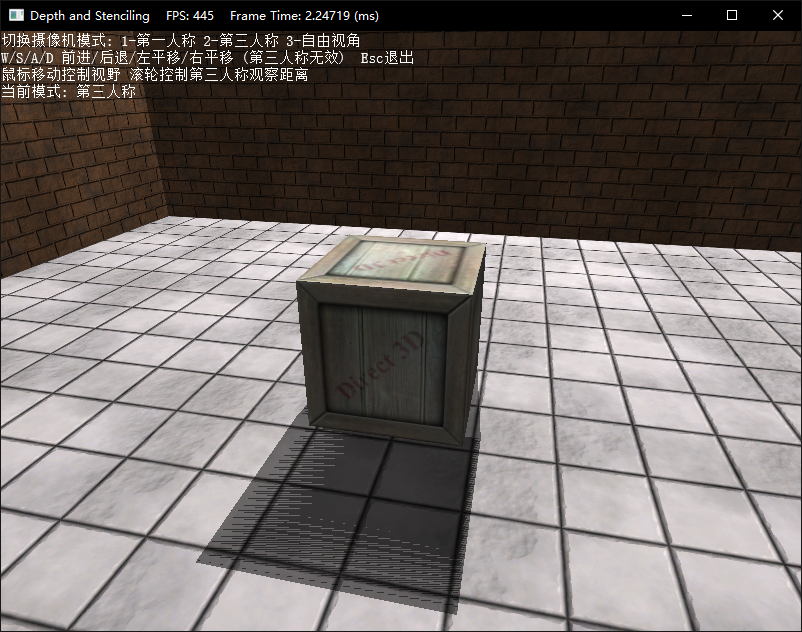
DirectX11 With Windows SDK--13 动手实现一个简易Effects框架、阴影效果绘制
前言
到现在为止,所有的教程项目都没有使用Effects11框架类来管理资源。因为在D3DCompile API (#47)版本中,如果你尝试编译fx_5_0的效果文件,会收到这样的警告:
X4717: Effects deprecated for D3DCompiler_47
在未来的版本中,D3DCompiler可能会停止对FX11的支持,所以我们需要自行去管理各种特效,并改用HLSL编译器去编译每一个着色器。同时,在阅读本章之前,你需要先学习本系列前面的一些重点章节再继续:
| 章节目录 |
|---|
| 01 DirectX11初始化 |
| 02 顶点/像素着色器的创建、顶点缓冲区 |
| 03 索引缓冲区、常量缓冲区 |
| 09 纹理映射与采样器状态 |
| 11 混合状态与光栅化状态 |
| 12 深度/模板状态、反射绘制 |
在DirectXTK中的Effects.h可以看到它实现了一系列Effects管理类,相比Effects11框架库,它缺少了反射机制,并且使用的是它内部已经写好、编译好的着色器。DirectXTK的Effects也只不过是为了简化游戏开发流程而设计出来的。当然,里面的一部分源码实现也值得我们去学习。
注意:这章经历了一次十分大的改动,原先所使用的BasicEffect类因为在后续的章节中发现很难扩展,所以进行了一次大幅度重构。并会逐渐替换掉后面教程的项目源码所使用的BasicEffect。
在这一章的学习过后,你将会理解Effects11的一部分运作机制是怎样的。如果想更深入了解的话,推荐阅读下面这篇,内部实现了一个功能和Effects11相仿的EffectHelper类,可以更好地帮助你简化代码:
| 章节目录 |
|---|
| 深入理解Effects11、使用着色器反射机制(Shader Reflection)实现一个复杂Effects框架 |
DirectX11 With Windows SDK完整目录
欢迎加入QQ群: 727623616 可以一起探讨DX11,以及有什么问题也可以在这里汇报。
回顾RenderStates类
目前的RenderStates类存放有比较常用的各种状态,原来在Effects11框架下是可以在fx文件初始化各种渲染状态,并设置到Technique11中。但现在我们只能在C++代码层中一次性创建好各种所需的渲染状态:
class RenderStates
{
public:
template <class T>
using ComPtr = Microsoft::WRL::ComPtr<T>;
static bool IsInit();
static void InitAll(ID3D11Device * device);
// 使用ComPtr无需手工释放
public:
static ComPtr<ID3D11RasterizerState> RSWireframe; // 光栅化器状态:线框模式
static ComPtr<ID3D11RasterizerState> RSNoCull; // 光栅化器状态:无背面裁剪模式
static ComPtr<ID3D11RasterizerState> RSCullClockWise; // 光栅化器状态:顺时针裁剪模式
static ComPtr<ID3D11SamplerState> SSLinearWrap; // 采样器状态:线性过滤
static ComPtr<ID3D11SamplerState> SSAnistropicWrap; // 采样器状态:各项异性过滤
static ComPtr<ID3D11BlendState> BSNoColorWrite; // 混合状态:不写入颜色
static ComPtr<ID3D11BlendState> BSTransparent; // 混合状态:透明混合
static ComPtr<ID3D11BlendState> BSAlphaToCoverage; // 混合状态:Alpha-To-Coverage
static ComPtr<ID3D11DepthStencilState> DSSWriteStencil; // 深度/模板状态:写入模板值
static ComPtr<ID3D11DepthStencilState> DSSDrawWithStencil; // 深度/模板状态:对指定模板值的区域进行绘制
static ComPtr<ID3D11DepthStencilState> DSSNoDoubleBlend; // 深度/模板状态:无二次混合区域
static ComPtr<ID3D11DepthStencilState> DSSNoDepthTest; // 深度/模板状态:关闭深度测试
static ComPtr<ID3D11DepthStencilState> DSSNoDepthWrite; // 深度/模板状态:仅深度测试,不写入深度值
};
具体的设置可以参照源码或者上一章内容。
简易Effects框架
该Effects框架支持的功能如下:
- 管理/修改常量缓冲区的内容,并应用(Apply)变更
- 编译HLSL着色器而不是fx文件
- 管理/使用四种渲染状态
- 切换渲染模式(涉及到渲染管线各种资源的绑定、切换)
- 仅更新修改的变量所对应的常量缓冲区块
不过它也有这样的缺陷:
- 一个特效类对应一套着色器和所使用的常量缓冲区,所属着色器代码的变动很可能会引起对框架类的修改,因为缺乏反射机制而导致灵活性差。
此外,该框架内部会对矩阵进行转置,因此在传递矩阵给Effects时只需要传递默认的行主矩阵即可。
文件结构
首先是文件结构:

其中能够暴露给程序使用的只有头文件Effects.h,里面可以存放多套不同的特效框架类的声明,而关于每个框架类的实现部分都应当用一个独立的源文件存放。而EffectHelper.h则是用来帮助管理常量缓冲区的,服务于各种框架类的实现部分以及所属的源文件,因此不应该直接使用。
理论上它也是可以做成静态库使用的,然后着色器代码稳定后也不应当变动。在使用的时候只需要包含头文件Effects.h即可。
EffectHelper.h
该头文件包含了一些有用的东西,但它需要在包含特效类实现的源文件中使用,且必须晚于Effects.h和d3dUtil.h包含。
在堆上进行类的内存对齐
有些类型需要在堆上按16字节对齐,比如XMVECTOR和XMMATRIX,虽然说拿这些对象作为类的成员不太合适,毕竟分配在堆上的话基本上无法保证内存按16字节对齐了,但还是希望能够做到。在VS的corecrt_malloc.h(只要有包含stdlib.h, malloc.h之一的头文件都可以)中有这样的一个函数:_aligned_malloc,它可以指定需要分配的内存字节大小以及按多少字节对齐。其中对齐值必须为2的整数次幂的字节数。
void * _aligned_malloc(
size_t size, // [In]分配内存字节数
size_t alignment // [In]按多少字节内存来对齐
);
若一个类中包含有已经指定内存对齐的成员,则需要优先把这些成员放到最前。
然后与之对应的就是_aligned_free函数了,它可以释放之前由_aligned_malloc分配得到的内存。
下面是类模板AlignedType的实现,让需要内存对齐的类去继承该类即可。它重载了operator new和operator delete的实现:
// 若类需要内存对齐,从该类派生
template<class DerivedType>
struct AlignedType
{
static void* operator new(size_t size)
{
const size_t alignedSize = __alignof(DerivedType);
static_assert(alignedSize > 8, "AlignedNew is only useful for types with > 8 byte alignment! Did you forget a __declspec(align) on DerivedType?");
void* ptr = _aligned_malloc(size, alignedSize);
if (!ptr)
throw std::bad_alloc();
return ptr;
}
static void operator delete(void * ptr)
{
_aligned_free(ptr);
}
};
需要注意的是,继承AlignedType的类或者其成员必须本身有__declspec(align)的标识。若是内部成员,在所有包含该标识的值中最大的align值 必须是2的整数次幂且必须大于8。
下面演示了正确的和错误的行为:
// 错误!VertexPosColor按4字节对齐!
