数据序列化导读(1)[JSON]
所谓数据序列化(Data Serialization), 就是将某个对象的状态信息转换为可以存储或传输的形式的过程。 那么,为什么要进行序列化?
- 首先,为了方便数据存储;
- 其次,为了方便数据传递。
在数据序列化期间,某个对象的当前状态被写入到临时或永久存储区。随后,可以把序列化到存储区的数据(通过网络)传输出去,然后进行反序列化,重新创建该对象。 运行在节点A上的某个对象X的当前状态,可以理解为保存在节点A的内存里的某个结构体。那么要把节点A上的对象X的状态信息传递到节点B上,把对象X的状态信息从内存中dump出来并序列化是必不可少的。支持数据序列化的常见格式有XML, JSON 和YAML。接下来本系列将首先介绍一下JSON。
1. 什么是JSON?
JSON是JavaScript Object Notation的缩写。简单来说,JSON是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,易于人类阅读和书写,同时也易于机器解析和生成。它基于JavaScript语言而实现, 是open ECMAScript standard的一个子集。 JSON采用完全独立于语言的文本格式,但也使用了类似于C语言家族的习惯。这些特性使得JSON成为了一种理想的数据交换格式。
特别注意: JSON的字符串必须用双引号引用起来。 (因为后面会讲到YAML, YAML的字符串没有这样的限制)
2. 构建JSON的结构
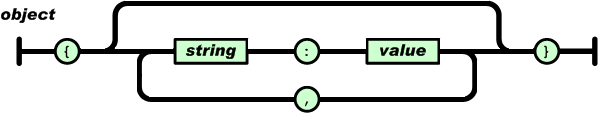
- A collection of name/value pairs(键/值对集合), 即对象(object), 也就是字典(dict)。使用{ }表示,与Python的dict类似。
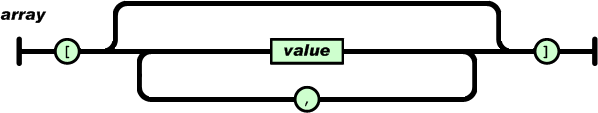
- An ordered list of values (值的有序表),即数组(array)。使用[ ]表示,与Python的list类似。

注意:上面的截图来源戳这里。
2.1 对象(object)
在其他语言中,对象(object)又称为字典(dict),纪录(record),结构(struct),哈希表(hash table),有键列表(keyed list),或者关联数组 (associative array)。在JSON中,通常把键/值对集合称之为对象(Object)(P.S. 本人习惯于字典的叫法)。对象是一个无序的“‘键/值’对”集合。一个对象以“{”开始,“}”结束。每个“键”后跟一个“:”(冒号);“‘键/值’ 对”之间使用“,”(逗号)分隔。例如:
var Goddess = {
"FirstName" : "Grace",
"LastName" : "Liu",
"Age" : "18"
};
2.2 数组(array)
数组很好理解,跟C语言的数组没什么不同,跟Python的list一样。数组是值(value)的有序集合。一个数组以“[”(左中括号)开始,“]”(右中括号)结束。值之间使用“,”(逗号)分隔。例如:
var Students = [
{"name":"John", "age":"23", "city":"Agra"},
{"name":"Steve", "age":"28", "city":"Delhi"},
{"name":"Peter", "age":"32", "city":"Chennai"},
{"name":"Chaitanya", "age":"28", "city":"Bangalore"}
];
3. 值(value)的类型
- 字符串(string)
- 数字(number)
- 对象(object(即字典))
- 数组(array)
- 布尔值(boolean)
- 空值(null)

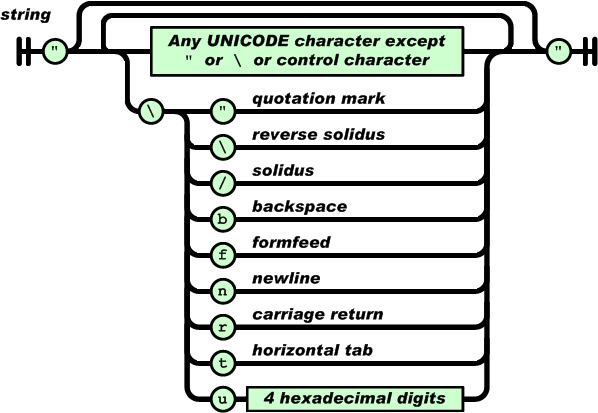
3.1 字符串(string)
- 字符串(string)是由双引号包围的任意数量Unicode字符的集合,使用反斜线转义。
- 单个字符(character)即一个单独的字符串(character string)。
- 字符串(string)与C语言的字符串非常相似。
3.2 数值(number)
- 数值(number)也与C的数值非常相似。
- 不使用8进制和16进制编码。

3.3 对象(object)
对象(object)即字典(dict),参见2.1。
3.4 数组(array)
数组(array)即列表(list),参见2.2。
3.5 布尔值(boolean)
要么为真(true), 要么为假(false)。对应于Python中的True/False。 注意在Python中, 真/假的开头字母是大写,而JSON一律用小写。
3.6 空值(null)
JSON的空值用null表示,类似于C语言的NULL, Python语言的None,Go语言的nil。
P.S. 由3.5和3.6可以看出,JSON偏好使用一律小写的关键字。
4 在Python中使用JSON
4.1 JSON值类型 v.s. Python值类型

4.2 将Python对象序列化(serialize)为JSON格式的文本
Python提供了专门的模块json, 使用json.dump()或者json.dumps()就可以把一个Python对象序列化为JSON格式的文本。 有关json模块的具体用法,请参见这里。
- foo_python2json.py
