[Scikit-learn] 2.1 Clustering - Variational Bayesian Gaussian Mixture
最重要的一点是:Bayesian GMM为什么拟合的更好?
PRML 这段文字做了解释:

Ref: http://freemind.pluskid.org/machine-learning/deciding-the-number-of-clusterings/
链接中提到了一些其他的无监督聚类。
From: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/mixture.html#variational-bayesian-gaussian-mixture
Due to its Bayesian nature, the variational algorithm needs more hyper- parameters than expectation-maximization,
the most important of these being the concentration parameter weight_concentration_prior.
- Specifying a low value for the concentration prior will make the model put most of the weight on few components set the remaining components weights very close to zero.
- High values of the concentration prior will allow a larger number of components to be active in the mixture.
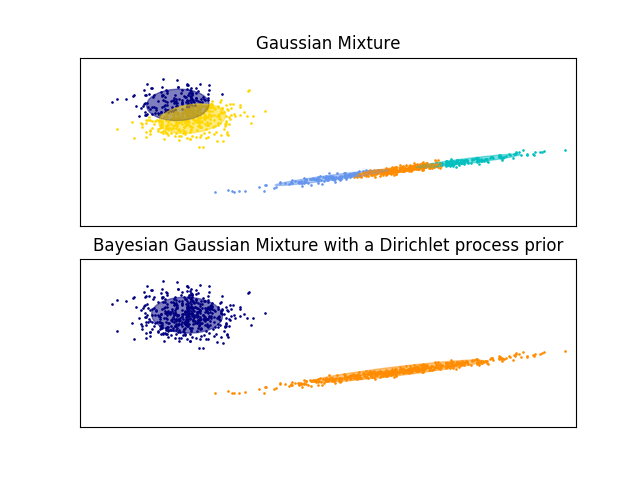
The examples below compare Gaussian mixture models with a fixed number of components, to the variational Gaussian mixture models with a Dirichlet process prior. Here, a classical Gaussian mixture is fitted with 5 components on a dataset composed of 2 clusters.
We can see that the variational Gaussian mixture with a Dirichlet process prior is able to limit itself to only 2 components whereas the Gaussian mixture fits the data with a fixed number of components that has to be set a priori by the user. In this case the user has selected n_components=5 which does not match the true generative distribution of this toy dataset. Note that with very little observations, the variational Gaussian mixture models with a Dirichlet process prior can take a conservative stand, and fit only one component.
Dirichlet distribution 具有自动的特征选取的作用,找出起主要作用的components。
5 for GMM
[ 0.1258077 0.23638361 0.23330578 0.26361639 0.14088652]
5 for Bayesian GMM
[ 0.001019 0.00101796 0.49948856 0.47955123 0.01892325]
问题来了:
为什么dirichlet会让三个的权重偏小,而GMM却没有,难道是收敛速度不同?
应该跟速度没有关系。加了先验后,后验变为了dirichlet,那么参数的估计过程中便具备了dirichlet的良好性质。
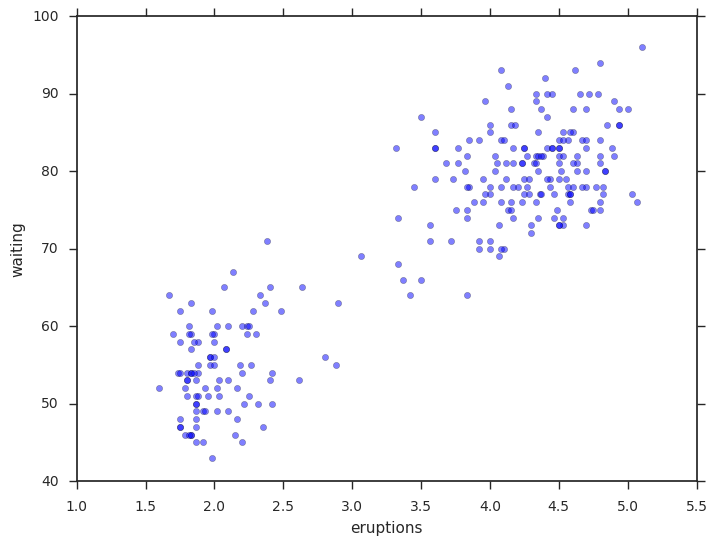
原始数据
Our data set will be the classic Old Faithful dataset.
