网络爬虫必备知识之concurrent.futures库
就库的范围,个人认为网络爬虫必备库知识包括urllib、requests、re、BeautifulSoup、concurrent.futures,接下来将结对concurrent.futures库的使用方法进行总结
建议阅读本博的博友先阅读下上篇博客:python究竟要不要使用多线程,将会对concurrent.futures库的使用有帮助。
1. concurrent.futures库简介
python标准库为我们提供了threading和mutiprocessing模块实现异步多线程/多进程功能。从python3.2版本开始,标准库又为我们提供了concurrent.futures模块来实现线程池和进程池功能,实现了对threading和mutiprocessing模块的高级抽象,更大程度上方便了我们python程序员。
concurrent.futures模块提供了ThreadPoolExecutor和ProcessPoolExecutor两个类
(1)看下来个类的继承关系和关键属性
- from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor,ProcessPoolExecutor
- print('ThreadPoolExecutor继承关系:',ThreadPoolExecutor.__mro__)
- print('ThreadPoolExecutor属性:',[attr for attr in dir(ThreadPoolExecutor) if not attr.startswith('_')])
- print('ProcessPoolExecutor继承关系:',ProcessPoolExecutor.__mro__)
- print('ThreadPoolExecutor属性:',[attr for attr in dir(ProcessPoolExecutor) if not attr.startswith('_')])

都继承自futures._base.Executor类,拥有三个重要方法map、submit和shutdow,这样看起来就很简单了
(2)再看下futures._base.Executor基类实现
- class Executor(object):
- """This is an abstract base class for concrete asynchronous executors."""
- def submit(self, fn, *args, **kwargs):
- """Submits a callable to be executed with the given arguments.
- Schedules the callable to be executed as fn(*args, **kwargs) and returns
- a Future instance representing the execution of the callable.
- Returns:
- A Future representing the given call.
- """
- raise NotImplementedError()
- def map(self, fn, *iterables, timeout=None, chunksize=):
- """Returns an iterator equivalent to map(fn, iter).
- Args:
- fn: A callable that will take as many arguments as there are
- passed iterables.
- timeout: The maximum number of seconds to wait. If None, then there
- is no limit on the wait time.
- chunksize: The size of the chunks the iterable will be broken into
- before being passed to a child process. This argument is only
- used by ProcessPoolExecutor; it is ignored by
- ThreadPoolExecutor.
- Returns:
- An iterator equivalent to: map(func, *iterables) but the calls may
- be evaluated out-of-order.
- Raises:
- TimeoutError: If the entire result iterator could not be generated
- before the given timeout.
- Exception: If fn(*args) raises for any values.
- """
- if timeout is not None:
- end_time = timeout + time.time()
- fs = [self.submit(fn, *args) for args in zip(*iterables)]
- # Yield must be hidden in closure so that the futures are submitted
- # before the first iterator value is required.
- def result_iterator():
- try:
- # reverse to keep finishing order
- fs.reverse()
- while fs:
- # Careful not to keep a reference to the popped future
- if timeout is None:
- yield fs.pop().result()
- else:
- yield fs.pop().result(end_time - time.time())
- finally:
- for future in fs:
- future.cancel()
- return result_iterator()
- def shutdown(self, wait=True):
- """Clean-up the resources associated with the Executor.
- It is safe to call this method several times. Otherwise, no other
- methods can be called after this one.
- Args:
- wait: If True then shutdown will not return until all running
- futures have finished executing and the resources used by the
- executor have been reclaimed.
- """
- pass
- def __enter__(self):
- return self
- def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
- self.shutdown(wait=True)
- return False
提供了map、submit、shutdow和with方法,下面首先对这个几个方法的使用进行说明
2. map函数
函数原型:def map(self, fn, *iterables, timeout=None, chunksize=1)
map函数和python自带的map函数用法一样,只不过该map函数从迭代器获取参数后异步执行,timeout用于设置超时时间
参数chunksize的理解:
- The size of the chunks the iterable will be broken into
- before being passed to a child process. This argument is only
- used by ProcessPoolExecutor; it is ignored by ThreadPoolExecutor.
