[libGDX游戏开发教程]使用Libgdx进行游戏开发(5)-关卡加载
在上一章我们介绍了如何管理和利用素材,但是我们注意到,这些素材都是零散的,比如岩石的左部等,这一章,我们将利用这些零件拼合成完整的游戏对象。
回顾最开始的设计类图,注意Level类和所有Level中的Object,看看它们的继承关系。
首先第一步就是创建所有对象的基类AbstractGameObject.
它应该包含所有公共的属性和功能。
package com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects; import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.SpriteBatch;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Vector2; public abstract class AbstractGameObject {
public Vector2 position;
public Vector2 dimension;
public Vector2 origin;
public Vector2 scale;
public float rotation; public AbstractGameObject() {
position = new Vector2();
dimension = new Vector2(1, 1);
origin = new Vector2();
scale = new Vector2(1, 1);
rotation = 0;
} public void update(float deltaTime) {
} public abstract void render(SpriteBatch batch);
}
这个抽象类包含很多基本的属性,update和render。update更新自己,render画自己。很多人虽然知道OOP,但是并没有在思维中形成OO的观念。对象的划分以及对象的行为(或者说对象的权责)是否分明,都能看出你编程的功力。
render是abstract的,这就限定了所有的子类需要自己去实现它。
我们先看Rock,Rock是由3个部分组成的,左中右,中间的部分是能够重复的。像这样
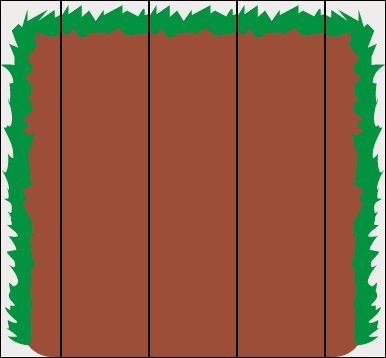
那么它的实现类似于:
package com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects; import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.SpriteBatch;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.TextureRegion;
import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.Assets; public class Rock extends AbstractGameObject {
private TextureRegion regEdge;
private TextureRegion regMiddle;
private int length; public Rock() {
init();
} private void init() {
dimension.set(1, 1.5f);
regEdge = Assets.instance.rock.edge;
regMiddle = Assets.instance.rock.middle;
// Start length of this rock
setLength(1);
} public void setLength(int length) {
this.length = length;
} public void increaseLength(int amount) {
setLength(length + amount);
} @Override
public void render(SpriteBatch batch) {
TextureRegion reg = null;
float relX = 0;
float relY = 0;
// Draw left edge
reg = regEdge;
relX -= dimension.x / 4;
batch.draw(reg.getTexture(), position.x + relX, position.y + relY,
origin.x, origin.y, dimension.x / 4, dimension.y, scale.x,
scale.y, rotation, reg.getRegionX(), reg.getRegionY(),
reg.getRegionWidth(), reg.getRegionHeight(), false, false);
// Draw middle
relX = 0;
reg = regMiddle;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
batch.draw(reg.getTexture(), position.x + relX, position.y + relY,
origin.x, origin.y, dimension.x, dimension.y, scale.x,
scale.y, rotation, reg.getRegionX(), reg.getRegionY(),
reg.getRegionWidth(), reg.getRegionHeight(), false, false);
relX += dimension.x;
}
// Draw right edge
reg = regEdge;
batch.draw(reg.getTexture(), position.x + relX, position.y + relY,
origin.x + dimension.x / 8, origin.y, dimension.x / 4,
dimension.y, scale.x, scale.y, rotation, reg.getRegionX(),
reg.getRegionY(), reg.getRegionWidth(), reg.getRegionHeight(),
true, false);
}
}
我们使用了一个length来表示rock的长度,就是中间可以重复的部分。
接下来是山,有人可能会奇怪,为什么用白色的山呢?用白色是为了方便着色的。Mountains类似于:
package com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects; import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.SpriteBatch;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.TextureRegion;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.MathUtils;
import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.Assets; public class Mountains extends AbstractGameObject {
