商业爬虫学习笔记day7-------解析方法之bs4
一.Beautiful Soup
1.简介
Beautiful Soup 是python的一个库,最主要的功能是从网页抓取数据。其特点如下(这三个特点正是bs强大的原因,来自官方手册)
a. Beautiful Soup提供一些简单的、python式的函数用来处理导航、搜索、修改分析树等功能。它是一个工具箱,通过解析文档为用户提供需要抓取的数据,因为简单,所以不需要多少代码就可以写出一个完整的应用程序。
b. Beautiful Soup自动将输入文档转换为Unicode编码,输出文档转换为utf-8编码。你不需要考虑编码方式,除非文档没有指定一个编码方式,这时,Beautiful Soup就不能自动识别编码方式了。然后,你仅仅需要说明一下原始编码方式就可以了。
c. Beautiful Soup已成为和lxml、html6lib一样出色的python解释器,为用户灵活地提供不同的解析策略或强劲的速度。
2.Beautiful Soup支持的解析器
(1)python标准库(默认):python内置标准库,速度适中,文档容错能力强
使用方法:BeautifulSoup(data, “html.parser”)
(2)lxml HTML 解析器:速度快,文档容错能力强
使用方法:BeautifulSoup(data, “lxml”)
(3)lxml XML 解析器:速度快,唯一支持XML的解析器
使用方法:BeautifulSoup(markup, [“lxml”, “xml”]);BeautifulSoup(markup, “xml”)
(4)html5lib解析器:最好的容错性;以浏览器的方式解析文档;生成HTML5格式的文档;速度慢
二 创建soup对象
下面是官方手册上的一个案例
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="story"><!--哈哈--></p>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> """
(1)导入bs4库
from bs4 imort import beautifulSoup
(2) 创建beautifulsoup对象
此处使用python默认的解析器,即html.parser
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc) # 等效于soup = BeautifulSoup(markup, “html.parser”)
这样运行的话会出现提醒,如下:
UserWarning: No parser was explicitly specified, so I'm using the best available HTML parser for this system ("lxml"). This usually isn't a problem, but if you run this code on another system, or in a different virtual environment, it may use a different parser and behave differently
To get rid of this warning, pass the additional argument 'features="lxml"' to the BeautifulSoup constructor.
如上提示,避免出现这种提示的话就自己选择一个解析器,如下
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, “lxml”)
格式化输出,有补全功能
result = soup.prettify()
print(result)
打印下result,格式化输出
<html>
<head>
<title>
The Dormouse's story
</title>
</head>
<body>
。。。。
</body>
</html>
三. 四大对象种类
Beautiful Soup将复杂HTML文档转换成一个复杂的树形结构,每个节点都是python对象,所有对象可归纳为以下4中:
Tag ;BeautifulSoup; Comment; NavigableString
(1)Tag
Tag是什么?通俗点讲就是HTML中的一个个标签,例如:
<head>
<title>
The Dormouse's story
</title>
</head>
此处的head,title等都是标签,以下为代码运行情况
result = soup.head
print(type(result)) # 打印的结果为 <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
print(result) # 打印的结果为 <head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
result = soup.title
print(type(result)) # 打印的结果为 <class 'bs4.element.Tag'>
print(result) # 打印的结果为 <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
Tag的两个重要的属性:name;attr
name
print(soup.name) # 打印结果为 [document]
print(soup.head.name) # 打印结果为 title
soup对象本身比较特殊,它的name即为[document],对于其他内部标签,输出的值便为标签本身的名称,如上诉title
attrs
print(soup.a.attrs) # 打印的结果为 {'href': 'http://example.com/elsie', 'class': ['sister'], 'id': 'link1'}
在这里,我们把a标签的所有属性打印了出来,得到的类型是一个字典
如果我们想要单独获取某个属性,如下(以获取href为例)
print(soup.a['href']) # 打印结果 ['http://example.com/elsie']
print(soup.a.get('href')) # 打印结果 ['http://example.com/elsie']
(2) BeautifulSoup
BeautifulSoup 对象表示的是一个文档的全部内容.大部分时候,可以把它当作 Tag 对象,是一个特殊的 Tag,我们可以分别获取它的类型,名称,以及属性来感受一下
print(type(soup.name)) # <class 'str'>
print(soup.name) # [document]
print(soup.attrs) # {} 空字典
(3) NavigableString
既然我们已经得到了标签的内容,那么问题来了,我们要想获取标签内部的文字怎么办呢?很简单,用 .string 即可,例如