例:
- from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
- import time
- import requests
- def download(url):
- headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:63.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/63.0',
- 'Connection':'keep-alive',
- 'Host':'example.webscraping.com'}
- response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
- return(response.status_code)
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- urllist = ['http://example.webscraping.com/places/default/view/Afghanistan-1',
- 'http://example.webscraping.com/places/default/view/Aland-Islands-2']
- pool = ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers = 2)
start = time.time()- result = list(pool.map(download, urllist))
- end = time.time()
- print('status_code:',result)
- print('使用多线程--timestamp:{:.3f}'.format(end-start))
3. submit函数
函数原型:def submit(self, fn, *args, **kwargs)
fn:需要异步执行的函数
args、kwargs:函数传递的参数
例:下例中future类的使用的as_complete后面介绍
- from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor,ProcessPoolExecutor,as_completed
- import time
- import requests
- def download(url):
- headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:63.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/63.0',
- 'Connection':'keep-alive',
- 'Host':'example.webscraping.com'}
- response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
- return response.status_code
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- urllist = ['http://example.webscraping.com/places/default/view/Afghanistan-1',
- 'http://example.webscraping.com/places/default/view/Aland-Islands-2']
- start = time.time()
- pool = ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers = )
- futures = [pool.submit(download,url) for url in urllist]
- for future in futures:
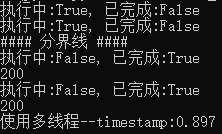
- print('执行中:%s, 已完成:%s' % (future.running(), future.done()))
- print('#### 分界线 ####')
- for future in as_completed(futures, timeout=):
- print('执行中:%s, 已完成:%s' % (future.running(), future.done()))
- print(future.result())
- end = time.time()
- print('使用多线程--timestamp:{:.3f}'.format(end-start))
输出:
4. shutdown函数
函数原型:def shutdown(self, wait=True)
此函数用于释放异步执行操作后的系统资源
由于_base.Executor类提供了上下文方法,将shutdown封装在了__exit__中,若使用with方法,将不需要自己进行资源释放
- with ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers = ) as pool:
5. Future类
submit函数返回Future对象,Future类提供了跟踪任务执行状态的方法:
future.running():判断任务是否执行
futurn.done:判断任务是否执行完成
futurn.result():返回函数执行结果
- futures = [pool.submit(download,url) for url in urllist]
- for future in futures:
- print('执行中:%s, 已完成:%s' % (future.running(), future.done()))
- print('#### 分界线 ####')
- for future in as_completed(futures, timeout=):
- print('执行中:%s, 已完成:%s' % (future.running(), future.done()))
- print(future.result())
as_completed方法传入futures迭代器和timeout两个参数
默认timeout=None,阻塞等待任务执行完成,并返回执行完成的future对象迭代器,迭代器是通过yield实现的。
timeout>0,等待timeout时间,如果timeout时间到仍有任务未能完成,不再执行并抛出异常TimeoutError
6. 回调函数
Future类提供了add_done_callback函数可以自定义回调函数:
- def add_done_callback(self, fn):
- """Attaches a callable that will be called when the future finishes.
- Args:
- fn: A callable that will be called with this future as its only
- argument when the future completes or is cancelled. The callable
- will always be called by a thread in the same process in which
- it was added. If the future has already completed or been
- cancelled then the callable will be called immediately. These
- callables are called in the order that they were added.
- """
- with self._condition:
- if self._state not in [CANCELLED, CANCELLED_AND_NOTIFIED, FINISHED]:
- self._done_callbacks.append(fn)
- return
- fn(self)
例子:
- from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor,ProcessPoolExecutor,as_completed
- import time
- import requests
- def download(url):
- headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:63.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/63.0',
- 'Connection':'keep-alive',
- 'Host':'example.webscraping.com'}
- response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
- return response.status_code
- def callback(future):
- print(future.result())
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- urllist = ['http://example.webscraping.com/places/default/view/Afghanistan-1',
- 'http://example.webscraping.com/places/default/view/Aland-Islands-2',
- 'http://example.webscraping.com/places/default/view/Albania-3',
- 'http://example.webscraping.com/places/default/view/Algeria-4',
- 'http://example.webscraping.com/places/default/view/American-Samoa-5']
- start = time.time()
- with ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers = ) as pool:
- futures = [pool.submit(download,url) for url in urllist]
- for future in futures:
- print('执行中:%s, 已完成:%s' % (future.running(), future.done()))
- print('#### 分界线 ####')
- for future in as_completed(futures, timeout=):
- future.add_done_callback(callback)
- print('执行中:%s, 已完成:%s' % (future.running(), future.done()))
- end = time.time()
- print('使用多线程--timestamp:{:.3f}'.format(end-start))
7. wait函数
函数原型:def wait(fs, timeout=None, return_when=ALL_COMPLETED)
- def wait(fs, timeout=None, return_when=ALL_COMPLETED):
- """Wait for the futures in the given sequence to complete.