plt.scatter(data['eruptions'], data['waiting'], alpha=0.5);
plt.xlabel('eruptions');
plt.ylabel('waiting');
如何拟合?
from sklearn.mixture import BayesianGaussianMixture mixture_model = BayesianGaussianMixture(
n_components=10,
random_state=5, # control the pseudo-random initialization
weight_concentration_prior_type='dirichlet_distribution',
weight_concentration_prior=1.0, # parameter of the Dirichlet component prior
max_iter=200, # choose this to be big in case it takes a long time to fit
)
mixture_model.fit(data);
Ref: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/mixture/plot_concentration_prior.html
可直接调用该程式:
plot_ellipses(ax1, model.weights_, model.means_, model.covariances_) def plot_ellipses(ax, weights, means, covars):
"""
Given a list of mixture component weights, means, and covariances,
plot ellipses to show the orientation and scale of the Gaussian mixture dispersal.
"""
for n in range(means.shape[0]):
eig_vals, eig_vecs = (covars[n])
unit_eig_vec = eig_vecs[0] / np.linalg.norm(eig_vecs[0])
angle = np.arctan2(unit_eig_vec[1], unit_eig_vec[0])
# Ellipse needs degrees
angle = 180 * angle / np.pi
# eigenvector normalization
eig_vals = 2 * np.sqrt(2) * np.sqrt(eig_vals)
ell = mpl.patches.Ellipse(
means[n], eig_vals[0], eig_vals[1],
180 + angle,
edgecolor=None,)
ell2 = mpl.patches.Ellipse(
means[n], eig_vals[0], eig_vals[1],
180 + angle,
edgecolor='black',
fill=False,
linewidth=1,)
ell.set_clip_box(ax.bbox)
ell2.set_clip_box(ax.bbox)
ell.set_alpha(weights[n])
ell.set_facecolor('#56B4E9')
ax.add_artist(ell)
ax.add_artist(ell2)