struct VertexPosColor : AlignedType<VertexPos>
{
XMFLOAT3 pos;
XMFLOAT4 color;
};
// 正确!Data按16字节对齐,因为pos本身是按16字节对齐的。
struct Data : AlignedType<VertexPos>
{
XMVECTOR pos;
int val;
};
// 正确!Vector类按16字节对齐
__declspec(align(16))
struct Vector : AlignedType<Vector>
{
float x;
float y;
float z;
float w;
};
这里AlignedType<T>主要是用于BasicEffect::Impl类,因为其内部包含了XMVECTOR和XMMATRIX类型的成员,且该类需要分配在堆上。
常量缓冲区管理
一个常量缓冲区可能会被创建、更新或者绑定到管线。若常量缓冲区的值没有发生变化,我们不希望它进行无意义的更新。这里可以使用一个dirty标记,确认它是否被修改过。在Effects调用Apply后,如果常量缓冲区的任一内部成员发生修改的话,我们就将数据更新到常量缓冲区并恢复该标记。
首先是抽象基类CBufferBase:
struct CBufferBase
{
template<class T>
using ComPtr = Microsoft::WRL::ComPtr<T>;
CBufferBase() : isDirty() {}
~CBufferBase() = default;
BOOL isDirty;
ComPtr<ID3D11Buffer> cBuffer;
virtual HRESULT CreateBuffer(ID3D11Device * device) = 0;
virtual void UpdateBuffer(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext) = 0;
virtual void BindVS(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext) = 0;
virtual void BindHS(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext) = 0;
virtual void BindDS(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext) = 0;
virtual void BindGS(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext) = 0;
virtual void BindCS(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext) = 0;
virtual void BindPS(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext) = 0;
};
这么做是为了方便我们放入数组进行遍历。
然后是派生类CBufferObject,startSlot指定了HLSL对应cbuffer的索引,T则是C++对应的结构体,存储临时数据:
template<UINT startSlot, class T>
struct CBufferObject : CBufferBase
{
T data;
CBufferObject() : CBufferBase(), data() {}
HRESULT CreateBuffer(ID3D11Device * device) override
{
if (cBuffer != nullptr)
return S_OK;
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC cbd;
ZeroMemory(&cbd, sizeof(cbd));
cbd.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DYNAMIC;
cbd.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_CONSTANT_BUFFER;
cbd.CPUAccessFlags = D3D11_CPU_ACCESS_WRITE;
cbd.ByteWidth = sizeof(T);
return device->CreateBuffer(&cbd, nullptr, cBuffer.GetAddressOf());
}
void UpdateBuffer(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext) override
{
if (isDirty)
{
isDirty = false;
D3D11_MAPPED_SUBRESOURCE mappedData;
deviceContext->Map(cBuffer.Get(), 0, D3D11_MAP_WRITE_DISCARD, 0, &mappedData);
memcpy_s(mappedData.pData, sizeof(T), &data, sizeof(T));
deviceContext->Unmap(cBuffer.Get(), 0);
}
}
void BindVS(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext) override
{
deviceContext->VSSetConstantBuffers(startSlot, 1, cBuffer.GetAddressOf());
}
void BindHS(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext) override
{
deviceContext->HSSetConstantBuffers(startSlot, 1, cBuffer.GetAddressOf());
}
void BindDS(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext) override
{
deviceContext->DSSetConstantBuffers(startSlot, 1, cBuffer.GetAddressOf());
}
void BindGS(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext) override
{
deviceContext->GSSetConstantBuffers(startSlot, 1, cBuffer.GetAddressOf());
}
void BindCS(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext) override
{
deviceContext->CSSetConstantBuffers(startSlot, 1, cBuffer.GetAddressOf());
}
void BindPS(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext) override
{
deviceContext->PSSetConstantBuffers(startSlot, 1, cBuffer.GetAddressOf());
}
};
关于常量缓冲区临时变量的修改则在后续的内容。
BasicEffect类--管理对象绘制的资源
首先是抽象基类IEffects,它仅允许被移动,并且仅包含Apply方法。
class IEffect
{
public:
// 使用模板别名(C++11)简化类型名
template <class T>
using ComPtr = Microsoft::WRL::ComPtr<T>;
IEffect() = default;
// 不支持复制构造
IEffect(const IEffect&) = delete;
IEffect& operator=(const IEffect&) = delete;
// 允许转移
IEffect(IEffect&& moveFrom) = default;
IEffect& operator=(IEffect&& moveFrom) = default;
virtual ~IEffect() = default;
// 更新并绑定常量缓冲区
virtual void Apply(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext) = 0;
};
原来的ID3DX11EffectPass包含的方法Apply用于在各个着色器阶段绑定所需要的常量缓冲区、纹理等资源,并更新之前有所修改的常量缓冲区。现在我们实现Effects框架中的Apply方法也是这么做的。
然后是派生类BasicEffect,从它的方法来看,包含了单例获取、渲染状态的切换、修改常量缓冲区某一成员的值、应用变更四个大块:
class BasicEffect : public IEffect
{
public:
BasicEffect();
virtual ~BasicEffect() override;
BasicEffect(BasicEffect&& moveFrom) noexcept;
BasicEffect& operator=(BasicEffect&& moveFrom) noexcept;
// 获取单例
static BasicEffect& Get();
// 初始化Basic.hlsli所需资源并初始化渲染状态
bool InitAll(ID3D11Device * device);
//
// 渲染模式的变更
//
// 默认状态来绘制