- Args:
- fs: The sequence of Futures (possibly created by different Executors) to
- wait upon.
- timeout: The maximum number of seconds to wait. If None, then there
- is no limit on the wait time.
- return_when: Indicates when this function should return. The options
- are:
- FIRST_COMPLETED - Return when any future finishes or is
- cancelled.
- FIRST_EXCEPTION - Return when any future finishes by raising an
- exception. If no future raises an exception
- then it is equivalent to ALL_COMPLETED.
- ALL_COMPLETED - Return when all futures finish or are cancelled.
- Returns:
- A named -tuple of sets. The first set, named 'done', contains the
- futures that completed (is finished or cancelled) before the wait
- completed. The second set, named 'not_done', contains uncompleted
- futures.
- """
- with _AcquireFutures(fs):
- done = set(f for f in fs
- if f._state in [CANCELLED_AND_NOTIFIED, FINISHED])
- not_done = set(fs) - done
- if (return_when == FIRST_COMPLETED) and done:
- return DoneAndNotDoneFutures(done, not_done)
- elif (return_when == FIRST_EXCEPTION) and done:
- if any(f for f in done
- if not f.cancelled() and f.exception() is not None):
- return DoneAndNotDoneFutures(done, not_done)
- if len(done) == len(fs):
- return DoneAndNotDoneFutures(done, not_done)
- waiter = _create_and_install_waiters(fs, return_when)
- waiter.event.wait(timeout)
- for f in fs:
- with f._condition:
- f._waiters.remove(waiter)
- done.update(waiter.finished_futures)
- return DoneAndNotDoneFutures(done, set(fs) - done)
wait方法返回一个中包含两个元组,元组中包含两个集合(set),一个是已经完成的(completed),一个是未完成的(uncompleted)
它接受三个参数,重点看下第三个参数:
FIRST_COMPLETED:Return when any future finishes or iscancelled.
- from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor,ProcessPoolExecutor,\
- as_completed,wait,ALL_COMPLETED, FIRST_COMPLETED, FIRST_EXCEPTION
- import time
- import requests
- def download(url):
- headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:63.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/63.0',
- 'Connection':'keep-alive',
- 'Host':'example.webscraping.com'}
- response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
- return response.status_code
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- urllist = ['http://example.webscraping.com/places/default/view/Afghanistan-1',
- 'http://example.webscraping.com/places/default/view/Aland-Islands-2',
- 'http://example.webscraping.com/places/default/view/Albania-3',
- 'http://example.webscraping.com/places/default/view/Algeria-4',
- 'http://example.webscraping.com/places/default/view/American-Samoa-5']
- start = time.time()
- with ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers = ) as pool:
- futures = [pool.submit(download,url) for url in urllist]
- for future in futures:
- print('执行中:%s, 已完成:%s' % (future.running(), future.done()))
- print('#### 分界线 ####')
- completed, uncompleted = wait(futures, timeout=, return_when=FIRST_COMPLETED)
- for cp in completed:
- print('执行中:%s, 已完成:%s' % (cp.running(), cp.done()))
- print(cp.result())
- end = time.time()
- print('使用多线程--timestamp:{:.3f}'.format(end-start))
输出:
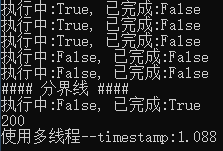
只返回了一个完成的
网络爬虫必备知识之concurrent.futures库的更多相关文章
- 网络爬虫必备知识之urllib库
就库的范围,个人认为网络爬虫必备库知识包括urllib.requests.re.BeautifulSoup.concurrent.futures,接下来将结合爬虫示例分别对urllib库的使用方法进行 ...
- 网络爬虫必备知识之requests库
就库的范围,个人认为网络爬虫必备库知识包括urllib.requests.re.BeautifulSoup.concurrent.futures,接下来将结对requests库的使用方法进行总结 1. ...
- 【网络爬虫入门02】HTTP客户端库Requests的基本原理与基础应用
[网络爬虫入门02]HTTP客户端库Requests的基本原理与基础应用 广东职业技术学院 欧浩源 1.引言 实现网络爬虫的第一步就是要建立网络连接并向服务器或网页等网络资源发起请求.urllib是 ...
