Service启动流程
Service启动流程从整个宏观上来看,它的模型如下
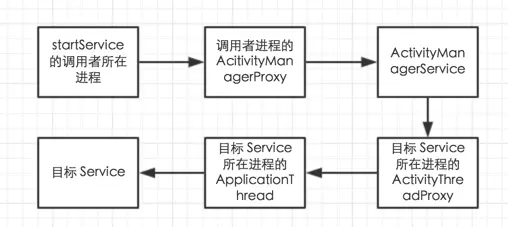
startService启动流程时序图
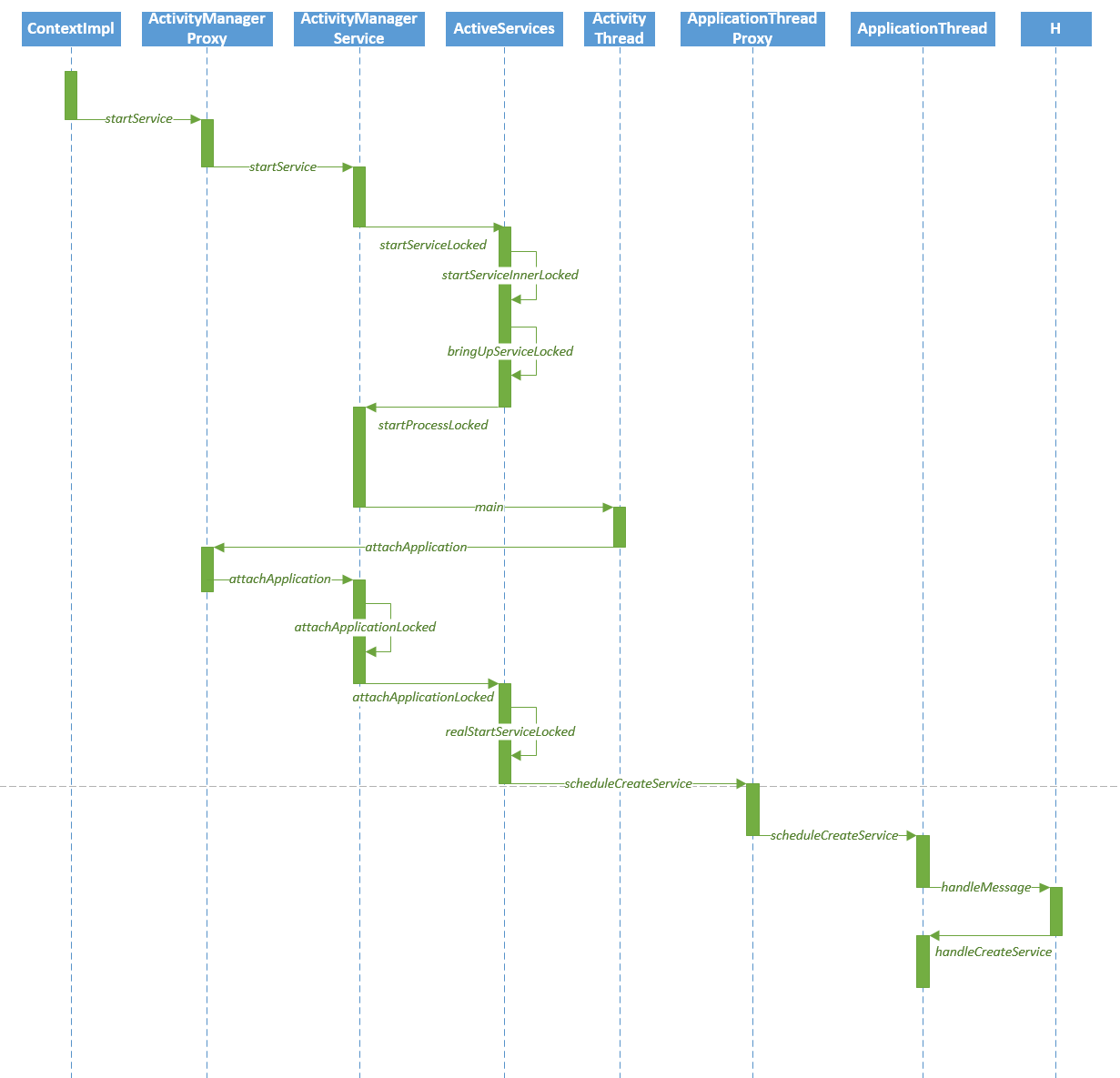
Activity中使用的startService方法是定义在Context的抽象类中,它的真正实现者是ContextImpl,所以我们首先进入ContextImpl类
(1)ContextImpl.startService()
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
@Override
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return startServiceCommon(service, mUser);
} private ComponentName startServiceCommon(Intent service, UserHandle user) {
try {
validateServiceIntent(service);
service.prepareToLeaveProcess();
ComponentName cn = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().startService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()), user.getIdentifier());
//......
