记一次有趣的 Netty 源码问题
背景
起因是一个朋友问我的一个关于 ServerBootstrap 启动的问题.
相关 issue
他的问题我复述一下:
ServerBootstrap 的绑定流程如下:
ServerBootstrap.bind ->
AbstractBootstrap.bind ->
AbstractBootstrap.doBind ->
AbstractBootstrap.initAndRegister ->
AbstractChannel#AbstractUnsafe.register ->
eventLoop.execute( () -> AbstractUnsafe.register0)
doBind0() ->
channel.eventLoop().execute( () -> channel.bind) ->
AbstractUnsafe.bind
在 AbstractUnsafe.register0 中可能会调用 pipeline.fireChannelActive(), 即:
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
...
boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered;
doRegister();
...
if (firstRegistration && isActive()) {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
}
并且在 AbstractUnsafe.bind 中也会有 pipeline.fireChannelActive() 的调用, 即:
public final void bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
...
boolean wasActive = isActive();
try {
doBind(localAddress);
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
if (!wasActive && isActive()) {
invokeLater(new OneTimeTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
});
}
...
}
那么有没有可能造成了两次的 pipeline.fireChannelActive() 调用?
我的回答是不会. 为什么呢? 对于直接想知道答案的朋友可以直接阅读到最后面的 回答 与 总结 两节..
下面我们就来根据代码详细分析一下.
分析
首先, 根据我们上面所列出的调用流程, 会有 AbstractBootstrap.doBind 的调用, 它的代码如下:
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
// 步骤1
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
...
// 步骤2
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
...
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
...
} else {
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
...
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
});
}
}
首先在 doBind 中, 执行步骤1, 即调用 initAndRegister 方法, 这个方法会最终调用到AbstractChannel#AbstractUnsafe.register. 而在 AbstractChannel#AbstractUnsafe.register 中, 会通过 eventLoop.execute 的形式将 AbstractUnsafe.register0 的调用提交到任务队列中(即提交到 eventLoop 线程中, 而当前代码所在的线程是 main 线程), 即:
Override
public final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {
// 当前线程是主线程, 因此这个判断是 false
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {
try {
eventLoop.execute(new OneTimeTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
// register0 在 eventLoop 线程中执行.
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
}
}
接着 AbstractBootstrap.initAndRegister 返回, 回到 AbstractBootstrap.doBind 中, 于是执行到步骤2. 注意, 因为 AbstractUnsafe.register0 是在 eventLoop 中执行的, 因此有可能主线程执行到步骤2 时, AbstractUnsafe.register0 已经执行完毕了, 此时必然有 regFuture.isDone() == true; 但也有可能 AbstractUnsafe.register0 没有来得及执行, 因此此时 regFuture.isDone() == false. 所以上面的步骤2 考虑到了这两种情况, 因此分别针对这两种情况做了区分, 即:
// 步骤2
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
...
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
...
} else {
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
...
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
});
}
一般情况下, regFuture.isDone() 为 false, 因为绑定操作是比较费时的, 因此很大几率会执行到 else 分支, 并且 if 分支和 else 分支从结果上说没有不同, 而且 if 分支逻辑还更简单一些, 因此我们以 else 分支来分析吧. 在 else 分支中, 会为 regFuture 设置一个回调监听器. regFuture 是一个 ChannelFuture, 而 ChannelFuture 代表了一个 Channel 的异步 IO 的操作结果, 因此这里 regFuture 代表了 Channel 注册(register) 的这个异步 IO 的操作结果.
Netty 这里之所以要为 regFuture 设置一个回调监听器, 是为了保证 register 和 bind 的时序上的正确性: Channel 的注册必须要发生在 Channel 的绑定之前.
(关于时序的正确性的问题, 我们在后面有证明)
接下来我们来看一下 AbstractUnsafe.register0 方法:
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
....
// neverRegistered 一开始是 true, 因此 firstRegistration == true
boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered;
doRegister();
neverRegistered = false;
registered = true;
safeSetSuccess(promise);
pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
// Only fire a channelActive if the channel has never been registered. This prevents firing
// multiple channel actives if the channel is deregistered and re-registered.
