netty系列之:EventExecutor,EventExecutorGroup和netty中的实现
简介
netty作为一个异步NIO框架,多线程肯定是它的基础,但是对于netty的实际使用者来说,一般是不需要接触到多线程的,我们只需要按照netty框架规定的流程走下去,自定义handler来处理对应的消息即可。
那么有朋友会问了,作为一个NIO框架,netty的多线程到底体现在什么地方呢?它的底层原理是什么呢?
今天带大家来看看netty中的任务执行器EventExecutor和EventExecutorGroup。
EventExecutorGroup
因为EventExecutor继承自EventExecutorGroup,这里我们先来详细讲解一下EventExecutorGroup。
先看下EventExecutorGroup的定义:
public interface EventExecutorGroup extends ScheduledExecutorService, Iterable<EventExecutor>
EventExecutorGroup继承自JDK的ScheduledExecutorService,即可以执行定时任务,也可以像普通的任务执行器一样提交任务去执行。
同时EventExecutorGroup还继承了Iterable接口,表示EventExecutorGroup是可遍历的,它的遍历对象是EventExecutor。
EventExecutorGroup有两个和Iterable相关的方法,分别是next和iterator:
EventExecutor next();
@Override
Iterator<EventExecutor> iterator();
在EventExecutorGroup中调用next方法会返回一个EventExecutor对象,那么EventExecutorGroup和EventExecutor是什么关系呢?
我们再来看一下EventExecutor的定义:
public interface EventExecutor extends EventExecutorGroup
可以看到EventExecutor实际上是EventExecutorGroup的子类。但是在父类EventExecutorGroup中居然有对子类EventExecutor的引用。
这种在父类的Group中引用返回子类的设计模式在netty中非常常见,大家可以自行体会一下这样的设计到底是好还是坏。
EventExecutorGroup作为一个EventExecutor的Group对象,它是用来管理group中的EventExecutor的。所以在EventExecutorGroup中设计了一些对EventExecutor的统一管理接口。
比如boolean isShuttingDown()方法用来判断这个group中的所有EventExecutor全都在被shutdown或者已经被shutdown。
另外EventExecutorGroupt提供了shutdown group中所有EventExector的方法:Future<?> shutdownGracefully() 和 terminate方法:Future<?> terminationFuture()。
这两个方法都返回了Future,所以我们可以认为这两个方法是异步方法。
EventExecutorGroup中其他的方法都是一些对JDK中ScheduledExecutorService方法的重写,比如submit,schedule,scheduleAtFixedRate,scheduleWithFixedDelay等。
EventExecutor
接下来我们再研究一下EventExecutor,在上一节中,我们简单的提到了EventExecutor继承自EventExecutorGroup,和EventExecutorGroup相比,EventExecutor有哪些新的方法呢?
我们知道EventExecutorGroup继承了Iterable,并且定义了一个next方法用来返回Group中的一个EventExecutor对象。
因为Group中有很多个EventExecutor,至于具体返回哪一个EventExecutor,还是由具体的实现类来实现的。
在EventExecutor中,它重写了这个方法:
@Override
EventExecutor next();
这里的next方法,返回的是EventExecutor本身。
另外,因为EventExecutor是由EventExecutorGroup来管理的,所以EventExecutor中还存在一个parent方法,用来返回管理EventExecutor的EventExecutorGroup:
EventExecutorGroup parent();
EventExecutor中新加了两个inEventLoop方法,用来判断给定的线程是否在event loop中执行。
boolean inEventLoop();
boolean inEventLoop(Thread thread);
EventExecutor还提供两个方法可以返回Promise和ProgressivePromise.
