,和Windows系统下DOS命令dir类似.当执行ls命令时,默认显示的只有非隐藏文件的文件名.以文件名进行排序及文件名代表的颜色显示.当不加参数时,默认列 ...
- 杀掉nginx进程
ps aux | grep nginx kill -INT 进程号(例如:2661)
- dockerfile:python-cuda-nvidia-cudnn
centos7 FROM centos:7 MAINTAINER yon@DataExa.com RUN yum -y install make wget \ && wget -O / ...
- Unity3D_(游戏)跳一跳超简单制作过程
跳一跳 工程文件界面 游戏界面 脚本 using DG.Tweening; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; us ...
- 如何将项目托管到Github上
将本地项目放到GitHub上托管并展示 传送门 利用Github Pages展示自己的项目 传送门 git Please tell me who you are解决方法 传送门 git config ...
- IDEA 无法显示项目目录结构解决
不要去网上看什么乱七八糟的骚教程,一点用都没有.直接按下列步骤操作: 1. 关闭IDEA, 2. 然后删除项目文件夹下的.idea文件夹3. 重新用IDEA工具打开项目
- leetcode-easy-others-20 Valid Parentheses
mycode 95.76% class Solution(object): def isValid(self, s): """ :type s: str :rtype ...
