题解——CodeForces 438D The Child and Sequence
题面
4 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]. Then he should perform a sequence of m operations. An operation can be one of the following:
- Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of
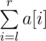 .
. - Modulo operation l, r, x. Picks should perform assignment a[i] = a[i] mod x for each i (l ≤ i ≤ r).
- Set operation k, x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in other words perform an assignment a[k] = x).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
The first line of input contains two integer: n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105). The second line contains n integers, separated by space: a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) — initial value of array elements.
Each of the next m lines begins with a number type 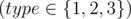 .
.
- If type = 1, there will be two integers more in the line: l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n), which correspond the operation 1.
- If type = 2, there will be three integers more in the line: l, r, x (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 2.
- If type = 3, there will be two integers more in the line: k, x (1 ≤ k ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 3.
For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
5 5
1 2 3 4 5
2 3 5 4
3 3 5
1 2 5
2 1 3 3
1 1 3
8
5
10 10
6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5
1 3 9
2 7 10 9
2 5 10 8
1 4 7
3 3 7
2 7 9 9
1 2 4
1 6 6
1 5 9
3 1 10
49
15
23
1
9
Consider the first testcase:
- At first, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
- After operation 1, a = {1, 2, 3, 0, 1}.
- After operation 2, a = {1, 2, 5, 0, 1}.
- At operation 3, 2 + 5 + 0 + 1 = 8.
- After operation 4, a = {1, 2, 2, 0, 1}.
- At operation 5, 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
简洁的题目翻译(取自luogu)
给定数列,区间查询和,区间取模,单点修改。
n,m小于10^5
题解
相当裸的一道线段树,但是思路相当神奇
首先我们会注意到,这题有要求区间修改和区间查询,学过线段树的神犇们可能就立刻会想到一系列诸如标记永久化,打lazytag等一系列高端操作来维护这颗线段树
但是实际上不用这样做哒qwq
否则你可能会像本蒟蒻一样在这道题上卡了一个半小时还一分都拿不到
因为这道题实际上是区间取模,取模实际上没办法像加法乘法一样做到利用一些lazytag的奇怪的做法把复杂度压成O(nlogn)
那么怎么做呢?
第四句话给了提示qwq
就是对要取模的区间暴力单点修改就行
这时候就有人要问了,这样暴力复杂度不对吧,当然不能,所以我们需要加一些玄学优化
首先我们要证明一些奇怪的东西
引理1:对一个数取模,如果能够取模,那么这个数至少会变成原来的\( \frac{1}{2} \),这非常的显然,所以我就懒得证明了23333
还是简单的证明一下,如果一个数能够被取模,则取模后它一定会变成小于模数的形式,如果模数大于原数的\( \frac {1}{2} \)则取模后结果一定会小于原数减去模数即结果一定小于原数的\( \frac {1}{2} \) ,现在考虑另一种情况,若模数小于原数的\( \frac {1}{2} \),则取模后的结果一定会小于模数,即结果一定小于等于原数的\( \frac {1}{2} \)
所以现在得证,一个数取模后规模至少缩小\( \frac{1}{2} \)
然后我们继续证明一些性质
引理2:若一个数被取模,则至多取模\( \lg N \)次
由引理1可知,一个数每次被取模规模都会缩小\( \frac{1}{2}\),所以只需要取模\( \lg N \)次就不可以继续取模了
现在有了这两个性质,我们再进行一些合理的猜想
取模运算很慢,那么为了减少运行时间,我们在能够不取模的时候应当不取模
引理3:若一个数小于模数,那么这个数取模后的结果和原数相等
显然,根据模除的性质,若这个数小于模数,那么除法运算最后的余数一定与原数相等
既然可能相等,我们就在出现相等情况时不取模就好了
因此,我们再在区间和之外多维护一个区间最大值即可,当模数大于区间最大值时,不对这个区间进行取模操作
下面就可以进行复杂度证明了
复杂度:O(nlogn)
证明:总共有n个数,因为一旦取模后结果可能不变就不会继续取模,所以每个数最多被取模\( \lg N \)次,所以最终的取模次数最多为nlogn次,时间复杂度为O(nlogn)
证毕
单点修改没什么好说的,现在我们就可以任性的取模了
贴代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = ;
long long maxm[MAXN<<],sum[MAXN<<],a[MAXN];
long long n,m;
void pushup(long long o){
maxm[o]=max(maxm[o<<],maxm[o<<|]);
sum[o]=(sum[o<<]+sum[o<<|]);
}
void build(long long l,long long r,long long o){
if(l==r){
sum[o]=a[l];
maxm[o]=a[l];
return;
}
long long mid=(l+r)>>;
build(l,mid,o<<);
build(mid+,r,o<<|);
pushup(o);
}
void updateadd(long long pos,long long l,long long r,long long o,long long v){
if(l==r){
sum[o]=v;
maxm[o]=v;
return;
}
long long mid=(l+r)>>;
if(pos<=mid)
updateadd(pos,l,mid,o<<,v);
else
updateadd(pos,mid+,r,o<<|,v);
pushup(o);
}
void updatemod(long long pos,long long l,long long r,long long o,long long v){
if(l==r){
sum[o]=sum[o]%v;
maxm[o]=maxm[o]%v;
}
long long mid=(l+r)>>;
if(pos<=mid)
updatemod(pos,l,mid,o<<,v);
else
updatemod(pos,mid+,r,o<<|,v);
pushup(o);
}
long long query(long long L,long long R,long long l,long long r,long long o){
if(L<=l&&r<=R){
return sum[o];
}
long long ans=,mid=(l+r)>>;
if(L<=mid)
ans+=query(L,R,l,mid,o<<);
if(R>mid)
ans+=query(L,R,mid+,r,o<<|);
return ans;
}
void update(long long L,long long R,long long l,long long r,long long o,long long v){
if(l==r){
sum[o]=sum[o]%v;
maxm[o]=maxm[o]%v;
return;
}
long long mid=(l+r)>>;
if(L<=mid&&maxm[o<<]>=v)
update(L,R,l,mid,o<<,v);
if(R>mid&&maxm[o<<|]>=v)
update(L,R,mid+,r,o<<|,v);
pushup(o);
}
int main(){
scanf("%lld %lld",&n,&m);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
build(,n,);
for(int i=;i<=m;i++){
int mode;
scanf("%d",&mode);
if(mode==){
long long lx,rx;
scanf("%lld %lld",&lx,&rx);
printf("%lld\n",query(lx,rx,,n,));
}
else if(mode==){
long long lx,rx,x;
scanf("%lld %lld %lld",&lx,&rx,&x);
update(lx,rx,,n,,x);
}
else{
long long k,x;
scanf("%lld %lld",&k,&x);
updateadd(k,,n,,x);
}
}
return ;
}
题解——CodeForces 438D The Child and Sequence的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 438D The Child and Sequence - 线段树
At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at ...
