python读取caffemodel文件
caffemodel是二进制的protobuf文件,利用protobuf的python接口可以读取它,解析出需要的内容
不少算法都是用预训练模型在自己数据上微调,即加载“caffemodel”作为网络初始参数取值,然后在此基础上更新。使用方式往往是:同时给定solver的prototxt文件,以及caffemodel权值文件,然后从solver创建网络,并从caffemodel读取网络权值的初值。能否不加载solver的prototxt,只加载caffemodel并看看它里面都有什么东西?
利用protobuf的python接口(C++接口也可以,不过编写代码和编译都略麻烦),能够读取caffemodel内容。教程当然是参考protobuf官网的例子了。
阶段1:完全模仿protobuf官网例子
我这里贴一个最noob的用法吧,用protobuf的python接口读取caffemodel文件。配合jupyter-notebook命令开启的jupyter笔记本,可以用tab键补全,比较方便:
# coding:utf-8
# 首先请确保编译了caffe的python接口,以及编译后的输出目录<caffe_root>/python加载到了PYTHONPATH环境变量中. 或者,在代码中向os.path中添加
import caffe.proto.caffe_pb2 as caffe_pb2 # 载入caffe.proto编译生成的caffe_pb2文件
# 载入模型
caffemodel_filename = '/home/chris/py-faster-rcnn/imagenet_models/ZF.v2.caffemodel'
ZFmodel = caffe_pb2.NetParameter() # 为啥是NetParameter()而不是其他类,呃,目前也还没有搞清楚,这个是试验的
f = open(caffemodel_filename, 'rb')
ZFmodel.ParseFromString(f.read())
f.close()
# noob阶段,只知道print输出
print ZFmodel.name
print ZFmodel.input
阶段2:根据caffe.proto,读取caffemodel中的字段
这一阶段从caffemodel中读取出了大量信息。首先把caffemodel作为一个NetParameter类的对象看待,那么解析出它的名字(name)和各层(layer)。然后,解析每一层(layer)。如何确定layer表示所有层,能被遍历呢?需要参考caffe.proto文件,发现layer定义为:
repeated LayerParameter layer = 100;
看到repeated关键字,可以确定layer是一个“数组”了。不断地、迭代第查看caffe.proto中的各个字段,就可以解析了。
能否从caffemodel文件中解析出信息并输出为网络训练的train.prototxt文件呢?:显然是可以的。这里以mnist训练10000次产生的caffemodel文件进行解析,将得到的信息拼接出网络训练所使用的lenet_train.prototxt(输出到stdout)(代码实现比较naive,是逐个字段枚举的方式进行输出的,后续可以改进):
# coding:utf-8
# author:ChrisZZ
# description: 从caffemodel文件解析出网络训练信息,以类似train.prototxt的形式输出到屏幕
import _init_paths
import caffe.proto.caffe_pb2 as caffe_pb2
caffemodel_filename = '/home/chris/work/py-faster-rcnn/caffe-fast-rcnn/examples/mnist/lenet_iter_10000.caffemodel'
model = caffe_pb2.NetParameter()
f=open(caffemodel_filename, 'rb')
model.ParseFromString(f.read())
f.close()
layers = model.layer
print 'name: "%s"'%model.name
layer_id=-1
for layer in layers:
layer_id = layer_id + 1
print 'layer {'
print ' name: "%s"'%layer.name
print ' type: "%s"'%layer.type
tops = layer.top
for top in tops:
print ' top: "%s"'%top
bottoms = layer.bottom
for bottom in bottoms:
print ' bottom: "%s"'%bottom
if len(layer.include)>0:
print ' include {'
includes = layer.include
phase_mapper={
'0': 'TRAIN',
'1': 'TEST'
}
for include in includes:
if include.phase is not None:
print ' phase: ', phase_mapper[str(include.phase)]
print ' }'
if layer.transform_param is not None and layer.transform_param.scale is not None and layer.transform_param.scale!=1:
print ' transform_param {'
print ' scale: %s'%layer.transform_param.scale
print ' }'
if layer.data_param is not None and (layer.data_param.source!="" or layer.data_param.batch_size!=0 or layer.data_param.backend!=0):
print ' data_param: {'
if layer.data_param.source is not None:
print ' source: "%s"'%layer.data_param.source
if layer.data_param.batch_size is not None:
print ' batch_size: %d'%layer.data_param.batch_size
if layer.data_param.backend is not None:
print ' backend: %s'%layer.data_param.backend
print ' }'
if layer.param is not None:
params = layer.param
for param in params:
print ' param {'
if param.lr_mult is not None:
print ' lr_mult: %s'% param.lr_mult
print ' }'
if layer.convolution_param is not None:
print ' convolution_param {'
conv_param = layer.convolution_param
if conv_param.num_output is not None:
print ' num_output: %d'%conv_param.num_output
if len(conv_param.kernel_size) > 0:
