FFmpeg开发实战(六):使用 FFmpeg 将YUV数据编码为视频文件
本文中实现的一个小功能是把一个YUV原始视频数据(时间序列图像)经过h264编码为视频码流,然后在使用mp4封装格式封装。
编码&封装的流程图如下:
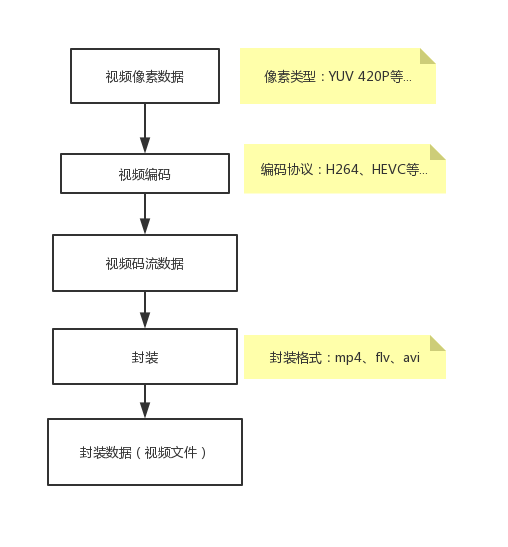
使用ffmpeg编码流程:
1、首先使用av_register_all()函数注册所有的编码器和复用器(理解为格式封装器)。该步骤必须放在所有ffmpeg代码前第一个执行
2、avformat_alloc_output_context2():初始化包含有输出码流(AVStream)和解复用器(AVInputFormat)的AVFormatContext
3、avio_open( )打开输出文件
4、av_new_stream() 创建视频码流 该函数生成一个空AVstream 该结构存放编码后的视频码流 。视频码流被拆分为AVPacket新式保存在AVStream中。
5、设置编码器信息,该步骤主要是为AVCodecContext(从AVStream->codec 获取指针)结构体设置一些参数,包括codec_id、codec_type、width、height、pix_fmt ..... 根据编码器的不同,还要额外设置一些参数(如 h264 要设置qmax、qmin、qcompress参数才能正常使用h264编码)
6、查找并打开编码器,根据前一步设置的编码器参数信息,来查找初始化一个编码其,并将其打开。用到函数为av_fine_encoder()和av_open2()。
7、写头文件 avformat_write_header()。这一步主要是将封装格式的信息写入文件头部位置。
8、编码帧。用到的函数 avcodec_encode_video2() 将AVFrame编码为AVPacket
9、在写入文件之前 还需要做一件事情就是设置AVPacket一些信息。这些信息关乎最后封装格式能否被正确读取。后面回详细讲述该部分内容
10、编码帧写入文件 av_write_frame()
11、flush_encoder():输入的像素数据读取完成后调用此函数。用于输出编码器中剩余的AVPacket。
12、av_write_trailer():写文件尾(对于某些没有文件头的封装格式,不需要此函数。比如说MPEG2TS)。
源码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pch.h"
#include <iostream> extern "C" {
#include "libavcodec/avcodec.h"
#include "libavformat/avformat.h"
#include "libavcodec/avcodec.h"
#include "libswscale/swscale.h"
#include <libavformat/avformat.h>
}; using namespace std; int flush_encoder(AVFormatContext *fmt_ctx, unsigned int stream_index); int YUV2H264()
{
AVFormatContext *pFormatCtx = nullptr;
AVOutputFormat *fmt = nullptr;
AVStream *video_st = nullptr;
AVCodecContext *pCodecCtx = nullptr;
AVCodec *pCodec = nullptr; uint8_t *picture_buf = nullptr;
AVFrame *picture = nullptr;
int size; //打开视频文件
FILE *in_file = fopen("111.yuv", "rb");
if (!in_file) {
cout << "can not open file!" << endl;
return -;
} //352x288
int in_w = , in_h = ;
int framenum = ;
const char* out_file = "111.H264"; //[1] --注册所有ffmpeg组件
avcodec_register_all();
av_register_all(); //[2] --初始化AVFormatContext结构体,根据文件名获取到合适的封装格式
avformat_alloc_output_context2(&pFormatCtx, NULL, NULL, out_file);
fmt = pFormatCtx->oformat; //[3] --打开文件
if (avio_open(&pFormatCtx->pb, out_file, AVIO_FLAG_READ_WRITE)) {
cout << "output file open fail!";
return -;
}
//[3] //[4] --初始化视频码流
video_st = avformat_new_stream(pFormatCtx, );
if (video_st == NULL)
{
printf("failed allocating output stram\n");
return -;
}
video_st->time_base.num = ;
video_st->time_base.den = ;
//[4] //[5] --编码器Context设置参数
pCodecCtx = video_st->codec;
pCodecCtx->codec_id = fmt->video_codec;
pCodecCtx->codec_type = AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO;
pCodecCtx->pix_fmt = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P;
pCodecCtx->width = in_w;
pCodecCtx->height = in_h;
pCodecCtx->time_base.num = ;
pCodecCtx->time_base.den = ;
pCodecCtx->bit_rate = ;
pCodecCtx->gop_size = ; if (pCodecCtx->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264)
{
pCodecCtx->qmin = ;
pCodecCtx->qmax = ;
pCodecCtx->qcompress = 0.6;