- Codeforces 438D The Child and Sequence
题意:给定一个n个数的序列,完成以下3个操作: 1.给定区间求和 2.给定区间对x取模 3.单点修改 对一个数取模,这个数至少折半.于是我们记一个最大值max,如果x>max则不做处理. #in ...
- 2018.07.23 codeforces 438D. The Child and Sequence(线段树)
传送门 线段树维护区间取模,单点修改,区间求和. 这题老套路了,对一个数来说,每次取模至少让它减少一半,这样每次单点修改对时间复杂度的贡献就是一个log" role="presen ...
- CodeForces 438D The Child and Sequence (线段树 暴力)
传送门 题目大意: 给你一个序列,要求在序列上维护三个操作: 1)区间求和 2)区间取模 3)单点修改 这里的操作二很讨厌,取模必须模到叶子节点上,否则跑出来肯定是错的.没有操作二就是线段树水题了. ...
- 438D - The Child and Sequence
D. The Child and Sequence time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input st ...
- CF(438D) The Child and Sequence(线段树)
题意:对数列有三种操作: Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of . Modulo operation l, r, x. ...
- Codeforces 438D (今日gg模拟第二题) | 线段树 考察时间复杂度的计算 -_-|||
Codeforces 438D The Child and Sequence 给出一个序列,进行如下三种操作: 区间求和 区间每个数模x 单点修改 如果没有第二个操作的话,就是一棵简单的线段树.那么如 ...
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence 线段树 区间取摸
D. The Child and Sequence Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest ...
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence 线段树 区间求和+点修改+区间取模
D. The Child and Sequence At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his h ...
随机推荐
- sublime text3配置及相关小技巧
1.下载&安装: 官方地址:http://www.sublimetext.com/,sublime text3又更新了,支持不依赖插件进行侧边栏颜色的更改,同时自带的皮肤颜色也有四种,十分方便 ...
- C# & ASP.NET Core 入门官方资料汇总
借助给公司实习生培训事宜,整理了一些微软官方的适合新同学入门的资料,这里分享一下: 工具: Visual Studio 2017 Community 版本下载地址:https://www.visual ...
- html5-块元素和内联元素
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="UTF-8&qu ...
- 最近点对HDU1007
利用二分的方法来计算,应该是说利用分治的方法吧! 刚开始感觉时间会爆 后来发现嘎嘎居然没有 ,嗨自己算错了时间: #include <iostream> #include<cstdi ...
- 设计模式之Command(命令)(转)
Command模式是最让我疑惑的一个模式,我在阅读了很多代码后,才感觉隐约掌握其大概原理,我认为理解设计模式最主要是掌握起原理构造,这样才对自己实际编程有指导作用.Command模式实际上不是个很具体 ...
- 面试题-JAVA算法题
1.编写一个程序,输入n,求n!(用递归的方式实现). public static long fac(int n){ if(n<=0) return 0; else if(n==1) retur ...
- springboot用@Autowired和@PostConstruct注解把config配置读取到bean变成静态方法
springboot用@Autowired和@PostConstruct注解把config配置读取到bean变成静态方法 @SpringBootApplication public class Sen ...
- [转载]DLL命名规则
程序集是一个部署单元,同时还代表托管代码程序的身份.一般来说一个程序集仅与一个DLL相对应.本节主要讲DLL命名约定,程序集的命名约定与此类似. 要记住,名字空间与DLL和程序集是不同的概念.名字空间 ...
- 详解:PHP加速器配置神器opcache
什么是opcode? 当解释器完成对脚本代码的分析后,便将它们生成可以直接运行的中间代码,也称为操作码(Operate Code,opcode).Opcode cache的目地是避免重复编译,减少CP ...
- vue2+animate.css
下载animate.css并引入项目, import './css/animate.css'使用: <template> <div class="box"> ...