for kernel_size in conv_param.kernel_size:
print ' kernel_size: ',kernel_size
if len(conv_param.stride) > 0:
for stride in conv_param.stride:
print ' stride: ', stride
if conv_param.weight_filler is not None:
print ' weight_filler {'
print ' type: "%s"'%conv_param.weight_filler.type
print ' }'
if conv_param.bias_filler is not None:
print ' bias_filler {'
print ' type: "%s"'%conv_param.bias_filler.type
print ' }'
print ' }'
print '}'
产生的输出如下:
name: "LeNet"
layer {
name: "mnist"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
include {
phase: TRAIN
}
transform_param {
scale: 0.00390625
}
data_param: {
source: "examples/mnist/mnist_train_lmdb"
batch_size: 64
backend: 1
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 0
weight_filler {
type: "constant"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "conv1"
type: "Convolution"
top: "conv1"
bottom: "data"
param {
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param {
lr_mult: 2.0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 20
kernel_size: 5
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool1"
type: "Pooling"
top: "pool1"
bottom: "conv1"
convolution_param {
num_output: 0
weight_filler {
type: "constant"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "conv2"
type: "Convolution"
top: "conv2"
bottom: "pool1"
param {
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param {
lr_mult: 2.0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 50
kernel_size: 5
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool2"
type: "Pooling"
top: "pool2"
bottom: "conv2"
convolution_param {
num_output: 0
weight_filler {
type: "constant"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "ip1"
type: "InnerProduct"
top: "ip1"
bottom: "pool2"
param {
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param {
lr_mult: 2.0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 0
weight_filler {
type: "constant"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu1"
type: "ReLU"
top: "ip1"
bottom: "ip1"
convolution_param {
num_output: 0
weight_filler {
type: "constant"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "ip2"
type: "InnerProduct"
top: "ip2"
bottom: "ip1"
param {
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param {
lr_mult: 2.0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 0
weight_filler {
type: "constant"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
top: "loss"
bottom: "ip2"
bottom: "label"
convolution_param {
num_output: 0
weight_filler {
type: "constant"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
阶段3:读出caffemodel的所有字段
阶段2是手工指定要打印输出的字段,需要参照caffe.proto,一个个字段去找,遇到嵌套的情况需要递归查找,比较繁琐。能否一口气读出caffemodel的所有字段呢?可以的,使用__str__就可以了,比如:
# coding:utf-8
import _init_paths
import caffe.proto.caffe_pb2 as caffe_pb2
caffemodel_filename = '/home/chris/work/py-faster-rcnn/caffe-fast-rcnn/examples/mnist/lenet_iter_10000.caffemodel'
model = caffe_pb2.NetParameter()
f = open(caffemodel_filename, 'rb')
model.ParseFromString(f.read())
f.close()
print model.__str__
得到的输出几乎就是网络训练用的train.prototxt了,只不过里面还把blobs字段给打印出来了。这个字段里面有太多的内容,是经过多次迭代学习出来的卷积核以及bias的数值。这些字段应当忽略。以及,__str__输出的首尾有不必要的字符串也要去掉,不妨将__str__输出到文件,然后用sed删除不必要的内容。除了过滤掉blobs字段包含的内容,还去掉了"phase: TRAIN"这个不必要显示的内容,处理完后再写回同一文件。代码如下(依然以lenet训练10000次的caffemodel为例):
# coding:utf-8
import _init_paths
import caffe.proto.caffe_pb2 as caffe_pb2
caffemodel_filename = '/home/chris/work/py-faster-rcnn/caffe-fast-rcnn/examples/mnist/lenet_iter_10000.caffemodel'