private TextureRegion regMountainLeft;
private TextureRegion regMountainRight;
private int length; public Mountains(int length) {
this.length = length;
init();
} private void init() {
dimension.set(10, 2);
regMountainLeft = Assets.instance.levelDecoration.mountainLeft;
regMountainRight = Assets.instance.levelDecoration.mountainRight;
// shift mountain and extend length
origin.x = -dimension.x * 2;
length += dimension.x * 2;
} private void drawMountain(SpriteBatch batch, float offsetX, float offsetY,
float tintColor) {
TextureRegion reg = null;
batch.setColor(tintColor, tintColor, tintColor, 1);
float xRel = dimension.x * offsetX;
float yRel = dimension.y * offsetY;
// mountains span the whole level
int mountainLength = 0;
mountainLength += MathUtils.ceil(length / (2 * dimension.x));
mountainLength += MathUtils.ceil(0.5f + offsetX);
for (int i = 0; i < mountainLength; i++) {
// mountain left
reg = regMountainLeft;
batch.draw(reg.getTexture(), origin.x + xRel, position.y + origin.y
+ yRel, origin.x, origin.y, dimension.x, dimension.y,
scale.x, scale.y, rotation, reg.getRegionX(),
reg.getRegionY(), reg.getRegionWidth(),
reg.getRegionHeight(), false, false);
xRel += dimension.x;
// mountain right
reg = regMountainRight;
batch.draw(reg.getTexture(), origin.x + xRel, position.y + origin.y
+ yRel, origin.x, origin.y, dimension.x, dimension.y,
scale.x, scale.y, rotation, reg.getRegionX(),
reg.getRegionY(), reg.getRegionWidth(),
reg.getRegionHeight(), false, false);
xRel += dimension.x;
}
// reset color to white
batch.setColor(1, 1, 1, 1);
} @Override
public void render(SpriteBatch batch) {
// distant mountains (dark gray)
drawMountain(batch, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);
// distant mountains (gray)
drawMountain(batch, 0.25f, 0.25f, 0.7f);
// distant mountains (light gray)
drawMountain(batch, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.9f);
}
}
这个跟Rock很像,也用了一个length来存储需要重复的次数。在render里调用了3个不同的drawMountain,这样大大的简化了画3层山的代码。
接下来是水面,这个类要比前面的简单多了,它只需要沿着x轴拉伸造成一直存在的假象就行了。(还有很多其他的方法可以达到这个目的:比如用一个摄像机视口一样宽的图片,跟着摄像机一起移动。不过这样你需要小心摄像机可能垂直移动)
package com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects; import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.SpriteBatch;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.TextureRegion;
import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.Assets; public class WaterOverlay extends AbstractGameObject {
private TextureRegion regWaterOverlay;
private float length; public WaterOverlay(float length) {
this.length = length;
init();
} private void init() {
dimension.set(length * 10, 3);
regWaterOverlay = Assets.instance.levelDecoration.waterOverlay;
origin.x = -dimension.x / 2;
} @Override
public void render(SpriteBatch batch) {
TextureRegion reg = null;
reg = regWaterOverlay;
batch.draw(reg.getTexture(), position.x + origin.x, position.y
+ origin.y, origin.x, origin.y, dimension.x, dimension.y,
scale.x, scale.y, rotation, reg.getRegionX(), reg.getRegionY(),
reg.getRegionWidth(), reg.getRegionHeight(), false, false);
}
}
接下来是云彩,云彩的分布由长度和间距两个参数决定。
package com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects; import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.SpriteBatch;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.TextureRegion;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.MathUtils;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Vector2;
