yolov1代码阅读
yolov1使用的backbone是由GoogLeNet启发而来,有24个卷积层,最后接2个全连接层,详细结构如下图:
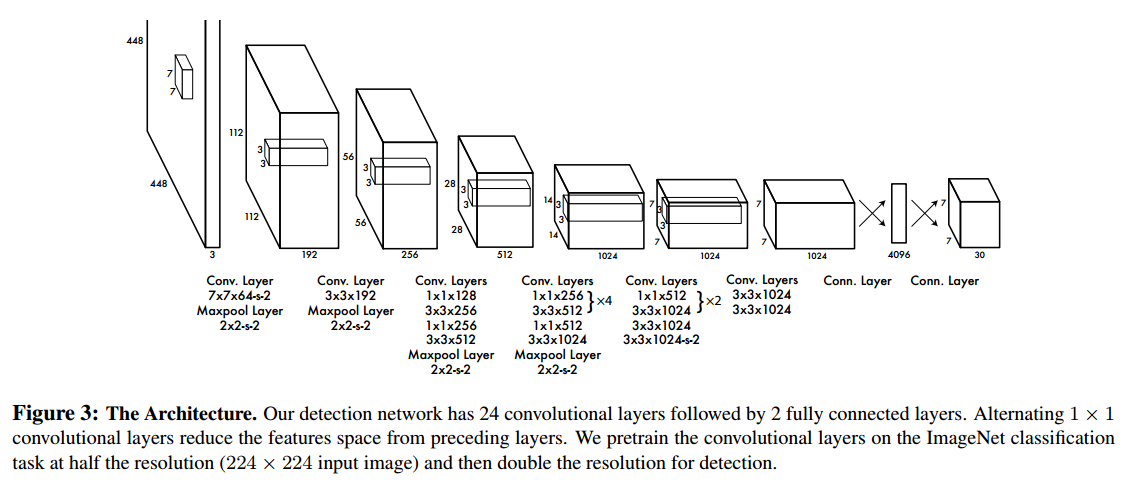
检测网络的输入分辨率是448X448,最后的特征图大小为7X7。在特征图的每一个位置都预测如下数据项:
1、一个C维的向量,表示在该位置含有物体的条件下,含有的物体属于C个类别中每一类别的条件概率;
2、一个B维的向量,网络为每个位置预测了B个bounding boxes,每个bounding boxes都有一个“分数”,表示该box与真正的物体框的IOU,也可以理解成该bounding box含有物体的概率。这里的“分数”和1中的每个类别的分数相乘就是每个框含有每一类物体的概率;
3、一个B*4维的向量。前两个数是bbox的中心点坐标,坐标值是在7X7的尺度下,相对于feature map当前位置的偏移量,范围为[0, 1],当前位置坐标和偏移量相加即为实际的中心点坐标。这个中心点坐标的范围实际上就在以当前位置为左上角顶点的grid cell内。
综上输出的Tensor元素的排列顺序为:7*7*C-->7*7*B-->7*7*4*B,而标签Tensor元素的排列顺序为(1-->C-->4)*7*7。
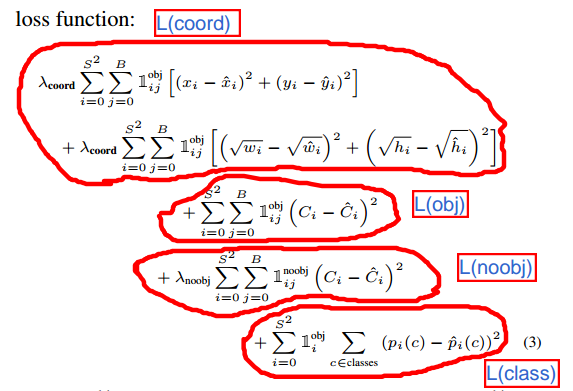
yolov1的Loss由4部分组成,如下图:
yolov1最后一层的代码如下:
/*
l.coord_scale=5
l.object_scale=1
l.noobject_scale=0.5
l.class_scale=1
l.delta[box_index+0] = l.coord_scale*(net.truth[tbox_index + 0] - l.output[box_index + 0]);
l.delta[box_index+1] = l.coord_scale*(net.truth[tbox_index + 1] - l.output[box_index + 1]);
l.delta[box_index+2] = l.coord_scale*(sqrt(net.truth[tbox_index + 2]) - l.output[box_index + 2]);
l.delta[box_index+3] = l.coord_scale*(sqrt(net.truth[tbox_index + 3]) - l.output[box_index + 3]);
l.delta[p_index] = l.object_scale * (iou - l.output[p_index]);
l.delta[p_index] = l.noobject_scale*(0 - l.output[p_index]);
l.delta[class_index+j] = l.class_scale * (net.truth[truth_index+1+j] - l.output[class_index+j]);
*/
void forward_detection_layer(const detection_layer l, network net)
{
int locations = l.side*l.side;
int i,j;
memcpy(l.output, net.input, l.outputs*l.batch*sizeof(float));
//if(l.reorg) reorg(l.output, l.w*l.h, size*l.n, l.batch, 1);
int b;
// l.softmax=0
if (l.softmax){
for(b = ; b < l.batch; ++b){
int index = b*l.inputs;
for (i = ; i < locations; ++i) {
int offset = i*l.classes;
softmax(l.output + index + offset, l.classes, , ,
l.output + index + offset);
}
}
}
if(net.train){
float avg_iou = ;
float avg_cat = ;
float avg_allcat = ;
float avg_obj = ;
float avg_anyobj = ;
int count = ;
*(l.cost) = ;
int size = l.inputs * l.batch;
memset(l.delta, , size * sizeof(float));
for (b = ; b < l.batch; ++b){
int index = b*l.inputs;
for (i = ; i < locations; ++i) {
int truth_index = (b*locations + i)*(+l.coords+l.classes);
int is_obj = net.truth[truth_index];
for (j = ; j < l.n; ++j) {
int p_index = index + locations*l.classes + i*l.n + j;
// l.noobject_scale=0.5
l.delta[p_index] = l.noobject_scale*( - l.output[p_index]);
*(l.cost) += l.noobject_scale*pow(l.output[p_index], );
avg_anyobj += l.output[p_index];
}
if (!is_obj){
continue;
} // l.class_scale=1
int class_index = index + i*l.classes;
for(j = ; j < l.classes; ++j) {
l.delta[class_index+j] = l.class_scale * (net.truth[truth_index++j] - l.output[class_index+j]);
*(l.cost) += l.class_scale * pow(net.truth[truth_index++j] - l.output[class_index+j], );
