Macro-Micro Adversarial Network for Human Parsing
Macro-Micro Adversarial Network for Human Parsing
ECCV-2018 2018-10-27 15:15:07
Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1807.08260.pdf
Code: https://github.com/RoyalVane/MMAN
Motiviation-1: Why use the Adversarial Loss ?
Based on CNN architecture, the pixel-wise classification loss is usually used [19,34,10] which punishes the classification error for each pixel. Despite providing an effective baseline, the pixel-wise classification loss which is designed for per-pixel category prediction, has two drawbacks.
First, the pixel-wise classification loss may lead to local inconsistency, such as holes and blur. The reason is that it merely penalizes the false prediction on every pixel without explicitly considering the correlation among the adjacent pixels.
Second, pixel-wise classification loss may lead to semantic inconsistency in the overall segmentation map, such as unreasonable human poses and incorrect spatial relationship of body parts. Compared to the local inconsistency, the semantic inconsistency is generated from deeper layers. When only looking at a local region, the learned model does not have an overall sense of the topology of body parts.
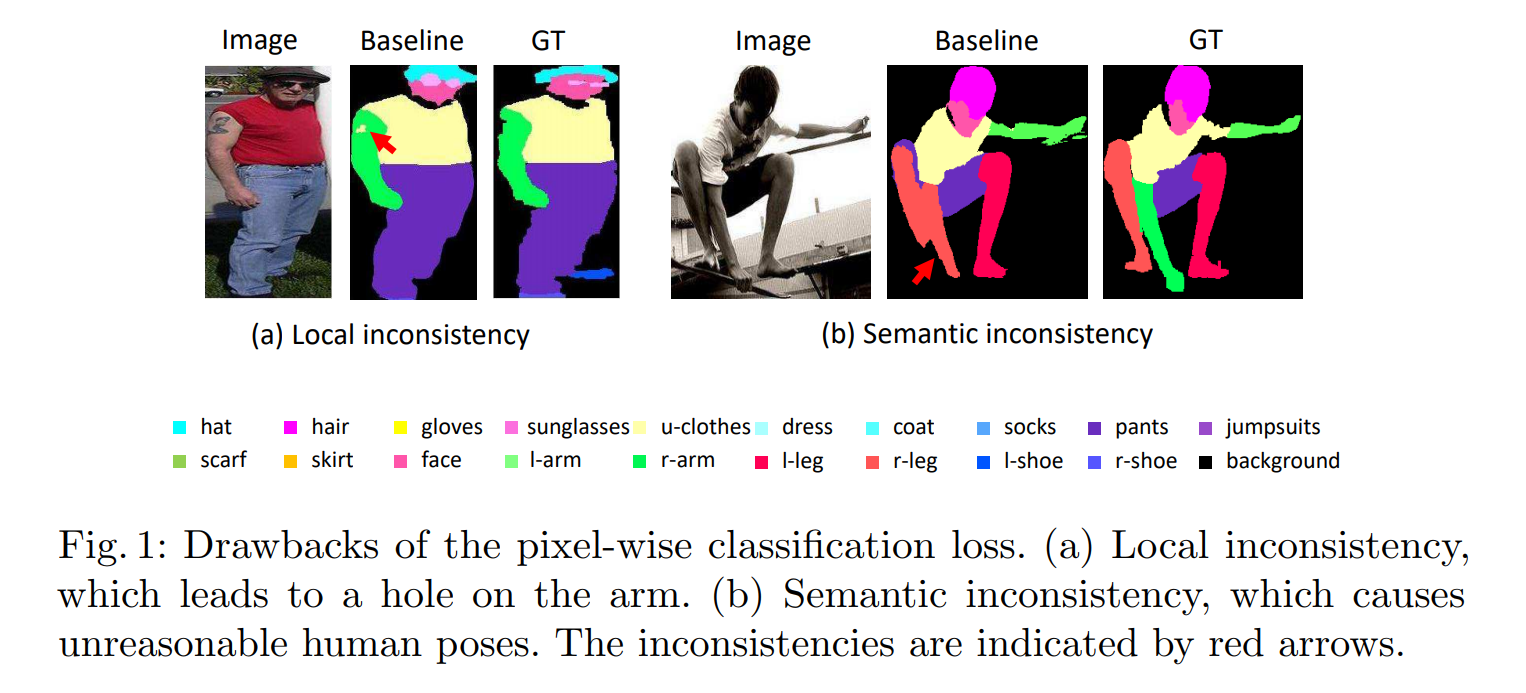
In the attempt to address the inconsistency problems, the conditional random fields (CRFs) [17] can be employed as a post processing method. However, CRFs usually handle inconsistency in very limited scope (locally) due to the pairwise potentials, and may even generate worse label maps given poor initial segmentation result. As an alternative to CRFs, a recent work proposes the use of adversarial network [24]. Since the adversarial loss assesses whether a label map is real or fake by joint configuration of many label variables, it can enforce higher-level consistency, which cannot be achieved with pairwise terms or the per-pixel classification loss. Now, an increasing number of works adopt the routine of combining the cross entropy loss with an adversarial loss to produce label maps closer to the ground truth [5,27,12].