#!/usr/bin/python3 """ Serialize a Python Object by using json.dumps() """ import sys
import json obj = {
"students":
[
{
"name": "John",
"age": 23,
"city": "Agra",
"married": False,
"spouse": None
},
{
"name": "Steve",
"age": 28,
"city": "Delhi",
"married": True,
"spouse": "Grace"
},
{
"name": "Peter",
"age": 32,
"city": "Chennai",
"married": True,
"spouse": "Rachel"
}
]
} def main(argc, argv):
if argc != 2:
sys.stderr.write("Usage: %s <json file to save obj>\n" % argv[0])
return 1 with open(argv[1], 'w') as f:
txt = json.dumps(obj, indent=4)
print("DEBUG> " + str(type(obj)))
print("DEBUG> " + str(obj))
print("DEBUG> " + str(type(txt)))
print("DEBUG> " + txt)
f.write(txt + '\n') return 0 if __name__ == '__main__':
sys.exit(main(len(sys.argv), sys.argv))
- Run foo_python2json.py
huanli$ rm -f /tmp/foo.json
huanli$ ./foo_python2json.py /tmp/foo.json
DEBUG> <class 'dict'>
DEBUG> {'students': [{'spouse': None, 'age': , 'city': 'Agra', 'name': 'John', 'married': False}, {'spouse': 'Grace', 'age': , 'city': 'Delhi', 'name': 'Steve', 'married': True}, {'spouse': 'Rachel', 'age': , 'city': 'Chennai', 'name': 'Peter', 'married': True}]}
DEBUG> <class 'str'>
DEBUG> {
"students": [
{
"spouse": null,
"age": ,
"city": "Agra",
"name": "John",
"married": false
},
{
"spouse": "Grace",
"age": ,
"city": "Delhi",
"name": "Steve",
"married": true
},
{
"spouse": "Rachel",
"age": ,
"city": "Chennai",
"name": "Peter",
"married": true
}
]
}
huanli$
huanli$ cat -n /tmp/foo.json
{
"students": [
{
"spouse": null,
"age": ,
"city": "Agra",
"name": "John",
"married": false
},
{
"spouse": "Grace",
"age": ,
"city": "Delhi",
"name": "Steve",
"married": true
},
{
"spouse": "Rachel",
"age": ,
"city": "Chennai",
"name": "Peter",
"married": true
}
]
}
huanli$
4.3 将JSON格式的文本反序列化(deserialize)为Python对象
使用json.load()或者json.loads()就可以将一个JSON格式的文本反序列化为一个Python对象。
- foo_json2python.py
#!/usr/bin/python3 """ Deserialize JSON text to a Python Object by using json.loads() """ import sys
import json def main(argc, argv):
if argc != 2:
sys.stderr.write("Usage: %s <json file>\n" % argv[0])
return 1 with open(argv[1], 'r') as f:
txt = ''.join(f.readlines())
obj = json.loads(txt)
print("DEBUG> " + str(type(txt)))
print("DEBUG> " + txt)
print("DEBUG> " + str(type(obj)))
print("DEBUG> " + str(obj)) return 0 if __name__ == '__main__':
sys.exit(main(len(sys.argv), sys.argv))
- Run foo_json2python.py
huanli$ cat -n /tmp/foo.json
{
"students": [