if(net.truth[truth_index + + j]) avg_cat += l.output[class_index+j];
avg_allcat += l.output[class_index+j];
}
int best_index = -;
float best_iou = ;
float best_rmse = ;
int row = i / l.side;
int col = i % l.side;
box truth = float_to_box(net.truth + truth_index + + l.classes, );
truth.x = (truth.x + col) / l.side;
truth.y = (truth.y + row) / l.side;
for(j = ; j < l.n; ++j){
int box_index = index + locations*(l.classes + l.n) + (i*l.n + j) * l.coords;
box out = float_to_box(l.output + box_index, );
out.x = (out.x + col) / l.side;
out.y = (out.y + row) / l.side;
// l.sqrt=1
if (l.sqrt){
out.w = out.w*out.w;
out.h = out.h*out.h;
}
float iou = box_iou(out, truth);
float rmse = box_rmse(out, truth);
if(best_iou > || iou > ){
if(iou > best_iou){
best_iou = iou;
best_index = j;
}
}else{
if(rmse < best_rmse){
best_rmse = rmse;
best_index = j;
}
}
}
// l.forced=0
if(l.forced){
if(truth.w*truth.h < .){
best_index = ;
}else{
best_index = ;
}
}
// l.random=0
if(l.random && *(net.seen) < ){
best_index = rand()%l.n;
} int box_index = index + locations*(l.classes + l.n) + (i*l.n + best_index) * l.coords;
int tbox_index = truth_index + + l.classes;
box out = float_to_box(l.output + box_index, );
out.x = (out.x + col) / l.side;
out.y = (out.y + row) / l.side;
if (l.sqrt) {
out.w = out.w*out.w;
out.h = out.h*out.h;
}
float iou = box_iou(out, truth);
// l.noobject_scale=0.5, l.object_scale=1
int p_index = index + locations*l.classes + i*l.n + best_index;
*(l.cost) -= l.noobject_scale * pow(l.output[p_index], );
*(l.cost) += l.object_scale * pow(-l.output[p_index], );
avg_obj += l.output[p_index];
l.delta[p_index] = l.object_scale * (.-l.output[p_index]);
// l.rescore=1
if(l.rescore){
l.delta[p_index] = l.object_scale * (iou - l.output[p_index]);
}
// l.coord_scale=5
l.delta[box_index+] = l.coord_scale*(net.truth[tbox_index + ] - l.output[box_index + ]);
l.delta[box_index+] = l.coord_scale*(net.truth[tbox_index + ] - l.output[box_index + ]);
l.delta[box_index+] = l.coord_scale*(net.truth[tbox_index + ] - l.output[box_index + ]);
l.delta[box_index+] = l.coord_scale*(net.truth[tbox_index + ] - l.output[box_index + ]);
if(l.sqrt){
l.delta[box_index+] = l.coord_scale*(sqrt(net.truth[tbox_index + ]) - l.output[box_index + ]);
l.delta[box_index+] = l.coord_scale*(sqrt(net.truth[tbox_index + ]) - l.output[box_index + ]);
} *(l.cost) += pow(-iou, );
avg_iou += iou;
++count;
}
}
*(l.cost) = pow(mag_array(l.delta, l.outputs * l.batch), );
printf("Detection Avg IOU: %f, Pos Cat: %f, All Cat: %f, Pos Obj: %f, Any Obj: %f, count: %d\n", avg_iou/count, avg_cat/count, avg_allcat/(count*l.classes), avg_obj/count, avg_anyobj/(l.batch*locations*l.n), count);
//if(l.reorg) reorg(l.delta, l.w*l.h, size*l.n, l.batch, 0);
