mit6.830 - lab1 - 存储模型 - 题解
1.Intro
github : https://github.com/CreatorsStack/CreatorDB
lab1实现数据库基本的存储逻辑结构,具体包括:Tuple,TupleDesc,HeapPage,HeapFile,SeqScan, BufferPool等。
- Tuple和TupleDesc是数据库表的最基本元素了。Tuple就是一个若干个
Field的,TupleDesc则是一个表的meta-data,包括每列的field name和type。 - HeapPage和HeapFile都分别是Page和DbFile interface的实现
- BufferPool是用来做缓存的,getPage会优先从这里拿,如果没有,才会调用File的readPage去从文件中读取对应page,disk中读入的page会缓存在其中。
- SeqScan用来遍历一个table的所有tuple,包装了HeapFile的iterator。
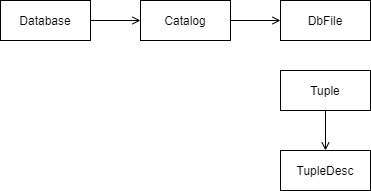
画了个大概的关系图:

2.SimpleDB Architecture and Implementation Guide
2.1. The Database Class
Database类提供了database中要用到的静态全局对象。其中,包括了访问catalog(database中所有表的集合)、buffer pool(现在驻留在内存中所有数据库文件页的集合)以及log file的方法。在这个lab中不需要关心log file。
2.2. Fields and Tuples
数据库中,行被称为记录(record)或元组(Tuple),列称为字段(Field)或属性(attribute)。tuples在SimpleDB中十分基础,是一组Field对象的集合,Field是不同数据类型(e.g.,integer,string)实现的接口,Tuple对象是由底层访问方法(e.g.,heap files,B trees)创建的,Tuple也有类型type(或称为组织结构schema),称为_tuple descriptor_,是TypleDesc对象,这个对象包括了Type对象的集合。
Exercise 1
Implement the skeleton methods in:
- src/simpledb/TupleDesc.java
- src/simpledb/Tuple.java
At this point, your code should pass the unit tests TupleTest and TupleDescTest. At this point, modifyRecordId() should fail because you havn't implemented it yet.
TupleDesc主要定义了Tuple结构,这里是一个TDItem类型的数组,一个TDItem对象包括fieldType和fieldName两个属性,通过这两个属性描述数据库的行。
TupleDesc.java代码如下:
private List<TDItem> descList;
private int fieldNum;
public static class TDItem implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* The type of the field
* */
public final Type fieldType;
/**
* The name of the field
* */
public String fieldName;
public TDItem(Type t, String n) {
this.fieldName = n;
this.fieldType = t;
}
}
public TupleDesc(Type[] typeAr, String[] fieldAr) {
// some code goes here
if (typeAr.length != fieldAr.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The typeAr length must be equal than fieldAr length");
}
this.descList = new ArrayList<>(typeAr.length);
this.fieldNum = typeAr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < typeAr.length; i++) {
final TDItem item = new TDItem(typeAr[i], fieldAr[i]);
this.descList.add(item);
}
}
Tuple代码如下:
private TupleDesc tupleDesc;
private Field[] fields;
private RecordId recordId;
public Tuple(TupleDesc td) {
// some code goes here
this.tupleDesc = td;
this.fields = new Field[this.tupleDesc.numFields()];
}
public void setField(int i, Field f) {
// some code goes here
if (i >= this.tupleDesc.numFields()) {
return;
}
this.fields[i] = f;
}
2.3. Catalog
catalog类描述的是数据库实例。包含了数据库现有的表信息以及表的schema信息。现在需要实现添加新表的功能,以及从特定的表中提取信息。提取信息时通过表对应的TupleDesc对象决定操作的字段类型和数量。
在整个 SimpleDb 中, CataLog 是全局唯一的,可以通过方法Database.getCatalog()获得,global buffer pool可以通过方法Database.getBufferPool()获得。
Exercise 2
Implement the skeleton methods in:
- src/simpledb/Catalog.java
At this point, your code should pass the unit tests in CatalogTest.