model = caffe_pb2.NetParameter()
f = open(caffemodel_filename, 'rb')
model.ParseFromString(f.read())
f.close()
import sys
old=sys.stdout
save_filename = 'lenet_from_caffemodel.prototxt'
sys.stdout=open( save_filename, 'w')
print model.__str__
sys.stdout=old
f.close()
import os
cmd_1 = 'sed -i "1s/^.\{38\}//" ' + save_filename # 删除第一行前面38个字符
cmd_2 = "sed -i '$d' " + save_filename # 删除最后一行
os.system(cmd_1)
os.system(cmd_2)
# 打开刚刚存储的文件,输出里面的内容,输出时过滤掉“blobs”块和"phase: TRAIN"行。
f=open(save_filename, 'r')
lines = f.readlines()
f.close()
wr = open(save_filename, 'w')
now_have_blobs = False
nu = 1
for line in lines:
#print nu
nu = nu + 1
content = line.strip('\n')
if (content == ' blobs {'):
now_have_blobs = True
elif (content == ' }' and now_have_blobs==True):
now_have_blobs = False
continue
if (content == ' phase: TRAIN'):
continue
if (now_have_blobs):
continue
else:
wr.write(content+'\n')
wr.close()
现在,查看下得到的lenet_from_caffemodel.prototxt文件内容,也就是从caffemodel文件解析出来的字段并过滤后的结果:
name: "LeNet"
layer {
name: "mnist"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
include {
phase: TRAIN
}
transform_param {
scale: 0.00390625
}
data_param {
source: "examples/mnist/mnist_train_lmdb"
batch_size: 64
backend: LMDB
}
}
layer {
name: "conv1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "data"
top: "conv1"
param {
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param {
lr_mult: 2.0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 20
kernel_size: 5
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool1"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "pool1"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool1"
top: "conv2"
param {
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param {
lr_mult: 2.0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 50
kernel_size: 5
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool2"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv2"
top: "pool2"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "ip1"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "pool2"
top: "ip1"
param {
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param {
lr_mult: 2.0
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 500
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "ip1"
top: "ip1"
}
layer {
name: "ip2"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "ip1"
top: "ip2"
param {
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param {
lr_mult: 2.0
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 10
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
bias_filler {
type: "constant"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
bottom: "ip2"
bottom: "label"
top: "loss"
loss_weight: 1.0
}
可以说,得到的这个lenet_from_caffemodel.prototxt就是用于网络训练的配置文件了。
这里其实还存在一个问题:caffemodel->__str__->文件,这个文件会比caffemodel大很多,因为各种blobs数据占据了太多空间。当把要解析的caffemodel从lenet_iter_10000.caffemodel换成imagenet数据集上训练的ZFnet的权值文件ZF.v2.caffemodel,这个文件本身就有200多M(lenet那个只有不到2M),再运行本阶段的python代码尝试得到网络结构,会报错提示说内存不足。看来,这个解析方法还需要改进。
阶段4:不完美的解析,但是肯定够用
既然阶段3的尝试失败,那就回到阶段2的方法,手动指定需要解析的字段,获取其内容,然后打印输出。对照着caffe.proto,把一些参数的默认值过滤掉,以及blobs过滤掉。
此处以比lenet5更复杂的ZFnet(论文:Visualizing and Understanding Convolutional Networks)来解析,因为在py-faster-rcnn中使用到了这个网络,而其配置文件中又增加了RPN和ROIPooling等层,想要知道到底增加了那些层以及换掉了哪些参数,不妨看看ZFnet的原版使用了哪些层:
# coding:utf-8
# author:ChrisZZ
# description: 从caffemodel文件解析出网络训练信息,以类似train.prototxt的形式输出到屏幕
import _init_paths
