Spring听课笔记(tg)AOP
好文:https://blog.csdn.net/javazejian/article/details/56267036
通过一个实例来理解
1. 需求:实现算术计算器,可以加减乘除,同时记录日志
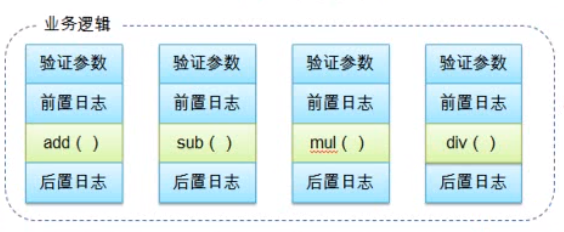
2. 实现方式:
① 高度耦合(直接pass)
② 自己实现动态代理
③ 利用Spring AOP框架
二. 自己实现动态代理
1. 定义接口及实现类:
-- 接口:ArithmeticCalculator
public interface ArithmeticCalculator {
int add(int i, int j);
int sub(int i, int j);
int mul(int i, int j);
int div(int i, int j);
}
-- 接口的实现类
public class ArithmeticCalculatorImpl implements ArithmeticCalculator{
public int add(int i, int j) {
int result = i + j;
System.out.println("[add] " + i + " + " + j + " = " + result);
return result;
}
public int sub(int i, int j) {
int result = i - j;
System.out.println("[sub] " + i + " - " + j + " = " + result);
return result;
}
public int mul(int i, int j) {
int result = i * j;
System.out.println("[mul] " + i + " * " + j + " = " + result);
return result;
}
public int div(int i, int j) {
int result = i / j;
System.out.println("[div] " + i + " / " + j + " = " + result);
return result;
}
}
-- 返回动态代理类
关键代码已经标红,利用JDK的Proxy类,加入参数,返回代理类
try-catch-finally分别对应四种通知
public class ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingProxy {
private ArithmeticCalculator target;
public ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingProxy(ArithmeticCalculator target) {
this.target = target;
}
public ArithmeticCalculator getLoggingProxy() {
ArithmeticCalculator proxy = null;
//代理对象由哪一个类加载器加载
ClassLoader loader = target.getClass().getClassLoader();
//代理对象的类型
Class[] interfaces = new Class[] {ArithmeticCalculator.class};
//调用代理对象的目标方法,并执行的代理方法
InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler() {
//proxy: 一般不用proxy中的方法,容易死循环
//method: 目标类中的方法
//args: 目标类方法的参数
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
Object result = null;
try {
System.out.println("这是前置通知...");
result = method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("这是返回通知,方法正常执行时执行...");
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("这是异常通知,方法异常时执行...");
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("这是后置通知,不论是否异常,都会执行");
}
return result;
}
};
proxy = (ArithmeticCalculator) Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, h);
return proxy;
}
}
-- 调用
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ArithmeticCalculator target = new ArithmeticCalculatorImpl();
ArithmeticCalculator proxy = new ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingProxy(target).getLoggingProxy();
proxy.add(1, 3);
System.out.println();
proxy.div(4, 2);
}
}
-- 结果(后置通知的执行顺序好像和spring aop不太一样)

三 通过Spring AOP + AspectJ注解方式
-- 配置文件(利用context和aop命名空间)
<!-- 配置bean自动扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring_1.aop"></context:component-scan> <!-- 配置aspectj起作用 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
-- 接口,实现类同前,需要注意,实现类要加到spring容器中

-- 日志切面类
需要注意,用@Component 加入到Spring IOC容器中, 用 @Aspect 让AspectJ自动扫描
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogginAspect { /**
* 定义一个方法,用于声明切入点表达式,一般的,方法中不需要其他代码
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.atguigu.spring_1.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))")
public void declareJointPointExpression() {}; /**
* 前置通知
*/
@Before("declareJointPointExpression()")
public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
// JoinPoint:链接点可以访问到方法的具体信息
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
List<Object> args = Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs());
System.out.println("前置通知: method " + methodName + " begin with arguments:" + args +"");
} /**
* 后置通知: 不论是否有异常,都会如期执行
* 但是无法访问到方法的返回值
*/
@After("declareJointPointExpression()")
public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("后置通知: method " + methodName + " end");
} /**
* 返回通知:只有正常执行时,才可以执行
* 能够访问到方法的返回值
*/
@AfterReturning(value="declareJointPointExpression()",
returning="result")
public void afterReturningMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("返回通知: method " + methodName + " end with result: " + result +"");
} /**
* 异常通知:抛出异常时执行
*/
@AfterThrowing(value="declareJointPointExpression()",
throwing="ex")
public void afterThrowingMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception ex) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("异常通知: method " + methodName + " throw an exception " + ex +"");
}
}
-- 调用
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop.xml");
ArithmeticCalculator target = ctx.getBean(ArithmeticCalculator.class);
target.add(1, 3);
System.out.println();
target.div(4, 2);
}
}
-- 结果