<V> Promise<V> newPromise();
<V> ProgressivePromise<V> newProgressivePromise();
熟悉ECMAScript的朋友可能知道,Promise是ES6引入的一个新的语法功能,用来解决回调地狱的问题。这里的netty引入的Promise继承自Future,并且添加了两个success和failure的状态。
ProgressivePromise更进一步,在Promise基础上,提供了一个progress来表示进度。
除此之外,EventExecutor还提供了对Succeeded的结果和Failed异常封装成为Future的方法。
<V> Future<V> newSucceededFuture(V result);
<V> Future<V> newFailedFuture(Throwable cause);
EventExecutorGroup在netty中的基本实现
EventExecutorGroup和EventExecutor在netty中有很多非常重要的实现,其中最常见的就是EventLoop和EventLoopGroup,鉴于EventLoop和EventLoopGroup的重要性,我们会在后面的章节中重点讲解他们。这里先来看下netty中的其他实现。
netty中EventExecutorGroup的默认实现叫做DefaultEventExecutorGroup,它的继承关系如下所示:
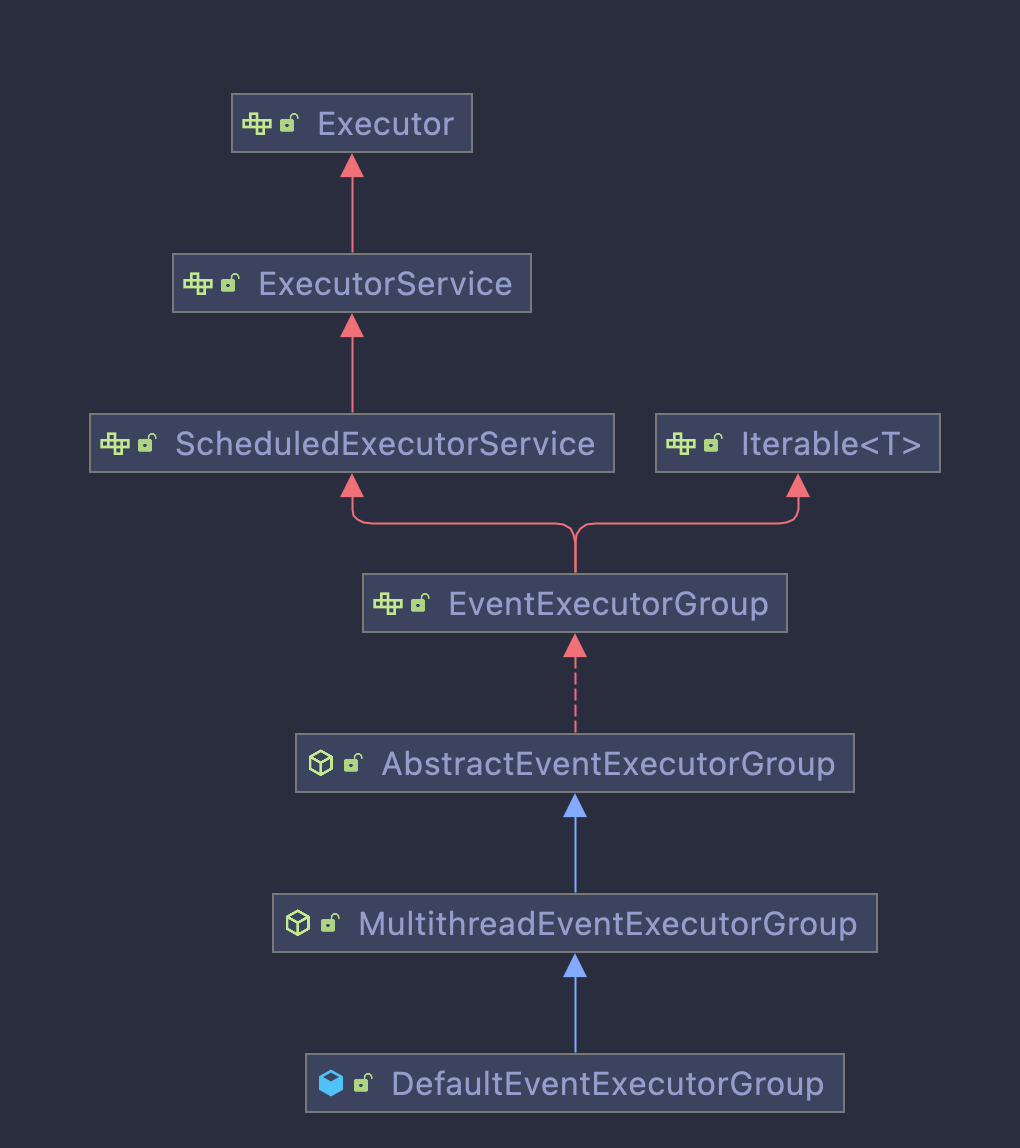
可以看到DefaultEventExecutorGroup继承自MultithreadEventExecutorGroup,而MultithreadEventExecutorGroup又继承自AbstractEventExecutorGroup。
先看下AbstractEventExecutorGroup的逻辑。AbstractEventExecutorGroup基本上是对EventExecutorGroup中接口的一些实现。
我们知道EventExecutorGroup中定义了一个next()方法,可以返回Group中的一个EventExecutor。
在AbstractEventExecutorGroup中,几乎所有EventExecutorGroup中的方法实现,都是调用next()方法来完成的,以submit方法为例:
public Future<?> submit(Runnable task) {
return next().submit(task);
}
可以看到submit方法首先调用next获取到的EventExecutor,然后再调用EventExecutor中的submit方法。
AbstractEventExecutorGroup中的其他方法都是这样的实现。但是AbstractEventExecutorGroup中并没有实现next()方法,具体如何从Group中获取到EventExecutor,还需要看底层的具体实现。
MultithreadEventExecutorGroup继承自AbstractEventExecutorGroup,提供了多线程任务的支持。
