Spring Boot 2.x 之 Spring Data JPA, Hibernate 5
1. Spring Boot常用配置项
基于Spring Boot 2.0.6.RELEASE
1.1 配置属性类
spring.jpa前缀的相关配置项定义在JpaProperties类中,
1.2 自动装配类
涉及到的自动配置类包括:JpaBaseConfiguration,HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration
1.3 常用配置项
# 是否开启JPA Repositories,缺省: true
spring.data.jpa.repositories.enabled=true
# JPA数据库类型,默认可以自动检测,也能通过设置spring.jpa.database-platform达到同样效果
spring.jpa.database=ORACLE
# 数据库平台,常见的值如:
# org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect
# org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle12cDialect
# 是否使用JPA初始化数据库,可以在启动时生成DDL创建数据库表,缺省为false
spring.jpa.generate-ddl = false
# 更细粒度的控制JPA初始化数据库特性,用来设定启动时DDL操作的类型,下文有详细介绍
# 内嵌数据库 hsqldb, h2, derby的缺省值为create-drop
# 非内嵌数据库的缺省值为none
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
# Hibernate操作时显示真实的SQL, 缺省:false
spring.jpa.show-sql = true
# Hibernate 5 隐含命名策略类的全限定名
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming.implicit-strategy=
# Hibernate 5 物理命名策略类的全限定名
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming.physical-strategy=org.hibernate.boot.model.naming.PhysicalNamingStrategyStandardImpl
# Use Hibernate's newer IdentifierGenerator for AUTO, TABLE and SEQUENCE.
spring.jpa.hibernate.use-new-id-generator-mappings=
# 额外设置JPA配置属性,通常配置项是特定实现支持的,如Hibernate常有下面的几条配置项
spring.jpa.properties.* =
# 将SQL中的标识符(表名,列名等)全部使用引号括起来
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.globally_quoted_identifiers=true
# 日志记录执行的SQL
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.show_sql = true
# 是否将格式化SQL日志
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql = true
# 是否注册OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor. 绑定JPA EntityManager 到请求线程中. 默认为: true.
spring.jpa.open-in-view=true
# Hibernate 4 命名策略的全类名,Hibernate 5不再适用
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming-strategy=
1.4 配置项 spring.jpa.database
配置项spring.jpa.database的值通常可以自动检测,可取值包括了:
public enum Database {
DEFAULT,
DB2,
DERBY,
H2,
HSQL,
INFORMIX,
MYSQL,
ORACLE,
POSTGRESQL,
SQL_SERVER,
SYBASE
}
1.5 配置项spring.jpa.generate-ddl 和 spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto
配置项spring.jpa.generate-ddl管理是否开启自动初始化Schema特性,
配置项spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto 进一步控制启动时初始化Schema的特性,有以下可选值:
create, 启动时删除上一次生成的表,并根据实体类生成表,表中的数据将被清空;create-drop,启动时根据实体类生成表,sessionFactory关闭时删除表;update,启动时根据实体类生成表,当实体的属性变动时,表结构也会更新,开发阶段可以使用该属性;validate,启动时验证实体类和数据表是否一致,在数据结构稳定时可以采取该选项;none,不采取任何操作;
1.6 配置项hibernate.globally_quoted_identifiers
配置项hibernate.globally_quoted_identifiers用来在SQL中加入引号,以解决某些场景中SQL标识符(表名,列名等)出现了数据库关键字的情形。
Oracle中,该属性给标识符加双引号,注意Oracle双引号中的内容区分大小写;
MySQL中,该属性给标识符加反引号(没错,就是键盘数字1左面的那个`),注意默认情况下,MySQL的表名区分大小写,但列名不区分大小写,在反引号中也是如此。
2. 开发常用注解——表/实体类使用
2.1 @Entity
@Entity用在实体类上,表示这是一个和数据库表映射的实体类。
2.2 @Table
@Table用来声明实体类对应的表信息。包括表名称、索引等。
2.3 @SQLDelete,
@SQLDelete用来自定义删除语句,
如果不想使用JPA Repository自带的删除语句,就可以使用该注解重写,如常见的软删除:
@Entity
@Table(name = "App")
@SQLDelete(sql = "Update App set isDeleted = 1 where id = ?")
