SpringMVC之处理流程
之前在学servlet时写过JavaWeb与Asp.net工作原理比较分析,那篇主要是大致描述了下servlet的工作流程,今天在家了解了下springmvc的工作原理,与asp.net中的mvc进行了一下比较asp.net MVC 的处理流程,思想都是差不多,都是通过一个url怎么映射到类中做完处理返回浏览器的过程,首先要解决三大问题,一是url映射转换成request和response对象的问题二是浏览器与服务端的数据交互问题三是服务端的request、response怎么响应给客户端。今天了解了下它的运行流畅,其实网上也有好多教程。
一图顶千言万语,用数据、用图说话,下图是springmvc的工作原理图。 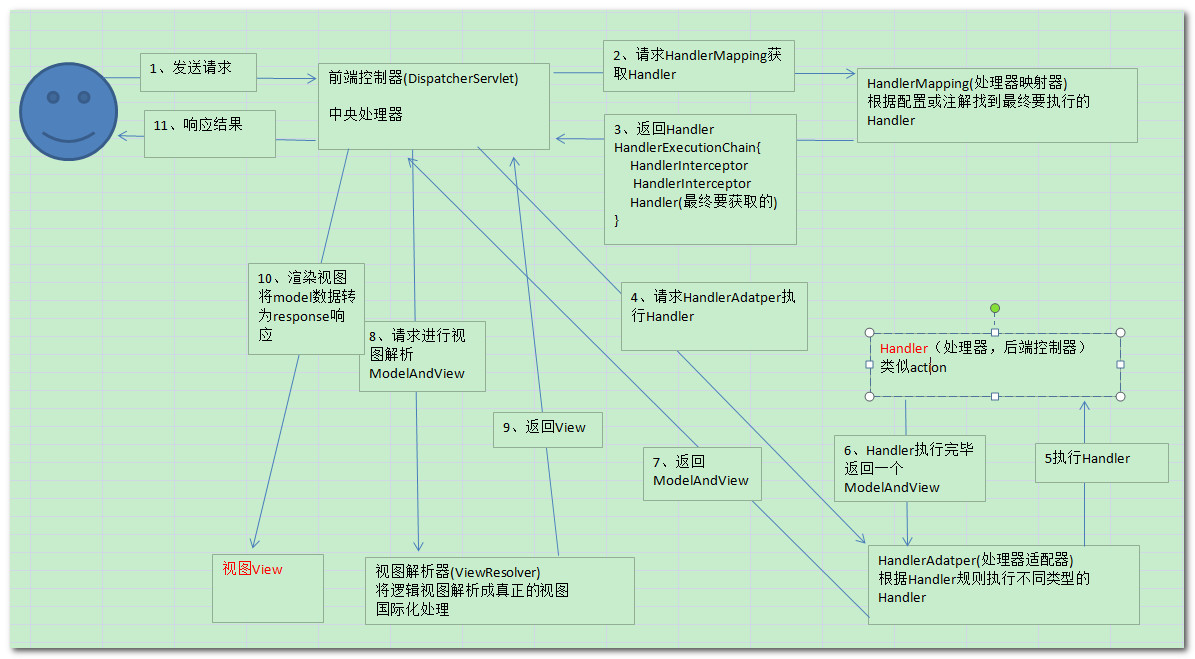
SpringMVC工作流程
一、 用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet。
1.DispatcherServlet它也是servlet,load-on-startup=1,tomcat启动时它也会初始化,初始化参数是contextConfigLocation上下文配置文件位置,参数值就是JavaWeb之Eclipse中使用Maven构建SpringMVC项目 配置的spring-mvc。在spring-mvc中可以配置自动扫描包名、默认注解映射支持、视图解释类、拦截器、对静态资源文件的访问等信息,通过自动扫描包名、注解映射支持、静态资源访问这些配置的信息在就会实例化HandlerMapping对象。这些对象是在tomcat进行参数初始化的时候也会实例化完成。在DispatcherServlet中维护着一个表,类似C#MVC中的RouteTable 路由表,存放的是HandlerMapping对象list.下面截图是DispatcherServlet中的部分代码,在DispatcherServlet中维护着handerMappings、handerAdapters等对象列表。在initStrategies中对上面的一些属性进行初始化。
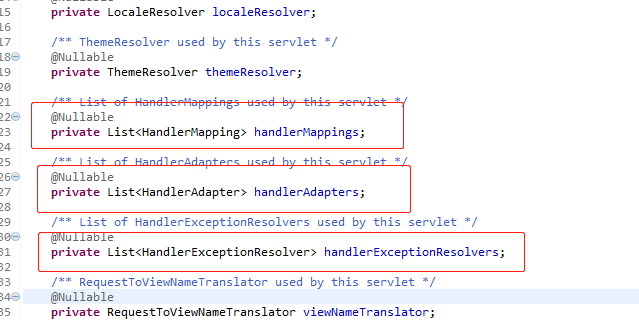
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
2.客户端发出请求,由 Tomcat 接收到这个请求,如果匹配 DispatcherServlet 在 web.xml 中配置的映射路径,Tomcat 就将请求转交给 DispatcherServlet 处理
二、 DispatcherServlet收到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器。
请求到达DispatcherServlet中之后,就是get、post这些请求,这些请求是DispatcherServlet的父类FrameworkServlet中定义着的,而在这些方法中又调用了processRequest,processRequest中调用了doService,DispatcherServlet重写了doService方法,doService中主要设置了一些属性和调用doDispatch方法,doDispatch用来做分发请求。