plot_results(
mixture_model,
data['eruptions'], data['waiting'],
'weight_concentration_prior={}'.format(1.0)) def plot_results(model, x, y, title, plot_title=False): fig, ax = plt.subplots(3, 1, sharex=False)
# 上面是ax没用,以下重新定义了ax1 ax2
gs = gridspec.GridSpec(3, 1) # 自定义子图位置
ax1 = plt.subplot(gs[0:2, 0])
# 以下四行是固定套路
ax1.set_title(title)
ax1.scatter(x, y, s=5, marker='o', alpha=0.8)
ax1.set_xticks(())
ax1.set_yticks(())
n_components = model.get_params()['n_components'] plot_ellipses(ax1, model.weights_, model.means_, model.covariances_)
# ax1:画椭圆
# ax2:画权重
ax2 = plt.subplot(gs[2, 0])
ax2.get_xaxis().set_tick_params(direction='out')
ax2.yaxis.grid(True, alpha=0.7)
for k, w in enumerate(model.weights_):
ax2.bar(k, w, width=0.9, color='#56B4E9', zorder=3,
align='center', edgecolor='black')
ax2.text(k, w + 0.007, "%.1f%%" % (w * 100.),
horizontalalignment='center')
ax2.set_xlim(-.6, n_components - .4)
ax2.set_ylim(0., 1.1)
ax2.tick_params(axis='y', which='both', left='off',
right='off', labelleft='off')
ax2.tick_params(axis='x', which='both', top='off') if plot_title:
ax1.set_ylabel('Estimated Mixtures')
ax2.set_ylabel('Weight of each component')
查看拟合过程:
lower_bounds = []
mixture_model = BayesianGaussianMixture(
n_components =10,
covariance_type ='full',
max_iter =1,
random_state =2,
weight_concentration_prior_type ='dirichlet_distribution',
warm_start =True,
)
# 设置model.fit为只递归一次
for i in range(200):
mixture_model.fit(data)
if mixture_model.converged_: break
lower_bounds.append(mixture_model.lower_bound_)
if i%5==0 and i<60:
plt.figure();