import caffe.proto.caffe_pb2 as caffe_pb2
#caffemodel_filename = '/home/chris/work/fuckubuntu/caffe-fast-rcnn/examples/mnist/lenet_iter_10000.caffemodel'
caffemodel_filename = '/home/chris/work/py-faster-rcnn/data/imagenet_models/ZF.v2.caffemodel'
model = caffe_pb2.NetParameter()
f=open(caffemodel_filename, 'rb')
model.ParseFromString(f.read())
f.close()
layers = model.layer
print 'name: ' + model.name
layer_id=-1
for layer in layers:
layer_id = layer_id + 1
res=list()
# name
res.append('layer {')
res.append(' name: "%s"' % layer.name)
# type
res.append(' type: "%s"' % layer.type)
# bottom
for bottom in layer.bottom:
res.append(' bottom: "%s"' % bottom)
# top
for top in layer.top:
res.append(' top: "%s"' % top)
# loss_weight
for loss_weight in layer.loss_weight:
res.append(' loss_weight: ' + loss_weight)
# param
for param in layer.param:
param_res = list()
if param.lr_mult is not None:
param_res.append(' lr_mult: %s' % param.lr_mult)
if param.decay_mult!=1:
param_res.append(' decay_mult: %s' % param.decay_mult)
if len(param_res)>0:
res.append(' param{')
res.extend(param_res)
res.append(' }')
# lrn_param
if layer.lrn_param is not None:
lrn_res = list()
if layer.lrn_param.local_size!=5:
lrn_res.append(' local_size: %d' % layer.lrn_param.local_size)
if layer.lrn_param.alpha!=1:
lrn_res.append(' alpha: %f' % layer.lrn_param.alpha)
if layer.lrn_param.beta!=0.75:
lrn_res.append(' beta: %f' % layer.lrn_param.beta)
NormRegionMapper={'0': 'ACROSS_CHANNELS', '1': 'WITHIN_CHANNEL'}
if layer.lrn_param.norm_region!=0:
lrn_res.append(' norm_region: %s' % NormRegionMapper[str(layer.lrn_param.norm_region)])
EngineMapper={'0': 'DEFAULT', '1':'CAFFE', '2':'CUDNN'}
if layer.lrn_param.engine!=0:
lrn_res.append(' engine: %s' % EngineMapper[str(layer.lrn_param.engine)])
if len(lrn_res)>0:
res.append(' lrn_param{')
res.extend(lrn_res)
res.append(' }')
# include
if len(layer.include)>0:
include_res = list()
includes = layer.include
phase_mapper={
'0': 'TRAIN',
'1': 'TEST'
}
for include in includes:
if include.phase is not None:
include_res.append(' phase: ', phase_mapper[str(include.phase)])
if len(include_res)>0:
res.append(' include {')
res.extend(include_res)
res.append(' }')
# transform_param
if layer.transform_param is not None:
transform_param_res = list()
if layer.transform_param.scale!=1:
transform_param_res.append(' scale: %s'%layer.transform_param.scale)
if layer.transform_param.mirror!=False:
transform_param.res.append(' mirror: ' + layer.transform_param.mirror)
if len(transform_param_res)>0:
res.append(' transform_param {')
res.extend(transform_param_res)
res.res.append(' }')
# data_param
if layer.data_param is not None and (layer.data_param.source!="" or layer.data_param.batch_size!=0 or layer.data_param.backend!=0):
data_param_res = list()
if layer.data_param.source is not None:
data_param_res.append(' source: "%s"'%layer.data_param.source)
if layer.data_param.batch_size is not None:
data_param_res.append(' batch_size: %d'%layer.data_param.batch_size)
if layer.data_param.backend is not None:
data_param_res.append(' backend: %s'%layer.data_param.backend)
if len(data_param_res)>0:
res.append(' data_param: {')
res.extend(data_param_res)
res.append(' }')
# convolution_param
if layer.convolution_param is not None:
convolution_param_res = list()
conv_param = layer.convolution_param
if conv_param.num_output!=0:
convolution_param_res.append(' num_output: %d'%conv_param.num_output)
if len(conv_param.kernel_size) > 0:
for kernel_size in conv_param.kernel_size:
convolution_param_res.append(' kernel_size: %d' % kernel_size)
if len(conv_param.pad) > 0:
for pad in conv_param.pad:
convolution_param_res.append(' pad: %d' % pad)
if len(conv_param.stride) > 0:
for stride in conv_param.stride:
convolution_param_res.append(' stride: %d' % stride)
if conv_param.weight_filler is not None and conv_param.weight_filler.type!='constant':
convolution_param_res.append(' weight_filler {')
convolution_param_res.append(' type: "%s"'%conv_param.weight_filler.type)
convolution_param_res.append(' }')
if conv_param.bias_filler is not None and conv_param.bias_filler.type!='constant':
convolution_param_res.append(' bias_filler {')
convolution_param_res.append(' type: "%s"'%conv_param.bias_filler.type)
convolution_param_res.append(' }')
if len(convolution_param_res)>0:
res.append(' convolution_param {')
res.extend(convolution_param_res)
res.append(' }')
# pooling_param
if layer.pooling_param is not None:
pooling_param_res = list()
if layer.pooling_param.kernel_size>0:
pooling_param_res.append(' kernel_size: %d' % layer.pooling_param.kernel_size)
pooling_param_res.append(' stride: %d' % layer.pooling_param.stride)
pooling_param_res.append(' pad: %d' % layer.pooling_param.pad)
PoolMethodMapper={'0':'MAX', '1':'AVE', '2':'STOCHASTIC'}
pooling_param_res.append(' pool: %s' % PoolMethodMapper[str(layer.pooling_param.pool)])
if len(pooling_param_res)>0:
res.append(' pooling_param {')
res.extend(pooling_param_res)
res.append(' }')
# inner_product_param
if layer.inner_product_param is not None:
inner_product_param_res = list()
if layer.inner_product_param.num_output!=0:
inner_product_param_res.append(' num_output: %d' % layer.inner_product_param.num_output)
if len(inner_product_param_res)>0:
res.append(' inner_product_param {')
res.extend(inner_product_param_res)
res.append(' }')
# drop_param
if layer.dropout_param is not None:
dropout_param_res = list()
if layer.dropout_param.dropout_ratio!=0.5 or layer.dropout_param.scale_train!=True:
dropout_param_res.append(' dropout_ratio: %f' % layer.dropout_param.dropout_ratio)
dropout_param_res.append(' scale_train: ' + str(layer.dropout_param.scale_train))
if len(dropout_param_res)>0:
res.append(' dropout_param {')
res.extend(dropout_param_res)
res.append(' }')
res.append('}')
for line in res:
print line
此处贴出ZFnet原版网络的prototxt描述文件:
name: "ImageNet_Zeiler_spm"
layer {
name: "conv1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "data"
top: "conv1"
param{
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param{
lr_mult: 2.0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 96
kernel_size: 7
pad: 1
stride: 2
weight_filler {
type: "gaussian"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "conv1"
}
layer {
name: "norm1"
type: "LRN"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "norm1"
lrn_param{
local_size: 3
alpha: 0.000050
norm_region: WITHIN_CHANNEL
}
}
layer {
name: "pool1"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "norm1"
top: "pool1"
pooling_param {
kernel_size: 3
stride: 2
pad: 0
pool: MAX
}
}
layer {
name: "conv2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool1"
top: "conv2"
param{
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param{
lr_mult: 2.0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 256
