Tensorflow实现LSTM识别MINIST
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.contrib import rnn
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
config=tf.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.allow_growth=True
sess=tf.Session(config=config)
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot=True)
print(mnist.train.images.shape)
Extracting MNIST_data\train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Extracting MNIST_data\train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
Extracting MNIST_data\t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
Extracting MNIST_data\t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
(55000, 784)
lr = 1e-3
input_size = 28 # 每个时刻的输入特征是28维的,就是每个时刻输入一行,一行有 28 个像素
timestep_size = 28 # 时序持续长度为28,即每做一次预测,需要先输入28行
hidden_size = 256 # 隐含层的数量
layer_num = 2 # LSTM layer 的层数
class_num = 10 # 最后输出分类类别数量,如果是回归预测的话应该是 1
_X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, class_num])
# 在训练和测试的时候,我们想用不同的 batch_size.所以采用占位符的方式
batch_size = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, []) # 注意类型必须为 tf.int32, batch_size = 128
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [])
# 把784个点的字符信息还原成 28 * 28 的图片
# 下面几个步骤是实现 RNN / LSTM 的关键
####################################################################
# **RNN 的输入shape = (batch_size, timestep_size, input_size)
X = tf.reshape(_X, [-1, 28, 28])
# 在 tf 1.2.1 版本中,可以通过下面方式来创建
def lstm_cell():
cell = rnn.LSTMCell(hidden_size, reuse=tf.get_variable_scope().reuse)
return rnn.DropoutWrapper(cell, output_keep_prob=keep_prob)
mlstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell([lstm_cell() for _ in range(layer_num)], state_is_tuple = True)
# **用全零来初始化state
init_state = mlstm_cell.zero_state(batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)
# **调用 dynamic_rnn() 来让我们构建好的网络运行起来
# ** 当 time_major==False 时, outputs.shape = [batch_size, timestep_size, hidden_size]
# ** 所以,可以取 h_state = outputs[:, -1, :] 作为最后输出
# ** state.shape = [layer_num, 2, batch_size, hidden_size],
# ** 或者,可以取 h_state = state[-1][1] 作为最后输出
# ** 最后输出维度是 [batch_size, hidden_size]
outputs, state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(mlstm_cell, inputs=X, initial_state=init_state, time_major=False)
h_state = state[-1][1]
W=tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([hidden_size,class_num],stddev=0.1),dtype=tf.float32)
bias=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape=[class_num]),dtype=tf.float32)
y_pred=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_state,W)+bias)
cross_entropy=-tf.reduce_mean(y*tf.log(y_pred))
train_op=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(lr).minimize(cross_entropy)
correct_prediction=tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_pred,1),tf.argmax(y,1))
accuracy=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,"float"))
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(2000):
_batch_size=128
batch=mnist.train.next_batch(_batch_size)
if (i+1)%200 ==0:
train_accuracy=sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={
_X:batch[0],y:batch[1],keep_prob:1.0,batch_size:_batch_size
})
print(y_pred)
print(batch[0].shape)
print("Iter%d, step %d, training accuracy %g" % (mnist.train.epochs_completed,(i+1),train_accuracy))
sess.run(train_op,feed_dict={_X:batch[0],y:batch[1],keep_prob:0.5,batch_size:_batch_size})
print("test accuracy %g"% sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={
_X:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels,keep_prob:1.0,batch_size:mnist.test.images.shape[0]
}))
Tensor("Softmax_1:0", shape=(?, 10), dtype=float32)
(128, 784)
Iter5, step 200, training accuracy 0.9375
Tensor("Softmax_1:0", shape=(?, 10), dtype=float32)
(128, 784)
Iter5, step 400, training accuracy 0.976562
Tensor("Softmax_1:0", shape=(?, 10), dtype=float32)
(128, 784)
Iter6, step 600, training accuracy 0.96875
Tensor("Softmax_1:0", shape=(?, 10), dtype=float32)
(128, 784)
Iter6, step 800, training accuracy 0.984375
