Etcd中Raft joint consensus的实现
Joint consensus

分为2个阶段,first switches to a transitional configuration we call joint consensus; once the joint consensus has been committed, the system then transitions to the new configuration. The joint consensus combines both the old and new configurations.
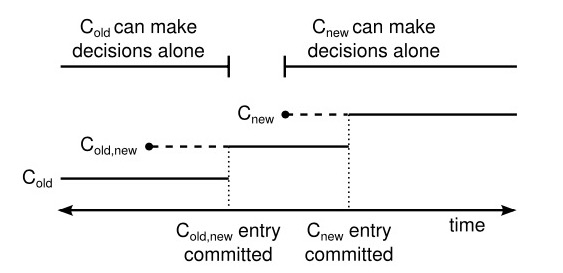
这样就非常直观,在joint consensus的配置中,包含了新老节点的配置,如果有节点变更,并进入了 joint consesus阶段,在日志复制的大多数同意策略中,达成一致就需要新老节点中都有节点出来同意。在 joint consensus 状态中,同意节点变更的应用也是需要大多数同意的,因为是基于日志复制来分发。
Raft log replication flow
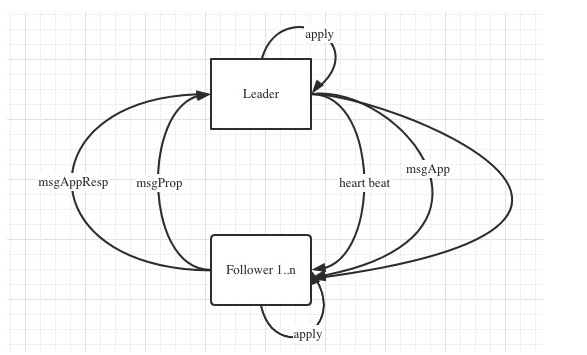
上图是etcd中raft提交的一个简约流程,没有标注顺序是因为都在自旋。
很有意思的是,我理解joint consensus的实现类似于log replication的应用,将joint consensus中带有的成员变更信息作为日志的内容通过log replication来应用到每个raft节点成员中。所以可以说,joint consensus是基于raft log replication。
如果将raft算法模块看作整体,说是自举其实也能部分说通,因为它改变了自身的成员信息,影响了raft将消息同步到谁的策略。
说是log replication的应用也是可以的,将raft算法模块白盒化,log replication算作一个子模块,joint consensus算作一个。
说本身就是raft算法模块,不将joint consensus看作是新增的部分,也是可行的。
Impl in Etcd
开始和结束joint consensus 的 message type 是定义在 pb中的。
const (
EntryNormal EntryType = 0
EntryConfChange EntryType = 1
EntryConfChangeV2 EntryType = 2
)
joint consensus的过程,首先是通过propose将EntryConfChange传入到raft算法模块内部,在leader应用了更改后,同样发送EntryConfChange消息到其他节点,大多数同意后,follower&learner才开始apply节点变更,并且leader 在 apply时发送EntryConfChangeV2结束节点变更的消息。
Structure of join consensus
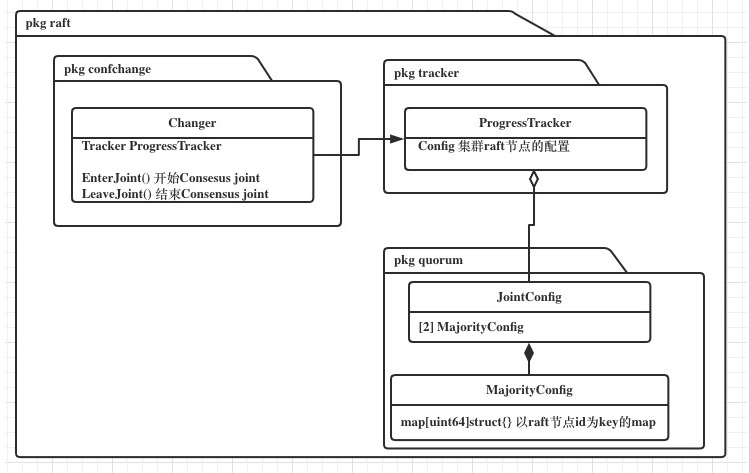
在Confchange中封装了joint consensus的阶段变更逻辑。
JointConfig是由2个MajorityConfig的map组成,一个对应变更节点集合,一个对应老节点集合。
由上图的引用关系最终在Confchange中来组装逻辑。
Confchange中将变更节点集合表示为 incoming,老节点集合表示为 outgoing。
func incoming(voters quorum.JointConfig) quorum.MajorityConfig { return voters[0] }
func outgoing(voters quorum.JointConfig) quorum.MajorityConfig { return voters[1] }
