CodeForces 909E Coprocessor(无脑拓扑排序)
Some of the tasks in the graph can only be executed on a coprocessor, and the rest can only be executed on the main processor. In one coprocessor call you can send it a set of tasks which can only be executed on it. For each task of the set, all tasks on which it depends must be either already completed or be included in the set. The main processor starts the program execution and gets the results of tasks executed on the coprocessor automatically.
Find the minimal number of coprocessor calls which are necessary to execute the given program.
The first line contains two space-separated integers N (1 ≤ N ≤ 105) — the total number of tasks given, and M (0 ≤ M ≤ 105) — the total number of dependencies between tasks.
The next line contains N space-separated integers 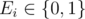 . If Ei = 0, task i can only be executed on the main processor, otherwise it can only be executed on the coprocessor.
. If Ei = 0, task i can only be executed on the main processor, otherwise it can only be executed on the coprocessor.
The next M lines describe the dependencies between tasks. Each line contains two space-separated integers T1 and T2 and means that task T1 depends on task T2 (T1 ≠ T2). Tasks are indexed from 0 to N - 1. All M pairs (T1, T2) are distinct. It is guaranteed that there are no circular dependencies between tasks.
Output one line containing an integer — the minimal number of coprocessor calls necessary to execute the program.
4 3
0 1 0 1
0 1
1 2
2 3
2
4 3
1 1 1 0
0 1
0 2
3 0
1
In the first test, tasks 1 and 3 can only be executed on the coprocessor. The dependency graph is linear, so the tasks must be executed in order 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 0. You have to call coprocessor twice: first you call it for task 3, then you execute task 2 on the main processor, then you call it for for task 1, and finally you execute task 0 on the main processor.
In the second test, tasks 0, 1 and 2 can only be executed on the coprocessor. Tasks 1 and 2 have no dependencies, and task 0 depends on tasks 1 and 2, so all three tasks 0, 1 and 2 can be sent in one coprocessor call. After that task 3 is executed on the main processor.
题意:给你一堆任务,有些要用主处理器处理,有些要用副处理器处理,副处理器可以一次处理很多个任务,一个任务能被执行的条件为前继任务已经被执行过了或者前继任务和自己同时被放进副处理器处理,现在给你这些前继任务的关系和每个任务处理要用的处理器,求副处理器最少运行了几次,保证关系是一张有向无环图
题解:
用贪心的思想,每次把所有当前能做得要用主处理器的任务都做光,那么此时能一锅端的副处理器任务肯定也是最多的。所以首先建两个队列,一个放拓扑排序搜到的要用主处理器做得任务,一个放副处理器做的任务,每次先拓扑排序搜到没有能用主处理器做的任务为止,然后如果副处理器的队列里还有别的数,那么ans++,把副处理器队列里的数继续拿出来进行拓扑排序,直到所有数都被搜过为止,复杂度就是拓扑排序的复杂度,还是很优越的。(恕我直言,这一场简直有毒,ab姑且不讲,c题无脑dp,d题滑稽模拟,e题竟然如此简单……不过f题还是不错的,有d题难度(雾)这不会就是传说中的div3吧2333)
代码如下:
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std; struct node
{
int val,du;
} a[]; int n,m,vis[],ans;
vector<int> g[]; int main()
{
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i].val);
}
for(int i=; i<=m; i++)
{
int from,to;
scanf("%d%d",&from,&to);
g[to+].push_back(from+);
a[from+].du++;
}
queue<int> q[];
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
if(!a[i].du)
{
q[a[i].val].push(i);
}
}
while((!q[].empty())||(!q[].empty()))
{
while(!q[].empty())
{
int u=q[].front();
vis[u]=;
q[].pop();
for(int i=; i<g[u].size(); i++)
{
if(!vis[g[u][i]])
{
a[g[u][i]].du--;
if(!a[g[u][i]].du)
{
q[a[g[u][i]].val].push(g[u][i]);
}
}
}
}
if(!q[].empty())
{
ans++;
while(!q[].empty())
{
int u=q[].front();
vis[u]=;
q[].pop();
for(int i=; i<g[u].size(); i++)
{
if(!vis[g[u][i]])
{
a[g[u][i]].du--;
if(!a[g[u][i]].du)
{
q[a[g[u][i]].val].push(g[u][i]);
}
}
}
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
CodeForces 909E Coprocessor(无脑拓扑排序)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 909E. Coprocessor (拓扑、模拟)
题目链接: Coprocessor 题意: 给出n个待处理的事件(0 - n-1),再给出了n个标(0表示只能在主处理器中处理这个事件,1表示只能在副处理器中处理这个事件),处理器每次能处理多个任务. ...
