Spring基础学习(四)—AOP
一、AOP基础
1.基本需求
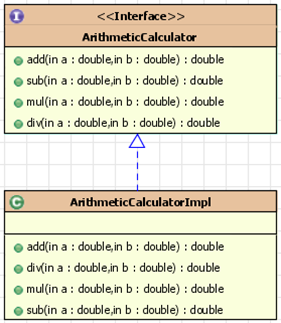
需求: 日志功能,在程序执行期间记录发生的活动。
ArithmeticCalculate.java
public interface ArithmeticCalculate{
public int add(int a,int b);
public int sub(int a,int b);
public int mul(int a,int b);
public int div(int a,int b);
}
ArithmeticCalculateImpl.java
public class ArithmeticCalculateImpl implements ArithmeticCalculate{
@Override
public int add(int a,int b){
System.out.println("The method add.....begin");
int result = a + b;
System.out.println("The method add.....end");
return result;
}
@Override
public int sub(int a,int b){
System.out.println("The method sub.....begin");
int result = a - b;
System.out.println("The method sub.....end");
return result;
}
@Override
public int mul(int a,int b){
System.out.println("The method mul.....begin");
int result = a * b;
System.out.println("The method mul.....end");
return result;
}
@Override
public int div(int a,int b){
System.out.println("The method div.....begin");
int result = a / b;
System.out.println("The method div.....end");
return result;
}
}
以上这样写会出现两种问题。
(1)代码混乱
越来越多的非业务需求加入后,原有的业务方法急剧膨胀。每个方法在处理核心逻辑的同时还必须兼顾其他多个关注点。
(2)代码分散
以日志需求为例,只是为了满足这个单一需求,就不得不在多个模块重复相同的代码日志,如果日志需求发生改变还得修改所有的需求。
使用动态代理
原理: 使用一个代理将对象包装起来,然后改代理对象取代原始对象。任何对原始对象的调用都要通过代理。代理对象决定是否以及何时将方法调用转到原始对象上。
ArithmeticCalculateProxy.java
public class ArithmeticCalculateProxy{
//要代理的对象
private ArithmeticCalculate target;
public ArithmeticCalculateProxy(){
}
public ArithmeticCalculateProxy(ArithmeticCalculate target){
this.target = target;
}
public ArithmeticCalculate getProxy(){
ArithmeticCalculate proxy = null;
//代理对象由哪一个类加载器负责加载
ClassLoader loader = target.getClass().getClassLoader();
//代理对象的类型,即有哪些方法
Class[] interfaces = new Class[]{ArithmeticCalculate.class};
//当调用代理对象其中方法时,该执行的代码
InvocationHandler handler = new InvocationHandler(){
/*
* proxy: 正在返回的那个代理对象,一般情况下,在invoke方法中都不使用
* method: 正在被调用的方法
* args:调用方法时传入的参数
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy,Method method,Object[] args) throws Throwable{
String methodName = method.getName();
//日志
System.out.println("The method " + methodName +" begin......");
//执行方法
Object result = method.invoke(target,args);
//日志
System.out.println("The method " + methodName +" end......");
return result;
}
};
proxy = (ArithmeticCalculate)Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader,interfaces,handler);
return proxy;
}
}
Test.java
@Test
public void testCalculate(){
ArithmeticCalculate target = new ArithmeticCalculateImpl();
ArithmeticCalculate proxy = new ArithmeticCalculateProxy(target).getProxy();
System.out.println(proxy.add(4,2));
System.out.println(proxy.sub(4,2));
}
结果:
The method add begin......
The method add end......
6
The method sub begin......
The method sub end......