为了维护一个表的信息, 我额外创建了一个 TableInfo 类:
public class TableInfo {
private int tableId;
private String tableName;
private DbFile dbFile;
private String primaryKeyName;
}
Catalog.java代码如下
private final Map<Integer, TableInfo> tableInfoMap;
// 维护 name -> tableId 的映射关系
private final Map<String, Integer> nameToIdMap;
/**
* Constructor.
* Creates a new, empty catalog.
*/
public Catalog() {
// some code goes here
this.tableInfoMap = new HashMap<>();
this.nameToIdMap = new HashMap<>();
}
public void addTable(DbFile file, String name, String pkeyField) {
// some code goes here
final int tableId = file.getId();
final TableInfo tableInfo = new TableInfo(tableId, name, file, pkeyField);
this.tableInfoMap.put(tableId, tableInfo);
this.nameToIdMap.put(name, tableId);
}
2.4. BufferPool
buffer pool(在 SimpleDB 中是 BufferPool 类)也是全局唯一的, 负责将最近访问过的 page 缓存下来。所有的读写操作通过buffer pool读写硬盘上不同文件,BufferPool里的 numPages 参数确定了读取的固定页数,我们可以直接搭配 Lru 最近未使用算法, 来实现 BufferPool.
此外, Database类提供了一个静态方法Database.getBufferPool(),返回整个SimpleDB进程的BufferPool实例引用。
Exercise 3
Implement the
getPage()method in:
- src/simpledb/BufferPool.java
We have not provided unit tests for BufferPool. The functionality you implemented will be tested in the implementation of HeapFile below. You should use the
DbFile.readPagemethod to access pages of a DbFile.
LruCache 代码:
public class LruCache<K, V> {
// LruCache node
public class Node {
public Node pre;
public Node next;
public K key;
public V value;
public Node(final K key, final V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
private final int maxSize;
private final Map<K, Node> nodeMap;
private final Node head;
private final Node tail;
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.head = new Node(null, null);
this.tail = new Node(null, null);
this.head.next = tail;
this.tail.pre = head;
this.nodeMap = new HashMap<>();
}
public void linkToHead(Node node) {
Node next = this.head.next;
node.next = next;
node.pre = this.head;
this.head.next = node;
next.pre = node;
}
public void moveToHead(Node node) {
removeNode(node);
linkToHead(node);
}
public void removeNode(Node node) {
if (node.pre != null && node.next != null) {
node.pre.next = node.next;
node.next.pre = node.pre;
}
}
public Node removeLast() {
Node last = this.tail.pre;
removeNode(last);
return last;
}
public synchronized void remove(K key) {
if (this.nodeMap.containsKey(key)) {
final Node node = this.nodeMap.get(key);
removeNode(node);
this.nodeMap.remove(key);
}
}
public synchronized V get(K key) {
if (this.nodeMap.containsKey(key)) {
Node node = this.nodeMap.get(key);
moveToHead(node);
return node.value;
}
return null;
}
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
if (this.nodeMap.containsKey(key)) {
Node node = this.nodeMap.get(key);
node.value = value;
moveToHead(node);
} else {
// We can't remove page here, because we should implement the logic of evict page in BufferPool
// if (this.nodeMap.size() == this.maxSize) {
// Node last = removeLast();
// this.nodeMap.remove(last.key);
// return last.value;
// }
Node node = new Node(key, value);
this.nodeMap.put(key, node);
linkToHead(node);
}
return null;
}
}
BufferPool.getPage() 代码如下:
public Page getPage(TransactionId tid, PageId pid, Permissions perm) throws TransactionAbortedException,
DbException {
final Page page = this.lruCache.get(pid);
if (page != null) {
return page;
}
return loadPageAndCache(pid);
}
private Page loadPageAndCache(final PageId pid) throws DbException {
final DbFile dbFile = Database.getCatalog().getDatabaseFile(pid.getTableId());
final Page dbPage = dbFile.readPage(pid);
if (dbPage != null) {
this.lruCache.put(pid, dbPage);
if (this.lruCache.getSize() == this.lruCache.getMaxSize()) {
// 驱逐缓存的 page, 如果空间满了
evictPage();
}
}
return dbPage;
}
2.5. HeapFile access method
access method 提供了硬盘读写数据的方式, 包括heap files和B-trees 的读写,在这里,只需要实现heap file访问方法。
HeapFile对象包含一组“物理页”,每一个页大小固定,大小由 BufferPool.DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE 定义,页内存储行数据。在SimpleDB中,数据库中每一个表对应一个HeapFile对象,HeapFile中每一页包含很多个slot,每个slot是留给一行的位置。除了这些slots,每个物理页包含一个header,heade是每个tuple slot的bitmap。如果bitmap中对应的某个tuple的bit是1,则这个tuple是有效的,否则无效(被删除或者没被初始化)。HeapFile对象中的物理页的类型是HeapPage,物理页是缓存在buffer pool中,通过HeapFile类读写。
计算每页所需tuple数量
计算header所需byte数量
提示:所有的java虚拟机都是big-endian。
- 大端模式是指数据的低位保存在内存的高地址中,而数据的高位保存在内存的低地址中.