Tensor("Softmax_1:0", shape=(?, 10), dtype=float32)
(128, 784)
Iter6, step 1000, training accuracy 0.984375
Tensor("Softmax_1:0", shape=(?, 10), dtype=float32)
(128, 784)
Iter7, step 1200, training accuracy 0.984375
Tensor("Softmax_1:0", shape=(?, 10), dtype=float32)
(128, 784)
Iter7, step 1400, training accuracy 0.984375
Tensor("Softmax_1:0", shape=(?, 10), dtype=float32)
(128, 784)
Iter8, step 1600, training accuracy 0.992188
Tensor("Softmax_1:0", shape=(?, 10), dtype=float32)
(128, 784)
Iter8, step 1800, training accuracy 0.984375
Tensor("Softmax_1:0", shape=(?, 10), dtype=float32)
(128, 784)
Iter9, step 2000, training accuracy 0.992188
test accuracy 0.9863
_batch_size=5
X_batch,y_batch=mnist.test.next_batch(_batch_size)
print(X_batch.shape,y_batch.shape)
_outputs,_state=sess.run([outputs,state],feed_dict={
_X:X_batch,y:y_batch,keep_prob:1.0,batch_size:_batch_size
})
print('outputs.shape=',np.asarray(_outputs).shape)
print('arr_state.shape=',np.asarray(_state).shape)
print(np.asarray(_state[-1][1]))
print(np.asarray(_state[0][1]))
(5, 784) (5, 10)
outputs.shape= (5, 28, 256)
arr_state.shape= (2, 2, 5, 256)
[[-0.29114476 -0.84908068 -0.02608863 ..., -0.26059726 -0.41139302
0.59013247]
[-0.6596756 0.1405973 0.32068741 ..., 0.78834546 -0.85109633
-0.55030227]
[ 0.91946286 -0.6195702 0.00405734 ..., 0.50050467 0.4910633
-0.59666592]
[-0.89336431 0.21388607 0.50573528 ..., 0.75225669 0.6082601
-0.56074399]
[-0.36205587 -0.87424242 0.77999097 ..., 0.395004 -0.788903
-0.25867409]]
[[ 0.02811883 -0.1008996 0.03933555 ..., -0.26678833 -0.0076026
-0.04358114]
[-0.27545795 0.08285692 -0.09781252 ..., -0.40972584 0.14314541
0.83173752]
[-0.21126685 0.08805162 0.52263641 ..., -0.16019027 0.06584492
0.14457463]
[ 0.10716452 0.02429411 0.23363011 ..., 0.07705231 0.1158627
0.38137382]
[ 0.10278453 -0.19593915 0.18716493 ..., -0.15240444 -0.24707885
0.18361446]]
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
print(mnist.train.labels[4])
[ 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0.]
X3=mnist.train.images[3]
img3=X3.reshape([28,28])
print(img3.shape)
plt.imshow(img3,cmap='gray')
plt.show()
(28, 28)
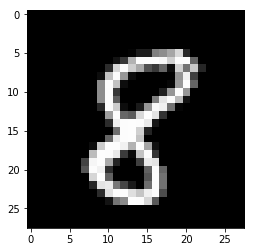
X3.shape=[-1,784]
y_batch=mnist.train.labels[0]
y_batch.shape=[-1,class_num]
X3_outputs=np.array(sess.run(outputs,feed_dict={
_X:X3,y:y_batch,keep_prob:1.0,batch_size:1
}))
print(X3_outputs.shape)
X3_outputs.shape=[28,hidden_size]
print(X3_outputs.shape)
(1, 28, 256)
(28, 256)
h_W=sess.run(W,feed_dict={
_X:X3,y:y_batch,keep_prob:1.0,batch_size:1
})
print(h_W)
h_bias=sess.run(bias,feed_dict={
_X:X3,y:y_batch,keep_prob:1.0,batch_size:1
})
print(h_bias)
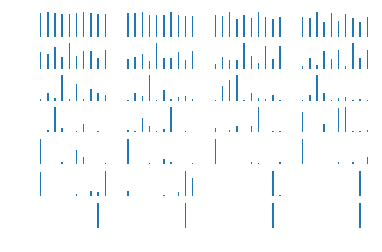
bar_index=range(class_num)
for i in range(X3_outputs.shape[0]):
plt.subplot(7,4,i+1)
x3_h_shate=X3_outputs[i,:].reshape([-1,hidden_size])
pro=sess.run(tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x3_h_shate,h_W)+h_bias))
plt.bar(bar_index,pro[0],width=0.2,align='center')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
[[-0.08456483 0.08745969 -0.07621165 ..., -0.00773322 -0.15107249
0.10566489]
[ 0.26069802 0.13171725 0.0247799 ..., 0.08384562 0.06285298
0.03339371]
[-0.02133826 -0.08564553 0.09821648 ..., 0.05742728 0.02910433
0.17623523]
...,
[ 0.14126052 0.15447645 -0.08539373 ..., -0.27805188 0.12536794
0.0209918 ]
[-0.11653625 0.07422358 0.14709686 ..., -0.03686545 0.01324715
-0.12571484]
[-0.14584878 0.00623576 0.01669303 ..., 0.08890152 -0.1124042
-0.15828955]]
[ 0.0999197 0.14981271 0.07992077 0.08728788 0.08243027 0.11954871
0.08033348 0.12624525 0.10010903 0.08718728]
该文章主要参考An understandable example to implement Multi-LSTM for MNIST
在自己的github中也有内容Tensorflow_LSTM
并且发现如果多次使用jupyter调用 tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell那一段的内容容易导致程序报错,后面的程序不能执行,具体原因不详,若遇到问题,可restart and clear outputs 并且重新 start all即可
Tensorflow实现LSTM识别MINIST的更多相关文章
- 用CNN及MLP等方法识别minist数据集
用CNN及MLP等方法识别minist数据集 2017年02月13日 21:13:09 hnsywangxin 阅读数:1124更多 个人分类: 深度学习.keras.tensorflow.cnn ...
