Netty:Reactor Pattern 与 Dubbo 底层传输中的 NettyServer
首先,我们需要了解Reactor模式的三种线程模型:
1)单线程模型
Reactor 单线程模型,指的是所有的 IO 操作都在同一个 NIO 线程上面完成,NIO 线程的职责如下:
- 作为 NIO 服务端,接收客户端的 TCP 连接;
- 作为 NIO 客户端,向服务端发起 TCP 连接;
- 读取通信对端的请求或者应答消息;
- 向通信对端发送消息请求或者应答消息。
Reactor 单线程模型示意图如下所示:

由于 Reactor 模式使用的是异步非阻塞 IO,所有的 IO 操作都不会导致阻塞,理论上一个线程可以独立处理所有 IO 相关的操作。从架构层面看,一个 NIO 线程确实可以完成其承担的职责。例如,通过 Acceptor 类接收客户端的 TCP 连接请求消息,链路建立成功之后,通过 Dispatch 将对应的 ByteBuffer 派发到指定的 Handler 上进行消息解码。用户线程可以通过消息编码通过 NIO 线程将消息发送给客户端。
对于一些小容量的应用场景,可以使用单线程模型。但是对于高负载、大并发的应用场景却不合适,主要原因如下:
- 一个 NIO 线程同时处理成百上千的链路,性能上无法支撑,即便 NIO 线程的 CPU 负荷达到 100%,也无法满足海量消息的编码、解码、读取和发送;
- 当 NIO 线程负载过重之后,处理速度将变慢,这会导致大量客户端连接超时,超时之后往往会进行重发,这更加重了 NIO 线程的负载,最终会导致大量消息积压和处理超时,成为系统的性能瓶颈;
- 可靠性问题:一旦 NIO 线程意外跑飞,或者进入死循环,会导致整个系统通信模块不可用,不能接收和处理外部消息,造成节点故障。
2)多线程模型
为了解决单线程在其他应用场景的不足,演进除了Rector 多线程模型。Reactor 多线程模型与单线程模型最大的区别就是有一组 NIO 线程处理 IO 操作,它的原理图如下:
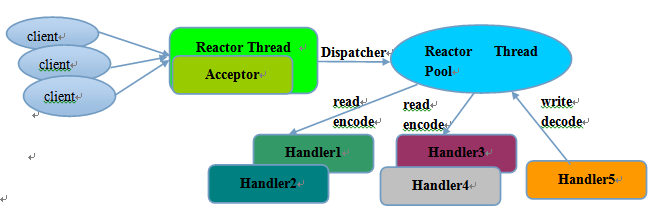
Reactor 多线程模型的特点:
- 有专门一个 NIO 线程 Acceptor 线程用于监听服务端,接收客户端的 TCP 连接请求;
- 网络 IO 操作 —— 读、写等由一个 NIO 线程池负责,线程池可以采用标准的 JDK 线程池实现,它包含一个任务队列和 N 个可用的线程,由这些 NIO 线程负责消息的读取、解码、编码和发送;
- 1 个 NIO 线程可以同时处理 N 条链路,但是 1 个链路只对应 1 个 NIO 线程,防止发生并发操作问题。
在绝大多数场景下,Reactor 多线程模型都可以满足性能需求;但是,在极个别特殊场景中,一个 NIO 线程负责监听和处理所有的客户端连接可能会存在性能问题。例如并发百万级别客户端连接,或者服务端需要对客户端握手进行安全认证,但是认证本身非常损耗性能。在这类场景下,单独一个 Acceptor 线程可能会存在性能不足问题,为了解决性能问题,产生了第三种 Reactor 线程模型 - 主从 Reactor 多线程模型。
3)主从多线程模型
主从 Reactor 线程模型的特点是:服务端用于接收客户端连接的不再是个 1 个单独的 NIO 线程,而是一个独立的 NIO 线程池。Acceptor 接收到客户端 TCP 连接请求处理完成后(可能包含接入认证等),将新创建的 SocketChannel 注册到 IO 线程池(sub reactor 线程池)的某个 IO 线程上,由它负责 SocketChannel 的读写和编解码工作。Acceptor 线程池仅仅只用于客户端的登陆、握手和安全认证,一旦链路建立成功,就将链路注册到后端 subReactor 线程池的 IO 线程上,由 IO 线程负责后续的 IO 操作。
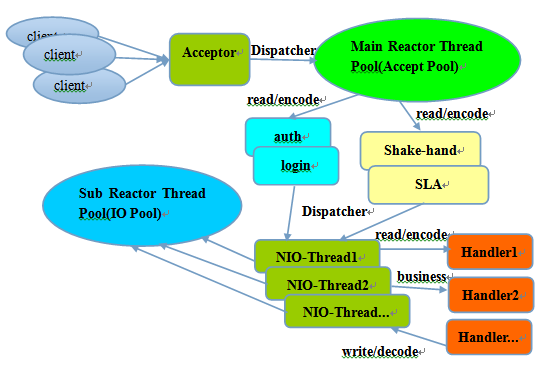
利用主从 NIO 线程模型,可以解决 1 个服务端监听线程无法有效处理所有客户端连接的性能不足问题。
它的工作流程总结如下:
从主线程池中随机选择一个 Reactor 线程作为 Acceptor 线程,用于绑定监听端口,接收客户端连接;
Acceptor 线程接收客户端连接请求之后创建新的 SocketChannel,将其注册到主线程池的其它 Reactor 线程上,由其负责接入认证、IP 黑白名单过滤、握手等操作;
步骤 2 完成之后,业务层的链路正式建立,将 SocketChannel 从主线程池的 Reactor 线程的多路复用器上摘除,重新注册到 Sub 线程池的线程上,用于处理 I/O 的读写操作。
Netty 的线程模型与上面介绍的三种 Reactor 线程模型相似
举个Dubbo底层传输时使用Netty4.x服务器端的例子:
1 org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty4.NettyServer.class
第一步:其中打开服务端的时候实例化了 2 个 EventLoopGroup,1 个 EventLoopGroup 实际就是一个 EventLoop 线程组,负责管理 EventLoop 的申请和释放。第一步:其中打开服务端的时候实例化了 2 个 EventLoopGroup,1 个 EventLoopGroup 实际就是一个 EventLoop 线程组,负责管理 EventLoop 的申请和释放。
1 @Override
2 protected void doOpen() throws Throwable {
3 bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
4
5 bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1, new DefaultThreadFactory("NettyServerBoss", true));
6 workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(getUrl().getPositiveParameter(IO_THREADS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_IO_THREADS),
7 new DefaultThreadFactory("NettyServerWorker", true));
8
9 final NettyServerHandler nettyServerHandler = new NettyServerHandler(getUrl(), this);