- codeforces 915D Almost Acyclic Graph 拓扑排序
大意:给出一个有向图,问能否在只去掉一条边的情况下破掉所有的环 解析:最直接的是枚举每个边,将其禁用,然后在图中找环,如果可以就YES,都不行就NO 复杂度O(N*M)看起来不超时 但是实现了以后发现 ...
- Codeforces 909E(Coprocessor,双队列维护)
题意:给出n个待处理的事件(0 ~n-1),再给出了n个标(0表示只能在主处理器中处理这个事件,1表示只能在副处理器中处理这个事件),处理器每次能处理多个任务.每个事件有关联,如果一个任务要在副处理器 ...
- CodeForces 510C Fox And Names (拓扑排序)
<题目链接> 题目大意: 给你一些只由小写字母组成的字符串,现在按一定顺序给出这些字符串,问你怎样从重排字典序,使得这些字符串按字典序排序后的顺序如题目所给的顺序相同. 解题分析:本题想到 ...
- Codeforces Round #290 (Div. 2) 拓扑排序
C. Fox And Names time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard in ...
- CodeForces 909E Coprocessor
题解. 贪心,拓扑排序. 和拓扑排序一样,先把$flag$为$0$的点能删的都删光,露出来的肯定都是$flag$为$0$的,然后疯狂删$flag$为$0$的,这些会使答案加$1$,反复操作就可以了. ...
- Codeforces 919D:Substring(拓扑排序+DP)
D. Substring time limit: per test3 seconds memory limit: per test256 megabytes inputstandard: input ...
- Codeforces Beta Round #29 (Div. 2, Codeforces format) C. Mail Stamps 拓扑排序
C. Mail Stamps One day Bob got a letter in an envelope. Bob knows that when Berland's post offic ...
- Codeforces 875C National Property(拓扑排序)
题目链接 National Property 给定n个单词,字符集为m 现在我们可以把其中某些字母变成大写的.大写字母字典序大于小写字母. 问是否存在一种方案使得给定的n个单词字典序不下降. 首先判 ...
随机推荐
- C++ STL 容器之栈的使用
Stack 栈是种先进后出的容器,C++中使用STL容器Stack<T> 完美封装了栈的常用功能. 下面来个demo 学习下使用栈的使用. //引入IO流头文件 #include<i ...
- PHP对大小写敏感问题
1. 变量名区分大小写 1 <?php 2 $abc = 'abcd'; 3 echo $abc; //输出 'abcd' 4 echo $aBc; //无输出 5 echo $ABC; //无 ...
- 巨人大哥谈Web应用中的Session(session详解)
巨人大哥谈Web应用中的Session(session详解) 虽然session机制在web应用程序中被采用已经很长时间了,但是仍然有很多人不清楚session机制的本质,以至不能正确的应用这一技术. ...
- mysql的存储过程,函数,事件,权限,触发器,事务,锁,视图,导入导出
1.创建过程 1.1 简单创建 -- 创建员工表 DROP TABLE IF EXISTS employee; CREATE TABLE employee( id int auto_increment ...
- Struts2学习笔记三 访问servlet
结果跳转方式 转发 <!-- 转发 --> <action name="Demo1Action" class="cn.itheima.a_result. ...
- Java源码之HashMap
一.HashMap和Hashtable的区别 (1)HashMapl的键值(key)和值(value)可以为null,而Hashtable不可以 (2)Hashtable是线程安全类,而HashMap ...
- vue.js下载及安装配置
环境 Deepin15.4 下载及配置 node下载地址:http://nodejs.cn/download/ 解压到文件夹 /home/maskerk/vue/ 下 设置软连接: $ ln -s / ...
- NOIP2017 列队
https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P3960 p<=500 50分 模拟 每个人的出队只会影响当前行和最后一列 p<=500,有用的行只有500行 ...
- D的下L
D的小L 时间限制:4000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB 难度:2 描述 一天TC的匡匡找ACM的小L玩三国杀,但是这会小L忙着哩,不想和匡匡玩但又怕匡匡生气,这时小L给 ...
- NFC驱动调试
1.NFC基本概念: NFC 又称为近场通信,是一种新兴技术,可以在彼此靠近的情况下进行数据交换,是由非接触式射频识别(RFID) 及互连互通技术整合演变而来,通过单一芯片集成感应式读卡器: NFC有 ...