Motiviation-2: Why use the Two Discriminator ?
Nevertheless, the previous adversarial network also has its limitations.
First, the single discriminator back propagates only one adversarial loss to the generator. However, the local inconsistency is generated from top layers and the semantic inconsistency is generated from deep layers. The two targeted layers can not be discretely trained with only one adversarial loss.
Second, a single discriminator has to look at overall high-resolution image (or a large part of it) in order to supervise the global consistency. As mentioned by numbers of literatures [7,14], it is very difficult for a generator to fool the discriminator on a high-resolution image. As a result, the single discriminator back propagates a maximum adversarial loss invariably, which makes the training unbalanced. We call it poor convergence problem, as shown in Fig. 2.
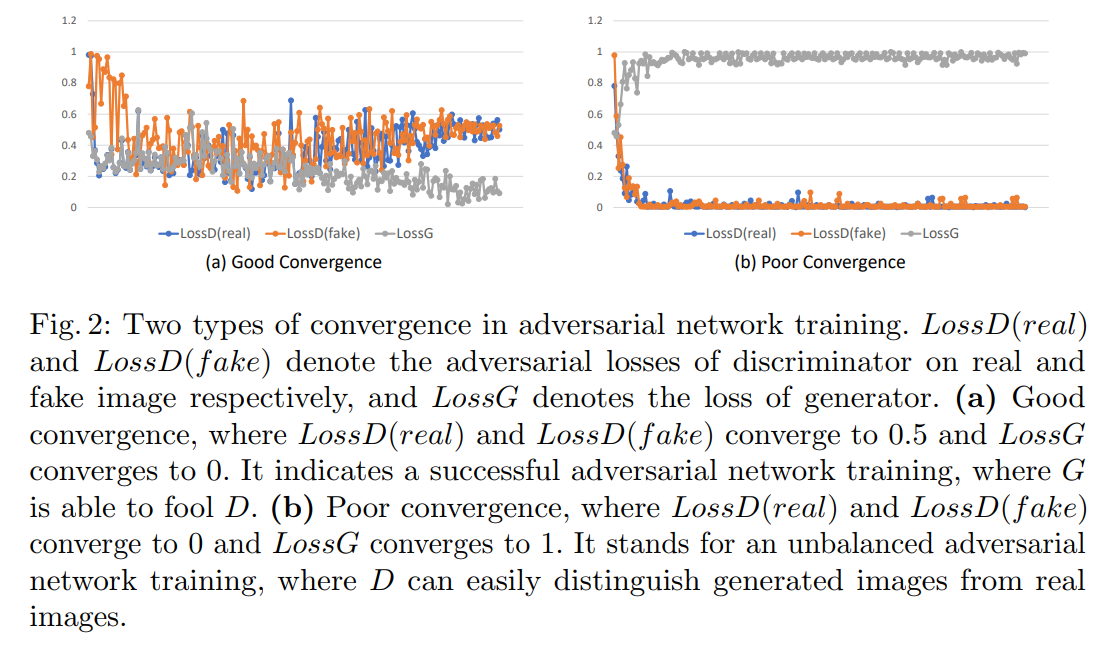
Our Proposed Approach:
In this paper, the basic objective is to improve the local and semantic consistency of label maps in human parsing. We adopt the idea of adversarial training and at the same time aim to addresses its limitations, i.e., the inferior ability in improving parsing consistency with a single adversarial loss and the poor convergence problem. Specifically, we introduce the Macro-Micro Adversarial Nets (MMAN). MMAN consists of a dual-output generator (G) and two discriminators (D), named Macro D and Micro D. The three modules constitute two adversarial networks (Macro AN, Micro AN), addressing the semantic consistency and the local consistency, respectively.

Difference with Previous Works:
A brief pipeline of the proposed framework is shown in Fig. 3. It is in two critical aspects that MMAN departs from previous works.
First, our method explicitly copes with the local inconsistency and semantic inconsistency problem using two task-specific adversarial networks individually.
Second, our method does not use large-sized FOVs on high-resolution image, so we can avoid the poor convergence problem. More detailed description of the merits of the proposed network is provided in Section 3.5.