void SetRenderDefault(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext);
// Alpha混合绘制
void SetRenderAlphaBlend(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext);
// 无二次混合
void SetRenderNoDoubleBlend(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext, UINT stencilRef);
// 仅写入模板值
void SetWriteStencilOnly(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext, UINT stencilRef);
// 对指定模板值的区域进行绘制,采用默认状态
void SetRenderDefaultWithStencil(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext, UINT stencilRef);
// 对指定模板值的区域进行绘制,采用Alpha混合
void SetRenderAlphaBlendWithStencil(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext, UINT stencilRef);
// 2D默认状态绘制
void Set2DRenderDefault(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext);
// 2D混合绘制
void Set2DRenderAlphaBlend(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext);
//
// 矩阵设置
//
void XM_CALLCONV SetWorldMatrix(DirectX::FXMMATRIX W);
void XM_CALLCONV SetViewMatrix(DirectX::FXMMATRIX V);
void XM_CALLCONV SetProjMatrix(DirectX::FXMMATRIX P);
void XM_CALLCONV SetReflectionMatrix(DirectX::FXMMATRIX R);
void XM_CALLCONV SetShadowMatrix(DirectX::FXMMATRIX S);
void XM_CALLCONV SetRefShadowMatrix(DirectX::FXMMATRIX RefS);
//
// 光照、材质和纹理相关设置
//
// 各种类型灯光允许的最大数目
static const int maxLights = 5;
void SetDirLight(size_t pos, const DirectionalLight& dirLight);
void SetPointLight(size_t pos, const PointLight& pointLight);
void SetSpotLight(size_t pos, const SpotLight& spotLight);
void SetMaterial(const Material& material);
void SetTexture(ID3D11ShaderResourceView * texture);
void XM_CALLCONV SetEyePos(DirectX::FXMVECTOR eyePos);
//
// 状态开关设置
//
void SetReflectionState(bool isOn);
void SetShadowState(bool isOn);
// 应用常量缓冲区和纹理资源的变更
void Apply(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext);
private:
class Impl;
std::unique_ptr<Impl> pImpl;
};
XM_CALLCONV即在第五章之前提到的__vectorcall或__fastcall约定。
BasicEffect::Impl类
之前在BasicEffect中声明了Impl类,主要目的是为了将类的成员和方法定义都转移到源文件中,并且还包含了HLSL五个cbuffer的C++结构体。不仅可以减少BasicEffect类的压力,还可以避免暴露上面的五个结构体:
class BasicEffect::Impl : public AlignedType<BasicEffect::Impl>
{
public:
//
// 这些结构体对应HLSL的结构体。需要按16字节对齐
//
struct CBChangesEveryDrawing
{
DirectX::XMMATRIX world;
DirectX::XMMATRIX worldInvTranspose;
Material material;
};
struct CBDrawingStates
{
int isReflection;
int isShadow;
DirectX::XMINT2 pad;
};
struct CBChangesEveryFrame
{
DirectX::XMMATRIX view;
DirectX::XMVECTOR eyePos;
};
struct CBChangesOnResize
{
DirectX::XMMATRIX proj;
};
struct CBChangesRarely
{
DirectX::XMMATRIX reflection;
DirectX::XMMATRIX shadow;
DirectX::XMMATRIX refShadow;
DirectionalLight dirLight[BasicEffect::maxLights];
PointLight pointLight[BasicEffect::maxLights];
SpotLight spotLight[BasicEffect::maxLights];
};
public:
// 必须显式指定
Impl() : m_IsDirty() {}
~Impl() = default;
public:
// 需要16字节对齐的优先放在前面
CBufferObject<0, CBChangesEveryDrawing> m_CBDrawing; // 每次对象绘制的常量缓冲区
CBufferObject<1, CBDrawingStates> m_CBStates; // 每次绘制状态变更的常量缓冲区
CBufferObject<2, CBChangesEveryFrame> m_CBFrame; // 每帧绘制的常量缓冲区
CBufferObject<3, CBChangesOnResize> m_CBOnResize; // 每次窗口大小变更的常量缓冲区
CBufferObject<4, CBChangesRarely> m_CBRarely; // 几乎不会变更的常量缓冲区
BOOL m_IsDirty; // 是否有值变更
std::vector<CBufferBase*> m_pCBuffers; // 统一管理上面所有的常量缓冲区
ComPtr<ID3D11VertexShader> m_pVertexShader3D; // 用于3D的顶点着色器
ComPtr<ID3D11PixelShader> m_pPixelShader3D; // 用于3D的像素着色器
ComPtr<ID3D11VertexShader> m_pVertexShader2D; // 用于2D的顶点着色器
ComPtr<ID3D11PixelShader> m_pPixelShader2D; // 用于2D的像素着色器
ComPtr<ID3D11InputLayout> m_pVertexLayout2D; // 用于2D的顶点输入布局
ComPtr<ID3D11InputLayout> m_pVertexLayout3D; // 用于3D的顶点输入布局
ComPtr<ID3D11ShaderResourceView> m_pTexture; // 用于绘制的纹理
};
构造/析构/单例
这里用一个匿名空间保管单例对象的指针。当有一个实例被构造出来的时候就会给其赋值。后续就不允许再被实例化了,可以使用Get方法获取该单例。
namespace
{
// BasicEffect单例
static BasicEffect * g_pInstance = nullptr;
}
BasicEffect::BasicEffect()
{
if (g_pInstance)
throw std::exception("BasicEffect is a singleton!");
g_pInstance = this;
pImpl = std::make_unique<BasicEffect::Impl>();
}
BasicEffect::~BasicEffect()
{
}
BasicEffect::BasicEffect(BasicEffect && moveFrom) noexcept
{
pImpl.swap(moveFrom.pImpl);
}
BasicEffect & BasicEffect::operator=(BasicEffect && moveFrom) noexcept
{
pImpl.swap(moveFrom.pImpl);
return *this;
}
BasicEffect & BasicEffect::Get()
{
if (!g_pInstance)
throw std::exception("BasicEffect needs an instance!");
return *g_pInstance;
}
BasicEffect::InitAll方法