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
上面的代码是核心代码,其实下面的几项其实就是代码的说明.
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
上面这两句是判断请求是不是上传文件的请求
三、 处理器映射器找到具体的处理器(可以根据xml配置、注解进行查找),生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器(如果有则生成)一并返回给DispatcherServlet。
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
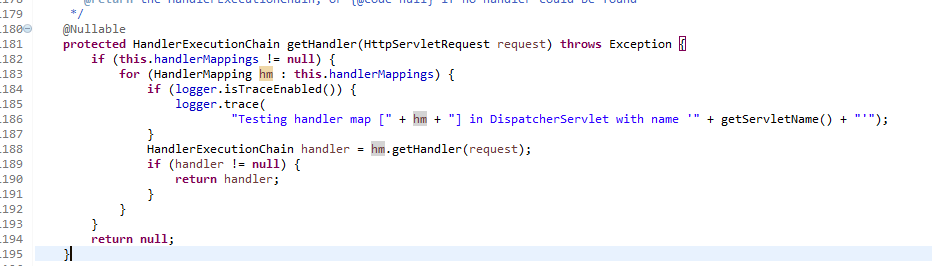
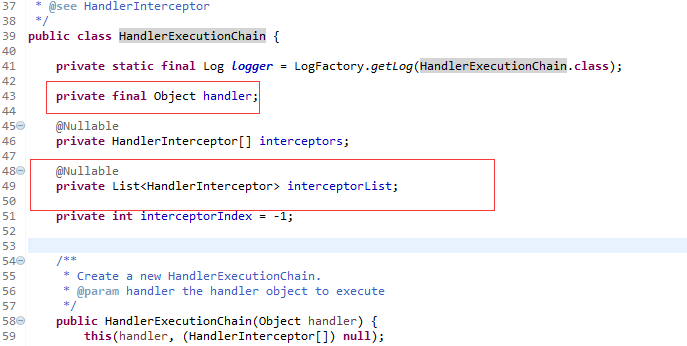
getHander返回的是一个HandlerExecutionChain,这个HandlerExecutionChain中包含一个handler和多个HandlerInterceptor(拦截器),这个和asp.net中的管道模型有点类似,一个httphandler和多个httpmodule,httpmodule也是用来做拦截操作的。同时要留意HandlerExecutionChain是通过HandlerMapping对象的getHandler获取的.其实这里还可以扩展比如拦截器的使用、HandlerMapping的介绍等,由于篇幅有限,会在以后的博客中一个一个的介绍。
四、 DispatcherServlet调用HandlerAdapter处理器适配器。
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]");
}
if (ha.supports(handler)) {
return ha;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
获取适配器是通过遍历handlerAdapters列表找的,HandlerAdapter包含了3个方法.boolean supports(Object handler);ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception;long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest request, Object handler);
/*
* Copyright 2002-2013 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.web.servlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; /**
* MVC framework SPI, allowing parameterization of the core MVC workflow.