2
2.AOP简介
AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming): 面向切面编程,而切面模块化横切关注点。
在AOP编程中,仍然需要定义公共功能,但可以明确的定义这个功能在哪里,以什么方式应用,并且不必修改受影响的类。这样横切关注点就被模块化到特殊的对象(切面)里。
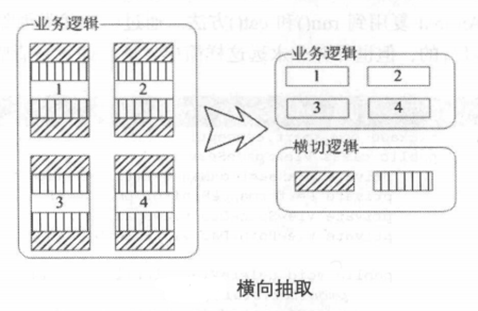
AOP希望将这些分散在各个业务逻辑代码中的相同代码,通过横向切割的方式抽取到一个独立的模块中,还业务逻辑类一个清新的世界。我们知道将这些重复性的横切逻辑独立出来很容易,但是将这些独立的逻辑融合到业务逻辑中完成和原来一样的业务操作,这才是事情的关键,也是AOP要解决的主要问题。
使用AspectJ解决以上问题
LoggerAspect.java
/*
* 把这个类声明为一个切面
* 1.把该类放到IOC容器中
* 2.再声明为切面
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggerAspect{ /*
* 声明该方法是一个前置通知
* 在目标方法开始之前执行
*/
@Before("execution(* com.kiwi.aop.ArithmeticCalculate.*add(..))")
public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("The method " + methodName +" begin......");
}
}
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 指定Spring IOC容器扫描的包 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.kiwi"/> <!-- 使AspectJ注解起作用,为匹配的类生成代理对象 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
</beans>
Test.java
@Test
public void testAop(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
ArithmeticCalculate ac = context.getBean(ArithmeticCalculate.class);
System.out.println(ac.add(2,2));
}
结果:
The method add begin......
4
二、使用AspectJ注解声明切面
(1)要在Spring中声明AspectJ切面,只需要在IOC容器中将切面声明为Bean实例. 当在Spring IOC容器中初始化AspectJ切面之后, Spring IOC容器就会为那些与AspectJ切面相匹配的Bean创建代理。
(2)在AspectJ注解中,切面只是一个带有@Aspect注解的Java类。
(3)AspectJ 支持 5 种类型的通知注解:
@Before: 前置通知,在方法执行之前执行。
@After: 后置通知,在方法执行之后执行。
@AfterRunning: 返回通知,在方法返回结果之后执行。
@AfterThrowing: 异常通知,在方法抛出异常之后。
@Around: 环绕通知,围绕着方法执行。
1.切点表达式函数
(1)切点表达式由关键字和操作参数组成。如:execution(* greetTo(..))。
execution为关键字,代表目标执行某一方法。
* greetTo(..)为操作数,描述目标方法的匹配模式串。
两者联合起来表示目标类greetTo()方法的连接点,为了描述方便面我们将前者称为函数,将匹配串称为入参。

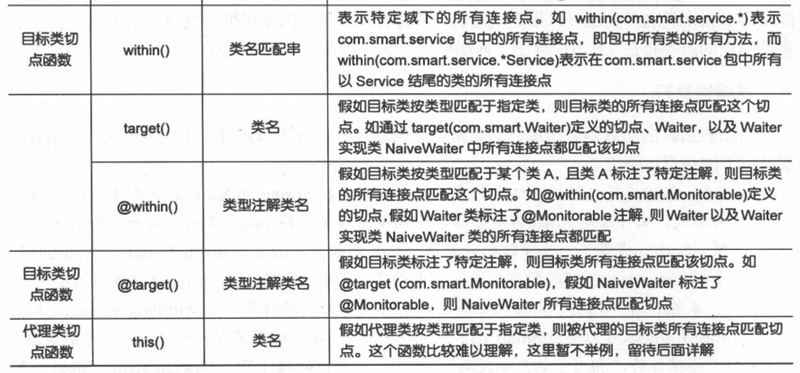
(2)在函数入参中使用通配符
* : 匹配任意字符,但它只能匹配上下文中一个元素。
.. : 匹配任意字符,可以匹配上下文多个元素,但在表示类的时候,必须和*联合使用,在表示入参的时候单独使用。
+ : 表示按类型匹配指定所以类,必须跟在类名后面。
2.前置通知
(1)在方法执行之前的通知。
(2)前置通知使用@Before注解,并将切入点表达式的值作为注解值。

3.后置通知
(1)后置通知是在连接点完成之后执行的,无论是否抛异常都会执行。
(2)后置通知中不能访问目标方法的执行的结果。
/*
* 后置通知
* 在目标方法执行后,无论是否发生异常,都执行的通知。
*/
@After("execution(* com.kiwi.aop.ArithmeticCalculate.*(..))")