return cn;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
return null;
}
}
从ContextImpl类的startService开始,然后进入本类的startServiceCommon方法,并最终调用ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()对象的startService方法。其实这里的ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()就是ActivityManagerProxy对象
(2)ActivityManagerProxy.startService()
源码:frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityManagerNative.java
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service,
String resolvedType, int userId) throws RemoteException
{
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null);
service.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeString(resolvedType);
data.writeInt(userId);
mRemote.transact(START_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
ComponentName res = ComponentName.readFromParcel(reply);
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
return res;
}
通过Binder调用ActivityManagerNative类中onTransact方法,其识别码为START_SERVICE_TRANSACTION,并最终调用ActivityManagerNative的实现类ActivityManagerService的startService方法。
(3)ActivityManagerService.startService()
源码:frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
@Override
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service,
String resolvedType, int userId) {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startService");
//......
synchronized(this) {
final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
ComponentName res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service,
resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid, userId);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
return res;
}
}
在这里调用mServices对象的startServiceLocked方法,这里的mServices对象是ActiveServices类。
(4)ActiveServices.startServiceLocked()
源码:frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller,
Intent service, String resolvedType,
int callingPid, int callingUid, int userId) { //......
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType,
callingPid, callingUid, userId, true, callerFg);
ServiceRecord r = res.record;
//......
return startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting);
}
相关内容,然后将解析结果放在res.record中,最后在调用startServiceInnerLocked方法。
(5)ActiveServices.startServiceInnerLocked()
源码:frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
ComponentName startServiceInnerLocked(ServiceMap smap, Intent service,
ServiceRecord r, boolean callerFg, boolean addToStarting) { //......
synchronized (r.stats.getBatteryStats()) {
r.stats.startRunningLocked();
}
String error = bringUpServiceLocked(r, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false);
//......
}
这里紧接着会调用bringUpServiceLocked方法。
(6)ActiveServices.bringUpServiceLocked()
源码:frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
private final String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
int intentFlags, boolean execInFg, boolean whileRestarting) { //(1)这里如果当前的ProcessRecord不为null,那就不需要重新创建进程,而是调用realStartServiceLocked方法来启动Service
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.versionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting service " + r.shortName, e);
} // If a dead object exception was thrown -- fall through to
// restart the application.
} //(2)如果是需要创建新进程,那么将调用ActivityManagerService.startProcessLocked方法来启动新进程
if (app == null) {
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
"service", r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null) {
//......
bringDownServiceLocked(r);
return msg;
}
if (isolated) {
r.isolatedProc = app;
}
} //最后将ServiceRecord保存到成员变量mPendingServices中
if (!mPendingServices.contains(r)) {
mPendingServices.add(r);
}
}
这个方法比较重要,这里有两种选择,当Service所在的进程存在时,将调用realStartServiceLocked方法来启动Service,否则的话调用startProcessLocked方法来启动新进程。
(7)ActivityManagerService.startProcessLocked()
源码:frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app, String hostingType,
String hostingNameStr, String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs) { boolean isActivityProcess = (entryPoint == null);
if (entryPoint == null) entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread";
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: asking zygote to start proc");
//通过processName,uid等启动新进程
Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, app.info.seinfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, entryPointArgs);
}
这里通过Process的start方法启动ActivityThread的新进程,我们进入该类的main方法。
(8)ActivityThread.main()
源码:frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
public static void main(String[] args) {
//......
Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
//创建ActivityThread对象,并调用其attach方法
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
private void attach(boolean system) {
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {
//这里调用了ActivityManagerProxy.attachApplication方法。
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
}
在Android应用程序中,每一个进程对应一个ActivityThread实例,然后这里创建了ActivityThread对象并调用了其attach方法,在attach方法中又调用了ActivityManagerProxy.attachApplication方法。
(9)ActivityManagerProxy.attachApplication()
源码:frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityManagerNative.java
public void attachApplication(IApplicationThread app) throws RemoteException
{
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(app.asBinder());
mRemote.transact(ATTACH_APPLICATION_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0);
reply.readException();
data.recycle();
reply.recycle();
}
通过Binder机制会调用ActivityManagerNative中的onTransact方法,其识别码为ATTACH_APPLICATION_TRANSACTION,并最终调用ActivityManagerService中的attachApplication方法。
(10)ActivityManagerService.attachApplication()
源码:frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
@Override
public final void attachApplication(IApplicationThread thread) {
synchronized (this) {
int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
attachApplicationLocked(thread, callingPid);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId); //......
}
}
这里调用attachApplicationLocked方法来进一步处理。
(11)ActivityManagerService.attachApplicationLocked()
源码:frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid) { // See if the top visible activity is waiting to run in this process...
if (normalMode) {
try {
if (mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app)) {
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown launching activities in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
} // Find any services that should be running in this process...
if (!badApp) {
try {
//这里会调用ActiveServices对象的attachApplicationLocked方法
didSomething |= mServices.attachApplicationLocked(app, processName);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown starting services in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
}
里如果是启动Service将调用ActiveServices对象的attachApplicationLocked方法,而如果是启动Activity将调用ActivityStackSupervisor对象的attachApplicationLocked方法。
(12)ActiveServices.attachApplicationLocked()
源码:frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
boolean attachApplicationLocked(ProcessRecord proc, String processName)
throws RemoteException { boolean didSomething = false;
// Collect any services that are waiting for this process to come up.
if (mPendingServices.size() > 0) {
ServiceRecord sr = null;
try {
for (int i=0; i<mPendingServices.size(); i++) {
sr = mPendingServices.get(i);
if (proc != sr.isolatedProc && (proc.uid != sr.appInfo.uid
|| !processName.equals(sr.processName))) {
continue;
} mPendingServices.remove(i);
i--;
proc.addPackage(sr.appInfo.packageName, sr.appInfo.versionCode,mAm.mProcessStats); //这里调用realStartServiceLocked方法
realStartServiceLocked(sr, proc, sr.createdFromFg);
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception in new application when starting service "+ sr.shortName, e);
throw e;
}
}
//......
}
(13)ActiveServices.realStartServiceLocked()
源码:frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException { if (app.thread == null) {
throw new RemoteException();
} //...... app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
}
此处的app.thread是一个IApplicationThread对象,而IApplicationThread的代理类是ApplicationThreadProxy,我们进入app.thread对象的scheduleCreateService方法。
(14)ApplicationThreadProxy.scheduleCreateService()
源码:frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ApplicationThreadNative.java
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token, ServiceInfo info,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) throws RemoteException {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread.descriptor);
data.writeStrongBinder(token);
info.writeToParcel(data, 0);
compatInfo.writeToParcel(data, 0);
data.writeInt(processState);
mRemote.transact(SCHEDULE_CREATE_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, null,
IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);
data.recycle();
}
通过Binder对象调用ApplicationThreadNative的onTransact方法,在其方法中调用子类的scheduleCreateService方法,即最终调用ApplicationThreadNative的子类ApplicationThread的scheduleCreateService方法。
(15)ApplicationThread.scheduleCreateService()
源码:frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo; sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}
通过Handler发送Message来处理该操作,并进入到H的handleMessage方法中,其识别码为CREATE_SERVICE。
(16)H.handleMessage()
源码:frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ApplicationThread.java
private class H extends Handler {
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceCreate");
//这里调用handleCreateService方法
handleCreateService((CreateServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
}
}
我们继续进入handleCreateService方法。
(17)ApplicationThread.handleCreateService()
源码:frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
Service service = null;
try {
//(1)通过类加载器来加载Service对象
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
//......