*
* <p>Interface that must be implemented for each handler type to handle a request.
* This interface is used to allow the {@link DispatcherServlet} to be indefinitely
* extensible. The {@code DispatcherServlet} accesses all installed handlers through
* this interface, meaning that it does not contain code specific to any handler type.
*
* <p>Note that a handler can be of type {@code Object}. This is to enable
* handlers from other frameworks to be integrated with this framework without
* custom coding, as well as to allow for annotation-driven handler objects that
* do not obey any specific Java interface.
*
* <p>This interface is not intended for application developers. It is available
* to handlers who want to develop their own web workflow.
*
* <p>Note: {@code HandlerAdapter} implementors may implement the {@link
* org.springframework.core.Ordered} interface to be able to specify a sorting
* order (and thus a priority) for getting applied by the {@code DispatcherServlet}.
* Non-Ordered instances get treated as lowest priority.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleServletHandlerAdapter
*/
public interface HandlerAdapter { /**
* Given a handler instance, return whether or not this {@code HandlerAdapter}
* can support it. Typical HandlerAdapters will base the decision on the handler
* type. HandlerAdapters will usually only support one handler type each.
* <p>A typical implementation:
* <p>{@code
* return (handler instanceof MyHandler);
* }
* @param handler handler object to check
* @return whether or not this object can use the given handler
*/
boolean supports(Object handler); /**
* Use the given handler to handle this request.
* The workflow that is required may vary widely.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param response current HTTP response
* @param handler handler to use. This object must have previously been passed
* to the {@code supports} method of this interface, which must have
* returned {@code true}.
* @throws Exception in case of errors
* @return ModelAndView object with the name of the view and the required
* model data, or {@code null} if the request has been handled directly
*/
@Nullable
ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception; /**
* Same contract as for HttpServlet's {@code getLastModified} method.
* Can simply return -1 if there's no support in the handler class.
* @param request current HTTP request
* @param handler handler to use
* @return the lastModified value for the given handler
* @see javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet#getLastModified
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.LastModified#getLastModified
*/
long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest request, Object handler); }
五、 HandlerAdapter经过适配调用具体的处理器(Controller,也叫后端控制器)。
六、 Controller执行完成返回ModelAndView。
七、 HandlerAdapter将controller执行结果ModelAndView返回给DispatcherServlet。
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
} if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
} // Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
上面的几行代码先判断如果是get请求更新下lastModified请求头,然后执行HandlerExecutionChain中的applyPreHandle这个方法.
boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) {
triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
return false;
}
this.interceptorIndex = i;
}
}
return true;
}
void triggerAfterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Exception ex)
throws Exception { HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i = this.interceptorIndex; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
try {
interceptor.afterCompletion(request, response, this.handler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
logger.error("HandlerInterceptor.afterCompletion threw exception", ex2);
}
}
}
}
在applyPreHandle中它会遍历该HandlerExecutionChain中所有的拦截器,然后使用拦截器通过preHandle对handler进行预处理,如果所有的拦截器都能处理那就会继续往下执行,如果一旦有一个拦截器不能处理,就没必要往下走了,那就会触发triggerAfterCompletion方法,在triggerAfterCompletion中它是倒序遍历的拦截器的,执行完triggerAfterCompletion返回false之后doDispatch这个方法就执行结束了,下面的八、九、十、十一就不再执行。从第五步括号里的备注也能猜出来HandlerExecutionChain.handler是什么,它可以是Controller。
八、 DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewReslover视图解析器。
九、 ViewReslover解析后返回具体View。
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
private void applyDefaultViewName(HttpServletRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndView mv) throws Exception {
if (mv != null && !mv.hasView()) {
String defaultViewName = getDefaultViewName(request);
if (defaultViewName != null) {
mv.setViewName(defaultViewName);
}
}
}
protected String getDefaultViewName(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
return (this.viewNameTranslator != null ? this.viewNameTranslator.getViewName(request) : null);
}
找到ModelAndView对应的viewname,设置成它的属性值。
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
applyPostHandle与applyPreHandle是对应着的,遍历handler的拦截器,执行postHandle方法。
十、DispatcherServlet根据View进行渲染视图(即将模型数据填充至视图中)。
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception { boolean errorView = false; if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
} // Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling");
}
} if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
} if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Determine locale for request and apply it to the response.