public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("The method " + name +" end......");
}
4.返回通知
(1)无论连接点是正常返回还是抛出异常,后置通知都会执行。如果只想在连接点正常返回的时候执行,可以使用返回通知。
(2)在返回通知中,只要将returnning属性添加到@AfterReturning注解中,就可以访问连接点的返回值,该属性的值即为用来传入返回值的参数名称。
(3)必须在通知方法的签名中添加一个同名的参数,Spring AOP才会通过这个参数传递返回值。
@AfterReturning(pointcut="execution(* com.kiwi.aop.ArithmeticCalculate.*(..))",returning="result")
public void afterReturningMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("The method " + name +" end......" + result);
}
5.异常通知
(1)只有在连接点抛出异常时才执行的异常通知。
(2)将throwing属性添加到@AfterThrowing注解中,也可以以访问连接点抛出的异常。
(3)如果只对某种特殊的异常类型感兴趣, 可以将参数声明为其他异常的参数类型. 然后通知就只在抛出这个类型及其子类的异常时才被执行。
@AfterThrowing(pointcut="execution(* com.kiwi.aop.ArithmeticCalculate.*(..))",throwing="ex")
public void afterReturningMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception ex){
String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("The method " + name +" end......" + ex);
}
6.环绕通知
(1)环绕通知需要携带ProceedingJoinPoint类型的参数。
(2)在环绕通知中需要明确调用 ProceedingJoinPoint 的proceed()方法来执行被代理的方法. 如果忘记这样做就会导致通知被执行了, 但目标方法没有被执行。
(3)环绕通知的方法需要返回目标方法执行之后的结果, 即调用 joinPoint.proceed()的返回值。
/*
* 1.环绕通知需要携带ProceedingJoinPoint类型的参数
* 2.在环绕通知中需要明确调用 ProceedingJoinPoint 的 proceed()
* 方法来执行被代理的方法. 如果忘记这样做就会导致通知被执行了, 但目标方法没有被执行.
* 3.环绕通知的方法需要返回目标方法执行之后的结果, 即调用 joinPoint.proceed()的返回值
*/
@Around("execution(* com.kiwi.aop.ArithmeticCalculate.*(..))")
public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint point){
String name = point.getSignature().getName(); //执行目标方法,返回值为目标方法的返回值
Object result = null;;
try{
//前置通知
System.out.println("The method " + name +" begin......" + Arrays.asList(point.getArgs()));
result = point.proceed();
//返回通知
System.out.println("The method " + name +" ends With......" + result);
}catch(Throwable e){
//异常通知
System.out.println("The method " + name +" occur Exception......");
throw new RuntimeException();
}
//后置通知
System.out.println("The method " + name +" end......"); return result;
}
7.切面的优先级
(1)在同一个连接点上应用不止一个切面时, 除非明确指定, 否则它们的优先级是不确定的。
(2)切面的优先级可以通过实现Ordered接口或利用@Order注解指定。
(3)实现 Ordered 接口,getOrder() 方法的返回值越小,优先级越高。
(4)若使用 @Order 注解,序号出现在注解中。

8.重用切点
(1)编写AspectJ切面时, 可以直接在通知注解中书写切入点表达式. 但同一个切点表达式可能会在多个通知中重复出现。
(2)在AspectJ切面中, 可以通过@Pointcut 注解将一个切入点声明成简单的方法. 切入点的方法体通常是空的, 因为将切入点定义与应用程序逻辑混在一起是不合理的。
Spring基础学习(四)—AOP的更多相关文章
- Python基础学习四
Python基础学习四 1.内置函数 help()函数:用于查看内置函数的用途. help(abs) isinstance()函数:用于判断变量类型. isinstance(x,(int,float) ...
