live555库中的testRTSPClient实例
1、testRTSPClient简介
testRTSPClient是个简单的客户端实例,这个实例对rtsp数据交互作了详细的描述,其中涉及到rtsp会话的两个概念Source和Sink.
Source是生产数据,Sink是消费数据.
testRTSPClient非常简洁,除了接收服务端发送过来的数据,什么都没干,所以我们很方便在这个基础上改造,做我们自己的项目.
2、testRTSPClient编译,运行
在linux下编译运行更方便,鉴于我的电脑太渣,虚拟机跑起来费劲,就转到windows下来折腾.
在windows下只需要加载这一个文件就可以编译,我们以mediaServer为服务端,以testRTSPClient为客户端。
当然也可以用支持rtsp协议的摄像机或其他实体设备作为服务端。

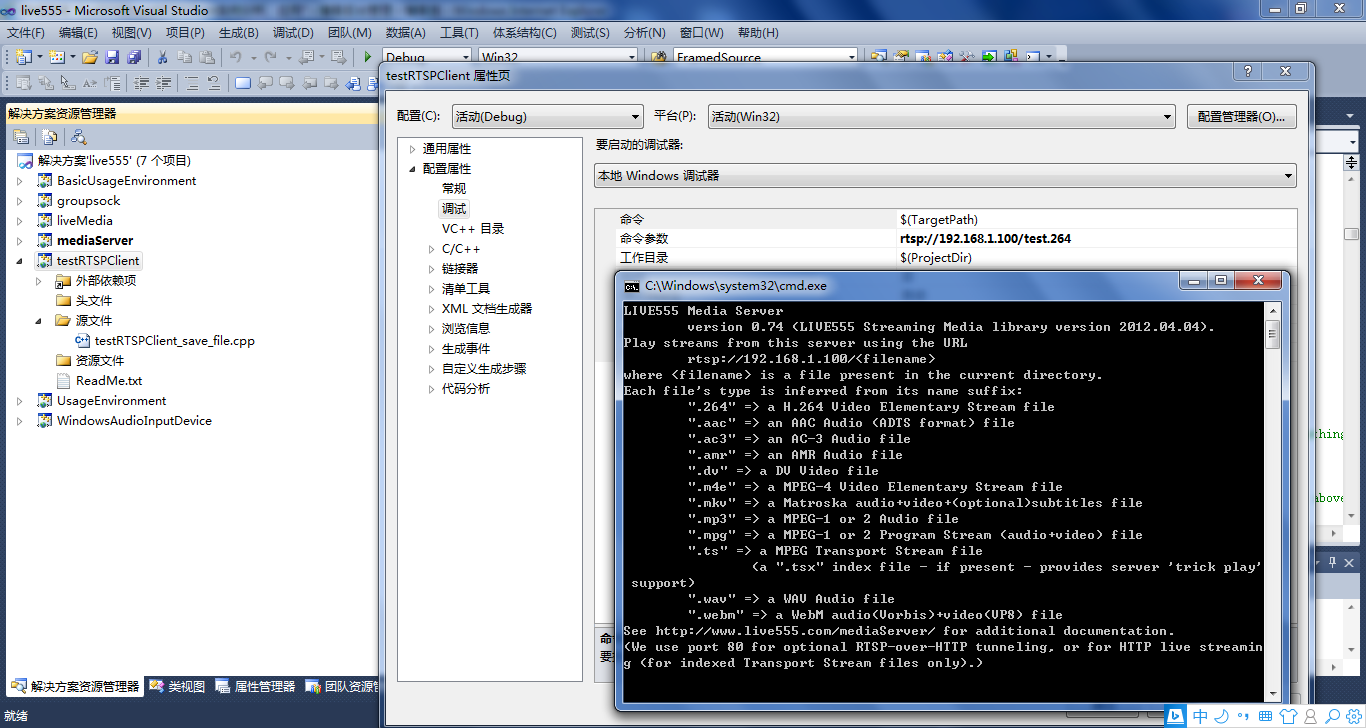
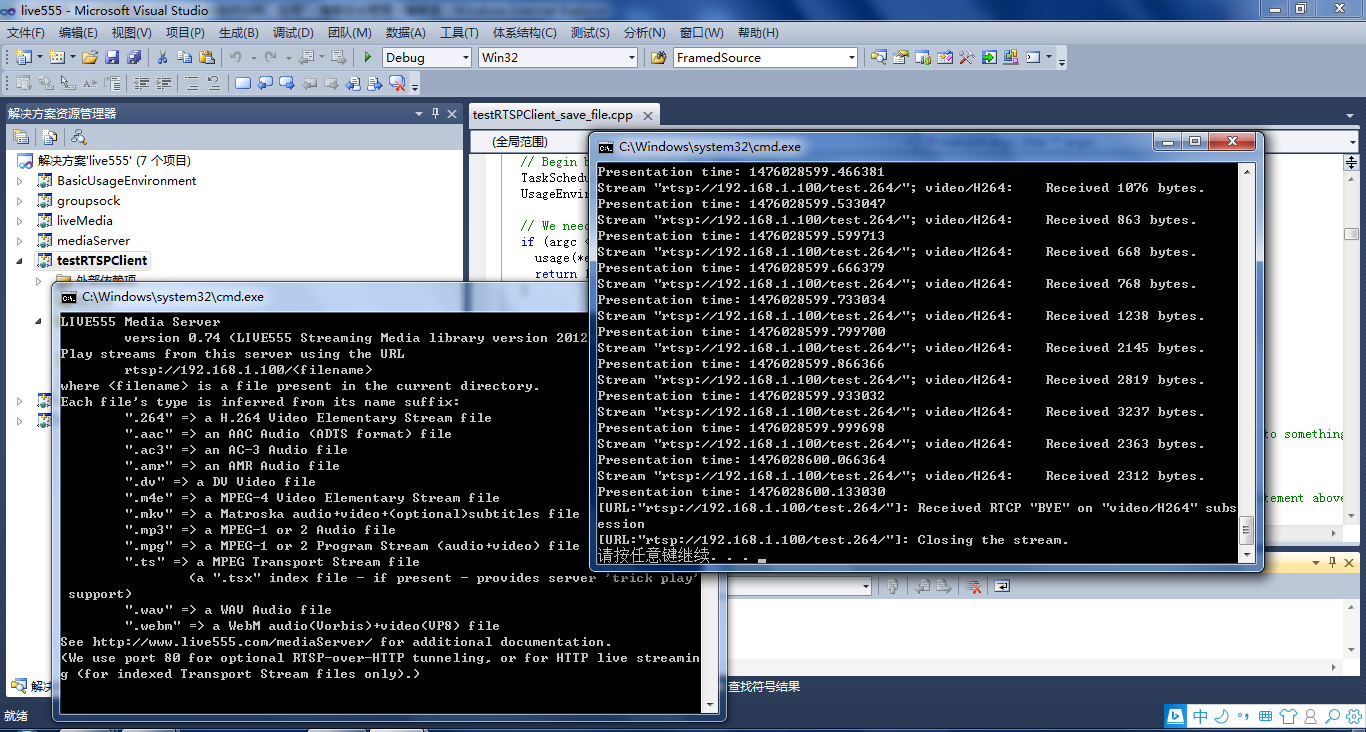
先启动mediaServer,然后在testRTSPClient项目的命令菜单里填入mediaServer 提示的IP, 再启动testRTSPClient即可。
3、testRTSPClient核心代码解读
1)看代码之前可以大致浏览一下总体的框架,这位博主画了个流程图http://blog.csdn.net/smilestone_322/article/details/17297817
void DummySink::afterGettingFrame(unsigned frameSize, unsigned numTruncatedBytes,
struct timeval presentationTime, unsigned /*durationInMicroseconds*/) {
// We've just received a frame of data. (Optionally) print out information about it:
#ifdef DEBUG_PRINT_EACH_RECEIVED_FRAME
if (fStreamId != NULL) envir() << "Stream \"" << fStreamId << "\"; ";
envir() << fSubsession.mediumName() << "/" << fSubsession.codecName() << ":\tReceived " << frameSize << " bytes";
if (numTruncatedBytes > 0) envir() << " (with " << numTruncatedBytes << " bytes truncated)";
char uSecsStr[6+1]; // used to output the 'microseconds' part of the presentation time
sprintf(uSecsStr, "%06u", (unsigned)presentationTime.tv_usec);
envir() << ".\tPresentation time: " << (unsigned)presentationTime.tv_sec << "." << uSecsStr;
if (fSubsession.rtpSource() != NULL && !fSubsession.rtpSource()->hasBeenSynchronizedUsingRTCP()) {
envir() << "!"; // mark the debugging output to indicate that this presentation time is not RTCP-synchronized
}
envir() << "\n";
#endif // Then continue, to request the next frame of data:
continuePlaying();
} Boolean DummySink::continuePlaying() {