}
if (pCodecCtx->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG2VIDEO)
pCodecCtx->max_b_frames = ;
if (pCodecCtx->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG1VIDEO)
pCodecCtx->mb_decision = ;
//[5] //[6] --寻找编码器并打开编码器
pCodec = avcodec_find_encoder(pCodecCtx->codec_id);
if (!pCodec)
{
cout << "no right encoder!" << endl;
return -;
}
if (avcodec_open2(pCodecCtx, pCodec, NULL) < )
{
cout << "open encoder fail!" << endl;
return -;
}
//[6] //输出格式信息
av_dump_format(pFormatCtx, , out_file, ); //初始化帧
picture = av_frame_alloc();
picture->width = pCodecCtx->width;
picture->height = pCodecCtx->height;
picture->format = pCodecCtx->pix_fmt;
size = avpicture_get_size(pCodecCtx->pix_fmt, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height);
picture_buf = (uint8_t*)av_malloc(size);
avpicture_fill((AVPicture*)picture, picture_buf, pCodecCtx->pix_fmt, pCodecCtx->width, pCodecCtx->height); //[7] --写头文件
avformat_write_header(pFormatCtx, NULL);
//[7] AVPacket pkt; //创建已编码帧
int y_size = pCodecCtx->width*pCodecCtx->height;
av_new_packet(&pkt, size * ); //[8] --循环编码每一帧
for (int i = ; i < framenum; i++)
{
//读入YUV
if (fread(picture_buf, , y_size * / , in_file) < )
{
cout << "read file fail!" << endl;
return -;
}
else if (feof(in_file))
break; picture->data[] = picture_buf; //亮度Y
picture->data[] = picture_buf + y_size; //U
picture->data[] = picture_buf + y_size * / ; //V
//AVFrame PTS
picture->pts = i;
int got_picture = ; //编码
int ret = avcodec_encode_video2(pCodecCtx, &pkt, picture, &got_picture);
if (ret < )
{
cout << "encoder fail!" << endl;
return -;
} if (got_picture == )
{
cout << "encoder success!" << endl; // parpare packet for muxing
pkt.stream_index = video_st->index;
av_packet_rescale_ts(&pkt, pCodecCtx->time_base, video_st->time_base);
pkt.pos = -;
ret = av_interleaved_write_frame(pFormatCtx, &pkt);
av_free_packet(&pkt);
}
}
//[8] //[9] --Flush encoder
int ret = flush_encoder(pFormatCtx, );
if (ret < )
{
cout << "flushing encoder failed!" << endl;
goto end;
}
//[9] //[10] --写文件尾
av_write_trailer(pFormatCtx);
//[10] end:
//释放内存
if (video_st)
{
avcodec_close(video_st->codec);
av_free(picture);
av_free(picture_buf);
}
if (pFormatCtx)
{
avio_close(pFormatCtx->pb);
avformat_free_context(pFormatCtx);
} fclose(in_file); return ;
} int flush_encoder(AVFormatContext *fmt_ctx, unsigned int stream_index)
{
int ret;
int got_frame;
AVPacket enc_pkt;
if (!(fmt_ctx->streams[stream_index]->codec->codec->capabilities & AV_CODEC_CAP_DELAY))
return ;
while () {
printf("Flushing stream #%u encoder\n", stream_index);
enc_pkt.data = NULL;
enc_pkt.size = ;
av_init_packet(&enc_pkt);
ret = avcodec_encode_video2(fmt_ctx->streams[stream_index]->codec, &enc_pkt,
NULL, &got_frame);
av_frame_free(NULL);
if (ret < )
break;
if (!got_frame)
{
ret = ; break;
}
cout << "success encoder 1 frame" << endl; // parpare packet for muxing
enc_pkt.stream_index = stream_index;