{
"spouse": null,
"age": ,
"city": "Agra",
"name": "John",
"married": false
},
{
"spouse": "Grace",
"age": ,
"city": "Delhi",
"name": "Steve",
"married": true
},
{
"spouse": "Rachel",
"age": ,
"city": "Chennai",
"name": "Peter",
"married": true
}
]
}
huanli$
huanli$ ./foo_json2python.py /tmp/foo.json
DEBUG> <class 'str'>
DEBUG> {
"students": [
{
"spouse": null,
"age": ,
"city": "Agra",
"name": "John",
"married": false
},
{
"spouse": "Grace",
"age": ,
"city": "Delhi",
"name": "Steve",
"married": true
},
{
"spouse": "Rachel",
"age": ,
"city": "Chennai",
"name": "Peter",
"married": true
}
]
} DEBUG> <class 'dict'>
DEBUG> {'students': [{'city': 'Agra', 'name': 'John', 'married': False, 'spouse': None, 'age': }, {'city': 'Delhi', 'name': 'Steve', 'married': True, 'spouse': 'Grace', 'age': }, {'city': 'Chennai', 'name': 'Peter', 'married': True, 'spouse': 'Rachel', 'age': }]}
huanli$
直接使用json.load()也可以,例如:
huanli$ python3
Python 3.5.2 (default, Nov 23 2017, 16:37:01)
...<snip>....................................
>>> import json
>>> fd = open("/tmp/foo.json", "r")
>>> obj = json.load(fd)
>>> type(obj)
<class 'dict'>
>>> obj
{'students': [{'name': 'John', 'married': False, 'age': 23, 'city': 'Agra', 'spouse': None}, {'name': 'Steve', 'married': True, 'age': 28, 'city': 'Delhi', 'spouse': 'Grace'}, {'name': 'Peter', 'married': True, 'age': 32, 'city': 'Chennai', 'spouse': 'Rachel'}]}
>>>
4.4 序列化/反序列化用户定制的Python对象
在Python中,有一个模块pickle能把所有的Python对象都序列化。例如:
>>> import pickle
>>>
>>> a = 1 + 2j
>>> s = pickle.dumps(a)
>>> s
b'\x80\x03cbuiltins\ncomplex\nq\x00G?\xf0\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00G@\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x86q\x01Rq\x02.'
>>> b = pickle.loads(s)
>>> b
(1+2j)
>>> b == a
True
>>>
但是,要把一个用户定制的Python对象序列化为JSON文本就没有这么容易了,不信请看:
>>> import json
>>> a = 1 + 2j
>>> type(a)
<class 'complex'>
>>> s = json.dumps(a)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
File "/usr/lib64/python3.6/json/__init__.py", line 231, in dumps
return _default_encoder.encode(obj)
File "/usr/lib64/python3.6/json/encoder.py", line 199, in encode
chunks = self.iterencode(o, _one_shot=True)
File "/usr/lib64/python3.6/json/encoder.py", line 257, in iterencode
return _iterencode(o, 0)
File "/usr/lib64/python3.6/json/encoder.py", line 180, in default
o.__class__.__name__)
TypeError: Object of type 'complex' is not JSON serializable
>>>
怎么办?