if (fSource == NULL) return False; // sanity check (should not happen) // Request the next frame of data from our input source. "afterGettingFrame()" will get called later, when it arrives:
fSource->getNextFrame(fReceiveBuffer, DUMMY_SINK_RECEIVE_BUFFER_SIZE,
afterGettingFrame, this,
onSourceClosure, this);
return True;
}
2)有网友在testRTSPClient基础上,把接收的数据写成h264文件了http://blog.csdn.net/occupy8/article/details/36426821
void DummySink::afterGettingFrame(void* clientData, unsigned frameSize, unsigned numTruncatedBytes,
struct timeval presentationTime, unsigned durationInMicroseconds) {
DummySink* sink = (DummySink*)clientData;
sink->afterGettingFrame(frameSize, numTruncatedBytes, presentationTime, durationInMicroseconds);
} // If you don't want to see debugging output for each received frame, then comment out the following line:
#define DEBUG_PRINT_EACH_RECEIVED_FRAME 1 void DummySink::afterGettingFrame(unsigned frameSize, unsigned numTruncatedBytes,
struct timeval presentationTime, unsigned /*durationInMicroseconds*/) {
// We've just received a frame of data. (Optionally) print out information about it:
#ifdef DEBUG_PRINT_EACH_RECEIVED_FRAME
if (fStreamId != NULL) envir() << "Stream \"" << fStreamId << "\"; ";
envir() << fSubsession.mediumName() << "/" << fSubsession.codecName() << ":\tReceived " << frameSize << " bytes";
if (numTruncatedBytes > 0) envir() << " (with " << numTruncatedBytes << " bytes truncated)";
char uSecsStr[6+1]; // used to output the 'microseconds' part of the presentation time
sprintf(uSecsStr, "%06u", (unsigned)presentationTime.tv_usec);
envir() << ".\tPresentation time: " << (unsigned)presentationTime.tv_sec << "." << uSecsStr;
if (fSubsession.rtpSource() != NULL && !fSubsession.rtpSource()->hasBeenSynchronizedUsingRTCP()) {
envir() << "!"; // mark the debugging output to indicate that this presentation time is not RTCP-synchronized