// firstRegistration == true, 而 isActive() == false,
// 因此不会执行到 pipeline.fireChannelActive()
if (firstRegistration && isActive()) {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Close the channel directly to avoid FD leak.
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
注意, 我需要再强调一下, 这里 AbstractUnsafe.register0 是在 eventLoop 中执行的.
AbstractUnsafe.register0 中会调用 doRegister() 注册 NioServerSocketChannel, 然后调用 safeSetSuccess() 设置 promise 的状态为成功. 而这个 promise 变量是什么呢? 我将 AbstractBootstrap.doBind 的调用链写详细一些:
AbstractBootstrap.doBind ->
AbstractBootstrap.initAndRegister ->
MultithreadEventLoopGroup.register ->
SingleThreadEventLoop.register ->
AbstractChannel#AbstractUnsafe.register ->
eventLoop.execute( () -> AbstractUnsafe.register0)
在 SingleThreadEventLoop.register 中会实例化一个 DefaultChannelPromise, 即:
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
return register(channel, new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, this));
}
接着调用重载的 SingleThreadEventLoop.register 方法:
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(final Channel channel, final ChannelPromise promise) {
if (channel == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("channel");
}
if (promise == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("promise");
}
channel.unsafe().register(this, promise);
return promise;
}
我们看到, 实例化的 DefaultChannelPromise 最终会以方法返回值的方式返回到调用方, 即返回到 AbstractBootstrap.doBind 中:
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
因此我们这里有一个共识: regFuture 是一个在 SingleThreadEventLoop.register 中实例化的 DefaultChannelPromise 对象.
再回到 SingleThreadEventLoop.register 中, 在这里会调用 channel.unsafe().register(this, promise), 将 promise 对象传递到 AbstractChannel#AbstractUnsafe.register 中, 因此在 AbstractUnsafe.register0 中的 promise 就是 AbstractBootstrap.doBind 中的 regFuture.
promise == regFuture 很关键.
既然我们已经确定了 promise 的身份, 那么调用的 safeSetSuccess(promise); 我们也知道是干嘛的了. safeSetSuccess 方法设置一个 Promise 的状态为成功态, 而 Promise 的 成功态 是最终状态, 即此时 promise.isDone() == true. 那么 设置 promise 为成功态后, 会发生什么呢?
还记得不 promise == regFuture, 而我们在 AbstractBootstrap.doBind 的 else 分支中设置了一个回调监听器:
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// Registration on the EventLoop failed so fail the ChannelPromise directly to not cause an
// IllegalStateException once we try to access the EventLoop of the Channel.
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
// Registration was successful, so set the correct executor to use.
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2586
promise.executor = channel.eventLoop();
}
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
});
因此当 safeSetSuccess(promise); 调用时, 根据 Netty 的 Promise/Future 机制, 会触发上面的 operationComplete 回调, 在回调中调用 doBind0 方法:
private static void doBind0(
final ChannelFuture regFuture, final Channel channel,
final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
// This method is invoked before channelRegistered() is triggered. Give user handlers a chance to set up
// the pipeline in its channelRegistered() implementation.
channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (regFuture.isSuccess()) {
channel.bind(localAddress, promise).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
} else {
promise.setFailure(regFuture.cause());
}
}
});
}
注意到, 有一个关键的地方, 代码中将 **channel.bind** 的调用放到了 eventLoop 中执行. doBind0 返回后, 代码继续执行 AbstractUnsafe.register0 方法的剩余部分代码, 即:
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
....
safeSetSuccess(promise);
// safeSetSuccess 返回后, 继续执行如下代码
pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
// Only fire a channelActive if the channel has never been registered. This prevents firing
// multiple channel actives if the channel is deregistered and re-registered.
// firstRegistration == true, 而 isActive() == false,
// 因此不会执行到 pipeline.fireChannelActive()
if (firstRegistration && isActive()) {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Close the channel directly to avoid FD leak.
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
当 AbstractUnsafe.register0 方法执行完毕后, 才执行到 channel.bind 方法.