Locale locale =
(this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale());
response.setLocale(locale);
View view;
String viewName = mv.getViewName();
if (viewName != null) {
// We need to resolve the view name.
view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() +
"' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
else {
// No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object.
view = mv.getView();
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " +
"View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
// Delegate to the View object for rendering.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
try {
if (mv.getStatus() != null) {
response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value());
}
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" +
getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
在processDispatchResult方法中有一句render(mv, request, response),在render中先是获取View对象然后调用view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);将view和model绑定来进行渲染试图。
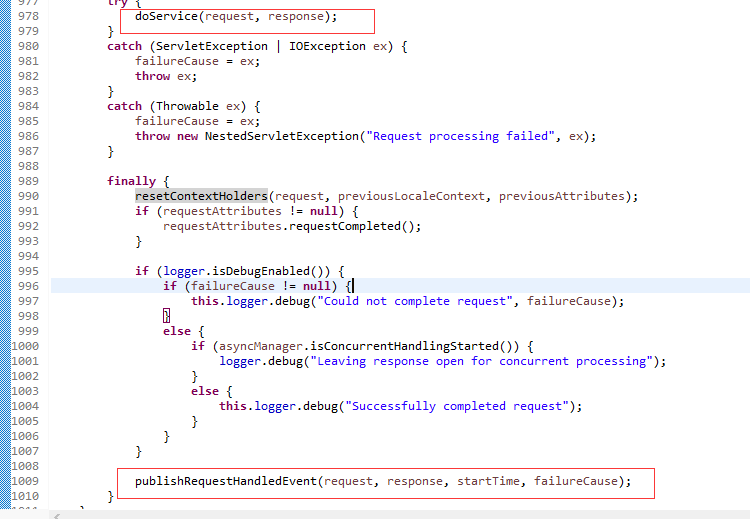
十一、 DispatcherServlet响应用户。
响应用户其实是在父类FrameworkServlet的processRequest方法中
十二、小结
上面黑字部分是参考其他博客的,红色的是通过读源码找的,现在基本清楚springmvc大致的流程,其实如果继续深入的话,还有好多知识点,这篇博客就写到这,以后再慢慢补充。好久没熬夜学习了,今天算是毕业之后最用功的一天了,哈哈...(今天四月一,愚人节!!!)
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxi/p/6164383.html
SpringMVC之处理流程的更多相关文章
- SpringMVC处理请求流程
SpringMVC核心处理流程: 1.DispatcherServlet前端控制器接收发过来的请求,交给HandlerMapping处理器映射器 2.HandlerMapping处理器映射器,根据请求 ...
- 《SpringMVC从入门到放肆》二、SpringMVC的执行流程及默认配置
上一篇博文我们做了一个hello world的程序,并且已经成功的跑起来了.这一篇我们来深入的了解一下SpringMVC的执行流程以及一些其它的配置. 一.执行流程 来解释一下上图中的各个名词1.Di ...
- SpringMVC的工作流程?Mybatis和hibernate区别?
SpringMVC的工作流程?1. 用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet2. DispatcherServlet收到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器.3. 处理器 ...