}
} void backward_detection_layer(const detection_layer l, network net)
{
axpy_cpu(l.batch*l.inputs, , l.delta, , net.delta, );
}
预测时根据最终的输出得到bbox的代码如下:(值得注意的是,在yolov1的训练阶段,会使用原图的宽、高将标注的bbox归一化,在预测阶段输出的bbox坐标也是归一化的。)
void get_detection_detections(layer l, int w, int h, float thresh, detection *dets)
{
int i,j,n;
float *predictions = l.output;
//int per_cell = 5*num+classes;
for (i = ; i < l.side*l.side; ++i){
int row = i / l.side;
int col = i % l.side;
for(n = ; n < l.n; ++n){
int index = i*l.n + n;
int p_index = l.side*l.side*l.classes + i*l.n + n;
float scale = predictions[p_index];
int box_index = l.side*l.side*(l.classes + l.n) + (i*l.n + n)*;
box b;
// b.x = (predictions[box_index + 0] + col) / l.side * w;
// b.y = (predictions[box_index + 1] + row) / l.side * h;
// b.w = pow(predictions[box_index + 2], (l.sqrt?2:1)) * w;
// b.h = pow(predictions[box_index + 3], (l.sqrt?2:1)) * h;
b.x = (predictions[box_index + ] + col) / l.side;
b.y = (predictions[box_index + ] + row) / l.side;
b.w = pow(predictions[box_index + ], (l.sqrt?:));
b.h = pow(predictions[box_index + ], (l.sqrt?:));
dets[index].bbox = b;
dets[index].objectness = scale;
for(j = ; j < l.classes; ++j){
int class_index = i*l.classes;
float prob = scale*predictions[class_index+j];
dets[index].prob[j] = (prob > thresh) ? prob : ;
}
}
}
}
生成net.truth的关键代码如下:
void fill_truth_region(char *path, float *truth, int classes, int num_boxes, int flip, float dx, float dy, float sx, float sy)
{
char labelpath[];
find_replace(path, "images", "labels", labelpath);
find_replace(labelpath, "JPEGImages", "labels", labelpath); find_replace(labelpath, ".jpg", ".txt", labelpath);
find_replace(labelpath, ".png", ".txt", labelpath);
find_replace(labelpath, ".JPG", ".txt", labelpath);
find_replace(labelpath, ".JPEG", ".txt", labelpath);
int count = ;
box_label *boxes = read_boxes(labelpath, &count);
randomize_boxes(boxes, count);
correct_boxes(boxes, count, dx, dy, sx, sy, flip);
float x,y,w,h;
int id;
int i; for (i = ; i < count; ++i) {
x = boxes[i].x;
y = boxes[i].y;
w = boxes[i].w;
h = boxes[i].h;
id = boxes[i].id; if (w < . || h < .) continue; // num_boxes is S in article, yolov1 divides the input image into SxS grid
int col = (int)(x*num_boxes);
int row = (int)(y*num_boxes); x = x*num_boxes - col;
y = y*num_boxes - row; int index = (col+row*num_boxes)*(+classes);
if (truth[index]) continue;
truth[index++] = ; if (id < classes) truth[index+id] = ;
index += classes; truth[index++] = x;
truth[index++] = y;
truth[index++] = w;
truth[index++] = h;
}
free(boxes);
}
yolov1代码阅读的更多相关文章
- 代码阅读分析工具Understand 2.0试用
Understand 2.0是一款源代码阅读分析软件,功能强大.试用过一段时间后,感觉相当不错,确实可以大大提高代码阅读效率.由于Understand功能十分强大,本文不可能详尽地介绍它的所有功能,所 ...