而 channel.bind 方法最终会调用到 AbstractChannel#AbstractUnsafe.bind 方法, 源码如下:
@Override
public final void bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
boolean wasActive = isActive();
logger.info("---wasActive: {}---", wasActive);
try {
// 调用 NioServerSocketChannel.bind 方法,
// 将底层的 Java NIO SocketChannel 绑定到指定的端口.
// 当 SocketChannel 绑定到端口后, isActive() 才为真.
doBind(localAddress);
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
boolean activeNow = isActive();
logger.info("---activeNow: {}---", activeNow);
// 这里 wasActive == false
// isActive() == true
if (!wasActive && isActive()) {
invokeLater(new OneTimeTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
});
}
safeSetSuccess(promise);
}
上面的代码中, 调用了 doBind(localAddress) 将底层的 Java NIO SocketChannel 绑定到指定的端口. 并且当 SocketChannel 绑定到端口后, isActive() 才为真.
因此我们知道, 如果 SocketChannel 第一次绑定时, 在调用 doBind 前, wasActive == false == isActive(), 而当调用了 doBind 后, isActive() == true, 因此第一次绑定端口时, if 判断成立, 会调用 pipeline.fireChannelActive().
关于 Channel 注册与绑定的时序问题
我们在前的分析中, 直接认定了 Channel 注册 在 Channel 的绑定 之前完成, 那么依据是什么呢?
其实所有的关键在于 EventLoop 的任务队列机制.
不要闲我啰嗦哦. 我们需要继续回到 AbstractUnsafe.register0 的调用中(再次强调一下, 在 eventLoop 线程中执行AbstractUnsafe.register0), 这个方法我们已经分析了, 它会调用 safeSetSuccess(promise), 并由 Netty 的 Promise/Future 机制, 导致了AbstractBootstrap.doBind 中的 regFuture 所设置的回调监听器的 operationComplete 方法调用, 而 operationComplete 中调用了 AbstractBootstrap.doBind0:
private static void doBind0(
final ChannelFuture regFuture, final Channel channel,
final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (regFuture.isSuccess()) {
channel.bind(localAddress, promise).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
} else {
promise.setFailure(regFuture.cause());
}
}
});
}
在 doBind0 中, 根据 EventLoop 的任务队列机制, 会使用 eventLoop().execute 将 channel.bind 封装为一个 Task, 放到 eventLoop 的 taskQueue 中.
如下用一幅图表示上面的过程:
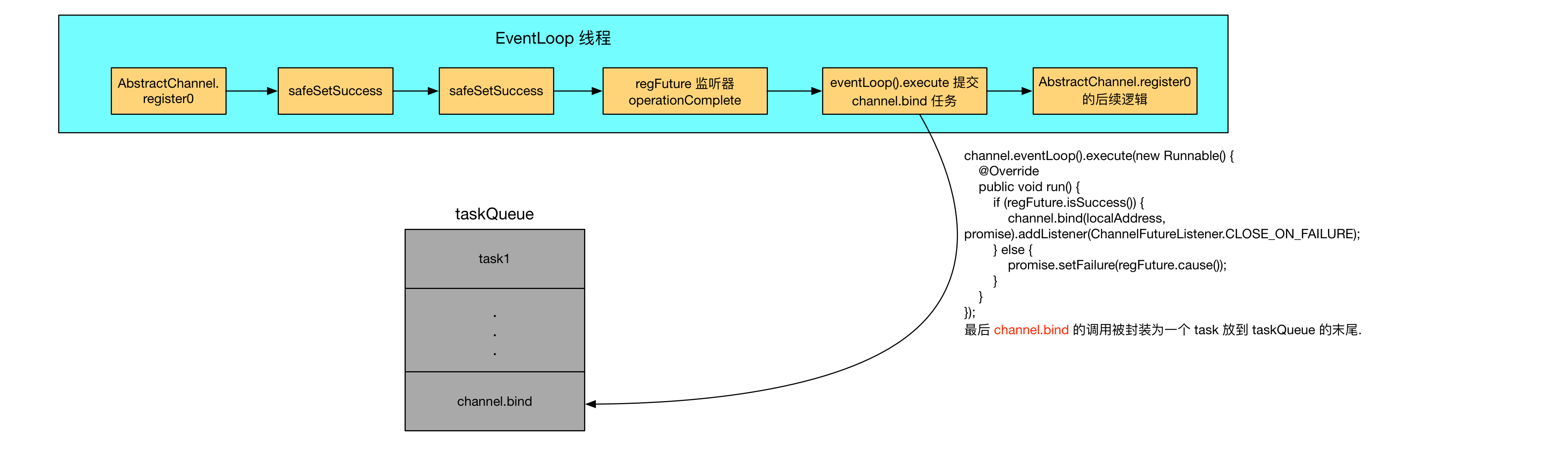
点此下载原图
而当 channel.bind 被调度时, AbstractUnsafe.register0 早就已经调用结束了.