- 小端模式是指数据的低位保存在内存的低地址中,而数据的高位保存在内存的高地址中。
Exercise 4
Implement the skeleton methods in:
- src/simpledb/HeapPageId.java
- src/simpledb/RecordID.java
- src/simpledb/HeapPage.java
Although you will not use them directly in Lab 1, we ask you to implement getNumEmptySlots() and isSlotUsed() in HeapPage. These require pushing around bits in the page header. You may find it helpful to look at the other methods that have been provided in HeapPage or in src/simpledb/HeapFileEncoder.java to understand the layout of pages.
You will also need to implement an Iterator over the tuples in the page, which may involve an auxiliary class or data structure.
At this point, your code should pass the unit tests in HeapPageIdTest, RecordIDTest, and HeapPageReadTest.
After you have implemented HeapPage, you will write methods for HeapFile in this lab to calculate the number of pages in a file and to read a page from the file. You will then be able to fetch tuples from a file stored on disk.
HeapPageId 和 RecordId 比较简单..
HeapPage 代码如下, 主要是要理解 header 和 slot 的对应关系:
/**
* Returns the number of empty slots on this page.
*/
public int getNumEmptySlots() {
// some code goes here
int emptyNum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < getNumTuples(); i++) {
if (!isSlotUsed(i)) {
emptyNum++;
}
}
return emptyNum;
}
/**
* Returns true if associated slot on this page is filled.
*/
public boolean isSlotUsed(int i) {
// some code goes here
// For Example, byte = 11110111 and posIndex = 3 -> we want 0
int byteIndex = i / 8;
int posIndex = i % 8;
byte target = this.header[byteIndex];
return (byte) (target << (7 - posIndex)) < 0;
}
/**
* Abstraction to fill or clear a slot on this page.
*/
private void markSlotUsed(int i, boolean value) {
// some code goes here
// not necessary for lab1
int byteIndex = i / 8;
int posIndex = i % 8;
byte v = (byte) (1 << posIndex);
byte headByte = this.header[byteIndex];
this.header[byteIndex] = value ? (byte) (headByte | v) : (byte) (headByte & ~v);
}
Exercise 5
Implement the skeleton methods in:
- src/simpledb/HeapFile.java
To read a page from disk, you will first need to calculate the correct offset in the file. Hint: you will need random access to the file in order to read and write pages at arbitrary offsets. You should not call BufferPool methods when reading a page from disk.
You will also need to implement the
HeapFile.iterator()method, which should iterate through through the tuples of each page in the HeapFile. The iterator must use theBufferPool.getPage()method to access pages in theHeapFile. This method loads the page into the buffer pool and will eventually be used (in a later lab) to implement locking-based concurrency control and recovery. Do not load the entire table into memory on the open() call -- this will cause an out of memory error for very large tables.At this point, your code should pass the unit tests in HeapFileReadTest.
HeapFile.java代码如下:
想要 readPage from file, 我们可以利用 java 的 randomAccessFile 来达到这个目的
randomAccessFile 支持随机 seek() 的功能:
// see DbFile.java for javadocs
public Page readPage(PageId pid) {
// some code goes here
final int pos = BufferPool.getPageSize() * pid.getPageNumber();
byte[] pageData = new byte[BufferPool.getPageSize()];
try {
this.randomAccessFile.seek(pos);
this.randomAccessFile.read(pageData, 0, pageData.length);
final HeapPage heapPage = new HeapPage((HeapPageId) pid, pageData);
return heapPage;
}
return null;
}
2.6. Operators
数据库Operators(操作符)负责查询语句的实际执行。在SimpleDB中,Operators是基于 volcano 实现的, 每个 operator 都需要实现 next() 方法
SimpleDP 和程序交互的过程中,现在root operator上调用getNext,之后在子节点上继续调用getNext,一直下去,直到leaf operators 被调用。他们从硬盘上读取tuples,并在树结构上传递。如图所示:
[
这个lab中,只需要实现一个SimpleDB operator, 也即 seqScan
Exercise 6.