- 单向LSTM笔记, LSTM做minist数据集分类
单向LSTM笔记, LSTM做minist数据集分类 先介绍下torch.nn.LSTM()这个API 1.input_size: 每一个时步(time_step)输入到lstm单元的维度.(实际输入 ...
- TensorFlow环境 人脸识别 FaceNet 应用(一)验证测试集
TensorFlow环境 人脸识别 FaceNet 应用(一)验证测试集 前提是TensorFlow环境以及相关的依赖环境已经安装,可以正常运行. 一.下载FaceNet源代码工程 git clone ...
- 学习Tensorflow的LSTM的RNN例子
学习Tensorflow的LSTM的RNN例子 基于TensorFlow一次简单的RNN实现 极客学院-递归神经网络 如何使用TensorFlow构建.训练和改进循环神经网络
- Tensorflow Mask-RCNN训练识别箱子的模型运行结果(练习)
Tensorflow Mask-RCNN训练识别箱子的模型
- tensorflow训练验证码识别模型
tensorflow训练验证码识别模型的样本可以使用captcha生成,captcha在linux中的安装也很简单: pip install captcha 生成验证码: # -*- coding: ...
- TensorFlow实现多层感知机MINIST分类
TensorFlow实现多层感知机MINIST分类 TensorFlow 支持自动求导,可以使用 TensorFlow 优化器来计算和使用梯度.使用梯度自动更新用变量定义的张量.本文将使用 Tenso ...
- 如何基于TensorFlow使用LSTM和CNN实现时序分类任务
https://www.jiqizhixin.com/articles/2017-09-12-5 By 蒋思源2017年9月12日 09:54 时序数据经常出现在很多领域中,如金融.信号处理.语音识别 ...
- Tensorflow的验证码识别
最近在弄深度学习,从网上找了一些资料.这是基于Tensorflow的深度学习的验证码识别.https://cuijiahua.com/blog/2018/01/dl_5.html http://blo ...
随机推荐
- spring依赖注入(转)
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/taijianyu/article/details/2338311/ Spring 能有效地组织J2EE应用各层的对象.不管是控 制层的Action对 ...
- H3C S2100配置管理vlan与交换机管理IP
管理 VLAN 简介:S2100系列以太网交换机任何时刻只能有一个VLAN对应的VLAN接口可以配置IP地址,该 VLAN 即为管理 VLAN.如果要对以太网交换机进行远程管理,必须配置交换机管理 V ...
- 2018.7.30 Oracle的Blog数据库类型读取和存
package com.lanqiao.shopping.test; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutput ...
- JS中的执行环境和作用域
window 是最大最外围的执行环境,然后每个函数都有自己的执行环境.JS代码是从上到下执行的,单纯的用语言描述可能会有点绕,而且不大直观.我们看着代码来 console.log('global be ...
- CentOS 7 下 jdk8 安装教程
方法一: 一.下载 官网下载地址 下载需要确认当前系统是32位还是64位,可通过命令查询: sudo uname --m 根据查询结果下载对应的jdk版本(如): i686 //表 ...
- JAVA文件操作工具类(读、增、删除、复制)
使用JAVA的JFinal框架 1.上传文件模型类UploadFile /** * Copyright (c) 2011-2017, James Zhan 詹波 (jfinal@126.com). * ...
- Linux Kernel ---- PCI Driver 分析
自己笔记使用. Kernel 版本 4.15.0 (ubuntu 18.04,intel skylake) 最近想学习VGA驱动去了解 DDCCP / EDID 等协议,然后顺便了解下驱动是如何工作的 ...
- 深入理解PHP7之zval
PHP7已经发布, 如承诺, 我也要开始这个系列的文章的编写, 今天我想先和大家聊聊zval的变化. 在讲zval变化的之前我们先来看看zval在PHP5下面是什么样子 PHP5zval回顾在PHP5 ...
- MySQL数据库 : 查询语句,连接查询及外键约束
查询指定字段 select 字段1,字段2 from 表名; 消除重复行(重复指的是结果集中的所有完全重复行) select distinct 字段1,字段2.. ...
- ubuntu安装wine 和sourceinsght
ubuntu安装wine: 1.sudo apt-get update 2.sudo apt-get install wine 安装完成后会在当前用户目录的的家目录下生成.wine目录,该目录就是wi ...
