jquery源码 Callback
工具方法。对函数的统一管理。
jquery2.0.3版本$.Callback()部分的源码如下:
// String to Object options format cache
var optionsCache = {}; // Convert String-formatted options into Object-formatted ones and store in cache
function createOptions( options ) {
var object = optionsCache[ options ] = {};
jQuery.each( options.match( core_rnotwhite ) || [], function( _, flag ) {
object[ flag ] = true;
});
return object;
} /*
* Create a callback list using the following parameters:
*
* options: an optional list of space-separated options that will change how
* the callback list behaves or a more traditional option object
*
* By default a callback list will act like an event callback list and can be
* "fired" multiple times.
*
* Possible options:
*
* once: will ensure the callback list can only be fired once (like a Deferred)
*
* memory: will keep track of previous values and will call any callback added
* after the list has been fired right away with the latest "memorized"
* values (like a Deferred)
*
* unique: will ensure a callback can only be added once (no duplicate in the list)
*
* stopOnFalse: interrupt callings when a callback returns false
*
*/
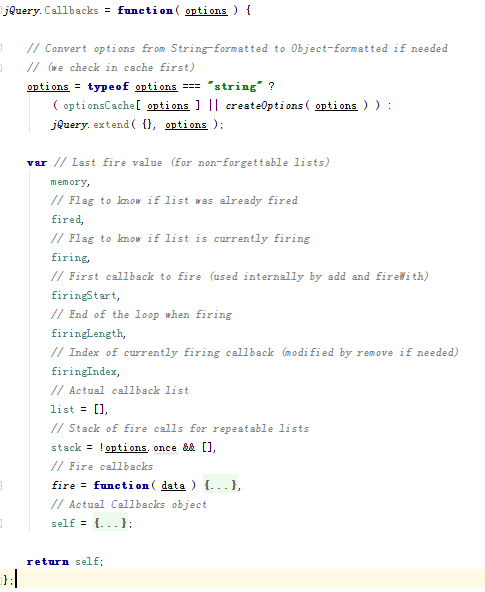
jQuery.Callbacks = function( options ) { // Convert options from String-formatted to Object-formatted if needed
// (we check in cache first)
options = typeof options === "string" ?
( optionsCache[ options ] || createOptions( options ) ) :
jQuery.extend( {}, options ); var // Last fire value (for non-forgettable lists)
memory,
// Flag to know if list was already fired
fired,
// Flag to know if list is currently firing
firing,
// First callback to fire (used internally by add and fireWith)
firingStart,
// End of the loop when firing
firingLength,
// Index of currently firing callback (modified by remove if needed)
firingIndex,
// Actual callback list
list = [],
// Stack of fire calls for repeatable lists
stack = !options.once && [],
// Fire callbacks
fire = function( data ) {
memory = options.memory && data;
fired = true;
firingIndex = firingStart || 0;
firingStart = 0;
firingLength = list.length;
firing = true;
for ( ; list && firingIndex < firingLength; firingIndex++ ) {
if ( list[ firingIndex ].apply( data[ 0 ], data[ 1 ] ) === false && options.stopOnFalse ) {
memory = false; // To prevent further calls using add
break;
}
}
firing = false;
if ( list ) {
if ( stack ) {
if ( stack.length ) {
fire( stack.shift() );
}
} else if ( memory ) {
list = [];
} else {
self.disable();
}
}
},
// Actual Callbacks object
self = {
// Add a callback or a collection of callbacks to the list
add: function() {
if ( list ) {
// First, we save the current length
var start = list.length;
(function add( args ) {
jQuery.each( args, function( _, arg ) {
var type = jQuery.type( arg );
if ( type === "function" ) {
if ( !options.unique || !self.has( arg ) ) {
list.push( arg );
}
} else if ( arg && arg.length && type !== "string" ) {
// Inspect recursively
add( arg );
}
});
})( arguments );
// Do we need to add the callbacks to the
// current firing batch?
if ( firing ) {
firingLength = list.length;
// With memory, if we're not firing then
// we should call right away
} else if ( memory ) {
firingStart = start;
fire( memory );
}
}
return this;
},
// Remove a callback from the list
remove: function() {
if ( list ) {
jQuery.each( arguments, function( _, arg ) {
var index;
while( ( index = jQuery.inArray( arg, list, index ) ) > -1 ) {
list.splice( index, 1 );
// Handle firing indexes
if ( firing ) {
if ( index <= firingLength ) {
firingLength--;
}
if ( index <= firingIndex ) {
firingIndex--;
}
}
}
});
}
return this;
},
// Check if a given callback is in the list.