plot_results(
mixture_model,
data['eruptions'], data['waiting'],
'EM step={}, lower_bound={}'.format(
i, mixture_model.lower_bound_)
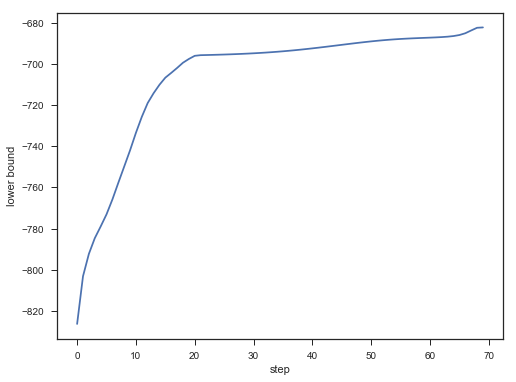
); plt.figure();
plt.plot(lower_bounds);
plt.gca().set_xlabel('step')
plt.gca().set_ylabel('lower bound')
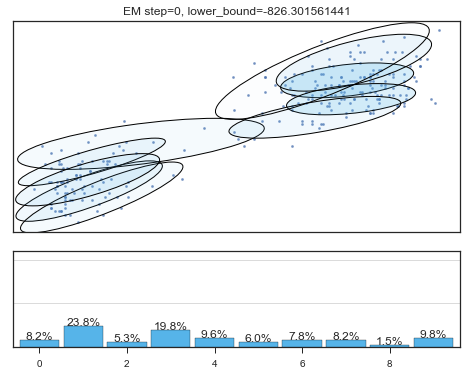
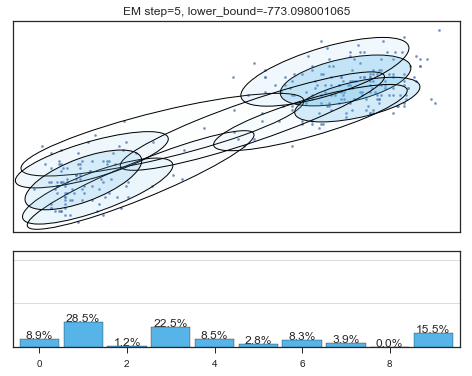
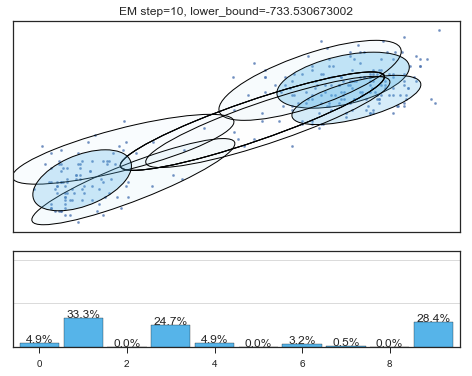
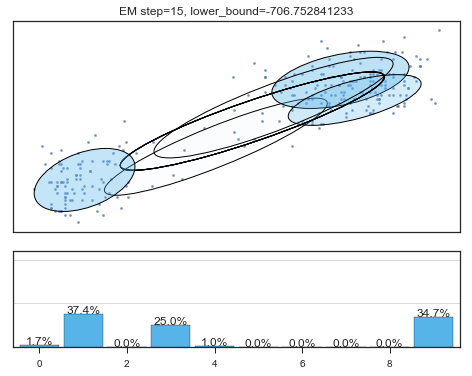
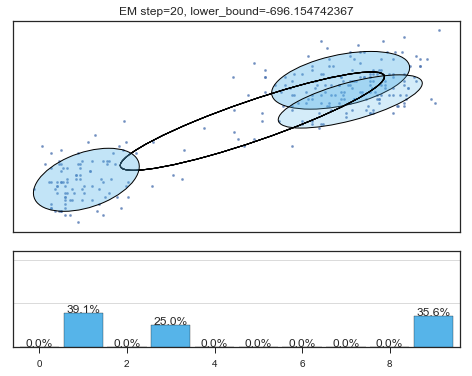
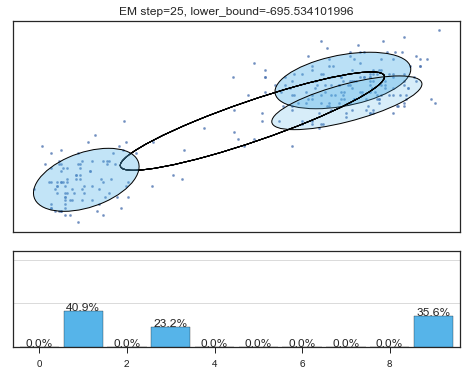
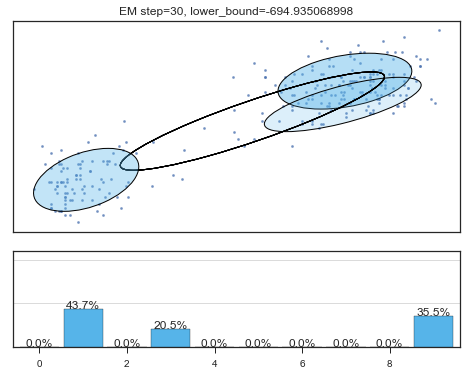
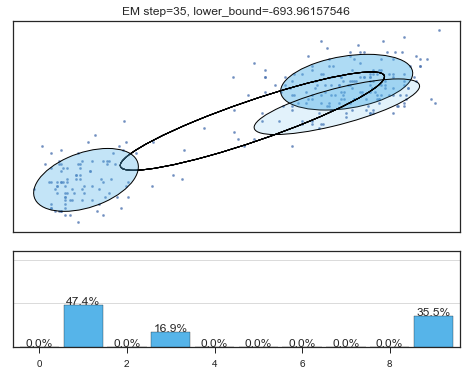
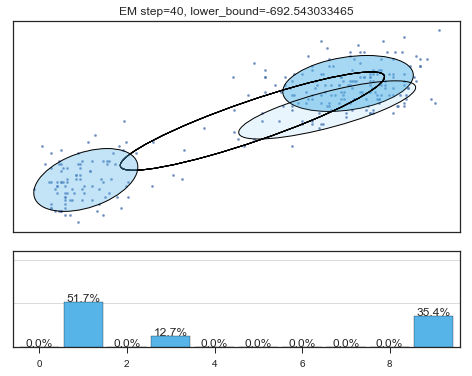

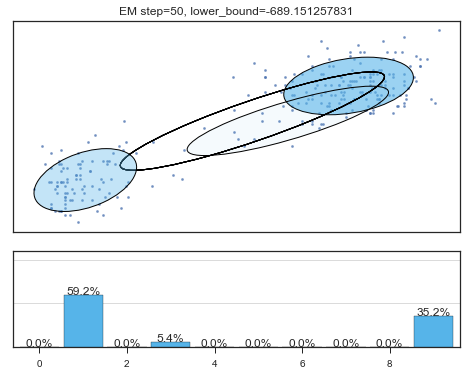
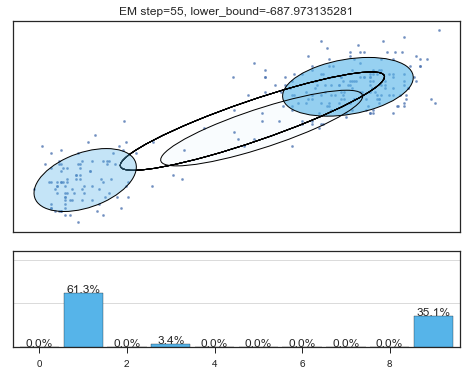
Lower bound 逐渐增加。
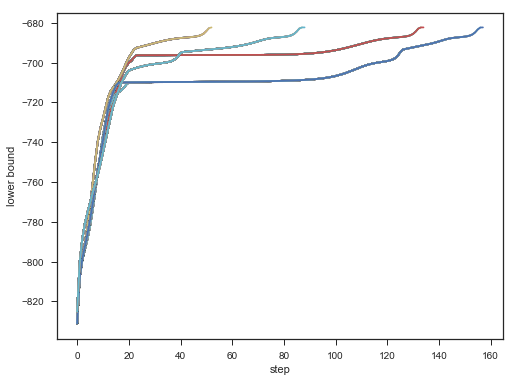
不同初始,效果对比:
for seed in range(6,11):
lower_bounds = []
mixture_model = BayesianGaussianMixture(
n_components=10,
covariance_type='full',
max_iter=1,
random_state=seed,
weight_concentration_prior_type='dirichlet_distribution',
warm_start=True,
)
for i in range(200):
mixture_model.fit(data)
if mixture_model.converged_: break
lower_bounds.append(mixture_model.lower_bound_)
plt.plot(lower_bounds);
plt.gca().set_xlabel('step')
plt.gca().set_ylabel('lower bound');
Result:
[Scikit-learn] 2.1 Clustering - Variational Bayesian Gaussian Mixture的更多相关文章
- 基于图嵌入的高斯混合变分自编码器的深度聚类(Deep Clustering by Gaussian Mixture Variational Autoencoders with Graph Embedding, DGG)
基于图嵌入的高斯混合变分自编码器的深度聚类 Deep Clustering by Gaussian Mixture Variational Autoencoders with Graph Embedd ...