func outgoingPtr(voters *quorum.JointConfig) *quorum.MajorityConfig { return &voters[1] }
节点未发生变更时,节点信息存储在JointConfig[0] ,即incoming的指向的集合中。
当EnterJoint时,将老节点拷贝至outgoing中,变更节点拷贝至incoming中。
LeaveJoint时,删除下线的节点,合并在线的节点并合并至incoming中,完成节点变更过程。
Logic flow of joint consensus
Proposal trigger
在EtcdServer中不论是AddMember()还是RemoveMembe()以及其他2个会修改Member成员的方法,都会触发
configure()函数
// configure sends a configuration change through consensus and
// then waits for it to be applied to the server. It
// will block until the change is performed or there is an error.
func (s *EtcdServer) configure(ctx context.Context, cc raftpb.ConfChange) ([]*membership.Member, error) {
lg := s.Logger()
cc.ID = s.reqIDGen.Next()
ch := s.w.Register(cc.ID)
start := time.Now()
if err := s.r.ProposeConfChange(ctx, cc); err != nil {
s.w.Trigger(cc.ID, nil)
return nil, err
}
select {
case x := <-ch:
if x == nil {
lg.Panic("failed to configure")
}
resp := x.(*confChangeResponse)
lg.Info(
"applied a configuration change through raft",
zap.String("local-member-id", s.ID().String()),
zap.String("raft-conf-change", cc.Type.String()),
zap.String("raft-conf-change-node-id", types.ID(cc.NodeID).String()),
)
return resp.membs, resp.err
case <-ctx.Done():
s.w.Trigger(cc.ID, nil) // GC wait
return nil, s.parseProposeCtxErr(ctx.Err(), start)
case <-s.stopping:
return nil, ErrStopped
}
}
s.r.ProposeConfChange(ctx, cc) 会将Config Change向Raft中 propose。
这段里面还有个有趣的逻辑,利用了一个channel等待操作完成再返回结果,和读一致性的实现异曲同工。
//向channel池中注册一个需要等待的channel
ch := s.w.Register(cc.ID)
//发送信号进该channel
s.w.Trigger(cc.ID, nil)
select {
//等待该channel返回信号
case x := <-ch:
if x == nil {
lg.Panic("failed to configure")
}
...