- 自己实现一个序列化/反序列化的hook;
- 然后交给json.encode()/json.decode()去处理。
4.4.1 序列化用户定制的Python对象
- foo_encode.py
#!/usr/bin/python3 import sys
import json def encode_complex(z):
d_out = {}
if isinstance(z, complex):
d_out['__complex__'] = True
d_out['real'] = z.real
d_out['imag'] = z.imag
return d_out
else:
type_name = z.__class__.__name__
raise TypeError(f"Object of type '{type_name}' is not JSON serializable") def main(argc, argv):
if argc != 3:
sys.stderr.write("Usage: %s <complex> <json file>\n" % argv[0])
return 1 z = complex(argv[1])
f = argv[2]
with open(f, 'w') as fd:
txt = json.dumps(z, indent=4, default=encode_complex)
fd.write(txt + '\n') if __name__ == '__main__':
sys.exit(main(len(sys.argv), sys.argv))
- Run foo_encode.py
huanli$ rm -f /tmp/foo.json
huanli$ ./foo_encode.py '20+1.8j' /tmp/foo.json
huanli$ cat -n /tmp/foo.json
{
"__complex__": true,
"real": 20.0,
"imag": 1.8
}
huanli$
4.4.2 反序列化用户定制的Python对象
- foo_decode.py
#!/usr/bin/python3 import sys
import json def decode_complex(dct):
if ('__complex__' in dct) and (dct['__complex__'] is True):
return complex(dct['real'], dct['imag'])
return dct def main(argc, argv):
if argc != 2:
sys.stderr.write("Usage: %s <json file>\n" % argv[0])
return 1 f = argv[1]
with open(f, 'r') as fd:
txt = ''.join(fd.readlines())
z = json.loads(txt, object_hook=decode_complex)
print(type(z))
print(z) if __name__ == '__main__':
sys.exit(main(len(sys.argv), sys.argv))
- Run foo_decode.py
huanli$ cat -n /tmp/foo.json
{
"__complex__": true,
"real": 20.0,
"imag": 1.8
}
huanli$ ./foo_decode.py /tmp/foo.json
<class 'complex'>
(+.8j)
5. JSON的注释
JSON本身并不支持注释,也就是说,不能使用#, //, /* ... */之类的给JSON文件加注释。但是,可以使用一种变通的办法,如果非要给JSON文件加注释的话。因为在JSON中,如果多个key相同,最后一个key被认为是有效的。例如:
- qian.json
{
"a": "# comments for field a: this is a string",
"a": "qian",
"b": "# comments for field b: this is a number",
"b": 35,
"c": "# comments for field c: this is a boolean",
"c": true,
"d": "# comments for field d: this is a null",
"d": null,
"e": "# comments for field e: this is an array",
"e": [1, "abc", false, null],
"f": "# comments for filed f: this is an object",
"f": {"name": "qian", "age": 35}
}
- 使用4.3的foo_json2python.py解析如下
$ ./foo_json2python.py /tmp/qian.json
DEBUG> <class 'str'>
DEBUG> {
"a": "# comments for field a: this is a string",
"a": "qian", "b": "# comments for field b: this is a number",
"b": , "c": "# comments for field c: this is a boolean",
"c": true, "d": "# comments for field d: this is a null",
"d": null, "e": "# comments for field e: this is an array",
"e": [, "abc", false, null], "f": "# comments for filed f: this is an object",
"f": {"name": "qian", "age": }
} DEBUG> <class 'dict'>
DEBUG> {'a': 'qian', 'b': , 'c': True, 'd': None, 'e': [, 'abc', False, None], 'f': {'name': 'qian', 'age': }}
小结:
JSON作为一种支持数据序列化的文本格式,简单易用,概括起来就是:
- It is light-weight 轻量级(相对于XML来说)
- It is language independent 与语言无关
- Easy to read and write 读写容易
- Text based, human readable data exchange format 基于文本的人类可读的数据交换格式
注意绝大多数语言都支持JSON, 所以进行数据序列化和反序列化非常容易。 本文以Python语言为例,给出了序列化和反序列化的代码样例。 默认情况下,我们使用json.dump()/json.dumps()和json.load()/json.loads()即可;但是,对于用户定制的对象类型,则需要使用json.encode()和json.decode()。
参考资料:
- Introducing JSON
- What is JSON
- JSON Tutorial: Learn JSON in 10 Minutes
- Working With JSON Data in Python
- Comparison between JSON and YAML for data serialization
后记:
如果一个JSON文件写得不够clean, 不妨使用jsonfmt.py进行格式化。另外,推荐使用工具jq (Command-line JSON processor), e.g.
$ jq -r <<< '{"name":"foo", "id": 123}'
{
"name": "foo",
"id":
}
$ jq -r .id <<< '{"name":"foo", "id": 123}'
$ jq -r .id,.name <<< '{"name":"foo", "id": 123}'
foo
数据序列化导读(1)[JSON]的更多相关文章
- 数据序列化导读(3)[JSON v.s. YAML]
前面两节介绍了JSON和YAML,本文则对下面的文章做一个中英文对照翻译. Comparison between JSON and YAML for data serialization用于数据序列化 ...
- 数据序列化导读(2)[YAML]
上一节讲了JSON, 这一节将介绍YAML.可以认为,YAML是JSON的超集,但是更加简单易用,适合人类阅读和书写. 1. 什么是YAML? YAML是YAML Ain't Markup Lang ...