四)四种通知的执行顺序
没有异常:前置通知->目标方法->后置通知->返回通知
有异常: 前置通知->目标方法->后置通知->异常通知
五)后置通知和返回通知的区别
-- 后置通知(@After)不能访问到目标方法的结果,而返回通知(@AfterReturning)则可以
六)切面等基本概念的理解
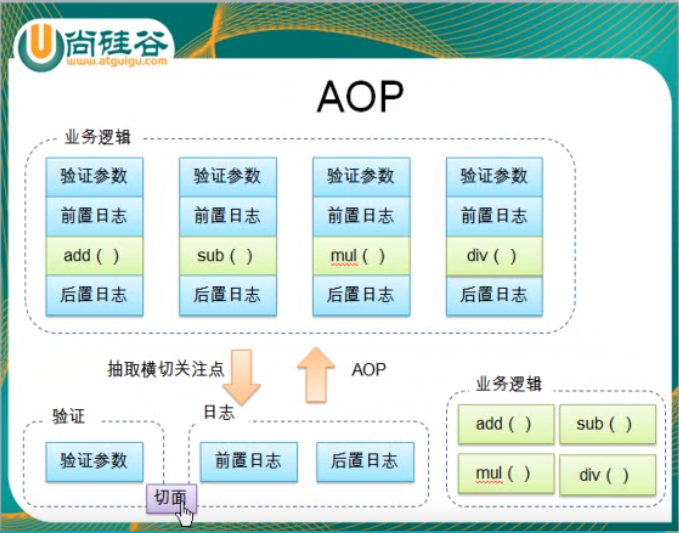

Spring听课笔记(tg)AOP的更多相关文章
- Spring学习笔记之aop动态代理(3)
Spring学习笔记之aop动态代理(3) 1.0 静态代理模式的缺点: 1.在该系统中有多少的dao就的写多少的proxy,麻烦 2.如果目标接口有方法的改动,则proxy也需要改动. Person ...
- Spring学习笔记4——AOP
AOP 即 Aspect Oriented Program 面向切面编程 首先,在面向切面编程的思想里面,把功能分为核心业务功能,和周边功能. 所谓的核心业务,比如登陆,增加数据,删除数据都叫核心业务 ...
- Spring听课笔记(tg)
0. 地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av21335209 1.综述,Spring主要的复习要点集中在以下几点 -- Spring的整体结构,Maven依赖(环境搭 ...
- Spring听课笔记(tg)2
配置Bean -- 配置形式:基于XML 文件的方式, 基于注解的方式 -- Bean的配置方式:通过全类名(反射).通过工厂方法(静态工厂方法&实例工厂方法).FactoryBean -- ...
- [Spring学习笔记 4 ] AOP 概念原理以及java动态代理
一.Spring IoC容器补充(1) Spring IoC容器,DI(依赖注入): 注入的方式:设值方法注入setter(属性注入)/构造子注入(构造函数传入依赖的对象)/字段注入Field(注解) ...
- Spring学习笔记2—AOP
1.AOP概念 AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming):面向切面编程,AOP能够将那些与业务无关,却为业务模块所共同调用的应用(例如事务处理.日志管理.权限控制等)封装起来, ...
- Spring听课笔记(专题一)
Spring入门课程:https://www.imooc.com/learn/196 第0章: Spring是为解决企业应用程序开发复杂性而创建的一个Java开源框架,应用非常广泛.业内非常流行的SS ...
- Spring学习笔记之AOP配置篇(一)
[TOC] 1. 创建并声明一个切面 首先,创建一个类,添加@Component注解使其添加到IoC容器 然后,添加@Aspect注解,使其成为一个切面 最后,在配置文件里面,使用<aop:as ...
- Spring听课笔记(专题二下)
第4章 Spring Bean基于注解的装配 4.1 Bean的定义及作用域的注解实现 1. Bean定义的注解 -- @Component是一个通用注解,可用于任何bean -- @Reposito ...
随机推荐
- jsonp详解及跨域请求
什么是JSONP? JSON是一种轻量级的数据传输格式语言,被广泛应用于当前Web应用中.JSON格式数据的编码和解析基本在所有主流语言中都被实现,所以现在大部分前后端分离的架构都以JSON格式进行数 ...
- python的22个基本语法
"人生苦短,我用Python".Python编程语言是最容易学习.并且功能强大的语言.只需会微信聊天.懂一点英文单词即可学会Python编程语言.但是很多人声称自己精通Python ...
- java中string、stringBuild、stringBuffer的区别
(1)string 1,Stirng是对象不是基本数据类型 2,String是final类,不能被继承.是不可变对象,一旦创建,就不能修改它的值. 3,对于已经存在的Sti ...
- JavaScript正则表达式详解
在JavaScript中,正则表达式由RegExp对象表示.RegExp对象呢,又可以通过直接量和构造函数RegExp两种方式创建,分别如下: //直接量 var re = /pattern/[g | ...
- try catch finally语句块中存在return语句时的执行情况剖析
2种场景 (1) try中有return,finally中没有return(注意会改变返回值的情形);(2) try中有return,finally中有return; 场景代码分析(idea亲测) 场 ...
- 结合MATLAB、Python、R语言,在求得显著差异的边(节点对)之后,怎么画circle图
先来看看成果图: OK,开始画图: 实验背景声明:在脑影像分析中,我们首先构建脑网络,然 ...
- docker进入mysql数据库并进行导入 导出
一:导入 1.首先查看docker运行的容器: docker ps 2.将宿主机文件拷贝到docker容器中: docker cp 2020415.sql af491d5466ea:/opt/2020 ...
- 每日CSS_滚动页面动画效果
每日CSS_滚动页面动画效果 2021_1_13 源码链接 1. 代码解析 1.1 html 代码片段 <section> <h2>开 始 滑 动</h2> < ...
- 【剑指 Offer】10-I.斐波那契数列
题目描述 写一个函数,输入 n ,求斐波那契(Fibonacci)数列的第 n 项.斐波那契数列的定义如下: F(0) = 0, F(1) = 1 F(N) = F(N - 1) + F(N - ...
- 【Flutter】功能型组件之对话框详解
前言 对话框本质上也是UI布局,通常一个对话框会包含标题.内容,以及一些操作按钮,为此,Material库中提供了一些现成的对话框组件来用于快速的构建出一个完整的对话框. 接口描述 // 1. Ale ...