MultithreadEventExecutorGroup有两类构造函数,在构造函数中可以指定多线程的个数,还有任务执行器Executor,如果没有提供Executor的话,可以提供一个ThreadFactory,MultithreadEventExecutorGroup会调用new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(threadFactory)来为每一个线程构造一个Executor:
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory, Object... args) {
this(nThreads, threadFactory == null ? null : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(threadFactory), args);
}
protected MultithreadEventExecutorGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor, Object... args) {
this(nThreads, executor, DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory.INSTANCE, args);
}
MultithreadEventExecutorGroup对多线程的支持是怎么实现的呢?
首先MultithreadEventExecutorGroup提供了两个children,分别是children和readonlyChildren:
private final EventExecutor[] children;
private final Set<EventExecutor> readonlyChildren;
children和MultithreadEventExecutorGroup中的线程个数是一一对应的,有多少个线程,children就有多大。
children = new EventExecutor[nThreads];
然后通过调用newChild方法,将传入的executor构造成为EventExecutor返回:
children[i] = newChild(executor, args);
看一下newChild方法的定义:
protected abstract EventExecutor newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception;
这个方法在MultithreadEventExecutorGroup中并没有实现,需要在更具体的类中实现它。
readonlyChildren是child的只读版本,用来在遍历方法中返回:
readonlyChildren = Collections.unmodifiableSet(childrenSet);
public Iterator<EventExecutor> iterator() {
return readonlyChildren.iterator();
}
我们现在有了Group中的所有EventExecutor,那么在MultithreadEventExecutorGroup中,next方法是怎么选择具体返回哪一个EventExecutor呢?