// If no argument is given, return whether or not list has callbacks attached.
has: function( fn ) {
return fn ? jQuery.inArray( fn, list ) > -1 : !!( list && list.length );
},
// Remove all callbacks from the list
empty: function() {
list = [];
firingLength = 0;
return this;
},
// Have the list do nothing anymore
disable: function() {
list = stack = memory = undefined;
return this;
},
// Is it disabled?
disabled: function() {
return !list;
},
// Lock the list in its current state
lock: function() {
stack = undefined;
if ( !memory ) {
self.disable();
}
return this;
},
// Is it locked?
locked: function() {
return !stack;
},
// Call all callbacks with the given context and arguments
fireWith: function( context, args ) {
if ( list && ( !fired || stack ) ) {
args = args || [];
args = [ context, args.slice ? args.slice() : args ];
if ( firing ) {
stack.push( args );
} else {
fire( args );
}
}
return this;
},
// Call all the callbacks with the given arguments
fire: function() {
self.fireWith( this, arguments );
return this;
},
// To know if the callbacks have already been called at least once
fired: function() {
return !!fired;
}
}; return self;
};
一、$.Callback()的简单使用及应用场景
1、$.Callback()的用法。
观察者模式,添加完后统一触发。
function aaa(){
alert(1);
}
function bbb(){
alert(2);
}
var cb= $.Callbacks();
cb.add(aaa);
cb.add(bbb);
cb.fire();
2、好处,应用场景。
要统一的管理aaa和bbb。有时候如下,很难对不同作用域下的函数进行统一管理。
function aaa(){
alert(1);
}
(function(){
function bbb(){
alert(2);
}
})();
aaa();
bbb();
只能弹出1,因为bbb是局部作用域中的。
$callback可以做到。如下,只要cb是全局的。
var cb= $.Callbacks();
function aaa(){
alert(1);
}
cb.add(aaa);
(function(){
function bbb(){
alert(2);
}
cb.add(bbb);
})();
cb.fire();
对应复杂情况很有用。统一管理,通过fire统一触发。
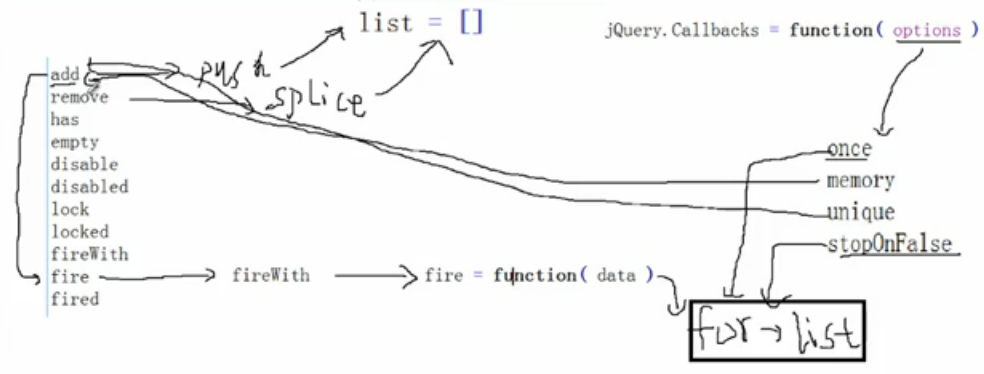
二、原理图
Callback接收一个参数,可以有4个选项,once,memory,unique,stopOnFalse。
self单体有这些方法:add,remove,has,empty,disable,disabled,lock,locked, fireWith,fire,fired。
list=[]数组变量,用来收集回调函数。fire的时候对其循环调用。
add:push数组
fire:调用fireWith,fireWith允许传参,fire可传可不传。
fireWith:调用私有函数fire,在私有函数fire中for循环list。
remove:splice数组。
4个参数:
- once针对fire()只循环一次
- memory 针对add,作用到add上,add时判断有memory就去执行fire。
- unique 针对add,添加的时候就可以去重
- stopOnFalse 针对fire,在for循环时遇到false,立即跳出循环
三、更多用法
1、callback4个参数的作用
- once: 只能够触发一次。
- memory: 当队列已经触发之后,再添加进来的函数就会直接被调用,不需要再触发一次。
- unique: 保证函数的唯一
- stopOnFalse: 只要有一个回调返回 false,就中断后续的调用。
举例:
不传参数,fire几次就触发几次。
function aaa() {
alert(1);
}
function bbb() {
alert(2);
}
var cb = $.Callbacks();
cb.add(aaa);
cb.add(bbb);
cb.fire(); //1 2
cb.fire();//1 2