Implement the skeleton methods in:
- src/simpledb/SeqScan.java
This operator sequentially scans all of the tuples from the pages of the table specified by the
tableidin the constructor. This operator should access tuples through theDbFile.iterator()method.At this point, you should be able to complete the ScanTest system test. Good work!
You will fill in other operators in subsequent labs.
SeqScan.java代码如下:
public SeqScan(TransactionId tid, int tableid, String tableAlias) {
// some code goes here
this.tid = tid;
this.tableId = tableid;
this.tableAlias = tableAlias;
// db file 的 iterator, 可以遍历 file 的每个 page
this.dbFileIterator = Database.getCatalog().getDatabaseFile(tableid).iterator(tid);
}
public SeqScan(TransactionId tid, int tableId) {
this(tid, tableId, Database.getCatalog().getTableName(tableId));
}
public void open() throws DbException, TransactionAbortedException {
// some code goes here
this.dbFileIterator.open();
}
public boolean hasNext() throws TransactionAbortedException, DbException {
// some code goes here
return this.dbFileIterator.hasNext();
}
public Tuple next() throws NoSuchElementException, TransactionAbortedException, DbException {
// some code goes here
final Tuple next = this.dbFileIterator.next();
final Tuple result = new Tuple(getTupleDesc());
for (int i = 0; i < next.getTupleDesc().numFields(); i++) {
result.setField(i, next.getField(i));
result.setRecordId(next.getRecordId());
}
return result;
}
2.7. A simple query
这一小节是要说明怎么综合上面的部分,执行一次简单的查询。
假如有一个数据文件"some_data_file.txt",内容如下:
1,1,1
2,2,2
3,4,4
可以将它转换成SimpleDB可以查询的二进制文件,转换格式为java -jar dist/simpledb.jar convert some_data_file.txt 3。其中参数3是告诉转换器输入有3列。
下列代码实现了对文件的简单查询,效果等同于SQL语句的SELECT * FROM some_data_file。
package simpledb;
import java.io.*;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] argv) {
// construct a 3-column table schema
Type types[] = new Type[]{ Type.INT_TYPE, Type.INT_TYPE, Type.INT_TYPE };
String names[] = new String[]{ "field0", "field1", "field2" };
TupleDesc descriptor = new TupleDesc(types, names);
// create the table, associate it with some_data_file.dat
// and tell the catalog about the schema of this table.
HeapFile table1 = new HeapFile(new File("some_data_file.dat"), descriptor);
Database.getCatalog().addTable(table1, "test");
// construct the query: we use a simple SeqScan, which spoonfeeds
// tuples via its iterator.
TransactionId tid = new TransactionId();
SeqScan f = new SeqScan(tid, table1.getId());
try {
// and run it
f.open();
while (f.hasNext()) {
Tuple tup = f.next();
System.out.println(tup);
}
f.close();
Database.getBufferPool().transactionComplete(tid);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println ("Exception : " + e);
}
}
}
mit6.830 - lab1 - 存储模型 - 题解的更多相关文章
- Mit6.830 - simpledb - 总览
总览 github 地址: https://github.com/CreatorsStack/CreatorDB 在开始 simpledb 旅途之前, 我们先从整体上来看看 SimpleDb 是一个 ...
- Entity Framework 6 Recipes 2nd Edition(10-5)译 -> 在存储模型中使用自定义函数
10-5. 在存储模型中使用自定义函数 问题 想在模型中使用自定义函数,而不是存储过程. 解决方案 假设我们数据库里有成员(members)和他们已经发送的信息(messages) 关系数据表,如Fi ...
- SQLite剖析之存储模型
前言 SQLite作为嵌入式数据库,通常针对的应用的数据量相对于DBMS的数据量小.所以它的存储模型设计得非常简单,总的来说,SQLite把一个数据文件分成若干大小相等的页面,然后以B树的形式来组织这 ...