import com.badlogic.gdx.utils.Array;
import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.Assets; public class Clouds extends AbstractGameObject {
private float length;
private Array<TextureRegion> regClouds;
private Array<Cloud> clouds; private class Cloud extends AbstractGameObject {
private TextureRegion regCloud; public Cloud() {
} public void setRegion(TextureRegion region) {
regCloud = region;
} @Override
public void render(SpriteBatch batch) {
TextureRegion reg = regCloud;
batch.draw(reg.getTexture(), position.x + origin.x, position.y
+ origin.y, origin.x, origin.y, dimension.x, dimension.y,
scale.x, scale.y, rotation, reg.getRegionX(),
reg.getRegionY(), reg.getRegionWidth(),
reg.getRegionHeight(), false, false);
}
} public Clouds(float length) {
this.length = length;
init();
} private void init() {
dimension.set(3.0f, 1.5f);
regClouds = new Array<TextureRegion>();
regClouds.add(Assets.instance.levelDecoration.cloud01);
regClouds.add(Assets.instance.levelDecoration.cloud02);
regClouds.add(Assets.instance.levelDecoration.cloud03);
int distFac = 5;
int numClouds = (int) (length / distFac);
clouds = new Array<Cloud>(2 * numClouds);
for (int i = 0; i < numClouds; i++) {
Cloud cloud = spawnCloud();
cloud.position.x = i * distFac;
clouds.add(cloud);
}
} private Cloud spawnCloud() {
Cloud cloud = new Cloud();
cloud.dimension.set(dimension);
// select random cloud image
cloud.setRegion(regClouds.random());
// position
Vector2 pos = new Vector2();
pos.x = length + 10; // position after end of level
pos.y += 1.75; // base position
// random additional position
pos.y += MathUtils.random(0.0f, 0.2f)
* (MathUtils.randomBoolean() ? 1 : -1);
cloud.position.set(pos);
return cloud;
} @Override
public void render(SpriteBatch batch) {
for (Cloud cloud : clouds)
cloud.render(batch);
}
}
显示代码
Clouds定义了内部类Cloud,Clouds是包含云彩的容器。
关卡加载
我们使用png图片来保存关卡数据:1像素代表1个对象,每一种不同的对象都有一种唯一的RGBA颜色值。我们使用纯色,不用透明色,那么一个RGBA就是32位,就是4字节。刚好java的int也是32位,用来存颜色刚刚好。
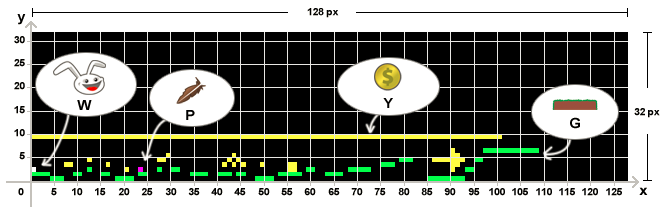
我们需要读取并解析它们:
package com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game; import com.badlogic.gdx.Gdx;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.Pixmap;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.SpriteBatch;
import com.badlogic.gdx.utils.Array;
import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.AbstractGameObject;
import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.Clouds;
import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.Mountains;
import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.Rock;
import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.WaterOverlay; public class Level {
public static final String TAG = Level.class.getName(); public enum BLOCK_TYPE {
EMPTY(0, 0, 0), // black
ROCK(0, 255, 0), // green
PLAYER_SPAWNPOINT(255, 255, 255), // white
ITEM_FEATHER(255, 0, 255), // purple
ITEM_GOLD_COIN(255, 255, 0); // yellow
private int color; private BLOCK_TYPE(int r, int g, int b) {
color = r << 24 | g << 16 | b << 8 | 0xff;
} public boolean sameColor(int color) {
return this.color == color;
} public int getColor() {
return color;
}
} // objects