@Where
@Where用来指定默认查询条件,可以用来配合软删除。
@Entity
@Table(name = "App")
@SQLDelete(sql = "Update App set isDeleted = 1 where id = ?")
@Where(clause = "isDeleted = 0")
2.4 @MappedSuperclass
@MappedSuperclass用来定义若干表中公共的字段,将它们封装在一个基类中,基类上使用该注解,则其子实体类将自动获得父类中的字段映射关系,同时不需要额外为父类建立真实的表,也就是真正的表只对应@MappedSuperclass的子类。
2.5 @Inheritance
@MappedSuperclass指定了实体类之间是可以存在层次关系的,通过@Inheritance可以进一步管理层次关系,其取值InheritanceType有以下枚举变量:
public enum InheritanceType {
/** A single table per class hierarchy. */
SINGLE_TABLE,
/** A table per concrete entity class. */
TABLE_PER_CLASS,
/**
* A strategy in which fields that are specific to a
* subclass are mapped to a separate table than the fields
* that are common to the parent class, and a join is
* performed to instantiate the subclass.
*/
JOINED
}
例如
父类声明如下,意味着每个子实体类对应了一张表
@MappedSuperclass
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.TABLE_PER_CLASS)
public abstract class BaseEntity
子实体类复用父类声明的域/字段:
@Entity
@Table(name="App")
public class AppEntity entends BaseEntity
3. 开发常用注解——字段/域使用
3.1 @Column
@Column声明一个表字段与域/方法的映射,其属性可以进一步指定是否可为NULL,是否唯一等细节。
3.2 @Id
@Id标注一个属性,表示该属性映射为数据库的主键。
单独使用@Id来标识实体类的单个域映射为数据库表的主键,对于联合主键而言,就要配合@IdClass使用。
- 定义一个(外部)主键类,主键类中声明了实体类(目标表)联合主键中的所有主属性,主键类需实现
Serializable接口; - 在真正的实体类上使用
@IdClass,以上一步定义的主键类作为参数; - 实体类的主属性必须和主键类中的主属性完全对应(个数,类型,名称);
- 在实体类的所有主属性上面添加
@Id注解;
示例
外部主键类:
public class RoleUserId implements Serializable {
private Long roleId;
private Long userId;
}
实体类:
@Entity
@Table(name = "TB_ROLE_USER")
@IdClass(RoleUserId.class)
public class RoleUserDO {
@Id
private Long roleId;
@Id
private Long userId;
// ...
}
3.3 @GeneratedValue
@GeneratedValue设置字段的自动生成方式。
其strategy属性取值为枚举GenerationType:
/**
* Indicates that the persistence provider must assign
* primary keys for the entity using an underlying
* database table to ensure uniqueness.
*/
TABLE,
/**
* Indicates that the persistence provider must assign
* primary keys for the entity using a database sequence.
*/
SEQUENCE,
/**
* Indicates that the persistence provider must assign
* primary keys for the entity using a database identity column.
*/
IDENTITY,
/**
* Indicates that the persistence provider should pick an
* appropriate strategy for the particular database. The
* <code>AUTO</code> generation strategy may expect a database
* resource to exist, or it may attempt to create one. A vendor
* may provide documentation on how to create such resources
* in the event that it does not support schema generation
* or cannot create the schema resource at runtime.