av_packet_rescale_ts(&enc_pkt,
fmt_ctx->streams[stream_index]->codec->time_base,
fmt_ctx->streams[stream_index]->time_base);
ret = av_interleaved_write_frame(fmt_ctx, &enc_pkt);
if (ret < )
break;
}
return ret;
} int H2642MP4() { AVOutputFormat *ofmt = NULL;
//Input AVFormatContext and Output AVFormatContext
AVFormatContext *ifmt_ctx_v = NULL, *ifmt_ctx_a = NULL, *ofmt_ctx = NULL;
AVPacket pkt;
int ret, i;
int videoindex_v = , videoindex_out = ;
int frame_index = ;
int64_t cur_pts_v = , cur_pts_a = ;
const char *in_filename_v = "111.H264";
const char *out_filename = "222.mp4";//Output file URL
av_register_all();
//Input
if ((ret = avformat_open_input(&ifmt_ctx_v, in_filename_v, , )) < ) {
printf("Could not open input file.");
goto end; }
if ((ret = avformat_find_stream_info(ifmt_ctx_v, )) < ) {
printf("Failed to retrieve input stream information");
goto end;
} printf("===========Input Information==========\n");
av_dump_format(ifmt_ctx_v, , in_filename_v, );
//av_dump_format(ifmt_ctx_a, 0, in_filename_a, 0);
printf("======================================\n");
//Output
avformat_alloc_output_context2(&ofmt_ctx, NULL, NULL, out_filename);
if (!ofmt_ctx) {
printf("Could not create output context\n");
ret = AVERROR_UNKNOWN;
goto end;
}
ofmt = ofmt_ctx->oformat;
printf("ifmt_ctx_v->nb_streams=%d\n", ifmt_ctx_v->nb_streams);
for (i = ; i < ifmt_ctx_v->nb_streams; i++) {
//Create output AVStream according to input AVStream
//if(ifmt_ctx_v->streams[i]->codec->codec_type==AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO)
{
AVStream *in_stream = ifmt_ctx_v->streams[i];
AVStream *out_stream = avformat_new_stream(ofmt_ctx, in_stream->codec->codec);
videoindex_v = i;
if (!out_stream) {
printf("Failed allocating output stream\n");
ret = AVERROR_UNKNOWN;
goto end;
}
videoindex_out = out_stream->index;
//Copy the settings of AVCodecContext
if (avcodec_copy_context(out_stream->codec, in_stream->codec) < ) {
printf("Failed to copy context from input to output stream codec context\n");
goto end;
}
out_stream->codec->codec_tag = ;
if (ofmt_ctx->oformat->flags & AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER)
out_stream->codec->flags |= AV_CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER;
//break;
}
} printf("==========Output Information==========\n");
av_dump_format(ofmt_ctx, , out_filename, );
printf("======================================\n");
//Open output file
if (!(ofmt->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE)) {
if (avio_open(&ofmt_ctx->pb, out_filename, AVIO_FLAG_WRITE) < ) {
printf("Could not open output file '%s'", out_filename);
goto end;
}
}
//Write file header
if (avformat_write_header(ofmt_ctx, NULL) < ) {
printf("Error occurred when opening output file\n");
goto end;
} while () {
AVFormatContext *ifmt_ctx;
int stream_index = ;
AVStream *in_stream, *out_stream;
//Get an AVPacket
//if(av_compare_ts(cur_pts_v,ifmt_ctx_v->streams[videoindex_v]->time_base,cur_pts_a,ifmt_ctx_a->streams[audioindex_a]->time_base) <= 0)