public Array<Rock> rocks;
// decoration
public Clouds clouds;
public Mountains mountains;
public WaterOverlay waterOverlay; public Level(String filename) {
init(filename);
} private void init(String filename) {
} public void render(SpriteBatch batch) {
}
}
在init中加入代码 读地图,然后解析:(使用tilemap也是一样的过程)
private void init(String filename) {
// objects
rocks = new Array<Rock>();
// load image file that represents the level data
Pixmap pixmap = new Pixmap(Gdx.files.internal(filename));
// scan pixels from top-left to bottom-right
int lastPixel = -1;
for (int pixelY = 0; pixelY < pixmap.getHeight(); pixelY++) {
for (int pixelX = 0; pixelX < pixmap.getWidth(); pixelX++) {
AbstractGameObject obj = null;
float offsetHeight = 0;
// height grows from bottom to top
float baseHeight = pixmap.getHeight() - pixelY;
// get color of current pixel as 32-bit RGBA value
int currentPixel = pixmap.getPixel(pixelX, pixelY);
// find matching color value to identify block type at (x,y)
// point and create the corresponding game object if there is
// a match
// empty space
if (BLOCK_TYPE.EMPTY.sameColor(currentPixel)) {
// do nothing
}
// rock
else if (BLOCK_TYPE.ROCK.sameColor(currentPixel)) {
if (lastPixel != currentPixel) {
obj = new Rock();
float heightIncreaseFactor = 0.25f;
offsetHeight = -2.5f;
obj.position.set(pixelX, baseHeight * obj.dimension.y
* heightIncreaseFactor + offsetHeight);
rocks.add((Rock) obj);
} else {
rocks.get(rocks.size - 1).increaseLength(1);
}
}
// player spawn point
else if (BLOCK_TYPE.PLAYER_SPAWNPOINT.sameColor(currentPixel)) {
}
// feather
else if (BLOCK_TYPE.ITEM_FEATHER.sameColor(currentPixel)) {
}
// gold coin
else if (BLOCK_TYPE.ITEM_GOLD_COIN.sameColor(currentPixel)) {
}
// unknown object/pixel color
else {
int r = 0xff & (currentPixel >>> 24); // red color channel
int g = 0xff & (currentPixel >>> 16); // green color channel
int b = 0xff & (currentPixel >>> 8); // blue color channel
int a = 0xff & currentPixel; // alpha channel
Gdx.app.error(TAG, "Unknown object at x<" + pixelX + "> y<"
+ pixelY + ">: r<" + r + "> g<" + g + "> b<" + b
+ "> a<" + a + ">");
}
lastPixel = currentPixel;
}
}
// decoration
clouds = new Clouds(pixmap.getWidth());
clouds.position.set(0, 2);
mountains = new Mountains(pixmap.getWidth());
mountains.position.set(-1, -1);
waterOverlay = new WaterOverlay(pixmap.getWidth());
waterOverlay.position.set(0, -3.75f);
// free memory
pixmap.dispose();
Gdx.app.debug(TAG, "level '" + filename + "' loaded");
}
以此遍历渲染:
public void render(SpriteBatch batch) {
// Draw Mountains
mountains.render(batch);
// Draw Rocks
for (Rock rock : rocks)
rock.render(batch);
// Draw Water Overlay
waterOverlay.render(batch);
// Draw Clouds
clouds.render(batch);
}
渲染的次序决定了相互覆盖的效果。你可以想象它们是不同的层(当然实际上它们没有分层画,这个跟Unity不是一样的,但你可以这么以为),从45°角来看是这样的。
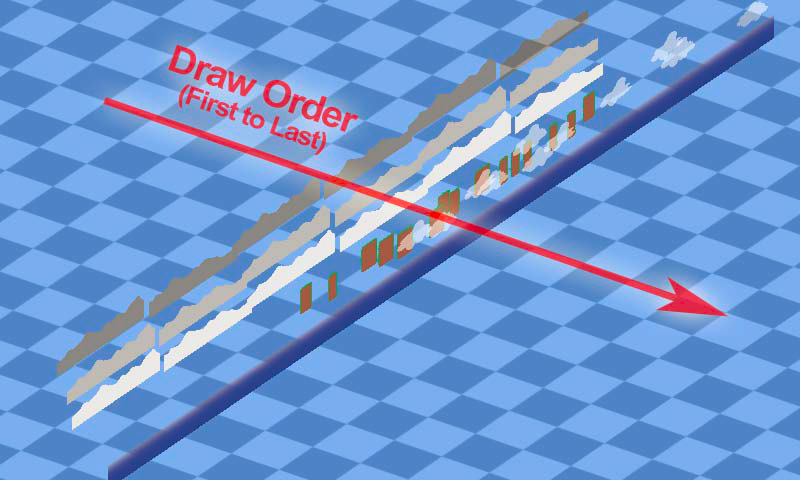
first to last,越后画的越显示在前边。
接下来,开始整合:
在Constants里加上一些游戏常量
public class Constants {
// Visible game world is 5 meters wide
public static final float VIEWPORT_WIDTH = 5.0f;
// Visible game world is 5 meters tall
public static final float VIEWPORT_HEIGHT = 5.0f;
// GUI Width
public static final float VIEWPORT_GUI_WIDTH = 800.0f;
// GUI Height
public static final float VIEWPORT_GUI_HEIGHT = 480.0f;
// Location of description file for texture atlas