因此由于 EventLoop 的任务队列机制, 我们知道, 在执行 AbstractUnsafe.register0 时, 是在 EventLoop 线程中的, 而 channel.bind 的调用是以 task 的形式添加到 taskQueue 队列的末尾, 因此必然是有 EventLoop 线程先执行完 AbstractUnsafe.register0 方法后, 才有机会从 taskQueue 中取出一个 task 来执行, 因此这个机制从根本上保证了 Channel 注册发生在绑定 之前.
回答
你的疑惑是, AbstractChannel#AbstractUnsafe.register0 中, 可能会调用 pipeline.fireChannelActive(), 即:
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
...
boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered;
doRegister();
...
if (firstRegistration && isActive()) {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
}
并且在 AbstractChannel#AbstractUnsafe.bind 中也可能会调用到pipeline.fireChannelActive(), 即:
public final void bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
...
boolean wasActive = isActive();
try {
doBind(localAddress);
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
if (!wasActive && isActive()) {
invokeLater(new OneTimeTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
});
}
...
}
我觉得是 不会. 因为根据上面我们分析的结果可知, Netty 的 Promise/Future 与 EventLoop 的任务队列机制保证了 NioServerSocketChannel 的注册和 Channel 的绑定的时序: Channel 的注册必须要发生在 Channel 的绑定之前, 而当一个 NioServerSocketChannel 没有绑定到具体的端口前, 它是不活跃的(Inactive), 进而在 register0 中, if (firstRegistration && isActive()) 就不成立, 因此就不会执行到 pipeline.fireChannelActive() 了.
而执行完注册操作后, 在 AbstractChannel#AbstractUnsafe.bind 才会调用pipeline.fireChannelActive(), 因此最终只有一次 fireChannelActive 调用.
总结
有两点需要注意的:
- isActive() == true 成立的关键是此 NioServerSocketChannel 已经绑定到端口上了.
- 由 Promise/Future 与 EventLoop 机制, 导致了 Channel 的注册 发生在 Channel 的绑定 之前, 因此在 AbstractChannel#AbstractUnsafe.register0 中的 isActive() == false, if 判断不成立, 最终就是 register0 中的 pipeline.fireChannelActive() 不会被调用.
记一次有趣的 Netty 源码问题的更多相关文章
- 脚踏实地的Netty源码研究笔记——开篇
1. 脚踏实地的Netty源码研究笔记--开篇 1.1. Netty介绍 Netty是一个老牌的高性能网络框架.在众多开源框架中都有它的身影,比如:grpc.dubbo.seata等. 里面有着非常多 ...
- Netty源码解读(二)-服务端源码讲解
简单Echo案例 注释版代码地址:netty 代码是netty的源码,我添加了自己理解的中文注释. 了解了Netty的线程模型和组件之后,我们先看看如何写一个简单的Echo案例,后续的源码讲解都基于此 ...
- Netty源码阅读(一) ServerBootstrap启动
Netty源码阅读(一) ServerBootstrap启动 转自我的Github Netty是由JBOSS提供的一个java开源框架.Netty提供异步的.事件驱动的网络应用程序框架和工具,用以快速 ...
- 【Netty源码学习】DefaultChannelPipeline(三)
上一篇博客中[Netty源码学习]ChannelPipeline(二)我们介绍了接口ChannelPipeline的提供的方法,接下来我们分析一下其实现类DefaultChannelPipeline具 ...