{
ifmt_ctx = ifmt_ctx_v;
stream_index = videoindex_out;
if (av_read_frame(ifmt_ctx, &pkt) >= ) {
do {
in_stream = ifmt_ctx->streams[pkt.stream_index];
out_stream = ofmt_ctx->streams[stream_index];
printf("stream_index==%d,pkt.stream_index==%d,videoindex_v=%d\n", stream_index, pkt.stream_index, videoindex_v);
if (pkt.stream_index == videoindex_v) {
//FIX:No PTS (Example: Raw H.264)
//Simple Write PTS
if (pkt.pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
printf("frame_index==%d\n", frame_index);
//Write PTS
AVRational time_base1 = in_stream->time_base;
//Duration between 2 frames (us)
int64_t calc_duration = (double)AV_TIME_BASE / av_q2d(in_stream->r_frame_rate);
//Parameters
pkt.pts = (double)(frame_index*calc_duration) / (double)(av_q2d(time_base1)*AV_TIME_BASE);
pkt.dts = pkt.pts;
pkt.duration = (double)calc_duration / (double)(av_q2d(time_base1)*AV_TIME_BASE);
frame_index++;
}
cur_pts_v = pkt.pts;
break;
}
} while (av_read_frame(ifmt_ctx, &pkt) >= );
}
else {
break;
}
} //Convert PTS/DTS
pkt.pts = av_rescale_q_rnd(pkt.pts, in_stream->time_base, out_stream->time_base, (AVRounding)(AV_ROUND_NEAR_INF | AV_ROUND_PASS_MINMAX));
pkt.dts = av_rescale_q_rnd(pkt.dts, in_stream->time_base, out_stream->time_base, (AVRounding)(AV_ROUND_NEAR_INF | AV_ROUND_PASS_MINMAX));
pkt.duration = av_rescale_q(pkt.duration, in_stream->time_base, out_stream->time_base);
pkt.pos = -;
pkt.stream_index = stream_index;
printf("Write 1 Packet. size:%5d\tpts:%lld\n", pkt.size, pkt.pts);
//Write
if (av_interleaved_write_frame(ofmt_ctx, &pkt) < ) {
printf("Error muxing packet\n");
break;
}
av_free_packet(&pkt);
}
//Write file trailer
av_write_trailer(ofmt_ctx); end:
avformat_close_input(&ifmt_ctx_v);
//avformat_close_input(&ifmt_ctx_a);
/* close output */
if (ofmt_ctx && !(ofmt->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE))
avio_close(ofmt_ctx->pb);
avformat_free_context(ofmt_ctx);
if (ret < && ret != AVERROR_EOF) {
printf("Error occurred.\n");
return -;
}
return ;
} int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
// 先将YUV文件转换为H264文件
YUV2H264();
// 在将H264转封装为MP4
H2642MP4();
}
总结其流程,其实就是一个编码+转封装的流程。
补充
音视频转码与转封装的区别:
音视频转码和转封装的不同之处在于音视频转码会占用大量的计算资源,而转封装主要是将音频数据或者视频数据取出,然后封装成另外一种封装格式。
转封装主要占用的IO资源,而转码主要是占用CPU资源,同时转码也会使用更多的内存资源。
FFmpeg开发实战(六):使用 FFmpeg 将YUV数据编码为视频文件的更多相关文章
- FFmpeg开发实战(一):FFmpeg 打印日志
在Visual Studio 开发(二):VS 2017配置FFmpeg开发环境一文中,我们配置好了FFmpeg的开发环境,下面我们开始边实战,边学习FFmpeg. 首先,我们要学习的就是FFmpeg ...
- FFmpeg开发实战(三):FFmpeg 打印音视频Meta信息
在之前使用FFmpeg命令行的时候,我们经常看到FFmpeg命令行在输出音视频文件的会打印一下文件的Meta信息,类似如图: 那么我们如何通过代码的方式输出这些Meta信息呢? FFmpeg提供了一个 ...
- FFmpeg开发实战(二):FFmpeg 文件操作
FFmpeg 提供了丰富的API供我们使用,下面我们来讲述一下文件操作相关的API: FFmpeg 删除文件:avpriv_io_delete() FFmpeg 重命名文件:avpriv_io_mov ...
- FFmpeg开发教程一、FFmpeg 版 Hello world
本系列根据项目ffmpeg-libav-tutorial翻译而来 Chapter 0 - 万物之源 -- hello world 然而,本节的程序并不会在终端打印"Hello world&q ...