}
//(2)这里创建ContextImpl对象
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());
//(3)这里调用Service的onCreate方法
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);
}
1)处通过类加载器ClassLoader来加载Service对象,此处的data.info.name就是我们要启动的Service,加载完成后需要将其强转换为Service对象,也就是说我们的Service必须要继承于Service基类。
(2)处这里先创建一个ContextImpl对象,每个Activity和Service都有一个Context对象。
(3)处这里调用Service的OnCreate方法。
好啦,到此整个Service通过startService的方式就启动起来了,接下来我们总结一下步骤。
总结
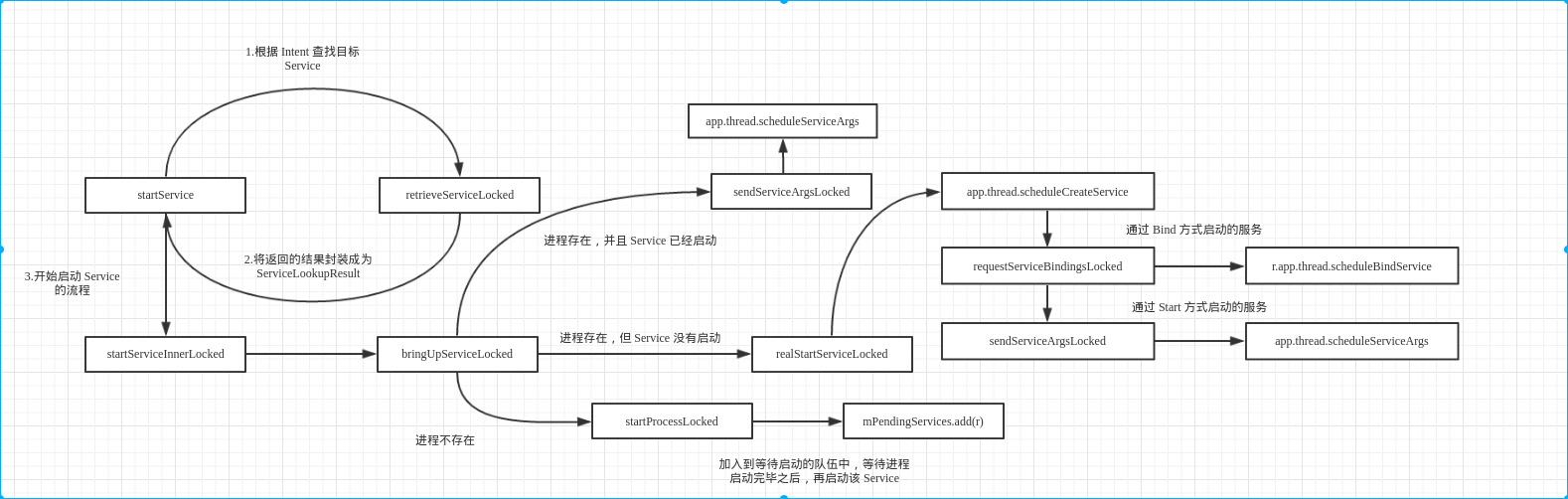
1、(1)-(7)从主进程调用到ActivityManagerService进程中,并调用其startProcessLocked方法来启动新的进程。
2、(8)-(11)从新进程调用到ActivityManagerService进程中,获取要启动的服务的相关信息。
3、(12)-(17)从ActivityManagerService进程回到新进程中并最终将服务启动起来。
Service启动流程的更多相关文章
- Android Service 启动流程
执行顺序 : startService -> bindService -> unbindService -> stopService 回调的结果为: 执行顺序 : startServ ...
- 【系统解读】SystemUI篇(一)SystemUI启动流程
前言 SystemUI是系统启动中第一个用户肉眼可见的应用,其功能包罗万象,比如开机后看到的锁屏界面,充电时充电界面,状态栏,导航栏,多任务栏等,都是与Android手机用户息息相关的功能.所以不止S ...
- 插件占坑,四大组件动态注册前奏(二) 系统Service的启动流程
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/hejjunlin/article/details/52203903 前言:为什么要了解系统Activity,Service,BroadCas ...
- Tomcat源码分析之—具体启动流程分析
从Tomcat启动调用栈可知,Bootstrap类的main方法为整个Tomcat的入口,在init初始化Bootstrap类的时候为设置Catalina的工作路径也就是Catalina_HOME信息 ...