- once:fire只能触发一次,源码中fire后如果有once就把list干掉了,list=undefined了。
function aaa() {
alert(1);
}
function bbb() {
alert(2);
}
var cb = $.Callbacks('once');
cb.add(aaa);
cb.add(bbb);
cb.fire(); //1 2
cb.fire();
不传参数,在fire之后add的回调不能被fire。
//不写参数,只弹出1,2不会弹出
function aaa() {
alert(1);
} function bbb() {
alert(2);
}
var cb = $.Callbacks();
cb.add(aaa);
cb.fire(); //
cb.add(bbb);
- memory记忆,在fire前面后面add的方法都能得到执行。
function aaa() {
alert(1);
}
function bbb() {
alert(2);
}
var cb = $.Callbacks('memory');
cb.add(aaa);
cb.fire(); //1 2
cb.add(bbb);
- unique:去重
//不加参数,add2次aaa,就会触发2次aaa
function aaa() {
alert(1);
} var cb = $.Callbacks();
cb.add(aaa);
cb.add(aaa);
cb.fire(); //1 1
function aaa() {
alert(1);
}
var cb = $.Callbacks('unique');
cb.add(aaa);
cb.add(aaa);
cb.fire(); //1 加了unique参数,同样的函数不能多次add
- stopOnFalse:函数返回false跳出循环
function aaa() {
alert(1);
return false;
}
function bbb() {
alert(2);
}
var cb = $.Callbacks();
cb.add(aaa);
cb.add(bbb);
cb.fire(); //1 2 不传参,第一个函数返回false时后面的函数也能正常执行
function aaa() {
alert(1);
return false;
}
function bbb() {
alert(2);
}
var cb = $.Callbacks('stopOnFalse');
cb.add(aaa);
cb.add(bbb);
cb.fire(); //
//传参stopOnFalse,第一个函数返回false时后面的函数不再执行
2、callback也可以接收组合的形式
function aaa() {
alert(1);
}
function bbb() {
alert(2);
}
//组合使用,只执行一次,并且弹出1 2
var cb = $.Callbacks('once memory');
cb.add(aaa);
cb.fire(); //
cb.add(bbb);
cb.fire();
源码中:
传入了 once和memory后,
options={once:true,memory:true}
optionCache={
"once memory":{once:true,memory:true}
}
6、fire()可以传参
参数作为每个回调函数的实参
function aaa(n) {
alert("aaa "+n);
}
function bbb(n) {
alert("bbb "+n);
}
var cb = $.Callbacks();
cb.add(aaa);
cb.add(bbb);
//fire传参
cb.fire("hello"); //弹出aaa hello 和bbb hello
四、源码
Callbacks就是一个工具函数,内部定义了一个self ,add和remove还有has等挂在self上。
1、参数处理
$.Callbacks有4个可选的参数,可以组合传入,用空格分隔。比如 $.Callbacks("once memory unique");
这样传入的构造函数字符串实际上是一个字符串,源码中做了处理会把这个字符串转成对象。
// String to Object options format cache
var optionsCache = {}; // Convert String-formatted options into Object-formatted ones and store in cache
function createOptions( options ) {
var object = optionsCache[ options ] = {};
jQuery.each( options.match( core_rnotwhite ) || [], function( _, flag ) {
object[ flag ] = true;
});
return object;
}
在构造函数中传入一个options后,先进行如下处理调用。把一个字符串处理成一个对象。
传入的options="once memory unique"处理后options={once:true,memory:true,unique:true}。
// Convert options from String-formatted to Object-formatted if needed
// (we check in cache first)
options = typeof options === "string" ?
