bigworld源码分析(3)——dbMgr分析
dbMgr主要是玩家数据的读取和保存的,例如在bigworld源码分析(3)中,玩家在认证的时候,loginApp需要通过dbMgr来验证玩家数据是否合法,这就是针对玩家的账号数据进行查询。本篇中,我们主要针对以下几个问题来分析dbMgr工作原理。
(1) dbMgr如何验证玩家的账号合法性
(2) dbMgr是如何读取玩家的游戏数据的
(3) dbMgr如何通知baseAppMgr创建entity
(4) dbMgr是如何保存玩家的游戏数据的
1. dbMgr验证玩家账号
dbMgr验证玩家账号的调用关系,入下图所示。
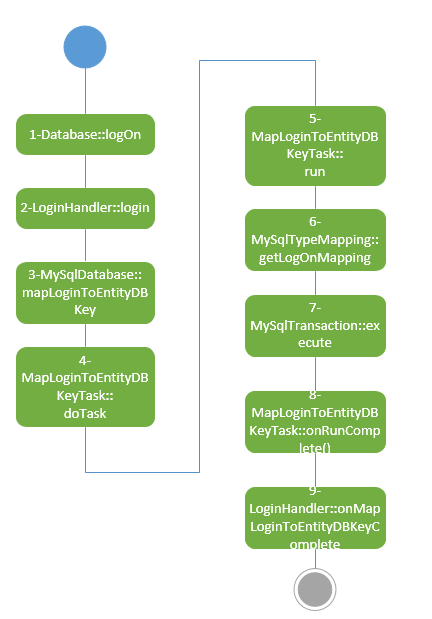
(1) DataBase在收到了logOn的消息之后,进行一些条件限制和判断之后,直接调用LoginHandler处理login
oid Database::logOn( const Mercury::Address & srcAddr,
Mercury::ReplyID replyID,
LogOnParamsPtr pParams,
const Mercury::Address & addrForProxy,
bool offChannel )
{
// 判断能否进行认证
// ....... LoginHandler * pHandler =
new LoginHandler( pParams, addrForProxy, srcAddr, offChannel, replyID ); pHandler->login();
}
(2) LoginHandler的login方法如下:
void LoginHandler::login()
{
// __glenc__ TODO: See if this needs to be converted to use params
Database::instance().getIDatabase().mapLoginToEntityDBKey(
pParams_->username(), pParams_->password(), *this ); // When mapLoginToEntityDBKey() completes, onMapLoginToEntityDBKeyComplete()
// will be called.
}
从代码中可以看出是通过getIDatabase方法返回的IDataBase接口,调用其mapLoginToEntityDBKey。 那么纠结是使用了哪个IDataBase实现类呢?在DataBase的init中我们可以看出来,主要可能是3中实现IDataBase接口的类。其类图关系如下。
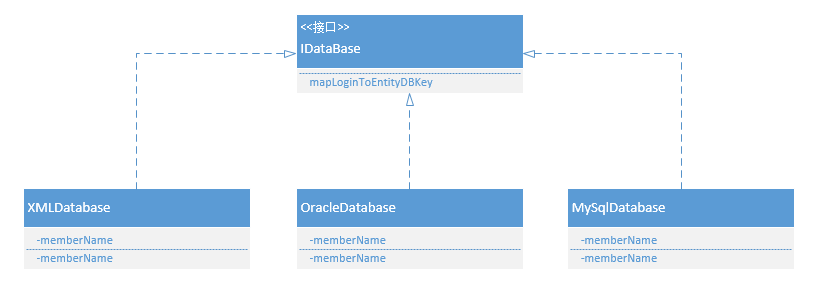
主要是XMLDataBase,OracleDatabase和MySqlDatabase,也就是说bigworld提供了这3种数据存取方式。其实只有2中,XML和Mysql。我们这里主要看Mysql方式。
(3) (4)(5)MapLoginToEntityDBKeyTask调用typeMapping.getLogOnMapping
void MapLoginToEntityDBKeyTask::run()
{
bool retry;
do
{
retry = false;
MySqlThreadData& threadData = this->getThreadData();
try
{
MySqlTransaction transaction( threadData.connection );
std::string actualPassword;
bool entryExists = threadData.typeMapping.getLogOnMapping( transaction,
logOnName_, actualPassword, threadData.ekey.typeID,
threadData.ekey.name );
// .....