}
envir() << "\n";
#endif //todo one frame
//save to file
if(!strcmp(fSubsession.mediumName(), "video"))
{
if(firstFrame)
{
unsigned int num;
SPropRecord *sps = parseSPropParameterSets(fSubsession.fmtp_spropparametersets(), num);
// For H.264 video stream, we use a special sink that insert start_codes:
struct timeval tv= {0,0};
unsigned char start_code[4] = {0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01};
FILE *fp = fopen("test.264", "a+b");
if(fp)
{
fwrite(start_code, 4, 1, fp);
fwrite(sps[0].sPropBytes, sps[0].sPropLength, 1, fp);
fwrite(start_code, 4, 1, fp);
fwrite(sps[1].sPropBytes, sps[1].sPropLength, 1, fp);
fclose(fp);
fp = NULL;
}
delete [] sps;
firstFrame = False;
} char *pbuf = (char *)fReceiveBuffer;
char head[4] = {0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01};
FILE *fp = fopen("test.264", "a+b");
if(fp)
{
fwrite(head, 4, 1, fp);
fwrite(fReceiveBuffer, frameSize, 1, fp);
fclose(fp);
fp = NULL;
}
} // Then continue, to request the next frame of data:
continuePlaying();
} Boolean DummySink::continuePlaying() {
if (fSource == NULL) return False; // sanity check (should not happen) // Request the next frame of data from our input source. "afterGettingFrame()" will get called later, when it arrives:
fSource->getNextFrame(fReceiveBuffer, DUMMY_SINK_RECEIVE_BUFFER_SIZE,
afterGettingFrame, this,
onSourceClosure, this);
return True;
}
testRTSPClient接收的fReceiveBuffer缓存没有起始码,start_code[4] = {0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x01}; 写成文件或者播放都需要自行加上。
3)testRTSPClient这个实例还支持多路录放,网上搜到有人已经实现了,搬过来.
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-15063109-id-4482932.html
——缺什么补什么
live555库中的testRTSPClient实例的更多相关文章
- RTSP客户端接收存储数据(live555库中的testRTSPClient实例)
1.testRTSPClient简介 testRTSPClient是个简单的客户端实例,这个实例对rtsp数据交互作了详细的描述,其中涉及到rtsp会话的两个概念Source和Sink. Source ...