先来看一下next方法的定义:
private final EventExecutorChooserFactory.EventExecutorChooser chooser;
chooser = chooserFactory.newChooser(children);
public EventExecutor next() {
return chooser.next();
}
next方法调用的是chooser的next方法,看一下chooser的next方法具体实现:
public EventExecutor next() {
return executors[(int) Math.abs(idx.getAndIncrement() % executors.length)];
}
可以看到,其实是一个很简单的根据index来获取对象的操作。
最后看一下DefaultEventExecutorGroup中对newChild方法的实现:
protected EventExecutor newChild(Executor executor, Object... args) throws Exception {
return new DefaultEventExecutor(this, executor, (Integer) args[0], (RejectedExecutionHandler) args[1]);
}
newChild返回的EventExecutor使用的是DefaultEventExecutor。这个类是EventExecutor在netty中的默认实现,我们在下一小结中详细进行讲解。
EventExecutor在netty中的基本实现
EventExecutor在netty中的默认实现是DefaultEventExecutor,先看下它的继承结构:
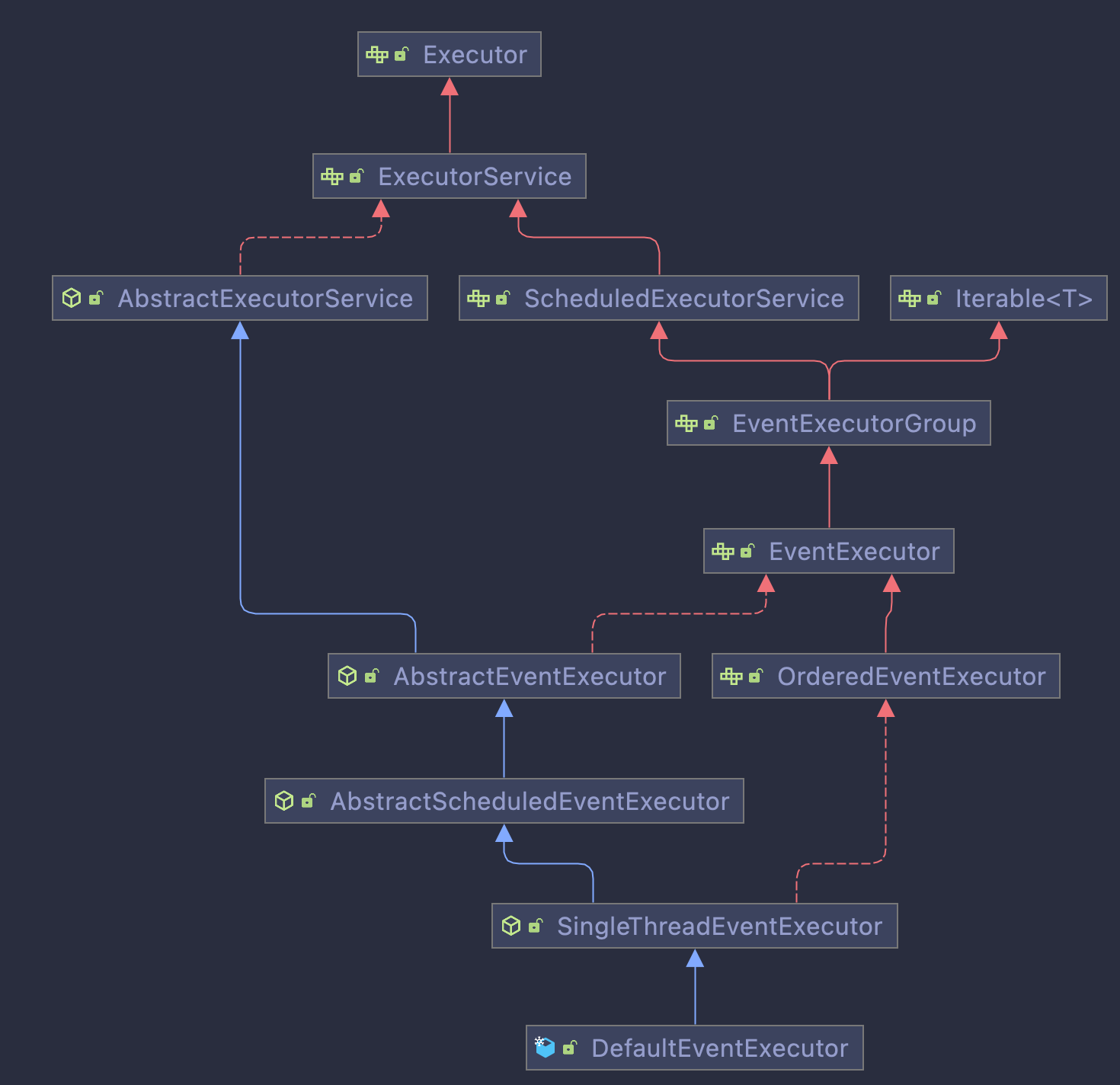
DefaultEventExecutor继承自SingleThreadEventExecutor,而SingleThreadEventExecutor又继承自AbstractScheduledEventExecutor,AbstractScheduledEventExecutor继承自AbstractEventExecutor。
先来看一下AbstractEventExecutor的定义:
public abstract class AbstractEventExecutor extends AbstractExecutorService implements EventExecutor
AbstractEventExecutor继承了AbstractExecutorService,并且实现了EventExecutor接口。
AbstractExecutorService是JDK中的类,它提供了 ExecutorService 的一些实现,比如submit, invokeAny and invokeAll等方法。
AbstractEventExecutor作为ExecutorGroup的一员,它提供了一个EventExecutorGroup类型的parent属性:
private final EventExecutorGroup parent;
public EventExecutorGroup parent() {
return parent;
}
对于next方法来说,AbstractEventExecutor返回的是它本身:
public EventExecutor next() {
return this;
}
AbstractScheduledEventExecutor继承自AbstractEventExecutor,它内部使用了一个PriorityQueue来存储包含定时任务的ScheduledFutureTask,从而实现定时任务的功能:
PriorityQueue<ScheduledFutureTask<?>> scheduledTaskQueue;
接下来是SingleThreadEventExecutor,从名字可以看出,SingleThreadEventExecutor使用的是单线程来执行提交的tasks,SingleThreadEventExecutor提供了一个默认的pending执行task的任务大小:DEFAULT_MAX_PENDING_EXECUTOR_TASKS,还定义了任务执行的几种状态:
private static final int ST_NOT_STARTED = 1;