public static final String TEXTURE_ATLAS_OBJECTS = "images/canyonbunny.pack";
// Location of image file for level 01
public static final String LEVEL_01 = "levels/level-01.png";
// Amount of extra lives at level start
public static final int LIVES_START = 3;
}
移除controller里的testSprites和selectedSprite;当然也要移除那些相应的方法initTestObjects(),updateTestObjects(),moveSelectedSprite()。
删除handleDebugInput()里WSAD的控制。KeyUp只保留R键。
package com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game; import com.badlogic.gdx.Application.ApplicationType;
import com.badlogic.gdx.Gdx;
import com.badlogic.gdx.Input.Keys;
import com.badlogic.gdx.InputAdapter;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.Pixmap;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.Pixmap.Format;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.Sprite;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.TextureAtlas;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.TextureRegion;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.MathUtils;
import com.badlogic.gdx.utils.Array;
import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.util.CameraHelper;
import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.util.Constants; public class WorldController extends InputAdapter {
private static final String TAG = WorldController.class.getName();
public CameraHelper cameraHelper;
public Level level;
public int lives;
public int score; private void initLevel() {
score = 0;
level = new Level(Constants.LEVEL_01);
} public WorldController() {
Gdx.input.setInputProcessor(this);
init();
} private void handleDebugInput(float deltaTime) {
if (Gdx.app.getType() != ApplicationType.Desktop)
return;
// Camera Controls (move)
float camMoveSpeed = 5 * deltaTime;
float camMoveSpeedAccelerationFactor = 5;
if (Gdx.input.isKeyPressed(Keys.SHIFT_LEFT))
camMoveSpeed *= camMoveSpeedAccelerationFactor;
if (Gdx.input.isKeyPressed(Keys.LEFT))
moveCamera(-camMoveSpeed, 0);
if (Gdx.input.isKeyPressed(Keys.RIGHT))
moveCamera(camMoveSpeed, 0);
if (Gdx.input.isKeyPressed(Keys.UP))
moveCamera(0, camMoveSpeed);
if (Gdx.input.isKeyPressed(Keys.DOWN))
moveCamera(0, -camMoveSpeed);
if (Gdx.input.isKeyPressed(Keys.BACKSPACE))
cameraHelper.setPosition(0, 0);
// Camera Controls (zoom)
float camZoomSpeed = 1 * deltaTime;
float camZoomSpeedAccelerationFactor = 5;
if (Gdx.input.isKeyPressed(Keys.SHIFT_LEFT))
camZoomSpeed *= camZoomSpeedAccelerationFactor;
if (Gdx.input.isKeyPressed(Keys.COMMA))
cameraHelper.addZoom(camZoomSpeed);
if (Gdx.input.isKeyPressed(Keys.PERIOD))
cameraHelper.addZoom(-camZoomSpeed);
if (Gdx.input.isKeyPressed(Keys.SLASH))
cameraHelper.setZoom(1);
} private void moveCamera(float x, float y) {
x += cameraHelper.getPosition().x;
y += cameraHelper.getPosition().y;
cameraHelper.setPosition(x, y);
} @Override
public boolean keyUp(int keycode) {
if (keycode == Keys.R) {
init();
Gdx.app.debug(TAG, "Game World Resetted!");
}
return false;
} public void init() {
Gdx.input.setInputProcessor(this);
cameraHelper = new CameraHelper();
lives = Constants.LIVES_START;
initLevel();
} private Pixmap createProceduralPixmap(int width, int height) {
Pixmap pixmap = new Pixmap(width, height, Format.RGBA8888);
// Fill square with red color at 50% opacity
pixmap.setColor(1, 0, 0, 0.5f);
pixmap.fill();