kernel_size: 5
pad: 0
stride: 2
weight_filler {
type: "gaussian"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu2"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv2"
top: "conv2"
}
layer {
name: "norm2"
type: "LRN"
bottom: "conv2"
top: "norm2"
lrn_param{
local_size: 3
alpha: 0.000050
norm_region: WITHIN_CHANNEL
}
}
layer {
name: "pool2"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "norm2"
top: "pool2"
pooling_param {
kernel_size: 3
stride: 2
pad: 0
pool: MAX
}
}
layer {
name: "conv3"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool2"
top: "conv3"
param{
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param{
lr_mult: 2.0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 384
kernel_size: 3
pad: 1
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "gaussian"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu3"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv3"
top: "conv3"
}
layer {
name: "conv4"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "conv3"
top: "conv4"
param{
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param{
lr_mult: 2.0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 384
kernel_size: 3
pad: 1
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "gaussian"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu4"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv4"
top: "conv4"
}
layer {
name: "conv5"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "conv4"
top: "conv5"
param{
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param{
lr_mult: 2.0
}
convolution_param {
num_output: 256
kernel_size: 3
pad: 1
stride: 1
weight_filler {
type: "gaussian"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu5"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "conv5"
top: "conv5"
}
layer {
name: "pool5_spm6"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv5"
top: "pool5_spm6"
pooling_param {
kernel_size: 3
stride: 2
pad: 0
pool: MAX
}
}
layer {
name: "pool5_spm6_flatten"
type: "Flatten"
bottom: "pool5_spm6"
top: "pool5_spm6_flatten"
}
layer {
name: "fc6"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "pool5_spm6_flatten"
top: "fc6"
param{
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param{
lr_mult: 2.0
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 4096
}
}
layer {
name: "relu6"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "fc6"
top: "fc6"
}
layer {
name: "drop6"
type: "Dropout"
bottom: "fc6"
top: "fc6"
}
layer {
name: "fc7"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "fc6"
top: "fc7"
param{
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param{
lr_mult: 2.0
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 4096
}
}
layer {
name: "relu7"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "fc7"
top: "fc7"
}
layer {
name: "drop7"
type: "Dropout"
bottom: "fc7"
top: "fc7"
}
layer {
name: "fc8"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "fc7"
top: "fc8"
param{
lr_mult: 1.0
}
param{
lr_mult: 2.0
}
inner_product_param {
num_output: 1000
}
}
layer {
name: "prob"
type: "Softmax"
bottom: "fc8"
top: "prob"
}
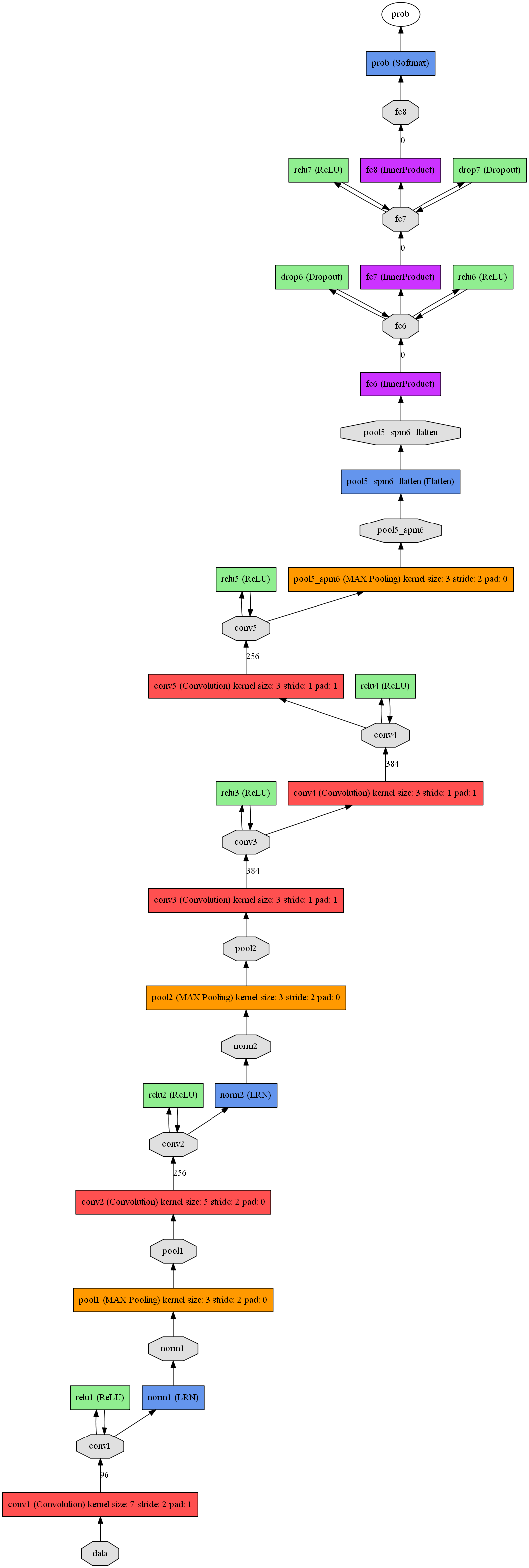
根据得到的prototxt文件,容易绘制出原版ZFnet对应的网络结构图:(可参考这篇博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/zjutzz/p/5955218.html)
python读取caffemodel文件的更多相关文章
- Python读取txt文件
Python读取txt文件,有两种方式: (1)逐行读取 data=open("data.txt") line=data.readline() while line: print ...