( optionsCache[ options ] || createOptions( options ) ) :
jQuery.extend( {}, options );
过程如下:options="once memory unique"是string类型,所以先从optionsCache中获取,现在optionsCache为{}所以optionsCache[ options ]是undefined走后面的createOptions( options ) 。create操作中先新建一个以options为键的空对象,再循环给对象中填充。循环操作完
optionCache为
optionCache={ "once memory unique":{once:true,memory:true,unique:true} }
options为
options={once:true,memory:true,unique:true}
2、add源码
主要是把回调函数Push到数组list中。
add: function() {
if ( list ) { //list初始化为[],if判断会返回true
// First, we save the current length
var start = list.length;
(function add( args ) {
jQuery.each( args, function( _, arg ) { ////处理cb.add(aaa,bbb)这种调用
var type = jQuery.type( arg );//arg就是每一个函数
if ( type === "function" ) {//arg是函数就push到list中,此时有个判断有没有unique
if ( !options.unique || !self.has( arg ) ) {//有unique走后面,判断list中有没有这个函数,有就不添加了
list.push( arg );
}
} else if ( arg && arg.length && type !== "string" ) { //处理cb.add([aaa,bbb])这种调用
// Inspect recursively
add( arg );//递归分解,最终还是push到list
}
});
})( arguments );
// Do we need to add the callbacks to the
// current firing batch?
if ( firing ) {
firingLength = list.length;
// With memory, if we're not firing then
// we should call right away
} else if ( memory ) {
firingStart = start;
fire( memory );
}
}
return this;
},
3、remove源码
// Remove a callback from the list
remove: function() {
if ( list ) {
jQuery.each( arguments, function( _, arg ) {
var index;
while( ( index = jQuery.inArray( arg, list, index ) ) > -1 ) {
list.splice( index, 1 );//主要就是splice删除操作
// Handle firing indexes
if ( firing ) {
if ( index <= firingLength ) {
firingLength--;
}
if ( index <= firingIndex ) {
firingIndex--;
}
}
}
});
}
return this;
},
4、fire源码
1、整体调用逻辑
self的fire调用self的fireWith,fireWith把参数传递到fire()函数。
// Call all callbacks with the given context and arguments
fireWith: function( context, args ) {
if ( list && ( !fired || stack ) ) {
args = args || [];
args = [ context, args.slice ? args.slice() : args ];
if ( firing ) {
stack.push( args );
} else {
fire( args );
}
}
return this;
},
// Call all the callbacks with the given arguments
fire: function() {
self.fireWith( this, arguments );
return this;
},
fire()时主要是for循环
// Fire callbacks
fire = function( data ) {
memory = options.memory && data;
fired = true;//fired变为true说明已经调用过一次了,
firingIndex = firingStart || 0;
firingStart = 0;
firingLength = list.length;
firing = true;//触发进行时
for ( ; list && firingIndex < firingLength; firingIndex++ ) {
if ( list[ firingIndex ].apply( data[ 0 ], data[ 1 ] ) === false && options.stopOnFalse ) {//每次函数调用同时处理stopOnFalse的情况
memory = false; // To prevent further calls using add //stopOnFalse后有memory也不好使了
break;
}
}
firing = false;//触发结束
if ( list ) {
if ( stack ) {
if ( stack.length ) {
fire( stack.shift() );
}
} else if ( memory ) {
list = [];
} else {
self.disable();
}
}
},
2、firing特殊情况
比如在 fire 处理队列中,某个函数又在队列中添加了一个回调函数,或者,在队列中又删除了某个回调函数。 fire 处理过程中,某个函数又调用了 fire 来触发事件呢?
先通过例子来看一下效果
function aaa() {
alert(1);
cb.fire(); //在这里调用fire()会出现什么问题 死循环
}
function bbb() {
alert(2);
}
var cb = $.Callbacks();
cb.add(aaa);
cb.add(bbb);
cb.fire();
在执行函数的过程中再次调用fire()的执行顺序是怎样的?