}
Proposal logic of Leader
Leader收到Proposal后,会进行如下处理:
e := &m.Entries[i]
var cc pb.ConfChangeI
if e.Type == pb.EntryConfChange {
var ccc pb.ConfChange
if err := ccc.Unmarshal(e.Data); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cc = ccc
} else if e.Type == pb.EntryConfChangeV2 {
var ccc pb.ConfChangeV2
if err := ccc.Unmarshal(e.Data); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
cc = ccc
}
if cc != nil {
alreadyPending := r.pendingConfIndex > r.raftLog.applied
alreadyJoint := len(r.prs.Config.Voters[1]) > 0
wantsLeaveJoint := len(cc.AsV2().Changes) == 0
var refused string
if alreadyPending {
refused = fmt.Sprintf("possible unapplied conf change at index %d (applied to %d)", r.pendingConfIndex, r.raftLog.applied)
} else if alreadyJoint && !wantsLeaveJoint {
refused = "must transition out of joint config first"
} else if !alreadyJoint && wantsLeaveJoint {
refused = "not in joint state; refusing empty conf change"
}
if refused != "" {
r.logger.Infof("%x ignoring conf change %v at config %s: %s", r.id, cc, r.prs.Config, refused)
m.Entries[i] = pb.Entry{Type: pb.EntryNormal}
} else {
r.pendingConfIndex = r.raftLog.lastIndex() + uint64(i) + 1
}
}
如果发现当前是在joint consensus过程中,拒绝变更,直接将message type 变成普通的entry。
处理完毕后,会等待将该消息分发。
Logic of apply
当大多数节点commit后,就会Ready至EtcdServer,然后开始apply config的过程,同apply log的过程是相同的。
自旋Ready从raft module 到 EtcdServer的过程在上一篇日志复制中已经描述过。
直接看raft module 中的代码。
apply分为2步,第1步是EtcdServer apply raft log的逻辑,第2步是raft 胶水 advance()的逻辑。
在joint consensus中就是首先应用节点配置,然后在advance中结束 joint consensus。
apply config
func (r *raft) applyConfChange(cc pb.ConfChangeV2) pb.ConfState {
cfg, prs, err := func() (tracker.Config, tracker.ProgressMap, error) {
changer := confchange.Changer{
Tracker: r.prs,
LastIndex: r.raftLog.lastIndex(),
}
if cc.LeaveJoint() {
return changer.LeaveJoint()
} else if autoLeave, ok := cc.EnterJoint(); ok {
return changer.EnterJoint(autoLeave, cc.Changes...)
}
return changer.Simple(cc.Changes...)
}()
if err != nil {
// TODO(tbg): return the error to the caller.
panic(err)
}
return r.switchToConfig(cfg, prs)
}
逻辑的解释在上面介绍Changer中。
joint consensus completely
func (r *raft) advance(rd Ready) {
r.reduceUncommittedSize(rd.CommittedEntries)
// If entries were applied (or a snapshot), update our cursor for
// the next Ready. Note that if the current HardState contains a
// new Commit index, this does not mean that we're also applying
// all of the new entries due to commit pagination by size.
if newApplied := rd.appliedCursor(); newApplied > 0 {
oldApplied := r.raftLog.applied
r.raftLog.appliedTo(newApplied)
if r.prs.Config.AutoLeave && oldApplied <= r.pendingConfIndex && newApplied >= r.pendingConfIndex && r.state == StateLeader {
// If the current (and most recent, at least for this leader's term)
// configuration should be auto-left, initiate that now. We use a
// nil Data which unmarshals into an empty ConfChangeV2 and has the
// benefit that appendEntry can never refuse it based on its size
// (which registers as zero).
ent := pb.Entry{
Type: pb.EntryConfChangeV2,
Data: nil,
}
// There's no way in which this proposal should be able to be rejected.
if !r.appendEntry(ent) {
panic("refused un-refusable auto-leaving ConfChangeV2")
}
r.pendingConfIndex = r.raftLog.lastIndex()
r.logger.Infof("initiating automatic transition out of joint configuration %s", r.prs.Config)
}
}
if len(rd.Entries) > 0 {
e := rd.Entries[len(rd.Entries)-1]
r.raftLog.stableTo(e.Index, e.Term)
}
if !IsEmptySnap(rd.Snapshot) {
r.raftLog.stableSnapTo(rd.Snapshot.Metadata.Index)
}
}
如果是Leader并且正在joint consensus过程中,将EntryConfChangeV2加入自己的日志中,通过Ready的自旋进行分发。
同样是日志复制的过程来结束joint consensus。
Summary
整个过程的逻辑还未用场景来做一些推导,等把读一致性写完,同大多数复制来一起验证一次。
Etcd中Raft joint consensus的实现的更多相关文章
- Etcd中Raft日志复制的实现
Raft state of log commitIndex : A log entry is committed once the leader that created the entry has ...
- etcd学习(6)-etcd实现raft源码解读
etcd中raft实现源码解读 前言 raft实现 看下etcd中的raftexample newRaftNode startRaft serveChannels 领导者选举 启动并初始化node节点 ...