} while (retry);
}
(6) MySqlTypeMapping::getLogOnMapping
bool MySqlTypeMapping::getLogOnMapping( MySqlTransaction& t, const std::string& logOnName,
std::string& password, EntityTypeID& typeID, std::string& recordName )
{
boundLogOnName_.setString( logOnName );
t.execute( stmtGetLogOnMapping_ );
// ......
}
可以看出来,这里的execute就是真正执行sql语句的地方,那么这个stmtGetLogOnMapping_ 是什么呢,其实就是一个简单的sql语句的封装,
MySqlTypeMapping::MySqlTypeMapping( MySql& con, const EntityDefs& entityDefs,
const char * tableNamePrefix ) :
mappings_(),
// ....
stmtGetLogOnMapping_( con, "SELECT m.password, t.bigworldID, m.recordName "
"FROM bigworldLogOnMapping m, bigworldEntityTypes t "
"WHERE m.logOnName=? and m.typeID=t.typeID" ),
在MySqlTypeMapping的构造函数中,我们可以看出stmtGetLogOnMapping_具体是一个什么样的sql语句。其实这里就是简单的将mysql业务,和sql语句直接简单做了一个映射关系,也就可以理解MySqlTypeMapping中TypeMapping的意思了,就是根据业务类型做了映射而已。
到这里,我们基本就知道dbMgr是如何对账号进行认证的了。
在MapLoginToEntityDBKeyTask::run执行完之后,会执行MapLoginToEntityDBKeyTask::onRunComplete(),那么就会在最后回调LoginHandler的onMapLoginToEntityDBKeyComplete,那么整个认证就结束了。
2. dbMgr获取玩家数据
在验证完玩家登陆login信息之后,如果成功,则需要从数据库中将玩家数据获取出来。在验证玩家登陆信息的时候,同时也从bigworldLogOnMapping 表中,将玩家的id获取到了,这个是后面读取玩家数据需要的key。具体的读取流程如下:

(1) (2)(3)(4)LoginHandler::onMapLoginToEntityDBKeyComplete中直接一层一层调用getEntity接口,没有复杂逻辑。
(5) (6)在GetEnitityTask中调用GetLogOnRecord,然后真正获取玩家数据,如果获取成功,最后再回调LoginHandler的onGetEntityCompleted
3. dbMgr通知baseAppMgr创建entity
LoginHandler::onMapLoginToEntityDBKeyComplete中,在getEntity之前,DataBase中的接口就开始通知BaseAppMgr去创建Entity了,甚至这个时候还不知道Entity能否创建成功。
void LoginHandler::onMapLoginToEntityDBKeyComplete( DatabaseLoginStatus status,
const EntityDBKey& ekey )
{
bool shouldLoadEntity = false;
bool shouldCreateEntity = false; if (status == DatabaseLoginStatus::LOGGED_ON)
{
ekey_ = ekey;
shouldLoadEntity = true;
state_ = StateWaitingForLoad;
}
.......
// 可以load玩家数据
if (shouldLoadEntity)
{
// Start "create new base" message even though we're not sure entity
// exists. This is to take advantage of getEntity() streaming properties
// into the bundle directly.
// 这个接口里就直接通知BaseAppMgr去创建玩家的entity。
pStrmDbID_ = Database::prepareCreateEntityBundle( ekey_.typeID,
ekey_.dbID, clientAddr_, this, bundle_, pParams_ ); // Get entity data
pBaseRef_ = &baseRef_;
outRec_.provideBaseMB( pBaseRef_ ); // Get entity mailbox
outRec_.provideStrm( bundle_ ); // Get entity data into bundle Database::instance().getEntity( *this );
// When getEntity() completes, onGetEntityCompleted() is called.
}
....... }
Database::prepareCreateEntityBundle函数代码。
/*
* This method inserts the "header" info into the bundle for a
* BaseAppMgrInterface::createEntity message, up till the point
* where entity properties should begin.
*
* @return If dbID is 0, then this function returns the position in the
* bundle where you should put the DatabaseID.