var bBtn=true;//用bBtn避免死循环
function aaa() {
alert(1);
if(bBtn){
cb.fire();//注意这里fire调用后执行顺序是1 2 1 2,而不是1 1 2 2
bBtn=false;
} }
function bbb() {
alert(2);
}
var cb = $.Callbacks();
cb.add(aaa);
cb.add(bbb); cb.fire();
结论:把函数运行过程中触发的fire()放到了运行过程的队列当中。
fire 处理过程中,某个函数又调用了 fire 来触发事件时,jQuery的处理方式如下:
将这个嵌套的事件先保存起来,等到当前的回调序列处理完成之后,再检查被保存的事件,继续完成处理。显然,使用队列是处理这种情况的理想数据结构,如果遇到这种状况,我们就将事件数据入队,待处理的时候,依次出队数据进行处理。什么时候需要这种处理呢?显然不是once的情况。在JavaScript中,堆队列也是通过数组来实现的,push用来将数据追加到数组的最后,而shift用来出队,从数据的最前面获取数据。
不过,jQuery没有称之为队列,而是取名stack。
// Stack of fire calls for repeatable lists
stack = !options.once && [],
入队
源码中,在fireWith的时候判断for循环有没有执行完
fireWith: function( context, args ) {
...if ( firing ) {//firing在for循环没有走完时一直是true
stack.push( args );//所以这句话意思就是函数执行时再去fire()调用就会push到stack数组中
} else {
fire( args );
}
}
return this;
},
出队
再去调用fire()的时候
// Fire callbacks
fire = function( data ) {
memory = options.memory && data;
fired = true;//fired变为true说明已经调用过一次了,
firingIndex = firingStart || 0;
firingStart = 0;
firingLength = list.length;
firing = true;//触发进行时
for ( ; list && firingIndex < firingLength; firingIndex++ ) {
if ( list[ firingIndex ].apply( data[ 0 ], data[ 1 ] ) === false && options.stopOnFalse ) {//每次函数调用同时处理stopOnFalse的情况
memory = false; // To prevent further calls using add //stopOnFalse后有memory也不好使了
break;
}
}
firing = false;//触发结束
if ( list ) {
if ( stack ) { //这就是出现在函数执行过程中再次fire()的时候,等循环执行完,再去按顺序执行
if ( stack.length ) {
fire( stack.shift() );
}
} else if ( memory ) {//只执行一次的时候,有once,memory就清空list,此时fire()就相当于一个执行一个空数组
list = [];
} else {
self.disable();//disable阻止后续任何的fire()操作
}
}
},
针对下面这段源码的一个例子:
once和memory同时存在的时候,fire()无效因为list为[]了,但是add仍然有效。
当有memory的时候,把之前添加的清空;允许添加并再次运行fire后清空;当不存在memory的时候既只有once配置,fire之后既不允许做任何操作了。
else if ( memory ) {//只执行一次的时候,有once,memory就清空list,此时fire()就相当于一个执行一个空数组
list = [];
} else {
self.disable();//disable阻止后续任何的fire()操作
}
disable阻止后续任何的fire()操作。
function aaa() {
alert(1);
}
function bbb() {
alert(2);
}
//组合使用,只执行一次,并且弹出1 2 3
var cb = $.Callbacks('once memory');
cb.add(aaa);
cb.fire(); //
cb.fire();//此时list为[]
cb.add(bbb);
cb.fire();
function ccc(){
alert(3);
}
cb.add(ccc);
5、其他源码
has(fn):判断list有没有fn
empty: 清空数组list=[]
disable:全部锁住,禁止了,如下
// Have the list do nothing anymore
disable: function() {
list = stack = memory = undefined;
return this;
},
disabled:判断是不是禁止了。return !list;
lock:只是把stack锁住
// Lock the list in its current state
lock: function() {
stack = undefined;
if ( !memory ) {
self.disable();
}
return this;
},
locked:是否locked。 return !stack;
6、 lock和disable的区别
disable禁止所有操作
function aaa() {
alert(1);
}
function bbb() {
alert(2);
}
var cb = $.Callbacks('memory');
cb.add(aaa);
cb.fire(); //
cb.disable();//disable()后只能弹出1 因为禁止所有操作了,虽然有Memory
cb.add(bbb);//不起作用了,此时list变为undefined了
cb.fire();//不起作用了
lock只是锁住数组
function aaa() {
alert(1);
}
function bbb() {
alert(2);
}
var cb = $.Callbacks('memory');
cb.add(aaa);
cb.fire(); //1 2
cb.lock();//lock()只是把后续的fire()锁住,其他操作是锁不住的
cb.add(bbb);
cb.fire();//不起作用了 此时list为[]
参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/haogj/p/4473477.html
本文作者starof,因知识本身在变化,作者也在不断学习成长,文章内容也不定时更新,为避免误导读者,方便追根溯源,请诸位转载注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/starof/p/6885500.html有问题欢迎与我讨论,共同进步。
jquery源码 Callback的更多相关文章
- jQuery源码分析系列
声明:本文为原创文章,如需转载,请注明来源并保留原文链接Aaron,谢谢! 版本截止到2013.8.24 jQuery官方发布最新的的2.0.3为准 附上每一章的源码注释分析 :https://git ...
- jQuery源码 Ajax模块分析
写在前面: 先讲讲ajax中的相关函数,然后结合函数功能来具体分析源代码. 相关函数: >>ajax全局事件处理程序 .ajaxStart(handler) 注册一个ajaxStart事件 ...