- 通过自己实现接口来加深理解SpringMVC的执行流程
功能介绍 上篇文章[从源码角度了解SpringMVC的执行流程]通过接口源码向大家介绍了SpringMVC的执行流程,主要偏重于源码.这篇文件我们来自己实现那几个关键接口,来真实体验下SpringMV ...
- 从源码角度了解SpringMVC的执行流程
目录 从源码角度了解SpringMVC的执行流程 SpringMVC介绍 源码分析思路 源码解读 几个关键接口和类 前端控制器 DispatcherServlet 结语 从源码角度了解SpringMV ...
- SpringMVC框架搭建流程(完整详细版)
SpringMVC框架搭建流程 开发过程 1)配置DispatcherServlet前端控制器 2)开发处理具体业务逻辑的Handler(@Controller. @RequestMapping) 3 ...
- Java程序员的日常——SpringMVC+Mybatis开发流程、推荐系统
今天大部分时间都在写业务代码,然后算是从无到有的配置了下spring与mybatis的集成. SpringMVC+Mybatis Web开发流程 配置数据源 在applicationContext.x ...
- 012医疗项目-模块一:统一异常处理器的设计思路及其实现(涉及到了Springmvc的异常处理流程)
我们上一篇文章是建立了一个自定义的异常类,来代替了原始的Exception类.在Serice层抛出异常,然后要在Action层捕获这个异常,这样的话在每个Action中都要有try{}catch{}代 ...
- SpringMvc的数据绑定流程
在SpringMvc中会将来自web页面的请求和响应数据与controller中对应的处理方法的入参进行绑定,即数据绑定.流程如下: -1.SpringMvc主框架将ServletRequest对象及 ...
随机推荐
- Struts2【OGNL、valueStack】就是这么简单
什么是OGNL表达式? OGNL是Object Graphic Navigation Language 是操作对象属性的开源表达式. Struts2框架使用OGNL作为默认的表达式语言. 为什么我们学 ...
- 第三方工具 - 关于echarts下钻功能的一些总结.js
废话:好久没有写博客了,每每看着自己的'战绩'都有点愧疚,但是这段时间确实学习了不少东西,待我慢慢地一 一梳理,将之消化并分享. ---------------------------$O_O$--- ...
- jxl 导出数据到excel
优点: Jxl对中文支持非常好,操作简单,方法看名知意. Jxl是纯javaAPI,在跨平台上表现的非常完美,代码可以再windows或者Linux上运行而无需重新编写 支持Excel 95-2000 ...
- ajax错误处理 500错误
在使用ajax请求的时候 ,如果服务器返回的是500错误,或者其他非正常的http错误状态码时 会提示下面的错误 而我们需要把错误信息处理出来 $.ajax({ type:'get', url:&q ...
- Win10下用Anaconda安装TensorFlow
什么是Anaconda anaconda指的是一个开源的Python发行版本,其包含了conda.Python等180多个科学包及其依赖项.它是一个用python开发机器学习的必备工具. 什么是ten ...
- vmstat结果在不同操作系统上的解释
vmstat是各种unix上的通用工具,但在不同系统上,结果的解释却不同,最容易混淆的是结果的memory部分: 1.linux: vmstat输出结果中: memory: swapd:已用swap区 ...
- 大数据(3):基于sogou.500w.utf8数据Hbase和Spark实践
1. HBase安装部署操作 a) 解压HBase安装包tar –zxvf hbase-0.98.0-hadoop2-bin.tar.gzb) 修改环境变量 hbase-env.shexport JA ...
- 关于slmgr命令
需要管理员的权限运行.这个命令可以用来卸载系统的序列号.使系统处于未激活状态.
- mysql 数据库基本命令语句
mysql mariadb 客户端连接 mysql -uroot -p; 客户端退出exit 或 \q 显示所有数据库show databases;show schemas; 创建数据库create ...
- MSIL实用指南-字段的加载和保存
字段有静态字段和非静态字段之分,它们的加载保存指令也是不一样的,并且非静态字段要生成this. 静态字段的加载加载静态字段的指令是Ldsfld.ilGenerator.Emit(OpCodes.Lds ...