// Draw a yellow-colored X shape on square
pixmap.setColor(1, 1, 0, 1);
pixmap.drawLine(0, 0, width, height);
pixmap.drawLine(width, 0, 0, height);
// Draw a cyan-colored border around square
pixmap.setColor(0, 1, 1, 1);
pixmap.drawRectangle(0, 0, width, height);
return pixmap;
} public void update(float deltaTime) {
handleDebugInput(deltaTime);
cameraHelper.update(deltaTime);
}
}
修改CameraHelper:(主要是将target的类型由Sprite改为AbstractGameObject)
package com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.util; import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.OrthographicCamera;
import com.badlogic.gdx.graphics.g2d.Sprite;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.MathUtils;
import com.badlogic.gdx.math.Vector2;
import com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny.game.objects.AbstractGameObject; public class CameraHelper {
private static final String TAG = CameraHelper.class.getName();
private final float MAX_ZOOM_IN = 0.25f;
private final float MAX_ZOOM_OUT = 10.0f;
private Vector2 position;
private float zoom;
private AbstractGameObject target; public CameraHelper() {
position = new Vector2();
zoom = 1.0f;
} public void update(float deltaTime) {
if (!hasTarget())
return;
position.x = target.position.x + target.origin.x;
position.y = target.position.y + target.origin.y;
} public void setPosition(float x, float y) {
this.position.set(x, y);
} public Vector2 getPosition() {
return position;
} public void addZoom(float amount) {
setZoom(zoom + amount);
} public void setZoom(float zoom) {
this.zoom = MathUtils.clamp(zoom, MAX_ZOOM_IN, MAX_ZOOM_OUT);
} public float getZoom() {
return zoom;
} public void setTarget(AbstractGameObject target) {
this.target = target;
} public AbstractGameObject getTarget() {
return target;
} public boolean hasTarget() {
return target != null;
} public boolean hasTarget(AbstractGameObject target) {
return hasTarget() && this.target.equals(target);
} public void applyTo(OrthographicCamera camera) {
camera.position.x = position.x;
camera.position.y = position.y;
camera.zoom = zoom;
camera.update();
}
}
修改WorldRender的render():
public void render(){
renderWorld(batch);
}
private void renderWorld (SpriteBatch batch) {
worldController.cameraHelper.applyTo(camera);
batch.setProjectionMatrix(camera.combined);
batch.begin();
worldController.level.render(batch);
batch.end();
}
实现GUI:
Libgdx提供了默认的bitmap字体文件,arial-15.fnt和arial-15.png。用的时候可以把它们copy到images下。
我们把要用的字体(内部类)加到Assets中:
public class AssetFonts {
public final BitmapFont defaultSmall;
public final BitmapFont defaultNormal;
public final BitmapFont defaultBig;
public AssetFonts() {
// create three fonts using Libgdx's 15px bitmap font
defaultSmall = new BitmapFont(
Gdx.files.internal("images/arial-15.fnt"), true);
defaultNormal = new BitmapFont(
Gdx.files.internal("images/arial-15.fnt"), true);
defaultBig = new BitmapFont(
Gdx.files.internal("images/arial-15.fnt"), true);
// set font sizes
defaultSmall.setScale(0.75f);
defaultNormal.setScale(1.0f);
defaultBig.setScale(2.0f);
// enable linear texture filtering for smooth fonts
defaultSmall.getRegion().getTexture()
.setFilter(TextureFilter.Linear, TextureFilter.Linear);
defaultNormal.getRegion().getTexture()
.setFilter(TextureFilter.Linear, TextureFilter.Linear);
defaultBig.getRegion().getTexture()