BasicEffect::InitAll方法负责创建出所有的着色器和常量缓冲区,以及所有的渲染状态:
bool BasicEffect::InitAll(ID3D11Device * device)
{
if (!device)
return false;
if (!pImpl->m_pCBuffers.empty())
return true;
if (!RenderStates::IsInit())
throw std::exception("RenderStates need to be initialized first!");
ComPtr<ID3DBlob> blob;
// 创建顶点着色器(2D)
HR(CreateShaderFromFile(L"HLSL\\Basic_VS_2D.cso", L"HLSL\\Basic_VS_2D.hlsl", "VS_2D", "vs_5_0", blob.GetAddressOf()));
HR(device->CreateVertexShader(blob->GetBufferPointer(), blob->GetBufferSize(), nullptr, pImpl->m_pVertexShader2D.GetAddressOf()));
// 创建顶点布局(2D)
HR(device->CreateInputLayout(VertexPosTex::inputLayout, ARRAYSIZE(VertexPosTex::inputLayout),
blob->GetBufferPointer(), blob->GetBufferSize(), pImpl->m_pVertexLayout2D.GetAddressOf()));
// 创建像素着色器(2D)
HR(CreateShaderFromFile(L"HLSL\\Basic_PS_2D.cso", L"HLSL\\Basic_PS_2D.hlsl", "PS_2D", "ps_5_0", blob.ReleaseAndGetAddressOf()));
HR(device->CreatePixelShader(blob->GetBufferPointer(), blob->GetBufferSize(), nullptr, pImpl->m_pPixelShader2D.GetAddressOf()));
// 创建顶点着色器(3D)
HR(CreateShaderFromFile(L"HLSL\\Basic_VS_3D.cso", L"HLSL\\Basic_VS_3D.hlsl", "VS_3D", "vs_5_0", blob.ReleaseAndGetAddressOf()));
HR(device->CreateVertexShader(blob->GetBufferPointer(), blob->GetBufferSize(), nullptr, pImpl->m_pVertexShader3D.GetAddressOf()));
// 创建顶点布局(3D)
HR(device->CreateInputLayout(VertexPosNormalTex::inputLayout, ARRAYSIZE(VertexPosNormalTex::inputLayout),
blob->GetBufferPointer(), blob->GetBufferSize(), pImpl->m_pVertexLayout3D.GetAddressOf()));
// 创建像素着色器(3D)
HR(CreateShaderFromFile(L"HLSL\\Basic_PS_3D.cso", L"HLSL\\Basic_PS_3D.hlsl", "PS_3D", "ps_5_0", blob.ReleaseAndGetAddressOf()));
HR(device->CreatePixelShader(blob->GetBufferPointer(), blob->GetBufferSize(), nullptr, pImpl->m_pPixelShader3D.GetAddressOf()));
pImpl->m_pCBuffers.assign({
&pImpl->m_CBDrawing,
&pImpl->m_CBFrame,
&pImpl->m_CBStates,
&pImpl->m_CBOnResize,
&pImpl->m_CBRarely});
// 创建常量缓冲区
for (auto& pBuffer : pImpl->m_pCBuffers)
{
HR(pBuffer->CreateBuffer(device));
}
return true;
}
各种渲染状态的切换
下面所有的渲染模式使用的是线性Wrap采样器。
BasicEffect::SetRenderDefault方法--默认渲染
BasicEffect::SetRenderDefault方法使用了默认的3D像素着色器和顶点着色器,并且其余各状态都保留使用默认状态:
void BasicEffect::SetRenderDefault(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext)
{
deviceContext->IASetPrimitiveTopology(D3D11_PRIMITIVE_TOPOLOGY_TRIANGLELIST);
deviceContext->IASetInputLayout(pImpl->m_pVertexLayout3D.Get());
deviceContext->VSSetShader(pImpl->m_pVertexShader3D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->RSSetState(nullptr);
deviceContext->PSSetShader(pImpl->m_pPixelShader3D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->PSSetSamplers(0, 1, RenderStates::SSLinearWrap.GetAddressOf());
deviceContext->OMSetDepthStencilState(nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->OMSetBlendState(nullptr, nullptr, 0xFFFFFFFF);
}
BasicEffect::SetRenderAlphaBlend方法--Alpha透明混合渲染
该绘制模式关闭了光栅化裁剪,并采用透明混合方式。
void BasicEffect::SetRenderAlphaBlend(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext)
{
deviceContext->IASetPrimitiveTopology(D3D11_PRIMITIVE_TOPOLOGY_TRIANGLELIST);
deviceContext->IASetInputLayout(pImpl->m_pVertexLayout3D.Get());
deviceContext->VSSetShader(pImpl->m_pVertexShader3D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->RSSetState(RenderStates::RSNoCull.Get());
deviceContext->PSSetShader(pImpl->m_pPixelShader3D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->PSSetSamplers(0, 1, RenderStates::SSLinearWrap.GetAddressOf());
deviceContext->OMSetDepthStencilState(nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->OMSetBlendState(RenderStates::BSTransparent.Get(), nullptr, 0xFFFFFFFF);
}
BasicEffect::SetRenderNoDoubleBlend方法--无重复混合(单次混合)
该绘制模式用于绘制阴影,防止过度混合。需要指定绘制区域的模板值。
void BasicEffect::SetRenderNoDoubleBlend(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext, UINT stencilRef)
{
deviceContext->IASetPrimitiveTopology(D3D11_PRIMITIVE_TOPOLOGY_TRIANGLELIST);
deviceContext->IASetInputLayout(pImpl->m_pVertexLayout3D.Get());
deviceContext->VSSetShader(pImpl->m_pVertexShader3D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->RSSetState(RenderStates::RSNoCull.Get());
deviceContext->PSSetShader(pImpl->m_pPixelShader3D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->PSSetSamplers(0, 1, RenderStates::SSLinearWrap.GetAddressOf());
deviceContext->OMSetDepthStencilState(RenderStates::DSSNoDoubleBlend.Get(), stencilRef);