*/
AUTO
使用自增的数据库列生成主键是一种常见的主键生成方式,MySQL支持Identity列。
Oracle 12c以后支持Identity Column(身份列),可以使用GenerationType.IDENTITY作为生成策略,此时无需再使用@SequenceGenerator指定对应序列。此前的Oracle通常使用序列实现自增字段,需要将生成策略指定为GenerationType.SEQUENCE并配合@SequenceGenerator(下文)使用。
Oracle 12c新增Identity Column的使用请阅读:https://www.cnblogs.com/zyon/p/11067115.html
使用身份列生成自增主键时,在主键属性上使用@Id和@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Entity
public class Author {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id", updatable = false, nullable = false)
private Long id;
// …
}
@GeneratedValue#generator属性指定主键生成器的名称,需要与@SequenceGenerator或@TableGenerator的名称对应起来。
3.4 @SequenceGenerator
如果使用序列方式生成主键,@SequenceGenerator指定自动生成主键时对应的序列(Sequence)。
@SequenceGenerator#name指定序列生成器的名称,@GeneratedValue#generator通过引用该值与具体的序列生成器关联,进而关联具体的序列。@SequenceGenerator#sequenceName指定自动生成主键时的物理序列名称;@SequenceGenerator#initialValue属性指定序列初值;@SequenceGenerator#allocationSize指定自增步长;
实例:
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE, generator = "sequence")
@SequenceGenerator(name = "sequence", sequenceName = "ID_SEQ", allocationSize = 1)
@Column(name = "Id")
private long id;
3.5 JPA大对象支持
常用相关注解
- @Lob
- @Basic
3.5.1 在字符串型域上用@Lob
@Lob
private String description;
- oracle映射字段的类型是
CLOB,java.sql.Clob,Character[],char[]和java.lang.String将被持久化为Clob类型。 - mysql中映射字段的类型是
longtext。
3.5.2 在二进制等类型域上用@Lob
- oracle中
java.sql.Blob,Byte[],byte[]和Serializable实现类将被持久化为Blob类型。 - mysql中对应
longblob。
@Lob持久化为Blob或者Clob类型,根据get方法的返回值不同,自动进行Clob和Blob的转换。
3.5.3 大对象字段的延迟加载
@Lob
@Basic(fetch=FetchType.LAZY)
private Byte[] file;
因为大对象数据一般占用的内存空间比较大,所以通常使用延迟加载的方式:@Basic注解设置加载方式为FetchType.LAZY。
问题:
延迟加载是延迟到什么时候?这个问题一直没有找到确切的解答。
4. 常用Repository开发
4.1 Repository接口
public interface Repository<T, ID>
最基础的Repository接口,不提供任何操作方法。
4.2 CrudRepository接口
public interface CrudRepository<T, ID> extends Repository<T, ID>
提供CRUD基本操作的Repository接口。
4.3 PagingAndSortingRepository 接口
public interface PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID> extends CrudRepository<T, ID>
它继承 CrudRepository 接口,在 CrudRepository 基础上新增了两个与分页有关的方法。