10 channels = nettyServerHandler.getChannels();
11
12 bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
13 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
14 .childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, Boolean.TRUE)
15 .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, Boolean.TRUE)
16 .childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT)
17 .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<NioSocketChannel>() {
18 @Override
19 protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
20 // FIXME: should we use getTimeout()?
21 int idleTimeout = UrlUtils.getIdleTimeout(getUrl());
22 NettyCodecAdapter adapter = new NettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(), getUrl(), NettyServer.this);
23 ch.pipeline()//.addLast("logging",new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))//for debug
24 .addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder())
25 .addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder())
26 .addLast("server-idle-handler", new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, idleTimeout, MILLISECONDS))
27 .addLast("handler", nettyServerHandler);
28 }
29 });
30 // bind
31 ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(getBindAddress());
32 channelFuture.syncUninterruptibly();
33 channel = channelFuture.channel();
34
35 }
bossGroup 线程组实际就是 Acceptor 线程池,负责处理客户端的 TCP 连接请求,如果系统只有一个服务端端口需要监听,则建议 bossGroup 线程组线程数设置为 1。这个boss线程组里面只设置了一个EventLoop线程。
workerGroup 是真正负责 I/O 读写操作的线程组,通过 ServerBootstrap 的 group 方法进行设置,用于后续的 Channel 绑定。
第二步:通过ServerBootStrap引导类bossgroup线程绑定监听端口,启动 NIO 服务端,相关代码如下:AbstractBootstrap#initAndRegister
1 final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
2 Channel channel = null;
3 try {
4 channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
5 init(channel);
6 } catch (Throwable t) {
7 if (channel != null) {
8 // channel can be null if newChannel crashed (eg SocketException("too many open files"))
9 channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
10 // as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor
11 return new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
12 }
13 // as the Channel is not registered yet we need to force the usage of the GlobalEventExecutor
14 return new DefaultChannelPromise(new FailedChannel(), GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
15 }
16
17 ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel); // 注册
18 if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
19 if (channel.isRegistered()) {
20 channel.close();
21 } else {
22 channel.unsafe().closeForcibly();
23 }
24 }
25
26 // If we are here and the promise is not failed, it's one of the following cases:
27 // 1) If we attempted registration from the event loop, the registration has been completed at this point.