- 网络爬虫基础知识(Python实现)
浏览器的请求 url=请求协议(http/https)+网站域名+资源路径+参数 http:超文本传输协议(以明文的形式进行传输),传输效率高,但不安全. https:由http+ssl(安全套接子层 ...
- python网络爬虫,知识储备,简单爬虫的必知必会,【核心】
知识储备,简单爬虫的必知必会,[核心] 一.实验说明 1. 环境登录 无需密码自动登录,系统用户名shiyanlou 2. 环境介绍 本实验环境采用带桌面的Ubuntu Linux环境,实验中会用到桌 ...
- 网络爬虫:利用selenium,pyquery库抓取并处理京东上的图片并存储到使用mongdb数据库进行存储
一,环境的搭建已经简单的工具介绍 1.selenium,一个用于Web应用程序测试的工具.其特点是直接运行在浏览器中,就像真正的用户在操作一样.新版本selenium2集成了 Selenium 1.0 ...
- Python 网络爬虫的常用库汇总
爬虫的编程语言有不少,但 Python 绝对是其中的主流之一.下面就为大家介绍下 Python 在编写网络爬虫常常用到的一些库. 请求库:实现 HTTP 请求操作 urllib:一系列用于操作URL的 ...
- python 爬虫基础知识一
网络爬虫(又被称为网页蜘蛛,网络机器人,在FOAF社区中间,更经常的称为网页追逐者),是一种按照一定的规则,自动的抓取万维网信息的程序或者脚本. 网络爬虫必备知识点 1. Python基础知识2. P ...
- 《Python3网络爬虫开发实战》
推荐:★ ★ ★ ★ ★ 第1章 开发环境配置 第2章 网页基础知识 第3章 网络爬虫基础 第4章 基本库的使用 第5章 解析库的使用 第6章 数据存储 第7章 Ajax数据爬取 第8章 动态渲染页面 ...
随机推荐
- spring 异步处理request
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/u012410733/article/details/52124333Spring MVC 3.2开始引入Servlet 3中的基于异步的处理reque ...
- Python 7 多线程及进程
进程与线程: 进程的概念: 1.程序的执行实例称为进程. 2.每个进程都提供执行程序所需的资源.一个进程有一个虚拟地址空间.可执行代码.对系统对象的开放句柄.一个安全上下文.一个独特的进程标识符.环境 ...
- python Selenium库的使用
一.什么是Selenium selenium 是一套完整的web应用程序测试系统,包含了测试的录制(selenium IDE),编写及运行(Selenium Remote Control)和测试的并行 ...
- 树莓派使用DHT11温湿度传感器(C语言)
硬件: 树莓派 2.0 DHT模块 接树莓派5V GND GPIO1 功能:读取传感器数据并打印出来 // //mydht11.c // #include <wiringPi.h> #i ...
- Shell编程之变量进阶
一.变量知识进阶 1.特殊的位置参数变量 实例1:测试$n(n为1...15) [root@codis-178 ~]# cat p.sh echo $1 [root@codis-178 ~]# sh ...
- 线程同步synchronized和ReentrantLock
一.线程同步问题的产生及解决方案 问题的产生: Java允许多线程并发控制,当多个线程同时操作一个可共享的资源变量时(如数据的增删改查),将会导致数据不准确,相互之间产生冲突. 如下例:假设有一个卖票 ...
- Hearbeat 介绍
Hearbeat 介绍 Linux-HA的全称是High-Availability Linux,它是一个开源项目,这个开源项目的目标是:通过社区开发者的共同努力,提供一个增强linux可靠性(reli ...
- .babelrc参数小解
.babelrc是用来设置转码规则和插件的,这种文件在window上无法直接创建,也无法在HBuilder中创建,甚至无法查看,但可以在sublime text中创建.查看并编辑. 当我们使用es6语 ...
- HDU 3449 Consumer
这是一道依赖背包问题.背包问题通常的解法都是由0/1背包拓展过来的,这道也不例外.我最初想到的做法是,由于有依赖关系,先对附件做个DP,得到1-w的附件背包结果f[i]表示i花费得到的最大收益,然后把 ...
- iOS应用网络安全之HTTPS
移动互联网开发中iOS应用的网络安全问题往往被大部分开发者忽略,iOS9和OS X 10.11开始Apple也默认提高了安全配置和要求.本文以iOS平台App开发中对后台数据接口的安全通信进行解析和加 ...