private static final int ST_STARTED = 2;
private static final int ST_SHUTTING_DOWN = 3;
private static final int ST_SHUTDOWN = 4;
private static final int ST_TERMINATED = 5;
之前提到了EventExecutor中有一个特有的inEventLoop方法,判断给定的thread是否在eventLoop中,在SingleThreadEventExecutor中,我们看一下具体的实现:
public boolean inEventLoop(Thread thread) {
return thread == this.thread;
}
具体而言就是判断给定的线程和SingleThreadEventExecutor中定义的thread属性是不是同一个thread,SingleThreadEventExecutor中的thread是这样定义的:
这个thread是在doStartThread方法中进行初始化的:
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
thread = Thread.currentThread();
所以这个thread是任务执行的线程,也就是executor中执行任务用到的线程。
再看一下非常关键的execute方法:
private void execute(Runnable task, boolean immediate) {
boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();
addTask(task);
if (!inEventLoop) {
startThread();
这个方法首先将task添加到任务队列中,然后调用startThread开启线程来执行任务。
最后来看一下DefaultEventExecutor,这个netty中的默认实现:
public final class DefaultEventExecutor extends SingleThreadEventExecutor
DefaultEventExecutor继承自SingleThreadEventExecutor,这个类中,它定义了run方法如何实现:
protected void run() {
for (;;) {
Runnable task = takeTask();
if (task != null) {
task.run();
updateLastExecutionTime();
}
if (confirmShutdown()) {
break;
}
}
}
在SingleThreadEventExecutor中,我们会把任务加入到task queue中,在run方法中,会从task queue中取出对应的task,然后调用task的run方法执行。
总结
DefaultEventExecutorGroup继承了MultithreadEventExecutorGroup,MultithreadEventExecutorGroup中实际调用的是SingleThreadEventExecutor来执行具体的任务。
本文已收录于 http://www.flydean.com/05-1-netty-event…entexecutorgroup/
最通俗的解读,最深刻的干货,最简洁的教程,众多你不知道的小技巧等你来发现!
欢迎关注我的公众号:「程序那些事」,懂技术,更懂你!
netty系列之:EventExecutor,EventExecutorGroup和netty中的实现的更多相关文章
- netty系列之:Bootstrap,ServerBootstrap和netty中的实现
目录 简介 Bootstrap和ServerBootstrap的联系 AbstractBootstrap Bootstrap和ServerBootstrap 总结 简介 虽然netty很强大,但是使用 ...
- netty系列之:EventLoop,EventLoopGroup和netty的默认实现
目录 简介 EventLoopGroup和EventLoop EventLoopGroup在netty中的默认实现 EventLoop在netty中的默认实现 总结 简介 在netty中不管是服务器端 ...