*/
DatabaseID* Database::prepareCreateEntityBundle( EntityTypeID typeID,
DatabaseID dbID, const Mercury::Address& addrForProxy,
Mercury::ReplyMessageHandler* pHandler, Mercury::Bundle& bundle,
LogOnParamsPtr pParams )
{
bundle.startRequest( BaseAppMgrInterface::createEntity, pHandler, ,
Mercury::DEFAULT_REQUEST_TIMEOUT + ); // 1 second extra ......
}
从这个函数和其注释,我们可以看出来,这里并没有真正的向BaseAppMgr去请求createEntity,而只是准备让它创建,具体发送这个指令,需要entity的属性准备完毕。
最后LoginHandler::sendCreateEntityMsg调用DataBase的send接口,将createEntity的消息发送给BaseAppMgr。这个中间发生了哪些事情,最后调用了sendCreateEntityMsg呢?调用关系如下图:
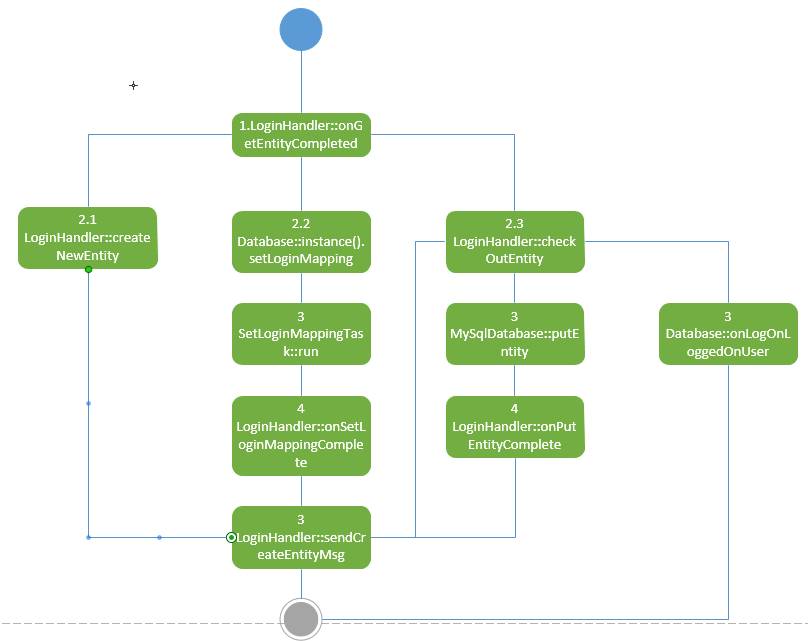
从上面的调用关系图可以看出,onGetEntityCompleted中可能会发生3中情况
(1) 在玩家数据不存在的情况下,需要创建新的玩家,也就是createNewEntity
(2) 需要对登陆数据进行映射,也就是setLoginMapping
(3) 需要校验玩家数据checkOutEntity
不过他们最终都是会回调到LoginHandler::sendCreateEntityMsg中!!
4. dbMgr是如何保存玩家的游戏数据的
dbMgr还有一个重要的功能就是保持玩家数据,相对于获取玩家数据,保存玩家数据流程相对更加简单,其流程如下:

DataBase中writeEntity调用WriteEntityHandler的writeEntity接口,然后后面还是调用MysqlDatabase的putEntity接口,最后回调WriteEntityHandler的finalise接口,在这个接口里面判断,是否需要返回保存结果。其代码如下:
void WriteEntityHandler::finalise( bool isOK )
{
// 如果需要返回保存结果
if (shouldReply_)
{
Mercury::ChannelSender sender( Database::getChannel( srcAddr_ ) );
sender.bundle().startReply( replyID_ );
sender.bundle() << isOK << ekey_.dbID;
} if (isOK && (flags_ & WRITE_LOG_OFF))
{
// 如果是玩家下线保存
Database::instance().onEntityLogOff( ekey_.typeID, ekey_.dbID );
} delete this;
}
至此,dbMgr的登录验证,玩家数据获取,玩家数据保存,以及如何通知baseAppMgr创建entity这4个我们一开始列出来的点,都已经基本分析清楚了
bigworld源码分析(3)——dbMgr分析的更多相关文章
- bigworld源码分析(1)—— 研究bigworld的意义和目标
对于网络游戏服务器开发熟悉的人,基本都知道bigworld引擎,此引擎包括客户端部分和服务器部分,已经有很多知名的网络游戏通过bigworld来构建游戏.我主要关注bigworld的服务器部分,它是一 ...