deviceContext->OMSetBlendState(RenderStates::BSTransparent.Get(), nullptr, 0xFFFFFFFF);
}
BasicEffect::SetWriteStencilOnly方法--仅写入模板值
该模式用于向模板缓冲区写入用户指定的模板值,并且不写入到深度缓冲区和后备缓冲区。
void BasicEffect::SetWriteStencilOnly(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext, UINT stencilRef)
{
deviceContext->IASetPrimitiveTopology(D3D11_PRIMITIVE_TOPOLOGY_TRIANGLELIST);
deviceContext->IASetInputLayout(pImpl->m_pVertexLayout3D.Get());
deviceContext->VSSetShader(pImpl->m_pVertexShader3D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->RSSetState(nullptr);
deviceContext->PSSetShader(pImpl->m_pPixelShader3D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->PSSetSamplers(0, 1, RenderStates::SSLinearWrap.GetAddressOf());
deviceContext->OMSetDepthStencilState(RenderStates::DSSWriteStencil.Get(), stencilRef);
deviceContext->OMSetBlendState(RenderStates::BSNoColorWrite.Get(), nullptr, 0xFFFFFFFF);
}
BasicEffect::SetRenderDefaultWithStencil方法--对指定模板值区域进行常规绘制
该模式下,仅对模板缓冲区的模板值和用户指定的相等的区域进行常规绘制。
void BasicEffect::SetRenderDefaultWithStencil(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext, UINT stencilRef)
{
deviceContext->IASetPrimitiveTopology(D3D11_PRIMITIVE_TOPOLOGY_TRIANGLELIST);
deviceContext->IASetInputLayout(pImpl->m_pVertexLayout3D.Get());
deviceContext->VSSetShader(pImpl->m_pVertexShader3D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->RSSetState(RenderStates::RSCullClockWise.Get());
deviceContext->PSSetShader(pImpl->m_pPixelShader3D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->PSSetSamplers(0, 1, RenderStates::SSLinearWrap.GetAddressOf());
deviceContext->OMSetDepthStencilState(RenderStates::DSSDrawWithStencil.Get(), stencilRef);
deviceContext->OMSetBlendState(nullptr, nullptr, 0xFFFFFFFF);
}
BasicEffect::SetRenderAlphaBlendWithStencil方法--对指定模板值区域进行Alpha透明混合绘制
该模式下,仅对模板缓冲区的模板值和用户指定的相等的区域进行Alpha透明混合绘制。
void BasicEffect::SetRenderAlphaBlendWithStencil(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext, UINT stencilRef)
{
deviceContext->IASetPrimitiveTopology(D3D11_PRIMITIVE_TOPOLOGY_TRIANGLELIST);
deviceContext->IASetInputLayout(pImpl->m_pVertexLayout3D.Get());
deviceContext->VSSetShader(pImpl->m_pVertexShader3D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->RSSetState(RenderStates::RSNoCull.Get());
deviceContext->PSSetShader(pImpl->m_pPixelShader3D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->PSSetSamplers(0, 1, RenderStates::SSLinearWrap.GetAddressOf());
deviceContext->OMSetDepthStencilState(RenderStates::DSSDrawWithStencil.Get(), stencilRef);
deviceContext->OMSetBlendState(RenderStates::BSTransparent.Get(), nullptr, 0xFFFFFFFF);
}
BasicEffect::Set2DRenderDefault方法--2D默认绘制
该模式使用的是2D顶点着色器和像素着色器,并修改为2D输入布局。
void BasicEffect::Set2DRenderDefault(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext)
{
deviceContext->IASetPrimitiveTopology(D3D11_PRIMITIVE_TOPOLOGY_TRIANGLELIST);
deviceContext->IASetInputLayout(pImpl->m_pVertexLayout2D.Get());
deviceContext->VSSetShader(pImpl->m_pVertexShader2D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->RSSetState(nullptr);
deviceContext->PSSetShader(pImpl->m_pPixelShader2D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->PSSetSamplers(0, 1, RenderStates::SSLinearWrap.GetAddressOf());
deviceContext->OMSetDepthStencilState(nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->OMSetBlendState(nullptr, nullptr, 0xFFFFFFFF);
}
BasicEffect::Set2DRenderAlphaBlend方法--2D透明混合绘制
相比上面,多了透明混合状态。
void BasicEffect::Set2DRenderAlphaBlend(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext)
{
deviceContext->IASetPrimitiveTopology(D3D11_PRIMITIVE_TOPOLOGY_TRIANGLELIST);
deviceContext->IASetInputLayout(pImpl->m_pVertexLayout2D.Get());
deviceContext->VSSetShader(pImpl->m_pVertexShader2D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->RSSetState(RenderStates::RSNoCull.Get());
deviceContext->PSSetShader(pImpl->m_pPixelShader2D.Get(), nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->PSSetSamplers(0, 1, RenderStates::SSLinearWrap.GetAddressOf());
deviceContext->OMSetDepthStencilState(nullptr, 0);
deviceContext->OMSetBlendState(RenderStates::BSTransparent.Get(), nullptr, 0xFFFFFFFF);
}
更新常量缓冲区
下面这些所有的方法会更新CBufferObject中的临时数据,数据脏标记被设为true:
void XM_CALLCONV BasicEffect::SetWorldMatrix(DirectX::FXMMATRIX W)
{
auto& cBuffer = pImpl->m_CBDrawing;
cBuffer.data.world = XMMatrixTranspose(W);