- netty系列之:真正的平等–UDT中的Rendezvous
目录 简介 建立支持Rendezvous的服务器 处理不同的消息 节点之间的交互 总结 简介 在我们之前提到的所有netty知识中,netty好像都被分为客户端和服务器端两部分.服务器端监听连接,并对 ...
- netty系列之:channel,ServerChannel和netty中的实现
目录 简介 channel和ServerChannel netty中channel的实现 AbstractChannel和AbstractServerChannel LocalChannel和Loca ...
- netty系列之:protobuf在UDP协议中的使用
目录 简介 UDP在netty中的表示 DatagramPacketEncoder DatagramPacketDecoder 总结 简介 netty中提供的protobuf编码解码器可以让我们直接在 ...
- netty系列之:netty中的懒人编码解码器
目录 简介 netty中的内置编码器 使用codec要注意的问题 netty内置的基本codec base64 bytes compression json marshalling protobuf ...
- netty系列之:在netty中使用protobuf协议
目录 简介 定义protobuf 定义handler 设置ChannelPipeline 构建client和server端并运行 总结 简介 netty中有很多适配不同协议的编码工具,对于流行的goo ...
- netty系列之:netty中的核心解码器json
目录 简介 java中对json的支持 netty对json的解码 总结 简介 程序和程序之间的数据传输方式有很多,可以通过二进制协议来传输,比较流行的像是thrift协议或者google的proto ...
- 聊聊 Netty 那些事儿之 Reactor 在 Netty 中的实现(创建篇)
本系列Netty源码解析文章基于 4.1.56.Final版本 在上篇文章<聊聊Netty那些事儿之从内核角度看IO模型>中我们花了大量的篇幅来从内核角度详细讲述了五种IO模型的演进过程以 ...
随机推荐
- golang中gomodule讲解
0. GOMODULES模式 1. GOPATH的缺点 1. 无版本控制概念 2. 无法同步一致第三方版本号 3. 无法指定当前项目引用的第三方版本号 2. go1.11版本之后可以使用GoModul ...
- 多线程-线程间通信-多生产者多消费者问题(JDK1.5后Lock,Condition解决办法及开发中代码范例)
1 package multithread4; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; 4 import java.util.concurre ...
- Linux下查找软件,rpm命令 dpkg命令 apt命令
centos: 1.查询一个包是否被安装 rpm -q < package name> 2.列出已安装软件相关的所有包 rpm -qa < package name> ubun ...
- docker 安装遇到404 not find
https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce/repodata/repomd.xml: [Errno 14] HTTPS E ...
- 微信 CLI 工具正式发布 v1.0
前言 为了让开发者可以更加方便舒适地获取到微信开发的资源,今天我们基于 Senparc.Weixin SDK 正式发布了基于 .NET 的微信 CLI 工具:Weixin.CLI(v1.0). 通过 ...
- 从服务端生成Excel电子表格(GcExcel + SpreadJS)
在服务端生成Excel电子表格,除了使用 Node.js + SpreadJS 外,葡萄城官方推荐使用 SpreadJS + GcExcel.该方案不仅能够解决批量绑定数据源并导出Excel.批量修改 ...
- java的四种引用:强软弱虚
简介 在JDK 1.2以前的版本中,若一个对象不被任何变量引用,那么程序就无法再使用这个对象.也就是说,只有对象处于(reachable)可达状态,程序才能使用它. 从JDK 1.2版本开始,对象的引 ...
- 类扩展(Class Extension)
类扩展(Class Extension) 也有人称为匿名分类 - 作用 - 能为某个类增加额外的属性.成员变量.方法声明 - 一般将类扩展写到.m文件中 - 一般将一些私有的属 ...
- Saas系统架构的思考,多租户Saas架构设计分析
ToB Saas系统最近几年都很火.很多创业公司都在尝试创建企业级别的应用 cRM, HR,销售, Desk Saas系统.很多Saas创业公司也拿了大额风投.毕竟Saas相对传统软件的优势非常明显. ...
- svn 用户名,密码 查看/删除
1.查看svn 的用户名,密码: 找到用户名,密码文件,都是明文的,你可以看到 例:linux ls ~/.subversion/auth/svn.simple 2ab598e9cb6d6d38761 ...