- Jackson序列化和反序列化Json数据完整示例
Jackson序列化和反序列化Json数据 Web技术发展的今天,Json和XML已经成为了web数据的事实标准,然而这种格式化的数据手工解析又非常麻烦,软件工程界永远不缺少工具,每当有需求的时候就会 ...
- JSON和php里的数据序列化
JSON就是一种数据结构,独立于语言 {"1":"one","2":"two","3":" ...
- Python-Day4 Python基础进阶之生成器/迭代器/装饰器/Json & pickle 数据序列化
一.生成器 通过列表生成式,我们可以直接创建一个列表.但是,受到内存限制,列表容量肯定是有限的.而且,创建一个包含100万个元素的列表,不仅占用很大的存储空间,如果我们仅仅需要访问前面几个元素,那后面 ...
- Redis 数据序列化方法 serialize, msgpack, json, hprose 比较
最近弄 Redis ,涉及数据序列化存储的问题,对比了:JSON, Serialize, Msgpack, Hprose 四种方式 1. 对序列化后的字符串长度对比: 测试代码: $arr = [0, ...
- Python之数据序列化(json、pickle、shelve)
本节内容 前言 json模块 pickle模块 shelve模块 总结 一.前言 1. 现实需求 每种编程语言都有各自的数据类型,其中面向对象的编程语言还允许开发者自定义数据类型(如:自定义类),Py ...
- python基础6之迭代器&生成器、json&pickle数据序列化
内容概要: 一.生成器 二.迭代器 三.json&pickle数据序列化 一.生成器generator 在学习生成器之前我们先了解下列表生成式,现在生产一个这样的列表[0,2,4,6,8,10 ...
- json&pickle数据序列化模块
用于序列化的模块 json,通用的序列化方式,序列化成为str类型,支持所有语言识别,序列化的数据具有局限性. pickle,python的所有数据类型都可以被序列化,序列化为bites格式,只适用于 ...
随机推荐
- Android-Android/APP-理解
Android 1.Google Android 给出的官方Android架构图就是大家都知道的四层,第一层是应用层(就是很多能够看得到的应用),第二层是应用框架层(为application提 供各种 ...
- Python学习-26.Python中的三角函数
Python中的三角函数位于math模块内. 引入模块: import math 输出pi import math print(math.pi) 得:3.141592653589793 math模块内 ...
- MVC4 项目开发日志(1)
最近一直在定义一个功能全面,层次结构分明的框架.一边学习一边应用.
- Alwayson--与复制的影响
在主副本上建立复制后,复制的事务日志读取代理(log reader)不会读取尚未同步到辅助副本的日志,因为辅助副本可能在下一时刻转化成为主副本,变为新的复制发布服务器,为此需要保证复制处理的日志总慢于 ...
- jenkins常用插件汇总
jenkins常用插件汇总: Build-timeout Plugin:任务构建超时插件 Naginator Plugin:任务重试插件 Build User Vars Plugin:用户变量获取插件 ...
- C#之数据类型学习
C#有以下几种数据类型: 数据类型案例以及取值范围: 界面: 选择int时: 选中long时: 选中float时: 选中double时: 选中decimal时: 选中string时: 选中char时: ...
- CPU的寄存器结构
计算机的硬件有三个基本要素,CPU.内存和I/O.CPU负责解释.执行程序,从内存或I/O输入数据,在内部进行运算,再把运算结果输出到内存或I/O.内存中存放着程序,程序是指令和数据的集合.I/O中临 ...
- Java 日期加减
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;import java.util.Calendar;import java.util.Date; public class Test ...
- 关于使用Iscroll.js异步加载数据后不能滑动到最底端的问题解决方案
关于使用Iscroll.js异步加载数据后不能滑动到最底端,拉到最下边又弹回去的问题困扰了我老半天,相信很多朋友都遇到了.我刚好不小心解决了,和大家分享一下.由于各种忙,下边就直接上代码吧. (前提是 ...
- Sublime Text shift+ctrl妙用(转载)
1 :按住shift+ctrl然后按←或→可快速选中一行中的某一部分,相当于双击鼠标选中. 当你想在代码末尾加注释的话,这个方法很好用 输入文字->光标移到文字末尾->按住shift+ct ...