Our Contributions:
– We propose a new framework called Macro-Micro Adversarial Network (MMAN) for human parsing. The Macro AN and Micro AN focus on semantic and local inconsistency respectively, and work in complementary way to improve the parsing quality.
– The two discriminators in our framework achieve local and global supervision on the label maps with small field of views (FOVs), which avoids the poor convergence problem caused by high-resolution images.
– The proposed adversarial net achieves very competitive mIoU on the LIP and PASCAL-Person-Part datasets, and can be well generalized on a relatively small dataset PPSS.
==
Macro-Micro Adversarial Network for Human Parsing的更多相关文章
- 《Macro-Micro Adversarial Network for Human Parsing》论文阅读笔记
<Macro-Micro Adversarial Network for Human Parsing> 摘要:在人体语义分割中,像素级别的分类损失在其低级局部不一致性和高级语义不一致性方面 ...
- 论文阅读之:Photo-Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution Using a Generative Adversarial Network
Photo-Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution Using a Generative Adversarial Network 2016.10.23 摘要: ...
- 论文笔记: Mutual Learning to Adapt for Joint Human Parsing and Pose Estimation
Mutual Learning to Adapt for Joint Human Parsing and Pose Estimation 2018-11-03 09:58:58 Paper: http ...
- Face Aging with Conditional Generative Adversarial Network 论文笔记
Face Aging with Conditional Generative Adversarial Network 论文笔记 2017.02.28 Motivation: 本文是要根据最新的条件产 ...
- 生成对抗网络(Generative Adversarial Network)阅读笔记
笔记持续更新中,请大家耐心等待 首先需要大概了解什么是生成对抗网络,参考维基百科给出的定义(https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/生成对抗网络): 生成对抗网络(英语:Gener ...
- GAN Generative Adversarial Network 生成式对抗网络-相关内容
参考: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1568663805038898&wfr=spider&for=pc Generative Adversari ...
- ASRWGAN: Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Network for Audio Super Resolution
ASEGAN:WGAN音频超分辨率 这篇文章并不具有权威性,因为没有发表,说不定是外国的某个大学的毕业设计,或者课程结束后的作业.或者实验报告. CS230: Deep Learning, Sprin ...
- 论文阅读:Single Image Dehazing via Conditional Generative Adversarial Network
Single Image Dehazing via Conditional Generative Adversarial Network Runde Li∗ Jinshan Pan∗ Zechao L ...
- Speech Super Resolution Generative Adversarial Network
博客作者:凌逆战 博客地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/LXP-Never/p/10874993.html 论文作者:Sefik Emre Eskimez , Kazuhito K ...
随机推荐
- C++ map的方法
参考文档:http://blog.csdn.net/allovexuwenqiang/article/details/5686583 Map是c++的一个标准容器,她提供了很好一对一的关系,在一些程序 ...
- 静态方法(staticmethod)和类方法(classmethod)
类方法:有个默认参数cls,并且可以直接用类名去调用,可以与类属性交互(也就是可以使用类属性) 静态方法:让类里的方法直接被类调用,就像正常调用函数一样 类方法和静态方法的相同点:都可以直接被类调用, ...
- Map 的putAll方法
如下段代码: public static void main(String[] args){ Map<String,String> map1 = new HashMap<>() ...
- javascript的数组之sort()
sort()方法用in-place的算法对原数组进行排序,但不会产生新的数组.这个方法不是一个稳定的排序,默认采用的是安字符串Unicode码点进行排序的. let fruit = ['cherri ...
- centOs6.5配置启动ssh
.非root用户则执行su或su - 或su root或su - root切换为root用户 2.查看SSH是否安装(检查是否装了SSH包) 输入命令:rpm -qa | grep ssh 注:若没安 ...
- 01day
01 cpu 内存 硬盘 操作系统 CPU:中央处理器,相当于人大脑. (运行速度飞机) 内存:临时存储数据. 8g,16g, (高铁) 1,成本高. 2,断电即消 ...
- ionic3 创建项目至apk打包全过程教程
主要流程: 安装node.js --> 安装jdk --> 安装AndroidSDK --> 安装cordova --> 安装ionic --> 创建项 ...
- Windows渗透利器之Pentest BOX使用详解(一)
内容概览: 知识科普 优缺点总结 功能参数详解翻译: 控制 ...
- JDBC事务(二)转账示例
示例采用三层框架 web层: package cn.sasa.web; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletExceptio ...
- JDK8新增接口的默认方法与静态方法
JDK8之前,interface中可以定义常量和抽象方法,访问修饰符是public. public interface A { /** a1和a2写法是等价的 */ public static fin ...