- Python读取Yaml文件
近期看到好多使用Yaml文件做为配置文件或者数据文件的工程,随即也研究了下,发现Yaml有几个优点:可读性好.和脚本语言的交互性好(确实非常好).使用实现语言的数据类型.有一个一致的数据模型.易于实现 ...
- python读取中文文件编码问题
python 读取中文文件后,作为参数使用,经常会遇到乱码或者报错asii错误等. 我们需要对中文进行decode('gbk') 如我有一个data.txt文件有如下内容: 百度 谷歌 现在想读取文件 ...
- Python读取SQLite文件数据
近日在做项目时,意外听说有一种SQLite的数据库,相比自己之前使用的SQL Service甚是轻便,在对数据完整性.并发性要求不高的场景下可以尝试! 1.SQLite简介: SQLite是一个进程内 ...
- Python读取xlsx文件
Python读取xlsx文件 脚本如下: from openpyxl import load_workbook workbook = load_workbook(u'/tmp/test.xlsx') ...
- Python 读取WAV文件并绘制波形图
aa Python 读取WAV文件并绘制波形图 ffmpeg -i test_pcm_mulaw.wav -f wav -codec:a pcm_s16le -ar 8000 -ac 1 out.wa ...
- 使用python读取yaml文件
在做APP测试时,通常需要把参数存到一个字典变量中,这时可以将参数写入yaml文件中,再读取出来. 新建yaml文件(android_caps.yaml),文件内容为: platformName: A ...
- python 读取bin文件
python读取bin文件并下发串口 # coding:utf-8import time, serialfrom struct import *import binascii file = ope ...
- 记录:python读取excel文件
由于最近老是用到python读取excel文件,所以特意记录一下python读取excel文件的大体框架. 库:xlrd(读),直接pip安装即可.想要写excel文件的话,安装xlwd库即可,也是直 ...
随机推荐
- 类型转换和类型相关函数.png
- [连载]《C#通讯(串口和网络)框架的设计与实现》- 8.总体控制器的设计
目 录 第八章 总体控制器的设计... 2 8.1 总控制器的职能... 2 8.2 组装和释放部件... 3 8.3 ...
- AngularJs最简单解决跨域问题案例
AngularJs最简单解决跨域问题案例 2016-05-20 09:18 82人阅读 评论(0) 收藏 举报 分类: javascript(1) 作者:白狼 出处:http://www.mank ...
- github源码学习之UIImage+YYWebImage
UIImage+YYWebImage是YYWebImage(https://github.com/ibireme/YYWebImage)中的一个分类,这个分类封装了一些image常用的变化方法,非常值 ...
- Google C++单元测试框架GoogleTest---值参数化测试
值参数化测试允许您使用不同的参数测试代码,而无需编写同一测试的多个副本. 假设您为代码编写测试,然后意识到您的代码受到布尔参数的影响. TEST(MyCodeTest, TestFoo) { // A ...
- Java中的经典算法之冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)
Java中的经典算法之冒泡排序(Bubble Sort) 神话丿小王子的博客主页 原理:比较两个相邻的元素,将值大的元素交换至右端. 思路:依次比较相邻的两个数,将小数放在前面,大数放在后面.即在第一 ...
- Windows 10不能拨L2TP协议的VPN
之前是Windows 10版本1607版本14393.102升级14393.187过后,突然出现不能拨公司防火墙的L2TPVPN了. 网上众说纷纭,原来遇到这个问题的人真不少,不过我是第一次遇到.结合 ...
- auto_clipboard
黄山松发表于博客园:http://www.cnblogs.com/tomview/p/6137179.html #ifndef __HSS_AUTO_CLIPBOARD_HSS__#define __ ...
- linux下创建文件与目录时默认被赋予了什么样的权限?
当我们创建一个新的文件或目录的时候,他的默认权限是什么? umask--指定当前使用者在创建文件或目录的时候默认的权限值 [root@iZ288fgkcpkZ default]# umask [roo ...
- Bootsrap基本应用
Bootsrap 用法: <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset=&q ...