也可以不将自定义的持久层接口直接继承PagingAndSortingRepository,而是继承 Repository 或 CrudRepository 的基础上,在自定义方法参数列表最后增加一个 Pageable 或 Sort 类型的参数,用于指定分页或排序信息,可以实现比直接继承 PagingAndSortingRepository 更大的灵活性。
4.4 JpaRepository接口
public interface JpaRepository<T, ID> extends PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID>, QueryByExampleExecutor<T>
JpaRepository 继承PagingAndSortingRepository,是针对 JPA 技术提供的接口,它在父接口的基础上,提供了其他一些方法,比如flush(),saveAndFlush(),deleteInBatch() 等。
4.5 自定义JPA Repository方法
自定义JPA Repository方法,应参考以下规范:
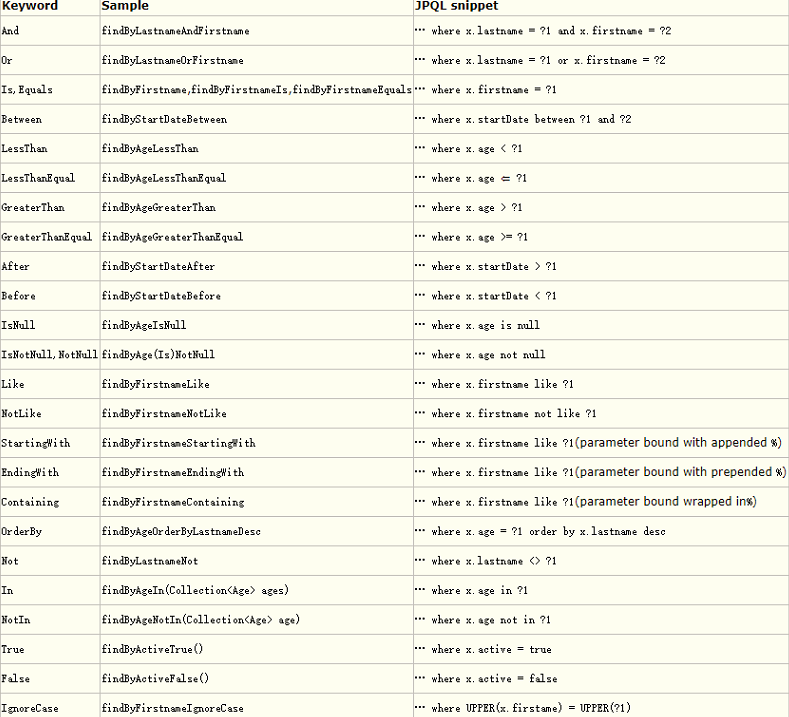
注意两点:
- 出现在方法名中用于组合查询条件等的是实体类的域名称,而不是数据库的表字段;
- 这种方式用来组合一些固定模式的SQL,生成SQL的过程对程序员是透明的,程序员不用自己写SQL。
4.6 @Query注解
org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query注解用来指定JPA Repository方法对应的查询HSQL。
示例:
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
//...
@Query("select a from App a where a.name LIKE %:name%")
List<App> findByName(@Param("name") String name);
需要注意的是,@Query中的参数HQL默认不是真实的SQL语句,而是面向对象的。
通常我们可以使用@Table指定实体类对应的表名,如果实体类的类名和对应的表名不同,@Query中应该使用类名,同时参数HQL中使用的是实体类的域名称而不是实际的字段名。
如不这样,例如在@Query的参数HQL中使用了实际的表名而非实体类名,则会报:QuerySyntaxException: XXX is not mapped.。
如果希望使用原生SQL,将@Query#nativeQuery设置为true即可:
@Query(nativeQuery = true, value = "SELECT * FROM AUTH_USER WHERE name = :name1 OR name = :name2 ")
List<UserDO> findSQL(@Param("name1") String name1, @Param("name2") String name2);
4.7 @Modifying注解
org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Modifying注解标识一个JPA Repository方法对应的SQL会修改数据库。
示例:
@Modifying
@Query("update appnamespace set isDeleted=1, dataChangeLastModifiedBy = ?3 where appId = ?1 and name = ?2")
int delete(String appId, String namespaceName, String operator);
参考:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/c14640b63653
Spring Boot 2.x 之 Spring Data JPA, Hibernate 5的更多相关文章
- Spring Boot (五)Spring Data JPA 操作 MySQL 8
一.Spring Data JPA 介绍 JPA(Java Persistence API)Java持久化API,是 Java 持久化的标准规范,Hibernate是持久化规范的技术实现,而Sprin ...
- Spring Boot 2.X 如何快速整合jpa?
本文目录 一.JPA介绍二.Spring Data JPA类结构图1.类的结构关系图三.代码实现1.添加对应的Starter2.添加连接数据库的配置3.主要代码 一.JPA介绍 JPA是Java Pe ...
- Spring Boot(十五):spring boot+jpa+thymeleaf增删改查示例
Spring Boot(十五):spring boot+jpa+thymeleaf增删改查示例 一.快速上手 1,配置文件 (1)pom包配置 pom包里面添加jpa和thymeleaf的相关包引用 ...