- Etcd中linearizable read实现
linearizable 有点疑惑,不确定是现在浏览的版本没开发完全,还是没有按照论文的linearizable来实现. 按照论文所说,在客户端请求的时候,实际上是一个强一致的 exactly onc ...
- etcd学习(5)-etcd的Raft一致性算法原理
ETCD的Raft一致性算法原理 前言 Raft原理了解 raft选举 raft中的几种状态 任期 leader选举 日志复制 安全性 leader宕机,新的leader未同步前任committed的 ...
- etcd学习(7)-etcd中的线性一致性实现
线性一致性 CAP 什么是CAP CAP的权衡 AP wihtout C CA without P CP without A 线性一致性 etcd中如何实现线性一致性 线性一致性写 线性一致性读 1. ...
- etcd学习(8)-etcd中Lease的续期
etcd中的Lease 前言 Lease Lease 整体架构 key 如何关联 Lease Lease的续期 过期 Lease 的删除 checkpoint 机制 总结 参考 etcd中的Lease ...
- etcd学习(9)-etcd中的存储实现
etcd中的存储实现 前言 V3和V2版本的对比 MVCC treeIndex 原理 MVCC 更新 key MVCC 查询 key MVCC 删除 key 压缩 周期性压缩 版本号压缩 boltdb ...
- 注册服务到etcd中
如上存放一些服务的key到etcd中,商品有两个,主要是为了负载均衡的key func NewService() *Service { config := clientv3.Config{ Endpo ...
- etcd中watch源码解读
etcd中watch的源码解析 前言 client端的代码 Watch newWatcherGrpcStream run newWatchClient serveSubstream server端的代 ...
随机推荐
- Google Hacking的用法
目录 Google Hacking 基本搜索 高级搜索 Index of inurl Google Hacking Google Hacking 是利用谷歌搜索的强大,来在浩瀚的互联网中搜索到我们需要 ...
- Windows PE导出表编程4(重构导出表实现私有函数导出)
本次是尝试调用DLL里面的私有函数. 一: 之前先探索一下,首先可以考虑用偏移量来调用,就是如果知道了某个私有函数和某个导出的公共函数的相对便宜的话,直接加载dll获取公共函数地址,然后自己手动去偏移 ...
- Flask 实现分页
pager.html <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset=&quo ...
- [LeetCode每日一题]81. 搜索旋转排序数组 II
[LeetCode每日一题]81. 搜索旋转排序数组 II 问题 已知存在一个按非降序排列的整数数组 nums ,数组中的值不必互不相同. 在传递给函数之前,nums 在预先未知的某个下标 k(0 & ...
- [网络编程之客户端/服务器架构,互联网通信协议,TCP协议]
[网络编程之客户端/服务器架构,互联网通信协议,TCP协议] 引子 网络编程 客户端/服务器架构 互联网通信协议 互联网的本质就是一系列的网络协议 OSI七层协议 tcp/ip五层模型 客户端/服务器 ...
- python介绍,计算机核心基础,与运行程序有关的三大核心硬件,操作系统
python介绍,计算机核心基础,与运行程序有关的三大核心硬件,操作系统 引子 python是什么? 什么是编程语言?为何要有编程语言? 什么是编程?什么是程序?什么是进程?为何要编程? 计算机基础 ...
- [bug] @Test注解无法使用
参考 https://blog.csdn.net/lixiangxiang666/article/details/83745901
- 对ansible不支持service模块的status命令进行修正
原生的ansible不支持service.status,在Google之后,发现有人提交了一个patch,可以支持status选项.见https://github.com/ritzk/ansible- ...
- Linux 用 ps 與 top 指令找出最耗費 CPU 與記憶體資源的程式最占cpu的进程
Linux 用 ps 與 top 指令找出最耗費 CPU 與記憶體資源的程式 2016/12/220 Comments ######### ps -eo pid,ppid,%mem,%cpu,cmd ...
- Jenkins远程代码执行漏洞
于一个月前,进行服务器巡检时,发现服务器存在不明进程,并且以Jenkins用户身份来运行.当时进行了处理并修复了漏洞.在此补上修复过程 第一反应是Jenkins存在漏洞,于是Google Jenkin ...