- Koa与Node.js开发实战(1)——Koa安装搭建(视频演示)
学习架构: 由于Koa2已经支持ES6及更高版本,包括支持async方法,所以请读者保证Node.js版本在7.6.0以上.如果需要在低于7.6的版本中应用Koa的async方法,建议使用Babel ...
- FFmpeg开发实战(五):FFmpeg 抽取音视频的视频数据
如何使用FFmpeg抽取音视频的视频数据,代码如下: // FFmpegTest.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数.程序执行将在此处开始并结束. // #include ...
- FFmpeg开发实战(四):FFmpeg 抽取音视频的音频数据
如何使用FFmpeg抽取音视频的音频数据,代码如下: void adts_header(char *szAdtsHeader, int dataLen); // 使用FFmpeg从视频中抽取音频 vo ...
- android 自定义View开发实战(六) 可拖动的GridView
1前言 由于项目需求,需要把项目的主界面采用GridView显示,并且需要根据模块优先级支持拖动图标(砍死产品狗).为此,自定义了一个支持拖拽图标的GridView.效果如下: 具体效果如上图 2 可 ...
- Android开发 多媒体提取器MediaExtractor详解_将一个视频文件分离视频与音频
前言 此篇博客讲解MediaExtractor将一个视频文件分离视频与音频,如果你对MediaExtractor还没有一个笼统的概念建议先了解我的另一篇入门博客:https://www.cnblogs ...
随机推荐
- jquery input 搜索自动补全、typeahead.js
最近做个一个功能需要用到自动补全,然后在网上找了很久,踩了各种的坑 最后用typeahead.js这个插件,经过自己的测试完美实现 使用方法:在页面中引入jquery.jquery.typeahead ...
- APNS导致消息丢失和发送效率原因
http://blog.csdn.net/tlq1988/article/details/9612237 首先说明一下,本文只是介绍一些容易被开发者忽视,而导致性能低下问题.并不是介绍如何向苹果设备成 ...
- 玩转Spring MVC(五)----在spring中整合log4j
在前边的基础上,本文主要总结一下如何在spring 中配置log4j,在本文末尾会给出完整项目的链接. 首先是web.xml中要新添加的代码: <!-- 6. 配置log4j --> &l ...
- Guava新增集合类型-Multiset
Guava新增集合类型-Multiset Guava引进了JDK里没有的,但是非常有用的一些新的集合类型.所有这些新集合类型都能和JDK里的集合平滑集成.Guava集合非常精准地实现了JDK定义的接口 ...
- BZOJ_1662_[Usaco2006 Nov]Round Numbers 圆环数_数位DP
BZOJ_1662_[Usaco2006 Nov]Round Numbers 圆环数_数位DP Description 正如你所知,奶牛们没有手指以至于不能玩“石头剪刀布”来任意地决定例如谁先挤奶的顺 ...
- k8s经典实战—搭建WordPress
k8s经典实战—搭建WordPress说明:需要在k8s上部署lnmp环境,建议跟着步骤来端口最好不要改,希望你也能搭建成功,完成这个搭建后你对Kubernetes的技术基本上是入门了.首先看下效果图 ...
- ssm日期格式转换
ssm日期格式转换 1 需求 前端传入字符串类型日期转化成java中的Date类型,存入数据库中;将数据库中的日期类型通过jstl标签在前端页面转换成字符串类型. 2 步骤 2.1 ...
- Redis 缓存失效和回收机制续
二.Redis Key失效机制 Redis的Key失效机制,主要借助借助EXPIRE命令: EXPIRE key 30 上面的命令即为key设置30秒的过期时间,超过这个时间,我们应该就访问不到这个值 ...
- 基于Unity的AR开发初探:发布AR应用到Android平台
本文接上一篇,介绍一下如何通过Unity发布第一个AR应用至Android平台,在Android手机上使用我们的第一个AR应用. 一.一些准备工作 1.1 准备Java JDK 这里选择的是JDK 1 ...
- asp.net core系列 55 IS4结合Identity密码保护API
一.概述 OAuth 2.资源所有者密码授权允许客户端(Client项目)向令牌服务(IdentityServer项目)发送用户名和密码,并获取代表该用户的访问令牌.本篇将IS4结合asp.net c ...