- live555库中的testH264VideoStreamer实例
1.h264文件的推送 testH264VideoStreamer.cpp文件的开头就定义了 char const* inputFileName = "test.264"; 后面接 ...
- live555库中的openRTSP实例
一.openRTSP编译运行 a)windows下编译运行 还是以mediaServer作为服务端,openRTSP作为客户端 b)Linux下编译运行 转自http://kuafu80.blog.1 ...
- RTSP客户端接收存储数据(live555库中的openRTSP实例)
一.openRTSP编译运行 a)windows下编译运行 还是以mediaServer作为服务端,openRTSP作为客户端 b)Linux下编译运行 转自http://kuafu80.blog.1 ...
- RTSP服务端转发服务(live555库中的testH264VideoStreamer.cpp和testOnDemandRTSPServer.cpp实例)
1.h264文件的推送 testH264VideoStreamer.cpp文件的开头就定义了 char const* inputFileName = "test.264"; 后面接 ...
- 宣布在 Azure 镜像库中正式推出 Windows Server 2012 R2 并降低 Windows Azure 的实例定价
我们今天将宣布两条消息,为使用基础结构服务的客户提供更多选择和成本节约:在镜像库中推出 Windows Server 2012 R2 以及降低 Memory Intensive 计算实例定价. 虚拟机 ...
- NSClassFromString 实例话静态库中的类
Class myClass = NSClassFromString("StaticLibyClassName"); StaticLibyClassName是从静态库中实例化一个Cl ...
- Solr的原理及在项目中的使用实例.
前面已经讲过 如果安装及配置Solr服务器了, 那么现在我们就来正式在代码中使用Solr.1,这里Solr主要是怎么使用的呢? 当我们在前台页面搜索商品名称关键词时, 我们这时是在Solr库中去查找 ...
- linux静态与动态库创建及使用实例
一,gcc基础语法: 基本语法结构:(由以下四部分组成) gcc -o 可执行文件名 依赖文件集(*.c/*.o) 依赖库文件及其头文件集(由-I或-L与-l指明) gcc 依赖文件集(*.c/*.o ...
随机推荐
- zabbix的使用
1,zabbix运行流程 2功能特性 1数据收集 2灵活触发器 3高度可定制告警 4实时绘图功能 5web监控能力 6多种可视化展示 7历史数据存储 8配置容易 9API功能 10.......... ...
- mybatis下报错:元素类型为 "mapper" 的内容必须匹配 "(cache-ref|cache|resultMap*|parameterMap
今天使用别人的代码报错,但是有时又不报错原来是配置文件的顺序要遵守 注意 "必须匹配" 四个字, 其意味着顺序很重要, 必须要一致, 试试将 resultMap 中各元素的顺序修改 ...
- Lead推荐学asp.net书籍
ASP.NET 3.5 Unleashed 中文版: ASP.NET3.5揭秘(卷1) ASP.NET3.5揭秘(卷2) JS A Smarter Way to Learn JavaScript
- BP神经网络推导过程详解
BP算法是一种最有效的多层神经网络学习方法,其主要特点是信号前向传递,而误差后向传播,通过不断调节网络权重值,使得网络的最终输出与期望输出尽可能接近,以达到训练的目的. 一.多层神经网络结构及其描述 ...
- pip卡住不动的解决方案
用的是anaconda2,也就是python在windows下的最好的一键安装包,有numpy scipy matplotlib等常用包预装好了 最近搞caffe的python接口,需要装protob ...
- springMVC-mvc:annotation-driven
<mvc:annotation-driven/>会自动注册 RequestMappingHandlerMapping RequestMappingHandlerAdapter Except ...
- C++开发的基于UDP协议的聊天工具
项目相关地址 源码:https://github.com/easonjim/UDPChat bug提交:https://github.com/easonjim/UDPChat/issues
- VS联调多个解决方案的项目
一.项目中经常出现一个解决方案里面有多个程序,如果想按F5启动多个实例进行操作调试那该怎么操作? 以前自己都使用附加进程的方法调试,这样的调试不需要按F5,自己只要运行多个程序后,使用vs的附加进程到 ...
- Android成长日记-LogCat
1. Log日志级别 Log.v(tag,messag) //verbose模式,打印最详细的日志输出颜色为黑色 Log.d(tag,messag) //debug级别的日志,颜色为蓝色 Log.i( ...
- xudyh的gcd模板
hdu 5019 #include <cstdlib> #include <cctype> #include <cstring> #include <cstd ...