- jQuery源码-dom操作之jQuery.fn.html
写在前面 前面陆陆续续写了jQuery源码的一些分析,尽可能地想要cover里面的源码细节,结果导致进度有些缓慢.jQuery的源码本来就比较晦涩,里面还有很多为了解决兼容问题很引入的神代码,如果不g ...
- jquery 源码解析
静态与实力方法共享设计 遍历方法 $(".a").each() //作为实例方法存在 $.each() //作为静态方法存在 Jquery源码 jQuery.prototype = ...
- jquery 源码学习(*)
最近在做日志统计程序,发现对方的程序是在Jquery基础上进行开发的,而公司的网站的框架是prototype.而且我也早就想了解一下Jquery源码,故决定研究Jquery源码,模拟它的方法 Jq ...
- [转]jQuery源码分析系列
文章转自:jQuery源码分析系列-Aaron 版本截止到2013.8.24 jQuery官方发布最新的的2.0.3为准 附上每一章的源码注释分析 :https://github.com/JsAaro ...
- jQuery 源码基本框架
抽丝剥茧, 7000+ 行的 jQuery 源码基本可以概括为以下的伪代码 (function (window, undefined) { //将 document 封装成 jQuery 对象并缓存 ...
- jquery源码 DOM加载
jQuery版本:2.0.3 DOM加载有关的扩展 isReady:DOM是否加载完(内部使用) readyWait:等待多少文件的计数器(内部使用) holdReady():推迟DOM触发 read ...
- jquery源码解读
最近一直在研读 jQuery 源码,初看源码一头雾水毫无头绪,真正静下心来细看写的真是精妙,其结构明晰,高内聚.低耦合,兼具优秀的性能与便利的扩展性,在浏览器的兼容性(功能缺陷.渐进增强)优雅的处理能 ...
随机推荐
- 2.Redis的基本配置
一.参数配置 redis.conf的主要配置参数的意义: daemonize:是否以后台daemon方式运行 pidfile:pid文件位置 port:监听的端口号 timeout:请求超时时间 lo ...
- android中的 Toast 和 AlertDialog
Toast 一般用来显示一些不需要用户操作的提示信息,举个栗子: public void toast(String msg) { //---创建并设置显示的内容和显示时长 Toast toast = ...
- (iOS)私有API的使用(原创)
最近在做企业级程序,需要搞设备的udid等信息,但是ios7把udid私有化了,不公开使用.所以研究了一下ios的私有api. 调查了一下文章,发现这方面的文章不多,国内更是不全,高手们都懒得写基础教 ...
- shiro基础学习(三)—shiro授权
一.入门程序 1.授权流程 2.授权的三种方式 (1)编程式: 通过写if/else 授权代码块完成. Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubjec ...
- 消息队列NetMQ 原理分析3-命令产生/处理和回收线程
消息队列NetMQ 原理分析3-命令产生/处理和回收线程 前言 介绍 目的 命令 命令结构 命令产生 命令处理 创建Socket(SocketBase) 创建连接 创建绑定 回收线程 释放Socket ...
- .net应用程序中添加chm帮助文档打开显示此程序无法显示网页问题
在做.net大作业时添加了chm帮助文档结果在打开时显示“此程序无法显示网页问题”,但是把帮助文档拷到别的路径下却显示正常, 经过从网上查找,终于找到了答案: (1).chm文件的路径中不能含有“#” ...
- jade模板引擎简明用法
①.特性 首个单词为标签,有一些不能识别的标签可作为code,如each for case if else if unless zen coding风格添加标签,如 .nb#hello 生成 & ...
- 记录下一个C++初始化的方式(很少有人这么用,但是却是一个使代码更加简洁的方式)
很多时候,在一个类创建的时候给它初始化,一般呢,99%的人都会这么用: //A.h Class CA { int a; char* p; int getValue(); }; //A.cpp CA:: ...
- javascript 函数和作用域(函数,this)(六)
重点. 一.函数 1.函数介绍 函数是一块JavaScript代码,被定义一次,但可执行和调用多次.JS中的函数也是对象,所以JS函数可以像其他对象那样操作和传递,所以我们也常叫JS中的函数为函数对象 ...
- percona-xtrabackup安装
二进制包安装(推荐安装方式,不用安装依赖包,非常方便): 1.下载安二进制包: wget https://www.percona.com/downloads/XtraBackup/Perco ...