- scikit learn 模块 调参 pipeline+girdsearch 数据举例:文档分类 (python代码)
scikit learn 模块 调参 pipeline+girdsearch 数据举例:文档分类数据集 fetch_20newsgroups #-*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import ...
- (原创)(三)机器学习笔记之Scikit Learn的线性回归模型初探
一.Scikit Learn中使用estimator三部曲 1. 构造estimator 2. 训练模型:fit 3. 利用模型进行预测:predict 二.模型评价 模型训练好后,度量模型拟合效果的 ...
- (原创)(四)机器学习笔记之Scikit Learn的Logistic回归初探
目录 5.3 使用LogisticRegressionCV进行正则化的 Logistic Regression 参数调优 一.Scikit Learn中有关logistics回归函数的介绍 1. 交叉 ...
- [Scikit-learn] 2.1 Clustering - Gaussian mixture models & EM
原理请观良心视频:机器学习课程 Expectation Maximisation Expectation-maximization is a well-founded statistical algo ...
- Scikit Learn: 在python中机器学习
转自:http://my.oschina.net/u/175377/blog/84420#OSC_h2_23 Scikit Learn: 在python中机器学习 Warning 警告:有些没能理解的 ...
- Scikit Learn
Scikit Learn Scikit-Learn简称sklearn,基于 Python 语言的,简单高效的数据挖掘和数据分析工具,建立在 NumPy,SciPy 和 matplotlib 上.
- 漫谈 Clustering (3): Gaussian Mixture Model
上一次我们谈到了用 k-means 进行聚类的方法,这次我们来说一下另一个很流行的算法:Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM).事实上,GMM 和 k-means 很像,不过 GMM ...
- [zz] 混合高斯模型 Gaussian Mixture Model
聚类(1)——混合高斯模型 Gaussian Mixture Model http://blog.csdn.net/jwh_bupt/article/details/7663885 聚类系列: 聚类( ...
随机推荐
- java控制台输入输出
一.比较传统的输入方法用输入流,得到字符串后要另行判断.转换 案例 import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import ...
- windows 下面安装gcc
0.环境说明: win7 家庭版64位 1.下载编译器 https://sourceforge.net/projects/mingw/?source=typ_redirect 如图所示: 注意,安装的 ...
- DialogFragment的应用
一.DialogFragment简单介绍: 1.基本概念 DialogFrament 指一个与fragment建立了关联的Dialog, 随fragment生, 随fragment死, 即Dialog ...
- 为什么要用深度学习来做个性化推荐 CTR 预估
欢迎大家前往腾讯云技术社区,获取更多腾讯海量技术实践干货哦~ 作者:苏博览 深度学习应该这一两年计算机圈子里最热的一个词了.基于深度学习,工程师们在图像,语音,NLP等领域都取得了令人振奋的进展.而深 ...
- hive自定义UDF
udf udaf udtf 使用方式 hiverc文件 1.jar包放到安装日录下或者指定目录下 2.${HIVE_HOME}/bin目录下有个.hiverc文件,它是隐藏文件. 3.把初始化语句加载 ...
- hdu1251字典树递归算法
统计难题 Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131070/65535 K (Java/Others) Total Subm ...
- IFrame父页面和子页面的交互
现在在页面里面用到iframe的情况越来越少了,但有时还是避免不了,甚至这些页面之间还需要用js来做交互,那么这些页面如何操作彼此的dom呢?下面将会逐步介绍. 1.父页面操作子页面里面的dom 下面 ...
- 云计算---OpenStack Neutron详解
简介: neutron是openstack核心项目之一,提供云计算环境下的虚拟网络功能 OpenStack网络(neutron)管理OpenStack环境中所有虚拟网络基础设施(VNI),物理网络基础 ...
- Python一维数据分析
1.Numpy数组 numpy的数组只能存放同一种数据类型,使用的方式和Python列表类似 1.1 声明: import numpy as np countries = np.array([ 'Af ...
- 改变oracle数据库归档模式_译文
Changing the Database Archiving Mode 改变数据库归档模式. Purpose 目的 This module describes how you can change ...