- Linux 的启动流程(转)
原文链接:http://blog.jobbole.com/46078/ 半年前,我写了<计算机是如何启动的?>,探讨BIOS和主引导记录的作用. 那篇文章不涉及操作系统,只与主板的板载程序 ...
- Tomcat学习 HttpConnector和HttpProcessor启动流程和线程交互
一.tomat启动流程 1.启动HttpConnector connector等待连接请求,只负责接受socket请求,具体处理过程交给HttpProcessor处理. tomcat用户只能访问到co ...
- Android FM模块学习之一 FM启动流程
最近在学习FM模块,FM是一个值得学习的模块,可以从上层看到底层. 上层就是FM的按扭操作和界面显示,从而调用到FM底层驱动来实现广播收听的功能. FM启动流程:如下图: 先进入FMRadio.jav ...
- Linux启动流程详解
在BIOS阶段,计算机的行为基本上被写死了,可以做的事情并不多:一般就是通电.BIOS.主引导记录.操作系统这四步.所以我们一般认为加载内核是linux启动流程的第一步. 第一步.加载内核 操作系统接 ...
- 【转】Linux 的启动流程
半年前,我写了<计算机是如何启动的?>,探讨BIOS和主引导记录的作用. 那篇文章不涉及操作系统,只与主板的板载程序有关.今天,我想接着往下写,探讨操作系统接管硬件以后发生的事情,也就是操 ...
随机推荐
- select右三角消除(转)
代码如下: select { /*Chrome和Firefox里面的边框是不一样的,所以复写了一下*/ border: solid 1px #; /*很关键:将默认的select选择框样式清除*/ a ...
- JavaEE互联网轻量级框架整合开发(书籍)阅读笔记(10):通过注解(annotation)装配Bean之(@Configguration、@Component、@Value、@ComponentScan、@Autowired、@Primary、@Qualifier、@Bean)
一.通过注解(annotation)装配Bean 通过之前的学习,我们已经知道如何使用XML装配Bean,但是更多的时候已经不再推荐使用XML的方式去装配Bean,更多的时候会考虑注解(annotat ...
- c_c++基础问题(平时读书时笔记)
1 IP私有地址: 10.0.0.0 -- 10.255.255.255 172.16.0.0 -- 172.31.255.255 192.168.0.0 -- 192.168.255.255 2OS ...
- Reporting Service服务SharePoint集成模式安装配置(9、PowerPivot for SharePoint 安装配置详细)
PowerPivot for SharePoint 增加了对发布到 SharePoint 中的 PowerPivot 工作簿的协作和文档管理支持. PowerPivot for SharePoint ...
- RobotFramework关键字返回参数
业务关键字[登录]返回参数 调用时直接把return的参数值写在业务关键字的最前面,就可以使用关键字的返回值了
- centos7 守护进程
ASP.NET Core应用程序发布linux在shell中运行是正常的.可一但shell关闭网站也就关闭了,所以要配置守护进程, 用的是Supervisor,本文主要记录配置的过程和过程遇到的问题 ...
- ES6—— iterator和for-of循环
Iterator 遍历器的作用:为各种数据结构,提供一个同意的,简便的访问接口.是的数据结构的成员能够按某种次序排列.ES6 新增了遍历命令 for...of 循环,Iterator接口主要供 for ...
- 高性能无锁队列 Disruptor 初体验
原文地址: haifeiWu和他朋友们的博客 博客地址:www.hchstudio.cn 欢迎转载,转载请注明作者及出处,谢谢! 最近一直在研究队列的一些问题,今天楼主要分享一个高性能的队列 Disr ...
- maven-compiler-plugin 版本错误解决方法
项目执行Maven build后出现WARNING提示.报如信息如下,根据报错信息猜测是maven-compiler-plugin的版本信息问题 [WARNING] [WARNING] Some pr ...
- 序列(DP)(组合数)
这是一个DP题. 我们设\(f[i][j][k]\)表示\(i\)序列长度中放入了\(j\)个元素,其中\(k\)是限定的众数的个数:状态转移方程是 \[f[k][i][j]=f[k][i-1][j- ...