28 // i.e. It's safe to attempt bind() or connect() now because the channel has been registered.
29 // 2) If we attempted registration from the other thread, the registration request has been successfully
30 // added to the event loop's task queue for later execution.
31 // i.e. It's safe to attempt bind() or connect() now:
32 // because bind() or connect() will be executed *after* the scheduled registration task is executed
33 // because register(), bind(), and connect() are all bound to the same thread.
34
35 return regFuture;
36 }
服务端 Channel 创建完成之后,将其注册到多路复用器 Selector 上,用于接收客户端的 TCP 连接,核心代码如下:AbstractNioChannel#doRegister
1 @Override
2 protected void doRegister() throws Exception {
3 boolean selected = false;
4 for (;;) {
5 try {
6 // 取出NioEventLoop中关联的Selector并注册这个NioChannel的相关操作, 0值表示注册, 没有其他操作
7 selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this);
8 return;
9 } catch (CancelledKeyException e) {
10 if (!selected) {
11 // Force the Selector to select now as the "canceled" SelectionKey may still be
12 // cached and not removed because no Select.select(..) operation was called yet.
13 eventLoop().selectNow();
14 selected = true;
15 } else {
16 // We forced a select operation on the selector before but the SelectionKey is still cached
17 // for whatever reason. JDK bug ?
18 throw e;
19 }
20 }
21 }
22 }
第三步,如果监听到客户端连接,则创建客户端 SocketChannel 连接,重新注册到 workerGroup 的 IO 线程上。首先看 Acceptor 线程如何处理客户端的接入:NioEventLoop#processSelectedKey
1 try {
2 int readyOps = k.readyOps();
3 // We first need to call finishConnect() before try to trigger a read(...) or write(...) as otherwise
4 // the NIO JDK channel implementation may throw a NotYetConnectedException.
5 if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) {
6 // remove OP_CONNECT as otherwise Selector.select(..) will always return without blocking
7 // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/924
8 int ops = k.interestOps();
9 ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;
10 k.interestOps(ops);
11
12 unsafe.finishConnect();
13 }
14
15 // Process OP_WRITE first as we may be able to write some queued buffers and so free memory.
16 if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
17 // Call forceFlush which will also take care of clear the OP_WRITE once there is nothing left to write
18 ch.unsafe().forceFlush();
19 }
20
21 // Also check for readOps of 0 to workaround possible JDK bug which may otherwise lead
22 // to a spin loop
23 if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
24 unsafe.read();
25 }
26 } catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) {
27 unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
28 }
上面调用了 unsafe 的 read()方法,对于 NioServerSocketChannel,它调用了 NioMessageUnsafe 的 read() 方法,代码如下:
1 try {
2 try {
3 do {
4 int localRead = doReadMessages(readBuf);
5 if (localRead == 0) {
6 break;
7 }
8 if (localRead < 0) {
9 closed = true;
10 break;
11 }
12
13 allocHandle.incMessagesRead(localRead);
14 } while (allocHandle.continueReading());
15 } catch (Throwable t) {
16 exception = t;
17 }
18 ...