- ArrayList源码和多线程安全问题分析
1.ArrayList源码和多线程安全问题分析 在分析ArrayList线程安全问题之前,我们线对此类的源码进行分析,找出可能出现线程安全问题的地方,然后代码进行验证和分析. 1.1 数据结构 Arr ...
- Okhttp3源码解析(3)-Call分析(整体流程)
### 前言 前面我们讲了 [Okhttp的基本用法](https://www.jianshu.com/p/8e404d9c160f) [Okhttp3源码解析(1)-OkHttpClient分析]( ...
- Okhttp3源码解析(2)-Request分析
### 前言 前面我们讲了 [Okhttp的基本用法](https://www.jianshu.com/p/8e404d9c160f) [Okhttp3源码解析(1)-OkHttpClient分析]( ...
- Spring mvc之源码 handlerMapping和handlerAdapter分析
Spring mvc之源码 handlerMapping和handlerAdapter分析 本篇并不是具体分析Spring mvc,所以好多细节都是一笔带过,主要是带大家梳理一下整个Spring mv ...
- HashMap的源码学习以及性能分析
HashMap的源码学习以及性能分析 一).Map接口的实现类 HashTable.HashMap.LinkedHashMap.TreeMap 二).HashMap和HashTable的区别 1).H ...
- ThreadLocal源码及相关问题分析
前言 在高并发的环境下,当我们使用一个公共的变量时如果不加锁会出现并发问题,例如SimpleDateFormat,但是加锁的话会影响性能,对于这种情况我们可以使用ThreadLocal.ThreadL ...
- 物联网防火墙himqtt源码之MQTT协议分析
物联网防火墙himqtt源码之MQTT协议分析 himqtt是首款完整源码的高性能MQTT物联网防火墙 - MQTT Application FireWall,C语言编写,采用epoll模式支持数十万 ...
- Netty 源码学习——客户端流程分析
Netty 源码学习--客户端流程分析 友情提醒: 需要观看者具备一些 NIO 的知识,否则看起来有的地方可能会不明白. 使用版本依赖 <dependency> <groupId&g ...
随机推荐
- Cenos(6.6/7.1)下从源码安装Python+Django+uwsgi+nginx到写nginx的环境部署(一)
梳理下这几个的关系: centos是redhat的社区版操作系统. Python2.7.5是开发语言(centos6.5下自带的python是2.6.6版本,所以需要源码更新,而centos7.1下面 ...
- 【Java】关于JVM运行时内存空间、JVM垃圾回收机制
参考的优秀文章 <深入理解Java虚拟机 JVM高级特性与最佳实线>(机械工业出版社) Java虚拟机的堆.栈.堆栈如何去理解? 聊聊JVM的年轻代 前言 本文是<深入理解Java虚 ...
- socket初级使用(客户端)
在国庆这段时间里用零星的一些时间看了一下socket的学习资料,由于笔者偏向学习实用方面的内容,因此此篇文章涉及理论知识较少,主要是以实现思路(怎么做)为主,但在实现之前还是需要了解一些基础的理论知识 ...
- python的异常小结与assert
异常的处理 一. 二. -----------------2016-4-20 18:04:06--
- 关于php语言的使用! ------php语言与JavaScript的使用 方法是相似
<script type="text/javascript"> </script>--js与PHP同是一种弱类型语言 弱类型语言只是不显示表现 定义变量时 ...
- SCCM 2007日志
原创作品,允许转载,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章 原始出处 .作者信息和本声明.否则将追究法律责任.http://ycrsjxy.blog.51cto.com/618627/203174 ...
- SQL Syntax
1.limit 语法:限制查询记录,进行分页处理:select * from article limit 0,10;(从0号记录开始,依次取10条记录) 2.like 语法:查询指定字符串的相似匹配记 ...
- mybatis批量更新 UPDATE mysql
oracle和mysql数据库的批量update在mybatis中配置不太一样: oracle数据库: <update id="batchUpdate" parameterT ...
- 字符串与Objec之间互相转换
字符串与Objec之间互相转换可通过json实现. JSON.parse(str);// 字符串转Json Object JSON.stringify(obj);// Obj转字符串
- linux hugepage
The intent of this file is to give a brief summary of hugetlbpage support inthe Linux kernel. This ...