.setFilter(TextureFilter.Linear, TextureFilter.Linear);
}
}
在init里加上字体的初始化:fonts = new AssetFonts();
在dispose里释放:fonts.defaultSmall.dispose();fonts.defaultNormal.dispose();fonts.defaultBig.dispose();
准备就绪了,我们需要先构想我们将要做的GUI图:(金币分数,兔子的额外性命,FPS)

接下来,我们在WorldRenderer中增加下面的代码:
private OrthographicCamera cameraGUI;
private void init() {
batch = new SpriteBatch();
camera = new OrthographicCamera(Constants.VIEWPORT_WIDTH,
Constants.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT);
camera.position.set(0, 0, 0);
camera.update();
cameraGUI = new OrthographicCamera(Constants.VIEWPORT_GUI_WIDTH,
Constants.VIEWPORT_GUI_HEIGHT);
cameraGUI.position.set(0, 0, 0);
cameraGUI.setToOrtho(true); // flip y-axis
cameraGUI.update();
}
public void resize(int width, int height) {
camera.viewportWidth = (Constants.VIEWPORT_HEIGHT / height) * width;
camera.update();
cameraGUI.viewportHeight = Constants.VIEWPORT_GUI_HEIGHT;
cameraGUI.viewportWidth = (Constants.VIEWPORT_GUI_HEIGHT/ (float)height) * (float)width;
cameraGUI.position.set(cameraGUI.viewportWidth / 2,
cameraGUI.viewportHeight / 2, 0);
cameraGUI.update();
}
第二个摄像机是专门用来做GUI投影渲染的。下面是每个GUI元素的具体实现方法:
private void renderGuiScore(SpriteBatch batch) {
float x = -15;
float y = -15;
batch.draw(Assets.instance.goldCoin.goldCoin, x, y, 50, 50, 100, 100,
0.35f, -0.35f, 0);
Assets.instance.fonts.defaultBig.draw(batch,
"" + worldController.score, x + 75, y + 37);
}
private void renderGuiExtraLive(SpriteBatch batch) {
float x = cameraGUI.viewportWidth - 50 - Constants.LIVES_START * 50;
float y = -15;
for (int i = 0; i < Constants.LIVES_START; i++) {
if (worldController.lives <= i)
batch.setColor(0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f);
batch.draw(Assets.instance.bunny.head, x + i * 50, y, 50, 50, 120,
100, 0.35f, -0.35f, 0);
batch.setColor(1, 1, 1, 1);
}
}
private void renderGuiFpsCounter(SpriteBatch batch) {
float x = cameraGUI.viewportWidth - 55;
float y = cameraGUI.viewportHeight - 15;
int fps = Gdx.graphics.getFramesPerSecond();
BitmapFont fpsFont = Assets.instance.fonts.defaultNormal;
if (fps >= 45) {
// 45 or more FPS show up in green
fpsFont.setColor(0, 1, 0, 1);
} else if (fps >= 30) {
// 30 or more FPS show up in yellow
fpsFont.setColor(1, 1, 0, 1);
} else {
// less than 30 FPS show up in red
fpsFont.setColor(1, 0, 0, 1);
}
fpsFont.draw(batch, "FPS: " + fps, x, y);
fpsFont.setColor(1, 1, 1, 1); // white
}
整合到WorldRenderer:
public void render() {
renderWorld(batch);
renderGui(batch);
}
private void renderGui(SpriteBatch batch) {
batch.setProjectionMatrix(cameraGUI.combined);
batch.begin();
// draw collected gold coins icon + text
// (anchored to top left edge)
renderGuiScore(batch);
// draw extra lives icon + text (anchored to top right edge)
renderGuiExtraLive(batch);
// draw FPS text (anchored to bottom right edge)
renderGuiFpsCounter(batch);
batch.end();
}
下一章我们继续完成一个完整的游戏需要的东东。
比如增加上主角(兔子头),关卡道具(羽毛,金币),控制主角移动,基本的碰撞检测(几乎所有的游戏都需要有的)等等。
本章素材:http://files.cnblogs.com/mignet/assets.zip
[libGDX游戏开发教程]使用Libgdx进行游戏开发(5)-关卡加载的更多相关文章
- [libGDX游戏开发教程]使用libGDX进行游戏开发(12)-Action动画
前文章节列表: 使用libGDX进行游戏开发(11)-高级编程技巧 使用libGDX进行游戏开发(10)-音乐音效不求人,程序员也可以DIY 使用libGDX进行游戏开发(9)-场景过渡 ...
- [libGDX游戏开发教程]使用libGDX进行游戏开发(1)-游戏设计
声明:<使用Libgdx进行游戏开发>是一个系列,文章的原文是<Learning Libgdx Game Development>,大家请周知.后续的文章连接在这里 使用Lib ...