- Spring基础学习,附例子代码讲解
什么是Spring.IOC.AOP.DI? Spring是一个基于IOC和AOP的结构J2EE系统的框架. IOC(Inversion Of Control)控制反转(Spring的基 ...
- spring基础学习01
spring基础 Spring是一个开放源代码的设计层面框架,他解决的是业务逻辑层和其他各层的松耦合问题,因此它将面向接口的编程思想贯穿整个系统应用 IOC控制反转 把创建对象和维护对象之间的关系权利 ...
- spring框架学习(四)——注解方式AOP
注解配置业务类 使用@Component("s") 注解ProductService 类 package com.how2java.service; import org.spri ...
- spring深入学习(四)-----spring aop
AOP概述 aop其实就是面向切面编程,举个例子,比如项目中有n个方法是对外提供http服务的,那么如果我需要对这些http服务进行响应时间的监控,按照传统的方式就是每个方法中添加相应的逻辑,但是这些 ...
- spring基础学习---aop
1:无参aop下面为项目结构 2:通知类.MyAdvice package cn.edu.aop; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; //通知类 ...
- Spring学习笔记(一) Spring基础IOC、AOP
1. 注入类型 a) Spring_0300_IOC_Injection_Type b) setter(重要) c) 构造方法(可以忘记) d) ...
- spring基础学习
ClassXmlAplicationContext和FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的区别 https://www.cnblogs.com/sxdcgaq808 ...
- Spring基础学习笔记
1. Spring入门 1. 1 Spring的体系结构 1.2 HelloWorld 1.2.1 Maven的使用 1)maven 的javase工程目录结构: 2)maven的settings.x ...
随机推荐
- 每天一个Linux命令(23)--linux 目录结构(二)
二./usr 的意义与内容 依据FHS的基本定义, /usr 里面放置的数据属于可分享的与不可变动的(shareable,static), 如果你知道如何透过网络进行分区的挂载(例如在服务器篇会谈到的 ...
- 关于adb重启的一些问题
有时候我们在使用eclipse启动虚拟机进行程序测试的时候会提示,要我们重启adb和eclipse,这个时候,重启adb的方式就是,使用cmd定位到adb所在的文件夹,然后输入指令:adb kill- ...
- solr 学习之简介及安装
一.solr简介 Solr 是Apache下的一个顶级开源项目,采用Java开发,它是基于Lucene的全文搜索服务器.Solr提供了比Lucene更为丰富的查询语言,同时实现了可配置.可扩展,并对索 ...
- C#基础——数组(冒泡排序)
数组 所谓数组,就是相同数据类型的元素按一定的顺序的集合,就是把有限个类型相同的变量用一个名字来命名,然后用编号区分他们的变量的集合,这个名字称为数组名,编号称为下标.组成数组的各个变量称为数组的分量 ...
- 【openstack N版】——块存储服务cinder
一.块存储服务介绍 1.1块存储服务通常包含以下组件 cinder-api: 接受API请求,并将其路由到"cinder-volume"执行. cinder-volume: 与块存 ...
- progID
ProgID程序员给CLSID指定的容易记住的名字ProgID命名约定:<Program>.<Component>.<Version>AppID:将某个APPID( ...
- jQuery的动态绑定事件的应用
注意:bind()的事件绑定是只对当前页面选中的元素有效.如果你想对动态创建的元素bind()事件,是没有办法达到效果的 <script src="jquery-1.11.2.min. ...
- Java面试01|JVM相关
1.JVM内存查看与分析,编写内存泄露实例 堆区.栈区.方法区.本机内存都有可能内存溢出.在这里编写堆区内存溢出实例.如下(来自<深入理解Java虚拟机>一书. // -Xms20m -X ...
- Java面试13|算法
1.冒泡排序 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ for(int j=0;j<n-1-i;j++){ if(temp[j]>temp[j+1]){ int t=temp[j] ...
- swift -- 单例
方式一: (类似OC) class SingletonDispatch{ class var shareInstance : SingletonDispatch { //结构体 struct Stat ...