- Bitcask 存储模型
Bitcask 存储模型 Bitcask 是一个日志型.基于hash表结构的key-value存储模型,以Bitcask为存储模型的K-V系统有 Riak和 beansdb新版本. 日志型数据存储 何 ...
- LSM存储模型
LSM存储模型 数据库有3种基本的存储引擎: 哈希表,支持增.删.改以及随机读取操作,但不支持顺序扫描,对应的存储系统为key-value存储系统.对于key-value的插入以及查询,哈希表的复杂度 ...
- SQLite入门与分析(八)---存储模型(1)
写在前面:SQLite作为嵌入式数据库,通常针对的应用的数据量相对于通常DBMS的数据量是较小的.所以它的存储模型设计得非常简单,总的来说,SQLite把一个数据文件分成若干大小相等的页面,然后以B树 ...
- LSM树存储模型
----<大规模分布式存储系统:原理解析与架构实战>读书笔记 之前研究了Bitcask存储模型,今天来看看LSM存储模型,两者尽管同属于基于键值的日志型存储模型.可是Bitcask使用哈希 ...
- 剖析Elasticsearch集群系列第一篇 Elasticsearch的存储模型和读写操作
剖析Elasticsearch集群系列涵盖了当今最流行的分布式搜索引擎Elasticsearch的底层架构和原型实例. 本文是这个系列的第一篇,在本文中,我们将讨论的Elasticsearch的底层存 ...
- 剖析Elasticsearch集群系列之一:Elasticsearch的存储模型和读写操作
转载:http://www.infoq.com/cn/articles/analysis-of-elasticsearch-cluster-part01 1.辨析Elasticsearch的索引与Lu ...
随机推荐
- Windows系统及硬件信息读取
Windows桌面端开发常常会需要读取系统信息或硬件信息作为用户标识,比如用于确认该设配是否已经激活程序.也可以使用随机生成的UUID来作为唯一标识,但是如果重装系统或重装软件都有可能导致标识丢失,因 ...
- 微前端框架 single-spa 技术分析
在理解微前端技术原理中我们介绍了微前端的概念和核心技术原理.本篇我们结合目前业内主流的微前端实现 single-spa 来说明在生产实践中是如何实现微前端的. single-spa 的文档略显凌乱,概 ...
- 【基因组预测】braker2基因结构注释要点记录
目录 流程使用 问题 记录下braker2的使用要点,以备忘记. 流程使用 braker2有很多流程,根据你的数据:组装的基因组.转录组.蛋白(同源,包括近缘或远缘)选择不同流程,官网有说明: htt ...
- 46.Valid Parentheses
Valid Parentheses My Submissions QuestionEditorial Solution Total Accepted: 106346 Total Submissions ...
- shell 的 功能语句--1
[1]说明性语句 (1)shell 程序和语句 shell 程序由零或多条shell语句构成. shell语句包括三类:说明性语句.功能性语句和结构性语句. 说明性语句: 以#号开始到该行结束,不被解 ...
- python2 第二天
requests库 编码和解码 输入和输出,在Python中,为了更好的调试和输出,我们需要对字符串进⾏格式化的输出,⽐如我们定义了姓名和年龄,但是我 们需要输出完整的信息,那么就涉及到字符串格式化的 ...
- 【模板】缩点(Tarjan算法)/洛谷P3387
题目链接 https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3387 题目大意 给定一个 \(n\) 个点 \(m\) 条边有向图,每个点有一个权值,求一条路径,使路径经过的点权值之 ...
- 一个简单的BypassUAC编写
什么是UAC? UAC是微软为提高系统安全而在Windows Vista中引入的新技术,它要求用户在执行可能会影响计算机运行的操作或执行更改影响其他用户的设置的操作之前,提供权限或管理员密码.通过在 ...
- acknowledge
accord+knowledge. accord好几个意思,knowledge不遑多让,We gotta acknowledge the word acknowledge has many meani ...
- 论文解读(GraRep)《GraRep: Learning Graph Representations with Global Structural Information》
论文题目:<GraRep: Learning Graph Representations with Global Structural Information>发表时间: CIKM论文作 ...