- 使用Html5+C#+微信 开发移动端游戏详细教程: (四)游戏中层的概念与设计
众所周知,网站的前端页面结构一般是由div组成,父div包涵子div,子div包涵各种标签和项, 同理,游戏中我们也将若干游戏模块拆分成层,在后续的代码维护和游戏程序逻辑中将更加清晰和便于控制. We ...
- 使用Html5+C#+微信 开发移动端游戏详细教程 :(五)游戏图像的加载与操作
当我们进入游戏时,是不可能看到所有的图像的,很多图像都是随着游戏功能的打开而出现, 比如只有我打开了"宝石"菜单才会显示宝石的图像,如果是需要显示的时候才加载, 会对用户体验大打折 ...
- 微信小程序开发教程 #043 - 在小程序开发中使用 npm
本文介绍了如何在微信小程序开发中使用 npm 中包的功能,大大提高微信小程序的开发效率,同时也是微信小程序系列教程的视频版更新. 微信小程序在发布之初没有对 npm 的支持功能,这也是目前很多前端开发 ...
- PythonWeb开发教程(一),开发之前需要准备什么
什么是web开发呢,其实就是开发一个网站了.那开发网站需要用到哪些知识呢 1.python基础,因为用python开发的,所以python指定要会,最起码你也得会条件判断,循环,函数,类这些知识: 2 ...
- [libgdx游戏开发教程]使用Libgdx进行游戏开发(11)-高级编程技巧 Box2d和Shader
高级编程技巧只是相对的,其实主要是讲物理模拟和着色器程序的使用. 本章主要讲解利用Box2D并用它来实现萝卜雨,然后是使用单色着色器shader让画面呈现单色状态:http://files.cnblo ...
- [libgdx游戏开发教程]使用Libgdx进行游戏开发(10)-音乐和音效
本章音效文件都来自于公共许可: http://files.cnblogs.com/mignet/sounds.zip 在游戏中,播放背景音乐和音效是基本的功能. Libgdx提供了跨平台的声音播放功能 ...
- [libgdx游戏开发教程]使用Libgdx进行游戏开发(2)-游戏框架搭建
让我们抛开理论开始code吧. 入口类CanyonBunnyMain的代码: package com.packtpub.libgdx.canyonbunny; import com.badlogic. ...
随机推荐
- PhoneGap & HTML5 学习资料网址
PhoneGap 与 Application Cache应用缓存 http://www.html5cn.org/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=40272 加速We ...
- 用AngularJS操作DOM
在angular中使用第三方插件时最好都封装到指令(directives)中去,DOM操作也最好都解构到指令中. <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="e ...
- Boosting&Bagging
Boosting&Bagging 集成学习方法不是单独的一个机器学习算法,而是通过构建多个机器学习算法来达到一个强学习器.集成学习可以用来进行分类,回归,特征选取和异常点检测等.随机森林算法就 ...
- vector 搜索
http://classfoo.com/ccby/article/cIBahI #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #includ ...
- POJ3020:Antenna Placement(二分图匹配)
Antnna Placement Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 11093 Accepted: 5459 ...
- URAL - 1486 Equal Squares 二维哈希+二分
During a discussion of problems at the Petrozavodsk Training Camp, Vova and Sasha argued about who o ...
- com.mongodb.MongoException$CursorNotFound: cursor not found on server异常处理
java链接MongoDB处理大量数据时经常碰到cursor not found 的异常,其实是超时所致 Exception in thread "main" com.mongod ...
- eclipse 主题文件配置
eclipse市场搜索 Eclipse Color Theme ----用于控制文本域主题 Eclipse 4 Chrome Theme chrome风格的主题 最新的:Jeeeyul's Them ...
- 程序员的那些问题---转载自veryCD
展望未来,总结过去10年的程序员生涯,给程序员小弟弟小妹妹们的一些总结性忠告 走过的路,回忆起来是那么曲折,把自己的一些心得体会分享给程序员兄弟姐妹们,虽然时代在变化,但是很可能你也会走我已经做过 ...
- Win7/8 绿色软件开机启动
在查找番茄工作法PC端软件时,发现了淡高的文章win8绿色软件开机启动,试用了一下wintabs,的确好用! 另外,office软件中有一款 OFFICE tabs的插件,标签式的管理,非常方便快捷, ...