19 }
它最终会调用 NioServerSocketChannel 的 doReadMessages 方法,为接受的套接字创建新的子通道,代码如下:
1 @Override
2 protected int doReadMessages(List<Object> buf) throws Exception {
3 SocketChannel ch = SocketUtils.accept(javaChannel());
4
5 try {
6 if (ch != null) {
7 buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));
8 return 1;
9 }
10 } catch (Throwable t) {
11 logger.warn("Failed to create a new channel from an accepted socket.", t);
12
13 try {
14 ch.close();
15 } catch (Throwable t2) {
16 logger.warn("Failed to close a socket.", t2);
17 }
18 }
19
20 return 0;
21 }
ServerSocketChannel有阻塞和非阻塞两种模式:
阻塞模式:ServerSocketChannel.accept() 方法监听新进来的连接,当 accept()方法返回的时候,它返回一个包含新进来的连接的 SocketChannel。阻塞模式下, accept()方法会一直阻塞到有新连接到达。
非阻塞模式: accept() 方法会立刻返回,如果还没有新进来的连接,返回的将是null。 因此,需要检查返回的SocketChannel是否是null。
在NioServerSocketChannel的构造函数分析中,它的抽象父类AbstractNioChannel在构造的时候就设置 ch.configureBlocking(false); 无阻塞模式,所以会立刻返回,NioMessageUnsafe#read()方法会不断的循环读取客户端的接入。
对于doReadMessages() 方法中创建了NioSocketChannel实例,NioSocketChannelConfig作用是配置这个Channel和JavaSocket的对应关系,主要是设置或获取一些参数,比如说 TCP_NODELAY ,设置发送缓冲区大小等。
1 public NioSocketChannel(Channel parent, SocketChannel socket) {
2 super(parent, socket);
3 config = new NioSocketChannelConfig(this, socket.socket());
4 }
其中的NioSocketChannel存储了这个这个子通道和Java Socket之间
第四步,将 SocketChannel 将 SocketChannel 注册到ServerSocketChannel的多路复用器上,监听 READ 操作。向上一直到 AbstractChannel ,为这个Channel创建一个Unsafe(与Channel相关,数据读取方面)和PipeLine。
1 protected AbstractNioByteChannel(Channel parent, SelectableChannel ch) {
2 super(parent, ch, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
3 }
第五步,处理网络的 I/O 读写事件,主要代码看第三步中的代码,也可以看以下的处理SelectedKey的方法
1 private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) {
2 final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe();
3 if (!k.isValid()) {
4 final EventLoop eventLoop;
5 try {
6 eventLoop = ch.eventLoop();
7 } catch (Throwable ignored) {
8 // If the channel implementation throws an exception because there is no event loop, we ignore this
9 // because we are only trying to determine if ch is registered to this event loop and thus has authority
10 // to close ch.
11 return;
12 }
13 // Only close ch if ch is still registered to this EventLoop. ch could have deregistered from the event loop
14 // and thus the SelectionKey could be cancelled as part of the deregistration process, but the channel is
15 // still healthy and should not be closed.
16 // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/5125
17 if (eventLoop != this || eventLoop == null) {
18 return;
19 }
20 // close the channel if the key is not valid anymore
21 unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
22 return;
23 }
24
25 try {
26 int readyOps = k.readyOps();
27 // We first need to call finishConnect() before try to trigger a read(...) or write(...) as otherwise
28 // the NIO JDK channel implementation may throw a NotYetConnectedException.
29 if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) {
30 // remove OP_CONNECT as otherwise Selector.select(..) will always return without blocking
31 // See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/924
32 int ops = k.interestOps();
33 ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;
34 k.interestOps(ops);
35
36 unsafe.finishConnect();
37 }
38
39 // Process OP_WRITE first as we may be able to write some queued buffers and so free memory.
40 if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
41 // Call forceFlush which will also take care of clear the OP_WRITE once there is nothing left to write
42 ch.unsafe().forceFlush();
43 }
44
45 // Also check for readOps of 0 to workaround possible JDK bug which may otherwise lead
46 // to a spin loop
47 if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
48 unsafe.read();
49 }
50 } catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) {
51 unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
52 }
53 }
参考: Netty 系列之 Netty 线程模型 ,Netty源码分析 (五)----- 数据如何在 pipeline 中流动
Netty:Reactor Pattern 与 Dubbo 底层传输中的 NettyServer的更多相关文章
- Dubbo底层采用Socket进行通信详解
由于Dubbo底层采用Socket进行通信,自己对通信理理论也不是很清楚,所以顺便把通信的知识也学习一下. n 通信理论 计算机与外界的信息交换称为通信.基本的通信方法有并行通信和串行通信两种. 1 ...
- 笔记-reactor pattern
笔记-reactor pattern 1. reactor模式 1.1. 什么是reactor模式 The reactor design pattern is an event han ...
- 详细图解 Netty Reactor 启动全流程 | 万字长文 | 多图预警
本系列Netty源码解析文章基于 4.1.56.Final版本 大家第一眼看到这幅流程图,是不是脑瓜子嗡嗡的呢? 大家先不要惊慌,问题不大,本文笔者的目的就是要让大家清晰的理解这幅流程图,从而深刻的理 ...