cBuffer.data.worldInvTranspose = XMMatrixInverse(nullptr, W); // 两次转置抵消
pImpl->m_IsDirty = cBuffer.isDirty = true;
}
void XM_CALLCONV BasicEffect::SetViewMatrix(FXMMATRIX V)
{
auto& cBuffer = pImpl->m_CBFrame;
cBuffer.data.view = XMMatrixTranspose(V);
pImpl->m_IsDirty = cBuffer.isDirty = true;
}
void XM_CALLCONV BasicEffect::SetProjMatrix(FXMMATRIX P)
{
auto& cBuffer = pImpl->m_CBOnResize;
cBuffer.data.proj = XMMatrixTranspose(P);
pImpl->m_IsDirty = cBuffer.isDirty = true;
}
void XM_CALLCONV BasicEffect::SetReflectionMatrix(FXMMATRIX R)
{
auto& cBuffer = pImpl->m_CBRarely;
cBuffer.data.reflection = XMMatrixTranspose(R);
pImpl->m_IsDirty = cBuffer.isDirty = true;
}
void XM_CALLCONV BasicEffect::SetShadowMatrix(FXMMATRIX S)
{
auto& cBuffer = pImpl->m_CBRarely;
cBuffer.data.shadow = XMMatrixTranspose(S);
pImpl->m_IsDirty = cBuffer.isDirty = true;
}
void XM_CALLCONV BasicEffect::SetRefShadowMatrix(DirectX::FXMMATRIX RefS)
{
auto& cBuffer = pImpl->m_CBRarely;
cBuffer.data.refShadow = XMMatrixTranspose(RefS);
pImpl->m_IsDirty = cBuffer.isDirty = true;
}
void BasicEffect::SetDirLight(size_t pos, const DirectionalLight & dirLight)
{
auto& cBuffer = pImpl->m_CBRarely;
cBuffer.data.dirLight[pos] = dirLight;
pImpl->m_IsDirty = cBuffer.isDirty = true;
}
void BasicEffect::SetPointLight(size_t pos, const PointLight & pointLight)
{
auto& cBuffer = pImpl->m_CBRarely;
cBuffer.data.pointLight[pos] = pointLight;
pImpl->m_IsDirty = cBuffer.isDirty = true;
}
void BasicEffect::SetSpotLight(size_t pos, const SpotLight & spotLight)
{
auto& cBuffer = pImpl->m_CBRarely;
cBuffer.data.spotLight[pos] = spotLight;
pImpl->m_IsDirty = cBuffer.isDirty = true;
}
void BasicEffect::SetMaterial(const Material & material)
{
auto& cBuffer = pImpl->m_CBDrawing;
cBuffer.data.material = material;
pImpl->m_IsDirty = cBuffer.isDirty = true;
}
void BasicEffect::SetTexture(ID3D11ShaderResourceView * m_pTexture)
{
pImpl->m_pTexture = m_pTexture;
}
void XM_CALLCONV BasicEffect::SetEyePos(FXMVECTOR eyePos)
{
auto& cBuffer = pImpl->m_CBFrame;
cBuffer.data.eyePos = eyePos;
pImpl->m_IsDirty = cBuffer.isDirty = true;
}
void BasicEffect::SetReflectionState(bool isOn)
{
auto& cBuffer = pImpl->m_CBStates;
cBuffer.data.isReflection = isOn;
pImpl->m_IsDirty = cBuffer.isDirty = true;
}
void BasicEffect::SetShadowState(bool isOn)
{
auto& cBuffer = pImpl->m_CBStates;
cBuffer.data.isShadow = isOn;
pImpl->m_IsDirty = cBuffer.isDirty = true;
}
BasicEffect::Apply方法--应用缓冲区、纹理资源并进行更新
BasicEffect::Apply首先将所需要用到的缓冲区绑定到渲染管线上,并设置纹理,然后才是视情况更新常量缓冲区。
下面的缓冲区数组索引值同时也对应了之前编译期指定的startSlot值。
首先检验总的脏标记是否为true,若有任意数据被修改,则检验每个常量缓冲区的脏标记,并根据该标记决定是否要更新常量缓冲区。
void BasicEffect::Apply(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext)
{
auto& pCBuffers = pImpl->m_pCBuffers;
// 将缓冲区绑定到渲染管线上
pCBuffers[0]->BindVS(deviceContext);
pCBuffers[1]->BindVS(deviceContext);
pCBuffers[2]->BindVS(deviceContext);
pCBuffers[3]->BindVS(deviceContext);
pCBuffers[4]->BindVS(deviceContext);
pCBuffers[0]->BindPS(deviceContext);
pCBuffers[1]->BindPS(deviceContext);
pCBuffers[2]->BindPS(deviceContext);
pCBuffers[4]->BindPS(deviceContext);
// 设置纹理
deviceContext->PSSetShaderResources(0, 1, pImpl->m_pTexture.GetAddressOf());
if (pImpl->m_IsDirty)
{
pImpl->m_IsDirty = false;
for (auto& pCBuffer : pCBuffers)
{
pCBuffer->UpdateBuffer(deviceContext);
}
}
}
当然,目前BasicEffect能做的事情还是比较有限的,并且还需要随着HLSL代码的变动而随之调整。更多的功能会在后续教程中实现。
绘制平面阴影
使用XMMatrixShadow可以生成阴影矩阵,根据光照类型和位置对几何体投影到平面上的。
XMMATRIX XMMatrixShadow(
FXMVECTOR ShadowPlane, // 平面向量(nx, ny, nz, d)
FXMVECTOR LightPosition); // w = 0时表示平行光方向, w = 1时表示光源位置
通常指定的平面会稍微比实际平面高那么一点点,以避免深度缓冲区资源争夺导致阴影显示有问题。
使用模板缓冲区防止过度混合
一个物体投影到平面上时,投影区域的某些位置可能位于多个三角形之内,这会导致这些位置会有多个像素通过测试并进行混合操作,渲染的次数越多,显示的颜色会越黑。
我们可以使用模板缓冲区来解决这个问题。
- 在之前的例子中,我们用模板值为0的区域表示非镜面反射区,模板值为1的区域表示为镜面反射区;
- 使用
RenderStates::DSSNoDoubleBlend的深度模板状态,当给定的模板值和深度/模板缓冲区的模板值一致时,通过模板测试并对模板值加1,绘制该像素的混合,然后下一次由于给定的模板值比深度/模板缓冲区的模板值小1,不会再通过模板测试,也就阻挡了后续像素的绘制; - 应当先绘制镜面的阴影区域,再绘制正常的阴影区域。
着色器代码的变化
Basic_PS_2D.hlsl文件变化如下:
#include "Basic.hlsli"
// 像素着色器(2D)
float4 PS_2D(VertexPosHTex pIn) : SV_Target
{
float4 color = g_Tex.Sample(g_Sam, pIn.Tex);
clip(color.a - 0.1f);
return color;
}
Basic_PS_3D.hlsl文件变化如下:
#include "Basic.hlsli"
// 像素着色器(3D)
// 像素着色器(3D)
float4 PS_3D(VertexPosHWNormalTex pIn) : SV_Target
{
// 提前进行裁剪,对不符合要求的像素可以避免后续运算
float4 texColor = g_Tex.Sample(g_Sam, pIn.Tex);
clip(texColor.a - 0.1f);
// 标准化法向量
pIn.NormalW = normalize(pIn.NormalW);