- 【Netty源码分析】发送数据过程
前面两篇博客[Netty源码分析]Netty服务端bind端口过程和[Netty源码分析]客户端connect服务端过程中我们分别介绍了服务端绑定端口和客户端连接到服务端的过程,接下来我们分析一下数据 ...
- 【Netty源码分析】客户端connect服务端过程
上一篇博客[Netty源码分析]Netty服务端bind端口过程 我们介绍了服务端绑定端口的过程,这一篇博客我们介绍一下客户端连接服务端的过程. ChannelFuture future = boos ...
- 【Netty源码分析】ChannelPipeline(二)
在上一篇博客[Netty源码学习]ChannelPipeline(一)中我们只是大体介绍了ChannelPipeline相关的知识,其实介绍的并不详细,接下来我们详细介绍一下ChannelPipeli ...
- 【Netty源码学习】ChannelPipeline(一)
ChannelPipeline类似于一个管道,管道中存放的是一系列对读取数据进行业务操作的ChannelHandler. 1.ChannelPipeline的结构图: 在之前的博客[Netty源码学习 ...
- 【Netty源码学习】ServerBootStrap
上一篇博客[Netty源码学习]BootStrap中我们介绍了客户端使用的启动服务,接下来我们介绍一下服务端使用的启动服务. 总体来说ServerBootStrap有两个主要功能: (1)调用父类Ab ...
随机推荐
- django 实现上传文件功能
需求:自己写一个文件上传功能 代码: urls.py from django.conf.urls import url from django.contrib import admin from ap ...
- 倾斜摄影三维建模软件photoscan教程 [转]
PhotoScan是一款基于影响自动生成高质量三维模型的优秀软件,这对于3D建模需求来说实在是一把利器. PhotoScan无需设置初始值,无须相机检校,它根据最新的多视图三维重建技术,可对任意照片进 ...
- 直播 背景 技术体系 乐视云直播Demo
背景 最近工作需要做一款直播APP,恩是的,从RTMP协议的实现开始到处理服务器高并发.负载均衡.客户端播放器实现等等等..... 估计全部写完我也到而立之年了吧...... BOSS们估计也是发现了 ...
- JSP学习笔记(五):日期处理、页面重定向、点击量统计、自动刷新和发送邮件
一.JSP 日期处理: 使用JSP最重要的优势之一,就是可以使用所有Java API.本节讲述Java中的Date类,它在java.util包下,封装了当前日期和时间. Date类有两个构造函数.第 ...
- (转)AS3 中,Function.apply、call中第一个参数的作用;与什么时候用
http://blog.csdn.net/linjf520/article/details/8746064 大家在使用Function.apply或是call时,是否发现,第一个参数不知道怎么用,赋值 ...
- Linux系统登录:本地登录与远程登录
安装登录系统的位置可以将登录方式分为两种:本地登录和远程登录.本地登录可以使用图形界面和命令行模式(也称字符界面)两种方式:远程登录可以使用SSH.Telnent.VNC.SFTP 4种方式. 常见的 ...
- 算法笔记_151:算法提高 01背包(Java)
目录 1 问题描述 2 解决方案 1 问题描述 问题描述 给定N个物品,每个物品有一个重量W和一个价值V.你有一个能装M重量的背包.问怎么装使得所装价值最大.每个物品只有一个. 输入格式 输入的第 ...
- 算法笔记_131:出现次数超过一半的数(Java)
目录 1 问题描述 2 解决方案 2.1 每次删除两个不同的数 2.2 记录两个值 1 问题描述 数组中有一个数出现的次数超过了数组长度的一半,请找出这个数. 2 解决方案 2.1 每次删除两个不 ...
- 微信群的id
今天网速慢了,竟然把微信群的id卡出来了,记录一下. 格式应该是一个像QQ群一样的数字,然后+@chatroom 看图! 文章来源:刘俊涛的博客 欢迎关注,有问题一起学习欢迎留言.评论.
- Android应用更新自动检测下载
由于Android项目开源所致,市面上出现了N多安卓软件市场.为了让我们开发的软件有更多的用户使用,我们需要向N多市场发布,软件升级后,我们也必须到安卓市场上进行更新,给我们增加了工作量.因此我们有必 ...