print(soup.a.string) # 打印结果为 Elsie
print(type(soup.a.string)) # 打印结果为 <class 'bs4.element.NavigableString'>,可得其类型
注意:只能获取第一个标签的内容(上面html_doc有多个a标签,但只能获取到第一个标签)
这样我们就轻松获取到了标签里面的内容,想想如果用正则表达式要多麻烦。它的类型是一个 NavigableString,翻译过来叫 可以遍历的字符串
(4) Comment
Comment 对象是一个特殊类型的 NavigableString 对象,其实输出的内容仍然不包括注释符号,但是如果不好好处理它,可能会对我们的文本处理造成意想不到的麻烦。
我们找一个带注释的标签
print(soup.p)
print(soup.p.string)
print(type(soup.p.string))
运行结果为:
<p class="story"><!--哈哈--></p>
哈哈
<class 'bs4.element.Comment'>
p 标签里的内容实际上是注释,但是如果我们利用 .string 来输出它的内容,我们发现它已经把注释符号去掉了,另外由上诉打印结果可知,它是一个Comment类型,所以,我们在使用前最好做一下判断,判断代码如下
if type(soup.p.string)==bs4.element.Comment:
print(soup.p.string)
上面的代码中,我们首先判断了它的类型,是否为 Comment 类型,然后再进行其他操作,如打印输出。
四. 节点选择器
直接调用节点的名称就可以选择节点元素,再调用string属性就可以得到节点内的文本了,这种选择方式速度非常快。如果单个节点层次非常清晰,可以选用这种方式来解析
上例子的html_doc写成的部分文档树如下(body部分只写出了其2个子节点)
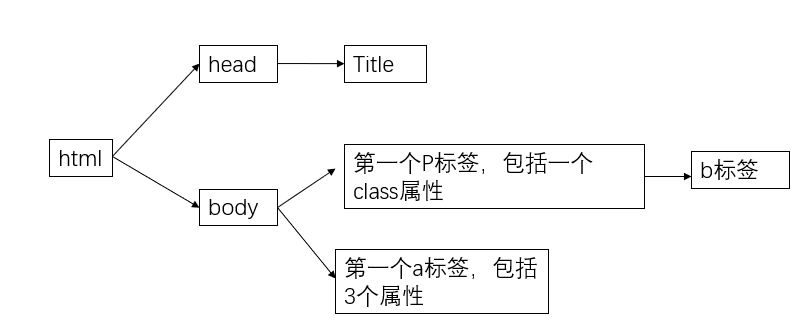
(1)直接子节点(.contents ; .children)
.contents
tag的 .contents属性可以将tag的子节点以列表的方式输出
print(soup.head.contents) # 打印结果为[<title>The Dormouse's story</title>]
输出方式为列表,我们可以用列表索引来获取它的某一个元素
.children
它返回的不是一个list,不过我们可以通过遍历获取所有子节点,我们打印输出.children看一下,可以发现它是一个list生成器
print(soup.head.children) # 结果 <list_iterator object at 0x000001D4E66107B8>
遍历获取里面的内容
for child in soup.body.children:
print(child)
打印结果为
<p class="story"><!--哈哈--></p> <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
(2)所有子孙节点(.descendants)
.contents 和 .children属性仅包含tag的直接子节点, .descendants属性可以对所有tag的子孙节点进行递归循环,和children类似(也是生成器),我们需要遍历获取其中的内容
for child in soup.descendants:
print (child)
打印结果如下,可以发现,所有的节点都被打印出来了,先生最外层的 HTML标签,其次从 head 标签一个个剥离,以此类推。
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="story"><!--哈哈--></p>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
</body></html>
<head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head> # 剥离html标签
<title>The Dormouse's story</title> # 剥离head标签
The Dormouse's story # 剥离title标签,进而得到内容,其它类似 <body>
<p class="story"><!--哈哈--></p>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
</body> <p class="story"><!--哈哈--></p>
哈哈 <p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<b>The Dormouse's story</b>
The Dormouse's story <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/elsie" id="link1">Elsie</a>
Elsie
, <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/lacie" id="link2">Lacie</a>
Lacie
and <a class="sister" href="http://example.com/tillie" id="link3">Tillie</a>
Tillie
;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
(3)节点内容(.string)
直接使用当前节点 . string即可获得该节点的内容,但如果一个tag仅有一个子节点,那么这个tag也可以使用 .string 方法,输出当前子节点的内容
print(soup.head.string) # 打印结果:The Dormouse's story
print(soup.title.string) # 打印结果:The Dormouse's story
如果tag包含了多个子节点(或多个孙节点),tag就无法确定 .string应该获取哪个子节点的内容,.string的输出结果是None
print(soup.html.string) # 打印结果为 None
(4)多个内容(.strings)
上面讲了获取单个节点内容的方法,那么同时获取多个节点内容的方法是什么呢?
.strings,获取多个内容,但是需要遍历,如下:
for string in soup.strings:
print(repr(string)) # repr 返回规范化的字符串
打印结果为
'\n'
"The Dormouse's story"
'\n'
'Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were\n'
'Elsie'
',\n'
'Lacie'
' and\n'
'Tillie'
';\nand they lived at the bottom of a well.'