// 顶点指向眼睛的向量
float3 toEyeW = normalize(g_EyePosW - pIn.PosW);
// 初始化为0
float4 ambient = float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
float4 diffuse = float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
float4 spec = float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
float4 A = float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
float4 D = float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
float4 S = float4(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
int i;
[unroll]
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
DirectionalLight dirLight = g_DirLight[i];
[flatten]
if (g_IsReflection)
{
dirLight.Direction = mul(dirLight.Direction, (float3x3) (g_Reflection));
}
ComputeDirectionalLight(g_Material, g_DirLight[i], pIn.NormalW, toEyeW, A, D, S);
ambient += A;
diffuse += D;
spec += S;
}
// 若当前在绘制反射物体,需要对光照进行反射矩阵变换
PointLight pointLight;
[unroll]
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
pointLight = g_PointLight[i];
[flatten]
if (g_IsReflection)
{
pointLight.Position = (float3) mul(float4(pointLight.Position, 1.0f), g_Reflection);
}
ComputePointLight(g_Material, pointLight, pIn.PosW, pIn.NormalW, toEyeW, A, D, S);
ambient += A;
diffuse += D;
spec += S;
}
SpotLight spotLight;
// 若当前在绘制反射物体,需要对光照进行反射矩阵变换
[unroll]
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
spotLight = g_SpotLight[i];
[flatten]
if (g_IsReflection)
{
spotLight.Position = (float3) mul(float4(spotLight.Position, 1.0f), g_Reflection);
spotLight.Direction = mul(spotLight.Direction, (float3x3) g_Reflection);
}
ComputeSpotLight(g_Material, spotLight, pIn.PosW, pIn.NormalW, toEyeW, A, D, S);
ambient += A;
diffuse += D;
spec += S;
}
float4 litColor = texColor * (ambient + diffuse) + spec;
litColor.a = texColor.a * g_Material.Diffuse.a;
return litColor;
}
Basic_VS_2D.hlsl变化如下:
#include "Basic.hlsli"
// 顶点着色器(2D)
VertexPosHTex VS_2D(VertexPosTex vIn)
{
VertexPosHTex vOut;
vOut.PosH = float4(vIn.PosL, 1.0f);
vOut.Tex = vIn.Tex;
return vOut;
}
Basic_VS_3D.hlsl变化如下:
#include "Basic.hlsli"
// 顶点着色器(3D)
VertexPosHWNormalTex VS_3D(VertexPosNormalTex vIn)
{
VertexPosHWNormalTex vOut;
matrix viewProj = mul(g_View, g_Proj);
float4 posW = mul(float4(vIn.PosL, 1.0f), g_World);
float3 normalW = mul(vIn.NormalL, (float3x3) g_WorldInvTranspose);
// 若当前在绘制反射物体,先进行反射操作
[flatten]
if (g_IsReflection)
{
posW = mul(posW, g_Reflection);
normalW = mul(normalW, (float3x3) g_Reflection);
}
// 若当前在绘制阴影,先进行投影操作
[flatten]
if (g_IsShadow)
{
posW = (g_IsReflection ? mul(posW, g_RefShadow) : mul(posW, g_Shadow));
}
vOut.PosH = mul(posW, viewProj);
vOut.PosW = posW.xyz;
vOut.NormalW = normalW;
vOut.Tex = vIn.Tex;
return vOut;
}
GameObject类与BasicEffect类的对接
由于GameObject类也承担了绘制方法,那么最后的Apply也需要交给游戏对象来调用。因此GameObject::Draw方法变更如下:
void GameObject::Draw(ID3D11DeviceContext * deviceContext, BasicEffect& effect)
{
// 设置顶点/索引缓冲区
UINT strides = m_VertexStride;
UINT offsets = 0;
deviceContext->IASetVertexBuffers(0, 1, m_pVertexBuffer.GetAddressOf(), &strides, &offsets);
deviceContext->IASetIndexBuffer(m_pIndexBuffer.Get(), DXGI_FORMAT_R32_UINT, 0);
// 更新数据并应用
effect.SetWorldMatrix(m_Transform.GetLocalToWorldMatrixXM());
effect.SetTexture(m_pTexture.Get());
effect.SetMaterial(m_Material);
effect.Apply(deviceContext);
deviceContext->DrawIndexed(m_IndexCount, 0, 0);
}
场景绘制
现在场景只有墙体、地板、木箱和镜面。
第1步: 镜面区域写入模板缓冲区
// *********************
// 1. 给镜面反射区域写入值1到模板缓冲区
//
m_BasicEffect.SetWriteStencilOnly(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), 1);
m_Mirror.Draw(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), m_BasicEffect);
第2步: 绘制不透明的反射物体
// ***********************
// 2. 绘制不透明的反射物体
//
// 开启反射绘制
m_BasicEffect.SetReflectionState(true);
m_BasicEffect.SetRenderDefaultWithStencil(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), 1);
m_Walls[2].Draw(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), m_BasicEffect);
m_Walls[3].Draw(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), m_BasicEffect);
m_Walls[4].Draw(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), m_BasicEffect);
m_Floor.Draw(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), m_BasicEffect);
m_WoodCrate.Draw(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), m_BasicEffect);
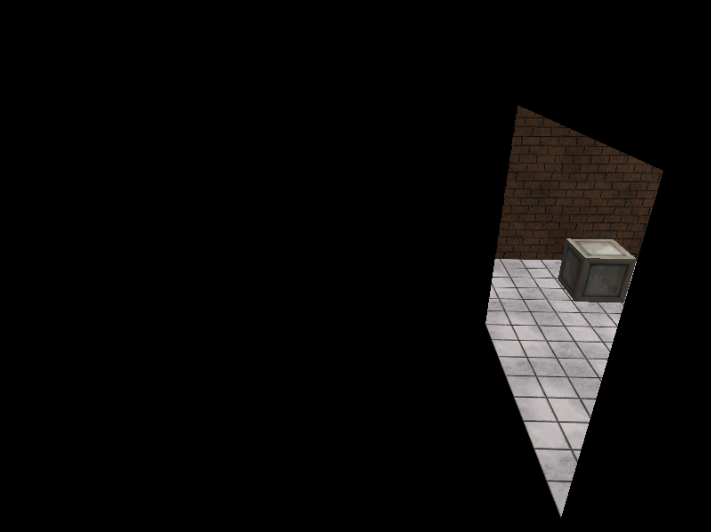
第3步: 绘制不透明反射物体的阴影
// ***********************
// 3. 绘制不透明反射物体的阴影
//
m_WoodCrate.SetMaterial(m_ShadowMat);