- [编织消息框架][网络IO模型]Netty Reactor
严格来讲Netty Reactor是一种设计模式,一听模式两字就知道了吧,套路哈哈 Reactor中文译为“反应堆”. 看图netty处理流程 1.netty server 至少有两组reactor. ...
- Netty Reactor 线程模型笔记
引用: https://www.cnblogs.com/TomSnail/p/6158249.html https://www.cnblogs.com/heavenhome/articles/6554 ...
- dubbo在项目中的应用
关于dubbo的使用,我们举个简单例子: 存在2个系统,A系统和B系统,A系统调用B系统的接口获取数据,用于查询用户列表. 在上一篇博文介绍了dubbo的创建,zookeeper的创建完成后,我们可以 ...
- the reactor pattern and java nio
在<java NIO>作者PPT<How to Build a Scalable Multiplexed Server With NIO> 和 Doug Lea <Sca ...
- Android网络传输中必用的两个加密算法:MD5 和 RSA (附java完成测试代码)
MD5和RSA是网络传输中最常用的两个算法,了解这两个算法原理后就能大致知道加密是怎么一回事了.但这两种算法使用环境有差异,刚好互补. 一.MD5算法 首先MD5是不可逆的,只能加密而不能解密.比如明 ...
- Android网络传输中必用的两个加密算法:MD5 和 RSA (附java完毕測试代码)
MD5和RSA是网络传输中最经常使用的两个算法,了解这两个算法原理后就能大致知道加密是怎么一回事了.但这两种算法使用环境有差异,刚好互补. 一.MD5算法 首先MD5是不可逆的,仅仅能加密而不能解密. ...
随机推荐
- Alex网络结构
AlexNet网络结构 网络包含8个带权重的层:前5层是卷积层,剩下的3层是全连接层.最后一层全连接层的输出是1000维softmax的输入,softmax会产生1000类标签的分布网络包含8个带 ...
- PTA——c++类与对象
对于给定的一个字符串,统计其中数字字符出现的次数. 类和函数接口定义: 设计一个类Solution,其中包含一个成员函数count_digits,其功能是统计传入的string类型参数中数字字符的个数 ...
- 【TP3.2.3】根据字段统计条数
// 省份查询 $province = M('hospital') -> field('area as label,count(*) as value') -> group('area') ...
- Dede后台广告管理模块增加图片上传功能插件
用户问题:网站广告后台管理非常方便,但是织梦后台的广告管理模块,发布广告时图片没有上传选项,只能用URL地址,很不方便,那么织梦帮就教大家一个方法实现广告图片后台直接上传,非常方便.先给大家看下修改后 ...
- ecshop不同的文章分类使用不同的模板的方法
ecshop文章模板做的太简单,页面很丑,怎么才能实现不同的文章使用不同的模板呢,方法是有的,就是没有shopex那么方便,但还可以实现,只要能用就行. 1.打开article_cat.php文件,在 ...
- vue实现事件代理(通过事件冒泡实现)
事件代理/事件委托以ul>li来模拟 使用冒泡的用法:使用冒泡的用法来实现事件代理 分离出来 动态根据索引添加类名:
- P6177-Count on a tree II/[模板]树分块
正题 题目链接:https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P6177 题目大意 \(n\)个点的一棵树\(m\)次询问树上颜色. 强制在线 \(1\leq n\leq 4\ti ...
- Python - __all__ 变量
import * 当我们向文件导入某个模块时,导入的是该模块中那些名称不以下划线(单下划线 _ 或者双下划线 __ )开头的变量.函数和类 因此,如果不想模块文件中的某个对象被引入到其它文件中使用,可 ...
- 【Azure 云服务】Azure Cloud Service 为 Web Role(IIS Host)增加自定义字段 (把HTTP Request Header中的User-Agent字段增加到IIS输出日志中)
问题描述 把Web Role服务发布到Azure Cloud Service后,需要在IIS的输出日志中,把每一个请求的HTTP Request Header中的User-Agent内容也输出到日志中 ...
- React Native之新架构中的Turbo Module实现原理分析
有段时间没更新博客了,之前计划由浅到深.从应用到原理,更新一些RN的相关博客.之前陆续的更新了6篇RN应用的相关博客(传送门),后边因时间问题没有继续更新.主要是平时空余时间都用来帮着带娃了,不过还是 ...