- Android 上的代码阅读器 CoderBrowserHD 修改支持 go 语言代码
我在Android上的代码阅读器用的是 https://github.com/zerob13/CoderBrowserHD 改造的版本,改造后的版本我放在 https://github.com/ghj ...
- Linux协议栈代码阅读笔记(二)网络接口的配置
Linux协议栈代码阅读笔记(二)网络接口的配置 (基于linux-2.6.11) (一)用户态通过C库函数ioctl进行网络接口的配置 例如,知名的ifconfig程序,就是通过C库函数sys_io ...
- [置顶] Linux协议栈代码阅读笔记(一)
Linux协议栈代码阅读笔记(一) (基于linux-2.6.21.7) (一)用户态通过诸如下面的C库函数访问协议栈服务 int socket(int domain, int type, int p ...
- 图形化代码阅读工具——Scitools Understand
Scitools出品的Understand 2.0.用了很多年了,比Source Insight强大很多.以前的名字叫Understand for C/C++,Understand for Java, ...
- Python - 关于代码阅读的一些建议
初始能力 让阅读思路保持清晰连贯,主力关注在流程架构和逻辑实现上,不被语法.技巧和业务流程等频繁地阻碍和打断. 建议基本满足以下条件,再开始进行代码阅读: 具备一定的语言基础:熟悉基础语法,常用的函数 ...
- MediaInfo代码阅读
MediaInfo是一个用来分析媒体文件的开源工具. 支持的文件非常全面,基本上支持所有的媒体文件. 最近是在做HEVC开发,所以比较关注MediaInfo中关于HEVC的分析与处理. 从Meid ...
- Tools - 一些代码阅读的方法
1 初始能力 让阅读思路清晰连贯,保持在程序的流程架构和逻辑实现上,不被语法.编程技巧和业务流程等频繁地阻碍和打断. 语言基础:熟悉基础语法,常用的函数.库.编程技巧等: 了解设计模式.构建工具.代码 ...
- Bleve代码阅读(二)——Index Mapping
引言 Bleve是Golang实现的一个全文检索库,类似Lucene之于Java.在这里通过阅读其代码,来学习如何使用及定制检索功能.也是为了通过阅读代码,学习在具体环境下Golang的一些使用方式. ...
随机推荐
- leetcode-12双周赛-1244-力扣排行榜
题目描述: class Leaderboard: def __init__(self): self.map = collections.Counter() def addScore(self, pla ...
- C存储类
C 存储类 存储类定义 C 程序中变量/函数的范围(可见性)和生命周期.这些说明符放置在它们所修饰的类型之前.下面列出 C 程序中可用的存储类: auto register static extern ...
- img引用网络图片资源无法加载问题解决
近期在自己项目中遇到引用一些网络图片资源,显示无法加载,但是在浏览器打开图片路径又可以显示的问题 解决办法: 在图片显示的界面把meta referrer标签改为never <meta name ...
- leyou_04_使用vue.js搭建页面—使用ajax完成品牌的查询
1.使用vue.js搭建页面 1.1使用的模板插件Vuetify 中文UI组件官网:https://vuetifyjs.com/zh-Hans/getting-started/quick-start ...
- Hdu-4757 Tree(可持久化字典树+lca)
题目链接:点这 我的github地址:点这 Problem Description Zero and One are good friends who always have fun wi ...
- 关于BUG管理工具的操作总结。(禅道)
禅道是第一款国产的优秀开源项目管理软件.先进的管理思想,合理的软件架构,简洁实效的操作,优雅的代码实现,灵活的扩展机制,强大而易用的api 调用机制,多语言支持,多风格支持,搜索功能,统计功能——这一 ...
- 文件下载java代码
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletExcepti ...
- IIS身份验证和文件操作权限(三、ASP.NET模拟)
一.配置ASP.NET模拟 注意:在配置[ASP.NET模拟]是还要配置[匿名身份验证]不知道为什么,有知道可以留言,互相学习 二.浏览站点 -- 操作文件 ①无操作权限 点击写入 ②有操作权限(特定 ...
- SQL比较时间查询语句
select * from table1 where datediff(mm,'2009-8-12 13:17:50', date)>0 select * from table1 select ...
- 洛谷 P4196 [CQOI2006]凸多边形 (半平面交)
题目链接:P4196 [CQOI2006]凸多边形 题意 给定 \(n\) 个凸多边形,求它们相交的面积. 思路 半平面交 半平面交的模板题. 代码 #include <bits/stdc++. ...