m_BasicEffect.SetShadowState(true); // 反射开启,阴影开启
m_BasicEffect.SetRenderNoDoubleBlend(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), 1);
m_WoodCrate.Draw(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), m_BasicEffect);
// 恢复到原来的状态
m_BasicEffect.SetShadowState(false);
m_WoodCrate.SetMaterial(m_WoodCrateMat);
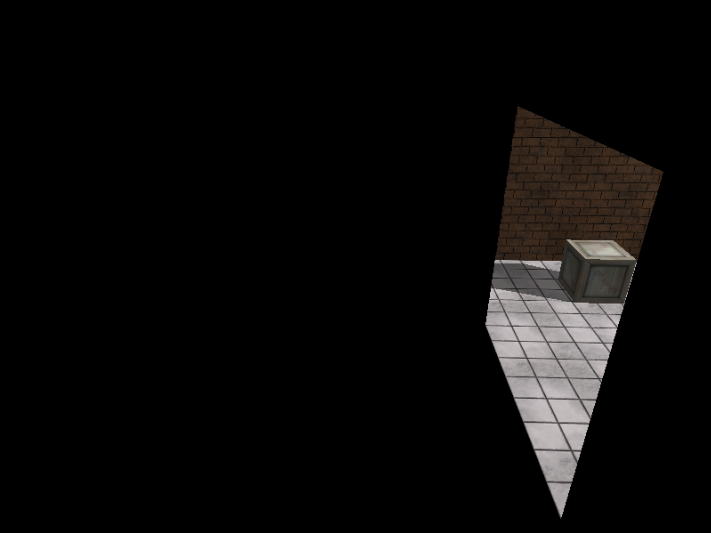
第4步: 绘制透明镜面
// ***********************
// 4. 绘制透明镜面
//
// 关闭反射绘制
m_BasicEffect.SetReflectionState(false);
m_BasicEffect.SetRenderAlphaBlendWithStencil(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), 1);
m_Mirror.Draw(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), m_BasicEffect);
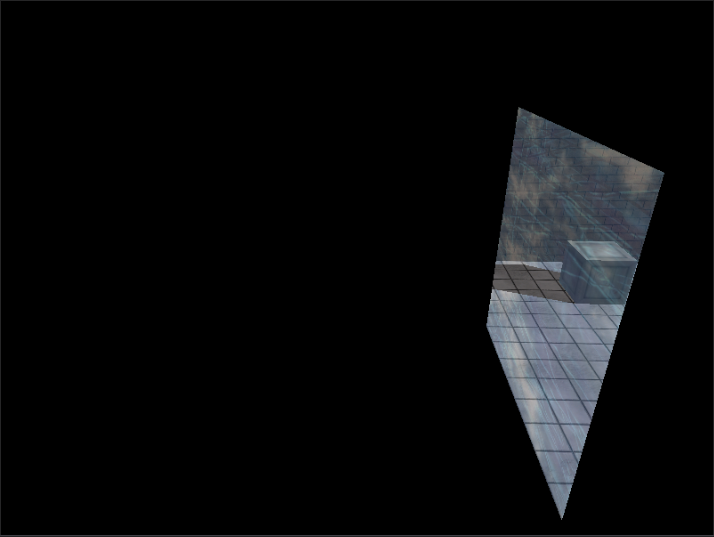
第5步:绘制不透明的正常物体
// ************************
// 5. 绘制不透明的正常物体
//
m_BasicEffect.SetRenderDefault(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get());
for (auto& wall : m_Walls)
wall.Draw(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), m_BasicEffect);
m_Floor.Draw(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), m_BasicEffect);
m_WoodCrate.Draw(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), m_BasicEffect);
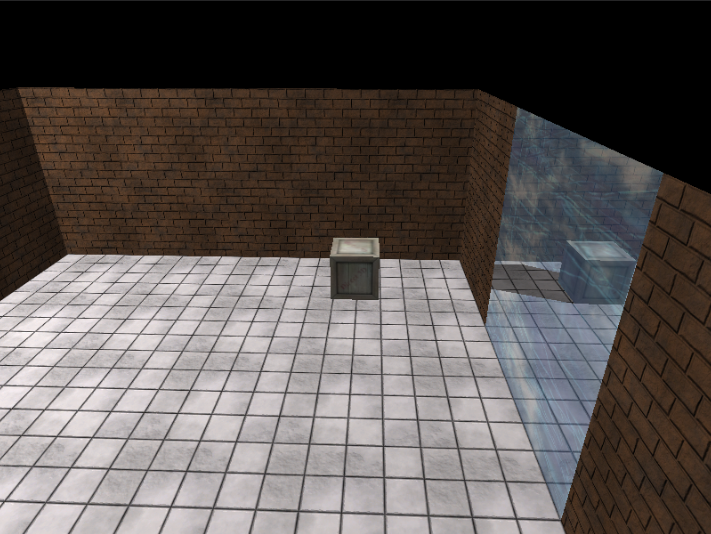
第6步:绘制不透明正常物体的阴影
// ************************
// 6. 绘制不透明正常物体的阴影
//
m_WoodCrate.SetMaterial(m_ShadowMat);
m_BasicEffect.SetShadowState(true); // 反射关闭,阴影开启
m_BasicEffect.SetRenderNoDoubleBlend(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), 0);
m_WoodCrate.Draw(m_pd3dImmediateContext.Get(), m_BasicEffect);
m_BasicEffect.SetShadowState(false); // 阴影关闭
m_WoodCrate.SetMaterial(m_WoodCrateMat);
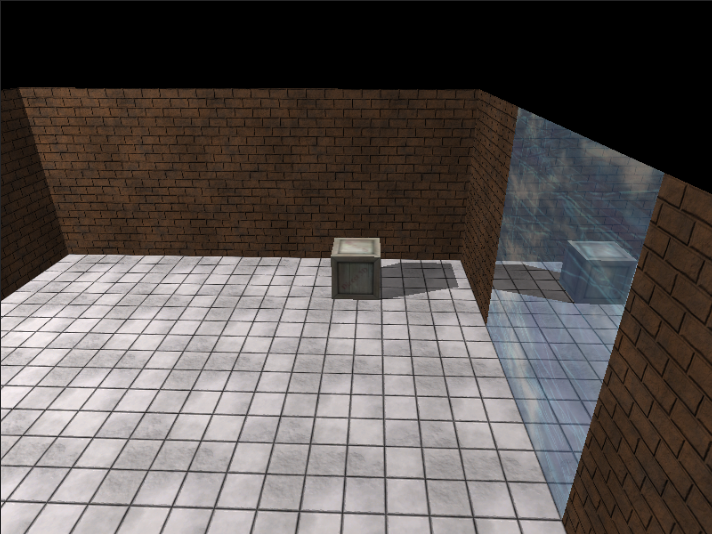
最终绘制效果如下:
注意该样例只生成点光灯到地板的阴影。你可以用各种摄像机模式来进行测试。
DirectX11 With Windows SDK完整目录
欢迎加入QQ群: 727623616 可以一起探讨DX11,以及有什么问题也可以在这里汇报。
DirectX11 With Windows SDK--13 动手实现一个简易Effects框架、阴影效果绘制的更多相关文章
- 粒子系统与雨的效果 (DirectX11 with Windows SDK)
前言 最近在学粒子系统,看这之前的<<3D图形编程基础 基于DirectX 11 >>是基于Direct SDK的,而DXSDK微软已经很久没有更新过了并且我学的DX11是用W ...
- DirectX11--深入理解Effects11、使用着色器反射机制(Shader Reflection)实现一个复杂Effects框架
前言 如果之前你是跟随本教程系列学习的话,应该能够初步了解Effects11(现FX11)的实现机制,并且可以编写一个简易的特效管理框架,但是随着特效种类的增多,要管理的着色器.资源等也随之变多.如果 ...
- 自行实现一个简易RPC框架
10分钟写一个RPC框架 1.RpcFramework package com.alibaba.study.rpc.framework; import java.io.ObjectInputStrea ...
- 自己动手搭建一个简易的SpringBoot环境
什么是springboot? Spring Boot俗称微服务.Spring Boot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程.该框架使用了特 ...
- 自己动手写一个简易对象关系映射,ORM(单例版和数据库池版)
准备知识 DBUtils模块 <<-----重点 DBUtils是Python的一个用于实现数据库连接池的模块 此连接池有两种连接模式: DBUtils提供两种外部接口: Persist ...
- 笔记:学习go语言的网络基础库,并尝试搭一个简易Web框架
在日常的 web 开发中,后端人员常基于现有的 web 框架进行开发.但单纯会用框架总感觉不太踏实,所以有空的时候还是看看这些框架是怎么实现的会比较好,万一要排查问题也快一些. 最近在学习 go 语言 ...
- 从零实现一个简易jQuery框架之一—jQuery框架概述
我们知道,不管学习任何一门框架,了解其设计的理念.目的.总体的结构及核心特性对我们使用和后续的深入理解框架都是有很大的帮助的.因此在这里先梳理一下本人对jQuery框架的一些理解. 设计目的(为什么要 ...
- DirectX11 With Windows SDK--00 目录
前言 (更新于 2019/4/10) 从第一次接触DirectX 11到现在已经有将近两年的时间了.还记得前年暑假被要求学习DirectX 11,在用龙书的源码配置项目运行环境的时候都花了好几天的时间 ...
- DirectX11 With Windows SDK--14 深度测试
前言 当使用加法/减法/乘法颜色混合,或者使用透明混合的时候,在经过深度测试时可能会引发一些问题.例如现在我们需要使用加法混合来绘制一系列对象,而这些对象彼此之间不会相互阻挡.若我们仍使用原来的深度测 ...
随机推荐
- Linux 用户关联命令
在执行useradd命令创建用户时,它首先读取/etc/default/useradd文件的配置参数,然后通过这些参数来配置新创建的用户,如创建名为luser的用户. [root@rhl5 -]# u ...
- nohup ./startWebLogic.sh >out.log 2>&1 & 解析
在启动weblogic的时候我们经常看到如下的命令: nohup ./startWebLogic.sh >out.log 2>&1 & 从09年开始用weblogic到现在 ...
- typeScript函数篇
typeScript的函数是在es6的函数特性的基础上加了一些后端的概念:泛型.参数类型声明.返回值类型声明.重载.装饰器等.其他的一些特性:箭头函数.生成器.async-await.promise等 ...
- SpringCloud(2)服务消费者(rest+ribbon)
1.准备工作 这一篇文章基于上一篇文章的工程.启动eureka-server 工程,端口为 8761.分别以端口 8762 和 8763 启动 service-hi 工程.访问 localhost:8 ...
- TypeError: sequence item 1: expected str instance, int found
Error Msg Traceback (most recent call last): File "E:/code/adva_code/my_orm.py", line 108, ...
- 全局css控制<td>标签属性
td { text-align: center; /*设置水平居中*/ vertical-align: middle; /*设置垂直居中*/ height:50px; / ...
- 小程序——阿里服务器配置https及什么是IIS
1.申请域名:阿里云 2.免费开启SSL证书:管理=>免费开启SSL证书>单域名>dev.xxx.top 3.配置服务器:下载=>IIS7证书 *注册一个域名,可以免费开启一个 ...
- Linux中什么是动态网站环境及如何部署
当谈论起网站时,我们可能听说过静态和动态这两个词,但却不知道它们的含义,或者从字面意思了解一些却不知道它们的区别. 这一切可以追溯到网站和网络应用程序,Web应用程序是一个网站,但很多网站不是Web应 ...
- springboot打jar包正常无法访问页面
网上看到太多说版本换成 1.4.2.RELEASE. 可以将程序打成war包发布, 1.启动类改为 @Overrideprotected SpringApplicationBuilder config ...
- Java的clone():深复制与浅复制
Java中要想自定义类的对象可以被复制,自定义类就必须实现Cloneable中的clone()方法,如下: public class Student implements Cloneable { pr ...