- Spring 5.x 、Spring Boot 2.x 、Spring Cloud 与常用技术栈整合
项目 GitHub 地址:https://github.com/heibaiying/spring-samples-for-all 版本说明: Spring: 5.1.3.RELEASE Spring ...
- spring boot 系列之五:spring boot 通过devtools进行热部署
前面已经分享过四篇随笔: spring boot 系列之一:spring boot 入门 spring boot 系列之二:spring boot 如何修改默认端口号和contextpath spri ...
- Spring Boot 2(一):Spring Boot 2.0新特性
Spring Boot 2(一):Spring Boot 2.0新特性 Spring Boot依赖于Spring,而Spring Cloud又依赖于Spring Boot,因此Spring Boot2 ...
- Spring Boot(十四):spring boot整合shiro-登录认证和权限管理
Spring Boot(十四):spring boot整合shiro-登录认证和权限管理 使用Spring Boot集成Apache Shiro.安全应该是互联网公司的一道生命线,几乎任何的公司都会涉 ...
- Spring Boot配置篇(基于Spring Boot 2.0系列)
1:概述 SpringBoot支持外部化配置,配置文件格式如下所示: properties files yaml files environment variables command-line ar ...
- 【自学Spring Boot】什么是Spring Boot
为啥要有Spring Boot? 以前大学刚开始学java web的时候,需要搭建起web框架,当时使用的是SSH(struts+spring+hibernate),那就开始搭建吧,初学者哪里知道整套 ...
随机推荐
- Numpy数组的组合与分割详解
在介绍数组的组合和分割前,我们需要先了解数组的维(ndim)和轴(axis)概念. 如果数组的元素是数组,即数组嵌套数组,我们就称其为多维数组.几层嵌套就称几维.比如形状为(a,b)的二维数组就可以看 ...
- SQL语法 - SELECT 语句
SELECT 语句用于从数据库中选取数据. SQL SELECT 语句 SELECT 语句用于从数据库中选取数据. 结果被存储在一个结果表中,称为结果集. SQL SELECT 语法 SELECT c ...
- druid与知乎平台
背景 知乎作为知名中文知识内容平台,业务增长和产品迭代速度很快,如何满足业务快速扩张中的灵活分析需求,是知乎数据平台组要面临的一大挑战. 知乎数据平台团队基于开源的 Druid 打造的业务自助式的数据 ...
- 官宣 .NET 6 预览版 6
我们很高兴宣布.NET 6 预览版6问世啦.预览版6 是我们RC版发布之前的倒数第二个预览版. 我们将有两个RC版. 此版本本身相对较小,而预览版7会更大. 在那之后,我们将进行质量修复,直到11 月 ...
- ARM的九种寻址方式
文章目录 1.立即数寻址 2.寄存器寻址 3.寄存器间接寻址 4.寄存器偏移寻址 5.寄存器基址变址寻址 6.批量寄存器寻址 7.相对寻址 8.堆栈寻址 9.块拷贝寻址 寻址方式就是CPU根据指令中的 ...
- efcore分表下"完美"实现
ShardingCore 如何呈现"完美"分表 这篇文章是我针对efcore的分表的简单介绍,如果您有以下需求那么可以自己选择是否使用本框架,本框架将一直持续更新下去,并且免费开源 ...
- Linux搭建Ldap服务器
一,服务器安装 yum install -y openldap openldap-clients openldap-servers migrationtools 二,配置ldap服务器 2.1配置ld ...
- NPM使用方法
什么是npm npm是nodejs的包管理器,在当今工程化前端开发过程中,npm包起着举足轻重的作用. 安装npm 作为nodejs的包管理器,npm随着nodejs一起安装的.通常情况下,当我们安装 ...
- Semaphore 的使用思路
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/klbc/p/9500947.html 最近在看一本书<Java并发编程 核心方法与框架>,打算一边学习一边把学习的经验记下来,所粘贴 ...
- springboot&&springcloud知识点
spring cloud 常见面试题: A.https://blog.csdn.net/panhaigang123/article/details/79587612 B.https://blog.cs ...