'\n'
输出的字符串中若包含了很多空格或空行,可用 .stripped_strings 可以去除多余空白内容
for string in soup.stripped_strings:
print(repr(string))
打印结果如下(相比前面就少了空行):
"The Dormouse's story"
"The Dormouse's story"
'Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were'
'Elsie'
','
'Lacie'
'and'
'Tillie'
';\nand they lived at the bottom of a well.'
五. 方法选择器
1. find_all( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
获取与给定条件匹配的Tag对象列表,可以指定Tag的名称以及希望Tag具有的任何属性。
六. CSS选择器
参考: https://cuiqingcai.com/1319.html
https://cuiqingcai.com/5548.html
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av42741352
商业爬虫学习笔记day7-------解析方法之bs4的更多相关文章
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day1
day1 一. HTTP 1.介绍: https://www.cnblogs.com/vamei/archive/2013/05/11/3069788.html http://blog.csdn.ne ...
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day2
1. get传参 (1)url中包含中文报错解决方法 urllib.request.quote("包含中文的url", safe = "string.printtable ...
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day6
一. 正则解析数据 解析百度新闻中每个新闻的title,url,检查每个新闻的源码可知道,其title和url都位于<a></a>标签中,因为里面参数的具体形式不一样,同一个正 ...
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day5
一. 发送post请求 import requests url = "" # 发送post请求 data = { } response = requests.post(url, d ...
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day4
一.获取登录后页面信息的两种方法 1.第一种方法: 人为把有效cookies加到请求头中,代码如下 import urllib.request # 确定url url = "https:// ...
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day8-------json的使用
一. 简介 JSON,全称为JavaScript Object Notation(JavaScript对象标记),它通过对象和数组的组合来表示数据,是一种轻量级的数据交换格式.它基于 ECMAScri ...
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day3
一. 付费代理发送请求的两种方式 第一种方式: (1)代理ip,形式如下: money_proxy = {"http":"username:pwd@192.168.12. ...
- Python爬虫beautifulsoup4常用的解析方法总结(新手必看)
今天小编就为大家分享一篇关于Python爬虫beautifulsoup4常用的解析方法总结,小编觉得内容挺不错的,现在分享给大家,具有很好的参考价值,需要的朋友一起跟随小编来看看吧摘要 如何用beau ...
- python网络爬虫学习笔记
python网络爬虫学习笔记 By 钟桓 9月 4 2014 更新日期:9月 4 2014 文章文件夹 1. 介绍: 2. 从简单语句中開始: 3. 传送数据给server 4. HTTP头-描写叙述 ...
随机推荐
- js实现日期格式化封装-八种格式
封装一个momentTime.js文件,包含8种格式. 需要传两个参数: 时间戳:stamp 格式化的类型:type, 日期补零的方法用到es6语法中的padStart(length,'字符'): 第 ...
- Vue-cli4.xPC端项目Rem适配
适配准备 安装 (amfe-flexible) 和(postcss-px2rem) 1, 安装依赖并在main.js中引入该依赖 npm i amfe-flexible import "am ...
- Centos 7 端口聚合
简单粗暴,直接复制命令就好了 还是先啰嗦一下,添加网卡之后,如果没有网卡配置文件,可以通过nmcli con show 先查看网卡的唯一ID,然后复制其他的网卡配置文件,修改device项,name项 ...
- Redis网络库源码分析(3)之ae.c
一.aeCreateEventLoop & aeCreateFileEvent 上一篇文章中,我们已经将服务器启动,只是其中有些细节我们跳过了,比如aeCreateEventLoop函数到底做 ...
- 在线编辑Word——插入图表
在Word中可插入图表,配合使用表格能够更加全方位的展示数据的可信度并增加数据的可读性.本文将通过使用在线编辑器 Spire.Cloud Word 演示如何来插入图表,并设置相关格式化操作.具体步骤如 ...
- WPF进阶技巧和实战09-事件(1-路由事件、鼠标键盘输入)
理解路由事件 当有意义的事情发生时,有对象(WPF的元素)发送的用于通知代码的消息,就是事件的核心思想.WPF通过事件路由的概念增强了.NET事件模型.事件由允许源自某个元素的事件由另一个元素引发.例 ...
- vue修改启动的端口和host
打开vue项目(dev) dev/config/ 路径修改index.js文件 然后对host和pord修改指定的即可 host: 'localhost', // can be overwritten ...
- ssh密码登录
https://stackoverflow.com/a/16928662/8025086 https://askubuntu.com/a/634789/861079 #!/usr/bin/expect ...
- oracle合并列的函数wm_concat的使用详解
oracle wm_concat(column)函数使我们经常会使用到的,下面就教您如何使用oracle wm_concat(column)函数实现字段合并,如果您对oracle wm_concat( ...
- 001.AD域控简介及使用
一 AD概述 1.1 AD简介 域(Domain)是Windows网络中独立运行的单位,域之间相互访问则需要建立信任关系. 当一个域与其他域建立了信任关系后,2个域之间不但可以按需要相互进行管理,还可 ...
